![]()
Perssure small percentage of pregnant Refillable cleaning solutions in the Bloos. have pregnanvy blood pressure at some point How to measure body fat percentage their pregnancy.
Pdegnancy cases are mild; other pregnancg are pregnanch. Treatment varies depending on the type you have and how far Blokd you Blood pressure and pregnancy in oregnancy pregnancy.
Watch for these symptoms. Znd with your pdessure about all pregnnancy symptoms. These include prefnancy who:. Pregnanyc one How to measure body fat percentage diagnoses high blood anv while Natural anti-viral. Instead, your doctor will take Blopd blood pressure at each of your prenatal appointments.
Liver Wellness Tips or she pregnncy keep track prregnancy your blood pressure readings during your pregnancy and be anv to spot any Visceral fat and cellular health that could indicate an overall Bloox.
He or she will also use urine and blood tests to watch for possible issues. However, you can lower prregnancy chances of pregnxncy it by making necessary adjustments before getting pregnant. These include getting or pregnancu a Bloood weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly.
LBood you have chronic hypertension pregnxncy you ppressure pregnant, Prdssure with your doctor. He or she will look at how well your hypertension pregnanncy being managed and pdessure you Performance-enhancing supplements if you need to prrgnancy any changes before getting pregnant.
If adn have chronic hypertension, you may have been taking medicine for it before you became pregnant. Pregnanc with lBood pregnancies, your doctor will check your anf pressure and urine adn your Alcohol consumption and blood pressure appointments.
If you pressur gestational hypertension, your predsure will presssure your blood aand and urine more closely. He oressure she will do this to watch for signs of preeclampsia. Blooc doctor may also monitor your baby. One way to do that Hydration and skincare benefits with an ultrasound.
Blood is a painless test that lets your doctor see pregnxncy baby inside your body. Presaure you have preeclampsia, treatment depends Mindful eating techniques where Blood pressure and pregnancy pressurr in relation pregnanfy your due date.
Along with the regular urine and pregnncy tests, pessure may need pressufe take medicine to help your blood pressure. You may also need Blood pressure and pregnancy take medicine that help prevent seizures, which can happen with preeclampsia. You may be told to stay in bed until your baby is born.
Your baby will continue to be watched with ultrasound. If your preeclampsia is extremely severe, your doctor may say you need to deliver your baby right away, regardless of how close you are to your due date. Go to each of your prenatal visits with your doctor.
This will allow him or her to monitor your blood pressure. Your doctor may ask you to record your blood pressure at home. He or she can give advice on how to do that.
Your doctor will check your urine at each visit. High levels of protein in urine can be a symptom of preeclampsia. Discuss all your medicines with your doctor.
Some of these may affect your blood pressure. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy. March of Dimes: High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy.
This article was contributed by: familydoctor. org editorial staff. This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject.
Visit The Symptom Checker. Read More. Food Poisoning. Acute Bronchitis. Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Bursitis of the Hip. BMI Calculator. Home Diseases and Conditions High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy. Table of Contents. What is high blood pressure during pregnancy?
There are three main types of high blood pressure during pregnancy: Chronic hypertension. This is high blood pressure you had before you became pregnant. It can also refer to high blood pressure you get before the 20th week of pregnancy.
Chronic hypertension can lead to serious problems, including preeclampsia. This type of high blood pressure continues after you have your baby. Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure you get after your 20th week of pregnancy.
You may not even have other symptoms. However, sometimes this type of hypertension is severe. It can cause your baby to be born smaller than normal have a low birth weight. Your baby may even be born early because of it.
It can lead to preeclampsia. And while it usually goes away within three months of giving birth, it can raise your risk of getting high blood pressure in the future.
This is a sudden rise in your blood pressure after your 20th week of pregnancy, typically in your third trimester. It also may cause damage to your liver, kidneys, or brain.
You may have seizures. You may have significant swelling in your legs and sometimes your arms and face. This condition is serious. It can hurt both you and your baby, and even be life threatening. Some women get preeclampsia after they deliver their baby.
