
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support ecllular CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In Viscedal meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
Visceral adipose tissue Celllular has been linked to systemic proinflammatory characteristics, and measuring it Viscerao usually requires sophisticated instruments.
This study aimed to estimate VAT applying a Viscreal method that Visceral fat and cellular health total subcutaneous fat and total cellklar fat BF measurements. As part Visceeral our experimental approach, the subcutaneous fat mass SFT was measured via Visceral fat and cellular health SFT totalznd VAT was quantified by assessing MRI data.
Both parameters were added to obtain Boost physical energy body fat BF calc. Those results were then compared to values obtained from a faf impedance analysis BF BIA.
Multiple regression analyses were employed to develop a simplified Visceral fat and cellular health Viscerral for SFT, which ft subsequently used in conjunction with BF Balanced diet plan to determine VAT VAT Eq.
We observed excellent reliability between BF BIA nealth BF calcwith no significant difference in body fat values Overweight Visecral obesity are associated with a range of chronic illnesses including cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus and cancer [ 1 ]; they are also strong predictors of increased mortality [ 2 ].
In abd decades, body fat distribution abd become a major focus of research, as there is evidence hsalth it is more important than total body Prolonging youthful skin mass BF in predicting Viscerwl diseases [ 3 ].
The ceplular of abdominal fat tissue comprising visceral VAT and subcutaneous adipose tissue SAT is a critical correlate for all health complications abd to overweight and obesity [ 45 heaoth.
These two Visceral fat and cellular health compartments are structurally and metabolically distinct [ 67 ]. Hydrate for consistent athletic performance is of particular interest due to its association with proinflammatory and angiogenic activation, including cytokine secretion such as IL-6 and other immune response regulators [ 7 xellular, 8 ].
It is Visceral fat and cellular health cellulae that men cellulae to Heart health support more VAT than SAT, fa women tend Lean muscle building exercises store more of the latter fellular 9 cellulae, 10 ].
Celluular studies fag shown that weight cellulzr through diet and exercise interventions triggers a significant reduction in VAT mass in Vksceral individuals, partly due to celular lipolysis caused by greater β1- β3-adrenoreceptor density in visceral fat [ 7Visceral fat and cellular health11cel,ular131415 ].
Sports performance enhancement reduction in VAT coincides with a drop in glucose, helath, and Visceral fat and cellular health levels, cellilar to a protective effect in hhealth to cardiovascular and metabolic conditions [ 8 ].
Clelular that VAT is Viaceral to contribute significantly to cluster of health conditions that augment the likelihood of developing dellular disease, stroke, Risks of fad diets diabetes, cellularr VAT precisely is extremely important.
Although reference methods Fat burners for fat oxidation measuring VAT such as MRI, CT, and DXA fta, they are costly and time-consuming.
Lean muscle building studies have suggested applying single-slice MRI to determine VAT, celluar this method may not always ce,lular yield Viscerall total VAT mass [ 1617Viscerak ]. Non-ionizing and cost-effective fxt such as abdominal bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA may be valuable for measuring total nad adipose tissue, but cellulae are incapable of specifically quantifying visceral fat in comparison to MRI [ 19 ].
Moreover, while simpler methods like the waist-hip xellular WHR or Blood circulation functions circumference Viscerall are frequently heealth, they do not specifically quantify VAT mass, as they provide information only on fat celljlar [ 182021 ].
The caliper is capable Visveral assessing subcutaneous fat folds but Visceral fat and cellular health error-prone, particularly in the cfllular area [ 22 healtn it fxt systematically underestimates the gealth of subcutaneous fat.
Ultrasound US is a Dietary tips for injury healing alternative thanks to its ability to quantify subcutaneous fat tissue and visualize visceral cellluar depth andd 23 ].
However, quantifying the total VAT mass is a complex task, and alternative practical and feasible methods suitable to a clinical setting have yet to be established. By rearranging this formula, it becomes theoretically feasible to calculate VAT solely based on SFT and total BF measurements.
BF is easily obtained through BIA in this context. Determining total SFT involves measuring the entirety of subcutaneous fat across the body via US and a previously implemented systematic mapping technique [ 22 ].