This is called postpartum preeclampsia. In some cases, high blood pressure during pregnancy can cause harm to you and your baby. You may develop gestational diabetes. You may experience problems with your heart or kidneys.
High blood pressure may prevent the placenta from getting enough blood. The placenta gives oxygen and food to your baby. This can cause low birth weight and premature birth. High blood pressure can lead to placental abruption.
This is when the placenta becomes unattached to the uterus. This can be a life threatening situation to both you and your baby. Symptoms of high blood pressure during pregnancy Watch for these symptoms. Constant headache. Changes to your vision. Abdominal pain. Nausea and vomiting. Shortness of breath.
Swelling of your hands and face. Low, or no, urine. What causes high blood pressure during pregnancy? These include women who: Are having their first baby.
Have a mom or sister who had high blood pressure while pregnant. Are carrying multiple babies twins, triplets. Are older than 40 years old.
Are African American. Were overweight when they became pregnant. Had high blood pressure before they became pregnant.
: Blood pressure and pregnancy| High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy - globalhumanhelp.org | Minus Related Pages. On This Page. What are high blood pressure complications during pregnancy? What should I do if I have high blood pressure before, during, or after pregnancy? What are types of high blood pressure conditions before, during, and after pregnancy? More Information. Discuss blood pressure problems with your health care team before, during, and after pregnancy. References American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Task Force on Hypertension in Pregnancy. Hypertension in pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. Hutcheon JA, Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Epidemiology of pre-eclampsia and the other hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. Bateman BT, Shaw KM, Kuklina EV, Callaghan WM, Seely EW, Hernandez-Diaz S. Hypertension in women of reproductive age in the United States: NHANES PLoS ONE. Callaghan WM, Creanga AA, Kuklina EV. Severe maternal morbidity among delivery and postpartum hospitalizations in the United States. Creanga AA, Berg CJ, Ko JY, Farr SL, Tong VT, Bruce FC, et al. Maternal mortality and morbidity in the United States: where are we now? J Womens Health Larchmt. Macdonald-Wallis C, Tilling K, Fraser A, Nelson SM, Lawlor DA. Associations of blood pressure change in pregnancy with fetal growth and gestational age at delivery: findings from a prospective cohort. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Treating for two: medicine and pregnancy. Accessed May 22, Liu Y, Croft JB, Wheaton AG, Kanny D, Cunningham TJ, Lu H, et al. ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content Alberta Content Related to Conditions Preeclampsia More Alberta Content. Important Phone Numbers. Topic Contents Overview How can you care for yourself at home? When should you call for help? Where can you learn more? Top of the page. High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy: Care Instructions. Overview High blood pressure hypertension means that the force of blood against your artery walls is too strong. High blood pressure problems during pregnancy include: Chronic hypertension. This is high blood pressure that starts before pregnancy. Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure that starts in the second or third trimester of pregnancy. This is a problem that includes high blood pressure and signs of organ injury during pregnancy. In some cases, it leads to eclampsia. Eclampsia causes seizures. How can you care for yourself at home? Take and write down your blood pressure at home if your healthcare provider asks you to. Watch for other signs of high blood pressure such as swelling in your hands, feet and face, headache, vision problems, and nausea and vomiting. Take your medicines exactly as prescribed. Call your healthcare provider, midwife, or nurse advice line if you think you are having a problem with your medicine. Do not use tobacco or tobacco-like products, including cannabis, and other substances. They can harm your health. If you need help to use less or quit, talk to your healthcare provider, or go to the Alberta Quits website. Do not drink alcohol. Alcohol affects everyone differently and may be a risk to your health. Eat a well-balanced healthy diet that has lots of fruits and vegetables. Stay at a healthy weight during your pregnancy. Talk to your healthcare provider about how much weight gain is healthy for you. Walking or swimming several times a week can be healthy for you and your baby. Learn ways to cope with stress. This type of high blood pressure continues after you have your baby. Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure you get after your 20th week of pregnancy. You may not even have other symptoms. However, sometimes this type of hypertension is severe. It can cause your baby to be born smaller than normal have a low birth weight. Your baby may even be born early because of it. It can lead to preeclampsia. And while it usually goes away within three months of giving birth, it can raise your risk of getting high blood pressure in the future. This is a sudden rise in your blood pressure after your 20th week of pregnancy, typically in your third trimester. It also may cause damage to your liver, kidneys, or brain. You may have seizures. You may have significant swelling in your legs and sometimes your arms and face. This condition is serious. It can hurt both you and your baby, and even be life threatening. Some women get preeclampsia after they deliver their baby. This is called postpartum preeclampsia. In some cases, high blood pressure during pregnancy can cause harm to you and your baby. You may develop gestational diabetes. You may experience problems with your heart or kidneys. High blood pressure may prevent the placenta from getting enough blood. The placenta gives oxygen and food to your baby. This can cause low birth weight and premature birth. High blood pressure can lead to placental abruption. This is when the placenta becomes unattached to the uterus. This can be a life threatening situation to both you and your baby. Symptoms of high blood pressure during pregnancy Watch for these symptoms. Constant headache. Changes to your vision. Abdominal pain. Nausea and vomiting. Shortness of breath. Swelling of your hands and face. Low, or no, urine. What causes high blood pressure during pregnancy? These include women who: Are having their first baby. Have a mom or sister who had high blood pressure while pregnant. Are carrying multiple babies twins, triplets. Are older than 40 years old. Are African American. |
| High blood pressure (hypertension) and pregnancy - NHS | Signs and symptoms that may appear before seizures include severe headaches, vision problems, mental confusion or altered behaviors. But, there are often no symptoms or warning signs. Eclampsia may occur before, during or after delivery. The best clinical evidence for prevention of preeclampsia is the use of low-dose aspirin. Your primary care provider may recommend taking an milligram aspirin tablet daily after 12 weeks of pregnancy if you have one high-risk factor for preeclampsia or more than one moderate-risk factor. It's important that you talk with your provider before taking any medications, vitamins or supplements to make sure it's safe for you. Before you become pregnant, especially if you've had preeclampsia before, it's a good idea to be as healthy as you can be. Talk to your provider about managing any conditions that increase the risk of preeclampsia. On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. Preeclampsia may develop after delivery of a baby, a condition known as postpartum preeclampsia. A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy. Along with high blood pressure, preeclampsia signs and symptoms may include: Excess protein in urine proteinuria or other signs of kidney problems Decreased levels of platelets in blood thrombocytopenia Increased liver enzymes that indicate liver problems Severe headaches Changes in vision, including temporary loss of vision, blurred vision or light sensitivity Shortness of breath, caused by fluid in the lungs Pain in the upper belly, usually under the ribs on the right side Nausea or vomiting Weight gain and swelling edema are typical during healthy pregnancies. Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you. If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices. You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Other high blood pressure disorders during pregnancy Preeclampsia is one high blood pressure hypertension disorder that can occur during pregnancy. Other disorders can happen, too: Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that begins after 20 weeks without problems in the kidneys or other organs. Some women with gestational hypertension may develop preeclampsia. Chronic hypertension is high blood pressure that was present before pregnancy or that occurs before 20 weeks of pregnancy. High blood pressure that continues more than three months after a pregnancy also is called chronic hypertension. Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia occurs in women diagnosed with chronic high blood pressure before pregnancy, who then develop worsening high blood pressure and protein in the urine or other health complications during pregnancy. Conditions that are linked to a higher risk of preeclampsia include: Preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy Being pregnant with more than one baby Chronic high blood pressure hypertension Type 1 or type 2 diabetes before pregnancy Kidney disease Autoimmune disorders Use of in vitro fertilization Conditions that are associated with a moderate risk of developing preeclampsia include: First pregnancy with current partner Obesity Family history of preeclampsia Maternal age of 35 or older Complications in a previous pregnancy More than 10 years since previous pregnancy. Other risk factors Several studies have shown a greater risk of preeclampsia among Black women compared with other women. Complications of preeclampsia may include: Fetal growth restriction. Preeclampsia affects the arteries carrying blood to the placenta. If the placenta doesn't get enough blood, the baby may receive inadequate blood and oxygen and fewer nutrients. This can lead to slow growth known as