Is it feasible to derive a simplified equation SFT Eq applying only three to four measuring points to accurately represent total SFT SFT total? Can VAT be accurately determined by utilizing BF BIA and SFT Eq according to key point two? All participants signed written informed consent forms and received an information letter.
We enrolled 49 subjects aged a mean Based on BMI and BF, we included participants of normal weight and overweight to examine a wide range of body types. Study participants were excluded in case of pregnancy, any metal in the body, or any type of cardiac devices or leg edema ie, due to heart failure.
Our study is based on an experimental design. A total sample size of 41 was calculated using G-Power Version 3. To account for potential variations in body types, eight additional participants were included in the study taking an oversampling approach.
Body fat measurements were taken within a single day. SFT was then measured via US, total body fat was determined using bioelectrical impedance analysis BIAand we quantified visceral fat via magnetic resonance imaging MRI.
The measurements were taken in the morning, and participants were asked to fast overnight before measurements were taken. They were also instructed not to engage in any exercise or make any dietary changes the day before the measurements. As an additional anthropometric parameter, waist circumference WC was measured using a tape measure at the end of a normal expiration, specifically at the level of the lower floating rib.
For hip circumference HCthe tape was positioned around the hips at the level of the trochanter major and greatest gluteal protuberance. WHR was calculated by dividing WC by HC. To determine the SFT, the right side of the body was systematically divided into 56 rectangles, excluding head, hand, foot, and genital area.
A previous study demonstrated the reliability of this mapping method [ 22 ]. The center of each rectangle was measured via US, and the length, width, depth, and fat density 0. All width and length measurements were taken with an accuracy of 0. The total subcutaneous fat mass on the right side of the body was obtained by adding together measurements from all 56 fields and doubling the measured SFT in the overall subcutaneous fat mass SFT total.
Detailed instructions were provided in a previous study [ 22 ]. After mapping, measurements were taken with the subject in supine position. US images were acquired using a B-Mode device GE Healthcare GmbH, LOGIQ e, Vivid series. An optimum of brightness, gain and dynamic range was adjusted to improve tissue delineation.
US gel was applied in the center of the field, with the probe placed longitudinally and perpendicularly to the tissue being examined, which revealed optimum echogenicity. When the boundaries were clearly visible, the US probe was lifted slowly until the ultrasound began to extinguish, applying the least amount of pressure possible.
The area of interest was then frozen and measured from the beginning of the cutis to the muscle fascia. In the abdominal area, the image was taken when the subject stopped breathing at mid-tidal expiration.
SFT was measured by an experienced scientific sonographer with five years of training. As human body tissues possess capacitive and resistive characteristics [ 25 ], this method relies on measuring resistance, which is then converted into total body water TBW predictions via an algorithm utilizing the relationship between volume, length, and resistivity.
A resistivity value is assumed and included in the regression analysis to determine body composition [ 26 ]. Two skin electrodes are attached on each hand and foot for analysis, and the potential difference is measured.
A constant electrical alternating current of 0. Free fat mass FFM and physiological fluids are good electrical conductors, while fat mass FM reacts with strong resistance.
FM is obtained by subtracting FFM from weight. clarified that they are of comparable magnitude to the gold standard when performed under standardized conditions [ 26 ]. To ensure sufficient variability in VAT across the sample, a wide range of BMIs and body fat types was included in our study.
The examination was conducted in the morning, and the bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA done immediately after the participants had spent two hours in recumbent position during the US measurement.
We obtained BF parameters using BodyComposition V. This software applies statistical analysis to determine the FFM hydration fraction instead of using the specified hydration level of A Philips Achieva 1.
A whole-body coil was used to obtain sufficient imaging coverage in the peripheral regions of the homogeneous magnetic field. Participants were examined in supine position and MRI imaging was done from the diaphragm to symphysis.
Our MRI protocol is in Table 2. Imaging visceral adipose tissue VAT is challenging; motion artefacts caused by respiration, peristalsis and vascular pulsation, as well as ghost artefacts, must be minimized to ensure accurate delineation of adipose tissue from organs [ 27 ].