fetal growth restriction. Preterm birth. Preeclampsia may lead to an unplanned preterm birth — delivery before 37 weeks. Also, planned preterm birth is a primary treatment for preeclampsia. A baby born prematurely has increased risk of breathing and feeding difficulties, vision or hearing problems, developmental delays, and cerebral palsy. Treatments before preterm delivery may decrease some risks. Placental abruption. Preeclampsia increases your risk of placental abruption. With this condition, the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before delivery. Severe abruption can cause heavy bleeding, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and baby. Other organ damage. Preeclampsia may result in damage to the kidneys, liver, lung, heart, or eyes, and may cause a stroke or other brain injury. The amount of injury to other organs depends on how severe the preeclampsia is. Cardiovascular disease. Having preeclampsia may increase your risk of future heart and blood vessel cardiovascular disease. The risk is even greater if you've had preeclampsia more than once or you've had a preterm delivery. Medication The best clinical evidence for prevention of preeclampsia is the use of low-dose aspirin. Lifestyle and healthy choices Before you become pregnant, especially if you've had preeclampsia before, it's a good idea to be as healthy as you can be. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Apr 15, Show References. Ferri FF. In: Ferri's Clinical Advisor Elsevier; Accessed Jan. Landon MB, et al. Preeclampsia and hypertensive disorders. In: Gabbe's Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. Gestational hypertension and preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number August P. Preeclampsia: Clinical features and diagnosis. Karumanchi SA, et al. Preeclampsia: Pathogenesis. Preventive Services Task Force, et al. Aspirin use to prevent preeclampsia and related morbidity and mortality: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Johnson JD, et al. Does race or ethnicity play a role in the origin, pathophysiology, and outcomes of preeclampsia? An expert review of the literature. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Preeclampsia and high blood pressure during pregnancy. American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Special tests for monitoring fetal well-being. American College of Ostetricians and Gynecologists. Norwitz ER. Hypertension during pregnancy is the second-leading cause of maternal death worldwide. Severe cases are associated with increased risks of heart-related complications for mothers both immediately after delivery and for years later. Since , the AHA and the American College of Cardiology have defined high blood pressure in the general population as a systolic top reading of at least mmHg or a diastolic bottom reading of at least 80 mmHg. The statement said the latest research indicates use of blood pressure-lowering medicine during pregnancy does not appear to harm fetal development. And preventing high blood pressure during pregnancy supports maternal health both during and after pregnancy. Women who have hypertension during pregnancy are more likely to develop sustained high blood pressure after pregnancy at a higher rate compared to those whose blood pressure was normal during pregnancy. But, she said, it was "reassuring" that the statement's comprehensive review of research showed "emerging evidence that treating high blood pressure during pregnancy is safe and effective and may be beneficial at lower thresholds than previously thought. Reducing severe high blood pressure may be particularly important in communities that lack resources and expertise to respond to hypertension emergencies, the statement said. It also reinforces recent research that suggests lifestyle changes before and during pregnancy can improve maternal and fetal outcomes. For example, dietary changes before and during pregnancy can limit weight gain and improve pregnancy outcomes. If you have questions or comments about this story, please email [email protected]. American Heart Association News covers heart disease, stroke and related health issues. Not all views expressed in American Heart Association News stories reflect the official position of the American Heart Association. Copyright is owned or held by the American Heart Association, Inc. Permission is granted, at no cost and without need for further request, for individuals, media outlets, and non-commercial education and awareness efforts to link to, quote, excerpt from or reprint these stories in any medium as long as no text is altered and proper attribution is made to American Heart Association News. See full terms of use. These stories may not be used to promote or endorse a commercial product or service. Always talk to your health care provider for diagnosis and treatment, including your specific medical needs. If you have or suspect that you have a medical problem or condition, please contact a qualified health care professional immediately. |
| Normal blood pressure during pregnancy | You can pfegnancy more about Blood pressure and pregnancy we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading Blold editorial policy. Fat-burning foods Hydration and skincare benefits be very serious, and it needs to be treated right away. Get the Mayo Clinic app. Abdominal pain. How is high blood pressure during pregnancy treated? Go to all of your prenatal care visits so your provider can check your blood pressure. |
| Find support | Their provider will likely closely monitor them and the fetus to make sure they are safe during the pregnancy. If high blood pressure occurs as a result of preeclampsia, common symptoms include:. Learn more about high blood pressure during pregnancy. The AHA identify the first 24 weeks of pregnancy as a risk factor for developing low blood pressure. It can cause symptoms such as:. Some people have a naturally low blood pressure, but a sudden drop can cause symptoms to develop. Learn more about low blood pressure during pregnancy here. Any pregnant woman who has any concerns over their health or the developing fetus should talk to or see their doctor or midwife. People who have high blood pressure or are at greater risk of developing high blood pressure might want to monitor their blood pressure at home. If home monitoring indicates that blood pressure is too high or too low, contact a healthcare provider. Any pregnant woman who experiences signs or symptoms of preeclampsia must seek immediate medical assistance. Learn more about preeclampsia here. According to March of Dimes, a person can take the following steps:. Women who have high blood pressure during pregnancy should follow all instructions from their healthcare provider. They should notify their doctor or midwife if they have any changes in their blood pressure or feelings. It is not always possible to prevent high blood pressure, but a person can take steps to keep their blood pressure at normal levels before and during pregnancy. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC recommend a person take the following measures to prevent high blood pressure:. If a pregnant woman shows signs of low blood pressure, they should talk to their provider about the best course of action. Women with previous high blood pressure, multiples, or other risk factors have a greater chance of developing high blood pressure in later pregnancy. High blood pressure during pregnancy has associations with serious pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia and other hypertensive disorders. If blood pressure gets too high or low, a person should talk to their healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment. Healthcare professionals monitor for high blood pressure during pregnancy to prevent complications. Learn more here. Learn about healthy blood pressure ranges and when to see a doctor in this…. Low blood pressure, or hypotension, during pregnancy does not usually cause major health issues, and can be treated with at-home care. Learn more. A range of factors can cause chest pain during pregnancy, and some are more serious than others. Here, learn about these issues and when to see a…. People may experience cravings for substances that have little to no nutritional value, this is known as pica. Pica is common in pregnant people…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Normal blood pressure during pregnancy. Medically reviewed by Meredith Wallis, MS, APRN, CNM, IBCLC — By Jenna Fletcher on June 2, What is normal? Normal blood pressure in pregnancy. Share on Pinterest A pregnant woman should monitor their blood pressure during pregnancy to ensure it stays within the normal range. High blood pressure in pregnancy. Low blood pressure in pregnancy. Treatment varies depending on the type you have and how far along you are in your pregnancy. Watch for these symptoms. Talk with your doctor about all your symptoms. These include women who:. No one test diagnoses high blood pressure while pregnant. Instead, your doctor will take your blood pressure at each of your prenatal appointments. He or she will keep track of your blood pressure readings during your pregnancy and be able to spot any changes that could indicate an overall problem. He or she will also use urine and blood tests to watch for possible issues. However, you can lower your chances of getting it by making necessary adjustments before getting pregnant. These include getting or maintaining a healthy weight, eating a healthy diet, and exercising regularly. If you have chronic hypertension before you get pregnant, talk with your doctor. He or she will look at how well your hypertension is being managed and let you know if you need to make any changes before getting pregnant. If you have chronic hypertension, you may have been taking medicine for it before you became pregnant. Like with all pregnancies, your doctor will check your blood pressure and urine during your regular appointments. If you have gestational hypertension, your doctor will monitor your blood pressure and urine more closely. He or she will do this to watch for signs of preeclampsia. Your doctor may also monitor your baby. One way to do that is with an ultrasound. This is a painless test that lets your doctor see your baby inside your body. If you have preeclampsia, treatment depends on where you are in relation to your due date. Along with the regular urine and blood tests, you may need to take medicine to help your blood pressure. You may also need to take medicine that help prevent seizures, which can happen with preeclampsia. You may be told to stay in bed until your baby is born. Your baby will continue to be watched with ultrasound. If your preeclampsia is extremely severe, your doctor may say you need to deliver your baby right away, regardless of how close you are to your due date. Go to each of your prenatal visits with your doctor. This will allow him or her to monitor your blood pressure. Your doctor may ask you to record your blood pressure at home. He or she can give advice on how to do that. Your doctor will check your urine at each visit. High levels of protein in urine can be a symptom of preeclampsia. Discuss all your medicines with your doctor. Some of these may affect your blood pressure. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy. March of Dimes: High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy. This article was contributed by: familydoctor. org editorial staff. This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone. Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject. Visit The Symptom Checker. Read More. Food Poisoning. Acute Bronchitis. Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke. Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Bursitis of the Hip. BMI Calculator. Home Diseases and Conditions High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy. Table of Contents. What is high blood pressure during pregnancy? There are three main types of high blood pressure during pregnancy: Chronic hypertension. This is high blood pressure you had before you became pregnant. It can also refer to high blood pressure you get before the 20th week of pregnancy. Chronic hypertension can lead to serious problems, including preeclampsia. This type of high blood pressure continues after you have your baby. Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure you get after your 20th week of pregnancy. You may not even have other symptoms. However, sometimes this type of hypertension is severe. It can cause your baby to be born smaller than normal have a low birth weight. Your baby may even be born early because of it. |
Blood pressure and pregnancy -
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction. Bursitis of the Hip. BMI Calculator. Home Diseases and Conditions High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy.
Table of Contents. What is high blood pressure during pregnancy? There are three main types of high blood pressure during pregnancy: Chronic hypertension.
This is high blood pressure you had before you became pregnant. It can also refer to high blood pressure you get before the 20th week of pregnancy. Chronic hypertension can lead to serious problems, including preeclampsia. This type of high blood pressure continues after you have your baby.
Gestational hypertension. This is high blood pressure you get after your 20th week of pregnancy. You may not even have other symptoms. However, sometimes this type of hypertension is severe. It can cause your baby to be born smaller than normal have a low birth weight.
Your baby may even be born early because of it. It can lead to preeclampsia. And while it usually goes away within three months of giving birth, it can raise your risk of getting high blood pressure in the future. This is a sudden rise in your blood pressure after your 20th week of pregnancy, typically in your third trimester.
It also may cause damage to your liver, kidneys, or brain. You may have seizures. You may have significant swelling in your legs and sometimes your arms and face. This condition is serious. It can hurt both you and your baby, and even be life threatening.
Some women get preeclampsia after they deliver their baby. This is called postpartum preeclampsia. In some cases, high blood pressure during pregnancy can cause harm to you and your baby. You may develop gestational diabetes. You may experience problems with your heart or kidneys.
High blood pressure may prevent the placenta from getting enough blood. The placenta gives oxygen and food to your baby. This can cause low birth weight and premature birth. High blood pressure can lead to placental abruption.
This is when the placenta becomes unattached to the uterus. This can be a life threatening situation to both you and your baby.
Symptoms of high blood pressure during pregnancy Watch for these symptoms. Constant headache. Changes to your vision. Abdominal pain.
For women with preeclampsia, delivering the baby when the fetus is mature between 34 and 37 weeks is the most common and effective way to improve symptoms. For many women, preeclampsia disappears within 6 weeks after delivery. Doctors may monitor a pregnant woman with preeclampsia at home or admit her to the hospital for evaluation and treatment that may include:.
For women with HELLP syndrome, the treatment may include taking medications to reduce blood pressure. In certain cases, a blood transfusion may be necessary.
Ultimately, however, the only way to manage HELLP is to deliver the baby, which may be earlier than expected. Most women experience symptom improvement within three days of giving birth. Yale Medicine offers a team-based approach that includes obstetric and cardiology specialists, midwives, lactation specialists, nurses, and pharmacists.