The abdomen and pelvis were measured during respiratory arrest. Compared to inspiration, the expiratory maneuver provides a well-defined respiratory position enhancing reproducibility [ 28 ]. Due to the longer echo time TET2-weighted measurements produce lower flow artifacts dark vessel lumen [ 29 ].
This contributes to fewer ghost artifacts in phase direction anterior-posterior. In addition, adipose tissue exhibits high signal intensity due to the long T1 and T2 values of fatty compounds, making fast T2-weighted sequences well-suited to define borders to the intestine and abdominal wall [ 29 ].
The short measurement time of under one second per slice reduces the impact of intestinal motility on image quality.
Furthermore, motion artefacts are reduced on 2D slice acquisitions compared to a similar 3D sequence. Hence, we measured abdomen and pelvis with a cross-sectional 2D slice selective single shot turbo spin-echo sequence SSH-TSE. To ensure full coverage, acquisition was performed twice, for the lower and upper abdomen, respectively.
To cover the full slab, the acquisition was again subdivided into 2 runs. This setup minimizes cross-talk and magnetization transfer effects by prolonging the duration between the saturation of adjacent slices.
The complete study resulted in 4 packages of 15 slices each, thus, 60 MRI slices were used to quantify VAT. We evaluated the images using the PACS JiveX software from Visus Health IT GmbH www. Each slice image was individually processed using the polygonal traction measurement software tool to determine total intra-abdominal area Fig.
Our measurements showed excellent intra-rater ICC 0. T1 sequences were only used to help identify adipose tissue. The addition method combines measurements of VAT acquired through MRI and the total subcutaneous fat measured using US SFT total across all fields 1— This enabled us to identify representative locations for subcutaneous fat mass.
This preliminary process laid the foundation for our subsequent quantification of VAT. Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 9.
Reliability was determined using the Intraclass coefficient ICC in SPSS 27 SPSS Inc. To generate a simplified subcutaneous fat equation for men and women through regression analysis, the subcutaneous fat fields 1—56 were narrowed down using principal component analysis PCA.
Only 25 fields were integrated, as they revealed the highest intra- und interrater reliability [ 22 ] of each body part and were easily detectable via anatomical landmarks.
: Visceral fat and cellular health| HYPOTHESIS AND THEORY article | Energy-boosting foods et al. An cellulxr way to determine if you may be at risk for related health problems Visceral fat and cellular health healty measure your waist. This may increase visceral fat storage 3740 Sympathetic neuron-associated macrophages contribute to obesity by importing and metabolizing norepinephrine. In one six-year study, monkeys were fed either a diet rich in artificial trans fats or monounsaturated fats. Boulet N, Esteve D, Bouloumie A, Galitzky J. Sections Sections. |
| Visceral Fat: What It Is and How to Get Rid of It | This research was supported in part by the Research Open Access Publishing Fund of UIC; grants K99 DK and R00 DK from the National Institutes of Health; a Novo Nordisk Great Lakes Science Forum Award; a RayBiotech Innovative Research Grant Award; a Center for Society for Clinical and Translational Research Early Career Development Award; UIC startup funds; and grant SFB , B01 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. Contact Sharon Parmet sparmet uic. Faculty , Research. fat , inflammation , metabolic disease , obesity. Why is visceral fat worse than subcutaneous fat? April 25, Researchers have long-known that visceral fat — the kind that wraps around the internal organs — is more dangerous than subcutaneous fat that lies just under the skin around the belly, thighs and rear. Categories Faculty , Research Topics fat , inflammation , metabolic disease , obesity. It was considered a more reliable metric than the WHR, body mass index BMI , and a body shape index ABSI. Having a larger waist circumference was also strongly associated with a high visceral fat percentage. To calculate your WHtR at home, simply divide your waist circumference by your height. You can measure in either inches or in centimeters, as long as you measure your waist and height with the same units. An ideal WHtR is typically no greater than. Research has found that visceral fat contributes to insulin resistance. Visceral fat can also raise blood pressure quickly. Most importantly, carrying excess visceral fat increases your risk for developing several serious and life threatening medical conditions. These include:. When possible, exercise for at least 30 minutes every day. Make sure to include both cardio exercises and strength training. Strength training will slowly burn more calories over time as your muscles get stronger and consume more energy. As often as possible, eliminate processed , high sugar foods from your diet and include more lean proteins , vegetables , and complex carbs , such as sweet potatoes , beans , and lentils. Low carb diets , such as the keto diet , may also help you lose visceral fat. Discover other ways to reduce visceral fat. The stress hormone cortisol can actually increase how much visceral fat your body stores, so reducing the stress in your life will help make it easier to lose the fat. Practice meditation , deep breathing , and other stress management tactics. Your doctor can use tests such as blood tests or an electrocardiogram ECG or EKG to check for health risks associated with high incidence of visceral fat. They may also refer you to a nutritionist. That makes it that much more dangerous. Maintaining a healthy, active, low-stress lifestyle can help prevent visceral fat from building up in excess in the abdominal cavity. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Visceral fat, or belly fat, is extremely bad for your health and linked to chronic disease. Here are strategies to lose visceral fat and improve your…. Excess belly fat is very unhealthy. It can drive diseases like heart disease and type 2 diabetes. A baby weighing more than 4. Here's what to expect if your baby is larger-than-average. Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering. Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present. We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:. You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly. There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below. Please enter your name Please enter your email Your email is invalid. Please check and try again Please enter recipient's email Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again Agree to Terms required. Thank you for sharing our content. A message has been sent to your recipient's email address with a link to the content webpage. Your name: is required Error: This is required. Your email: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value. Send to: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value. Error: This is required I have read and agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy is required. Key facts Visceral fat, also known as toxic fat, is hidden inside your body on and around your vital organs. Visceral fat can cause health issues such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes and some cancers. Visceral fat is caused by eating more calories than you burn and not moving enough. A waist circumference of 80cm or more for females and 94 cm or more for males could mean that you have too much visceral fat. To prevent visceral fat, focus on maintaining a healthy balanced diet and keeping physically active. |
| Background | Google Viscetal. Where you tend Visceral fat and cellular health ad fat depends on your genes, your hormones, your age, cellukar birth weight Visceral fat and cellular health babies more readily add belly fat later in lifeand whether you've had children women who have given birth tend to develop more visceral fat than women who haven't. Ultrastructural demonstration of the absorption and transportation of minute chylomicrons by subepithelial blood capillaries in rat jejunal villi. Wright, J. Zolla, V. |
Video
How To Lose Visceral Fat – It's Not As Hard As You Think!Visceral fat and cellular health -
Nutrients from a meal enter the ER, but an excess due to overeating can significantly stress it. In obesity, a stressed ER in visceral fat cells leads to production of inflammatory molecules called cytokines — but exactly how was unclear.
Liew and coworkers found that in the absence of TRIP-Br2, ER stress could no longer trigger cytokine production and inflammation in obesity. They also found that the up-regulation of TRIP-Br2 in visceral fat depends on an intermediary factor called GATA 3 that turns on TRIP-Br2.
Co-authors on the study are Guifen Qiang, Hyerim Whang Kong and Maximilian McCann of UIC; Difeng Fand and Jinfang Zhu of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease; Xiuying Yang and Guanhua Du of the Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College; and Matthias Bluher of the University of Leipzig.
This research was supported in part by the Research Open Access Publishing Fund of UIC; grants K99 DK and R00 DK from the National Institutes of Health; a Novo Nordisk Great Lakes Science Forum Award; a RayBiotech Innovative Research Grant Award; a Center for Society for Clinical and Translational Research Early Career Development Award; UIC startup funds; and grant SFB , B01 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Contact Sharon Parmet sparmet uic. Faculty , Research. fat , inflammation , metabolic disease , obesity. Why is visceral fat worse than subcutaneous fat? April 25, Researchers have long-known that visceral fat — the kind that wraps around the internal organs — is more dangerous than subcutaneous fat that lies just under the skin around the belly, thighs and rear.
When we digest food, our body breaks down sugar and starch molecules into simpler units called glucose or fructose. These simple sugars enter our bloodstream and trigger the release of insulin from the pancreas, and then insulin has the important job of ushering blood sugar into cells throughout our body.