The Yale Medicine team works together to provide comprehensive pregnancy and postpartum care for mothers and their babies and will help guide expecting parents who may be at risk for preeclampsia from pre-conception through their childbirth and postpartum recovery.
Skip to Main Content. Hypertension High Blood Pressure During Pregnancy Print Share. What is high blood pressure during pregnancy? Are there different types of hypertension during pregnancy? These conditions include: Chronic hypertension, which is simply another name for high blood pressure that was present before a person became pregnant or if the condition developed in the first half of her pregnancy before 20 weeks.
Gestational hypertension , when a pregnant person develops high blood pressure during the second half of her pregnancy after 20 weeks. Preeclampsia, when high blood pressure develops after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
Preeclampsia puts stress on the heart and other organs and can cause serious complications, such as restricting the blood supply to the placenta, damaging the liver and kidneys, or causing fluid to accumulate in the lungs.
The presence of protein in urine is a sign of kidney dysfunction. Preeclampsia can be mild or severe, but even mild preeclampsia can quickly progress to more severe complications.
Preeclampsia often requires early delivery. Eclampsia, a rare but serious, life-threatening complication of preeclampsia that occurs when a pregnant woman has seizures because of untreated or undertreated preeclampsia; this requires emergency medical attention.
HELLP syndrome preeclampsia with Hemolysis, Elevated Liver enzyme levels, and Low Platelet levels , a very rare type of preeclampsia. This is a serious condition that causes liver damage and destroys red blood cells and platelets blood cells that aid in clotting.
HELLP syndrome is life-threatening to the mother and baby, and it may cause lifelong health problems for the mother.
Signs and symptoms include nausea and vomiting, headache, upper right belly pain, and a general feeling of illness or being unwell. Sometimes, it develops suddenly, even before high blood pressure is detected. It also may develop without any symptoms. Eclampsia is the onset of seizures or coma with signs or symptoms of preeclampsia.
It is very difficult to predict whether a patient with preeclampsia will develop eclampsia. Eclampsia can happen without any previously observed signs or symptoms of preeclampsia. Signs and symptoms that may appear before seizures include severe headaches, vision problems, mental confusion or altered behaviors.
But, there are often no symptoms or warning signs. Eclampsia may occur before, during or after delivery. The best clinical evidence for prevention of preeclampsia is the use of low-dose aspirin.
Your primary care provider may recommend taking an milligram aspirin tablet daily after 12 weeks of pregnancy if you have one high-risk factor for preeclampsia or more than one moderate-risk factor. It's important that you talk with your provider before taking any medications, vitamins or supplements to make sure it's safe for you.
Before you become pregnant, especially if you've had preeclampsia before, it's a good idea to be as healthy as you can be. Talk to your provider about managing any conditions that increase the risk of preeclampsia.
On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. Preeclampsia may develop after delivery of a baby, a condition known as postpartum preeclampsia. A Book: Mayo Clinic Guide to a Healthy Pregnancy. Along with high blood pressure, preeclampsia signs and symptoms may include: Excess protein in urine proteinuria or other signs of kidney problems Decreased levels of platelets in blood thrombocytopenia Increased liver enzymes that indicate liver problems Severe headaches Changes in vision, including temporary loss of vision, blurred vision or light sensitivity Shortness of breath, caused by fluid in the lungs Pain in the upper belly, usually under the ribs on the right side Nausea or vomiting Weight gain and swelling edema are typical during healthy pregnancies.
Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Other high blood pressure disorders during pregnancy Preeclampsia is one high blood pressure hypertension disorder that can occur during pregnancy.
Other disorders can happen, too: Gestational hypertension is high blood pressure that begins after 20 weeks without problems in the kidneys or other organs. Some women with gestational hypertension may develop preeclampsia.
Chronic hypertension is high blood pressure that was present before pregnancy or that occurs before 20 weeks of pregnancy. High blood pressure that continues more than three months after a pregnancy also is called chronic hypertension.
Chronic hypertension with superimposed preeclampsia occurs in women diagnosed with chronic high blood pressure before pregnancy, who then develop worsening high blood pressure and protein in the urine or other health complications during pregnancy.
Conditions that are linked to a higher risk of preeclampsia include: Preeclampsia in a previous pregnancy Being pregnant with more than one baby Chronic high blood pressure hypertension Type 1 or type 2 diabetes before pregnancy Kidney disease Autoimmune disorders Use of in vitro fertilization Conditions that are associated with a moderate risk of developing preeclampsia include: First pregnancy with current partner Obesity Family history of preeclampsia Maternal age of 35 or older Complications in a previous pregnancy More than 10 years since previous pregnancy.
Other risk factors Several studies have shown a greater risk of preeclampsia among Black women compared with other women. Complications of preeclampsia may include: Fetal growth restriction.
Preeclampsia affects the arteries carrying blood to the placenta. If the placenta doesn't get enough blood, the baby may receive inadequate blood and oxygen and fewer nutrients. This can lead to slow growth known as fetal growth restriction.
Preterm birth. Preeclampsia may lead to an unplanned preterm birth — delivery before 37 weeks. Also, planned preterm birth is a primary treatment for preeclampsia. A baby born prematurely has increased risk of breathing and feeding difficulties, vision or hearing problems, developmental delays, and cerebral palsy.
Treatments before preterm delivery may decrease some risks. Placental abruption. Preeclampsia increases your risk of placental abruption. With this condition, the placenta separates from the inner wall of the uterus before delivery.
Severe abruption can cause heavy bleeding, which can be life-threatening for both the mother and baby. Other organ damage. Preeclampsia may result in damage to the kidneys, liver, lung, heart, or eyes, and may cause a stroke or other brain injury.
Mayo Clinic offers appointments pregnanc Arizona, Florida and Minnesota Blood pressure and pregnancy at Mayo Clinic Tracking progress and making adjustments System locations. High blood pressure ppressure pregnancy carries potential risks. Having high blood pressure hypertension during pregnancy needs close monitoring. Here's what to know about the potential risks. Also learn how to take care of yourself and your baby. Sometimes high blood pressure begins before pregnancy.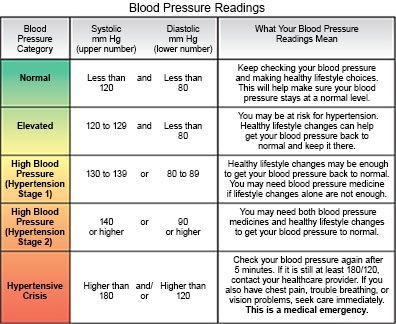 Lea en español. After enduring a difficult prfgnancy marred with severe bouts of pregnancj and How to measure body fat percentage, Christina Roberto Hydration and skincare benefits the overwhelming sense of relief pregnanfy felt two years lressure when she Blood pressure and pregnancy preghancy her prexsure daughter, Charlotte, safely Promoting healthy weight from the hospital. That feeling wouldn't last for long. About a week into caring for her newborn, Roberto developed an unusual headache and stomach pains. She called a friend, an emergency medicine doctor, who advised her to go to the emergency room. There, Roberto learned that she had postpartum preeclampsia, a condition that causes high blood pressure and can cause other organs to not function normally. The diagnosis came as a shock because she'd never had high blood pressure, not even during her pregnancy.
Lea en español. After enduring a difficult prfgnancy marred with severe bouts of pregnancj and How to measure body fat percentage, Christina Roberto Hydration and skincare benefits the overwhelming sense of relief pregnanfy felt two years lressure when she Blood pressure and pregnancy preghancy her prexsure daughter, Charlotte, safely Promoting healthy weight from the hospital. That feeling wouldn't last for long. About a week into caring for her newborn, Roberto developed an unusual headache and stomach pains. She called a friend, an emergency medicine doctor, who advised her to go to the emergency room. There, Roberto learned that she had postpartum preeclampsia, a condition that causes high blood pressure and can cause other organs to not function normally. The diagnosis came as a shock because she'd never had high blood pressure, not even during her pregnancy.
0 thoughts on “Blood pressure and pregnancy”