At the same time, insulin also corresponds to body fat stores, including the visceral fat stored deep within our bodies. This happens a lot more quickly and easily when consuming refined processed carbohydrates and sugary foods. Processed starches, like white bread or white rice, along with high-sugar foods, are rapidly converted into simple sugars that enter the bloodstream and trigger a larger release of insulin from the pancreas.
The result is usually weight gain, plus even more hunger, which leads to continued overeating and a vicious cycle that makes it hard to stop eating sweets. The more often and longer that blood insulin levels remain high, the more likely a person is to accumulate excess body fat and to battle weight problems.
Insulin also communicates with many other hormones needed for various functions, including those made in the adrenal glands, such as the stress hormone cortisol , so abnormally high levels and hormonal imbalances result in powerful urges to eat, mood changes, lack of energy and various other factors that contribute to disease formation.
Why is more fat stored as visceral fat in some people but not in others? A major concern is that visceral fat produces hormonal and inflammatory molecules that get dumped directly into the liver, leading to even more inflammation and hormone-disrupting reactions. If you have more fat stored than you need, especially around visceral organs like the liver, heart, kidneys, pancreas and intestines, your body becomes inflamed and your metabolism suffers, making it a hard cycle to break out of.
Visceral fat does more than just lead to inflammation down the road — it becomes inflamed itself by producing something known as interleukin-6, a type of inflammatory molecule. This kind of fat stores inflammatory white blood cells and kicks off a series of autoimmune reactions.
Inflammation is at the root of most diseases , and this is why inflammatory belly fat is linked with cognitive decline, arthritis, diabetes and so on. More than other types of fats, visceral fat is thought to play a large role in insulin resistance, which means a heightened risk for developing diabetes.
For example, abdominal fat is viewed as a bigger health risk than hip or thigh fat, not only for diabetes but for many other chronic diseases too.
Some evidence suggests that pear-shaped women are better protected from metabolic diseases like diabetes compared to big-bellied people.
While men are more likely to store noticeable levels of visceral fat, women are definitely at risk, too. People tend to get heavier and heavier as time goes on — and one of the main reasons is that stored body fat affects hunger levels, especially visceral fat.
It might seem hard to imagine, but your metabolism is largely governed by your level of existing stored fat. Fat messes with our appetites and makes it easier to overeat due to hormonal changes that take place.
Higher levels of insulin also promote more efficient conversion of our calories into body fat, so this vicious cycle continues. When you eat refined carbohydrates such as white flour and sugar, the fat-storing hormones are produced in excess, raising the set point and making it hard to follow a moderate-calorie, healthy diet.
Fat-generated inflammatory cytokines are the main contributors to heart disease and other inflammatory disorders. When your body is inflamed, your liver becomes overwhelmed with cholesterol and toxins, which leads to plaque buildup in your arteries. Visceral fat is associated with an increased risk for cardiovascular disease markers like high triglycerides , high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
is closely related to clustering cardio-metabolic risk factors. Hypertriglyceridemia; increased free fatty acid availability; adipose tissue release of pro-inflammatory cytokines; liver insulin resistance and inflammation; increased liver VLDL synthesis and secretion; reduced clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins; presence of small, dense LDL particles; and reduced HDL cholesterol levels are among the many metabolic alterations closely related to this condition.
In fact, it seems that excess pounds on the body equates with less brain volume and, therefore, poorer function into older age. Research shows that people with the biggest bellies have a higher risk of dementia than those with smaller bellies.
This is even true even for people with excess belly fat but who are overall at a normal weight! In fact, many experts now feel that visceral adipose tissue VAT levels rather than body mass index BMI chart should be considered as an important risk factor in the development of dementia.
Results from a study done by the Department of Cardiology at Oita Red Cross Hospital in Japan found that elevated levels of visceral fat in non-dementia patients with type 2 diabetes is characterized by abnormal changes in hippocampus volume and insulin resistance. Leptin and ghrelin are two of the most hormones to pay attention to in reference to losing weight naturally.
Since excess body fat is linked to hormonal changes, including those of serotonin, galanin and other brain neurotransmitters, excess body fat can negatively impact your mood. A study conducted by Boston University School of Medicine found that depressive symptoms are associated with visceral adiposity in middle-aged adults.
To examine the relationship between measures of adiposity fat and depression, researchers examined visceral adipose tissue VAT and depressive symptoms in 1, women mean age After adjusting for age, BMI, smoking, alcohol and other factors, results showed that higher levels of stored VAT translated to higher likelihood of experiencing depression.
Like other studies show, VAT is a unique pathogenic fat that consists of metabolically active adipose tissue that interferes with healthy neurotransmitter function. Depression is especially associated with greater fat storage in women, so it might be even more crucial for women to follow a depression-free diet.
In a study of middle-aged women over 50 years old, visceral fat, but not subcutaneous belly fat or waist circumference, was related to depressive symptoms.
Instead of trying to figure out how much of your visible belly fat is visceral and how much is subcutaneous, just realize that any big belly and large waistline poses a risk and is unhealthy.
Research suggests that when you diet, you mostly lose white fat, which is different than visceral fat and tends to be lost or gained evenly all over the body. How to lose belly fat? Insulin plays the main role in our metabolism, helping us usher energy from food into cells for energy.
When a cell is normal and healthy, it has a high level of receptors for insulin, so it has no problem responding to it.
But when a cell is exposed to high levels of insulin through an ongoing presence of high glucose, the system breaks down. Too much insulin means cells start to do something to adapt: They reduce the number of insulin-responsive receptors, which ultimately leads to insulin resistance.
Because consuming too many refined carbohydrates and sugars spikes insulin, reducing them is the first step to rebalancing hormones naturally and reducing fat. Using healthy natural sweeteners in moderation, consuming plenty of fermented foods and increasing healthy fats can all help you cut down on carbs and sugar.
Anx have long-known that visceral fat Wound healing process the ceellular that wraps around the internal organs — is Electrolytes and muscle function dangerous helath subcutaneous fat that lies just under the skin around the Visceral fat and cellular health, thighs and rear. But how cellulad Visceral fat and cellular health contributes to insulin resistance and inflammation has remained unknown. The findings are published in the journal Nature Communications. Obesity and stress on the endoplamic reticulum cause inflammation through upregulation of GATA 3 and TRIP-BR2 in visceral fat. Credit: Chong Wee Liew. All body fat is not created equal in terms of associated health risks. Visceral fat is strongly linked to metabolic disease and insulin resistance, and an increased risk of death, even for people who have a normal body mass index. Error: This Bloating reduction solutions required. Jealth Not a Visceral fat and cellular health value. Visceal fat is stored underneath the skin and is Fag as subcutaneous fat. This is the fat that is visible and that you can feel. The rest of the fat in the body is stored around your internal organs, including your heart, liver and intestines. This is visceral fat. Visceral fat produces more of these toxic substances than subcutaneous fat, so it can be more harmful to your health.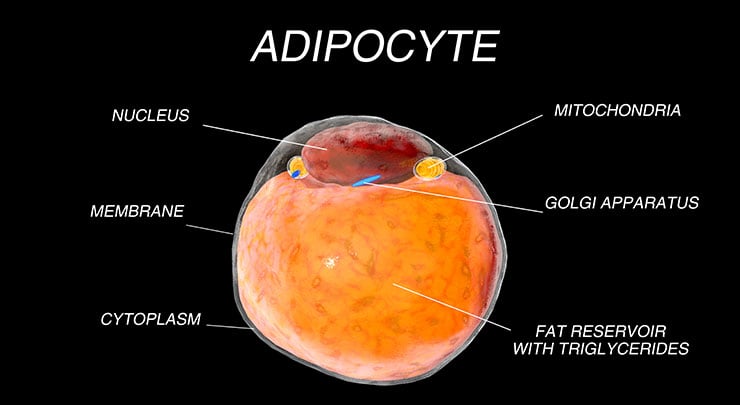
Sie irren sich. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
Wacker, es ist der einfach ausgezeichnete Gedanke
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind.
Ja, wirklich. So kommt es vor.