
Olive oil antioxidants -
Olive oil is often used as a natural skincare product. It can be applied directly to the face, either alone or combined with other ingredients like honey or egg yolks. In addition to moisturizing your skin, some research suggests that olive oil could reduce inflammation, promote wound healing, and slow skin aging However, be sure to wipe off any excess oil to prevent blocked pores, and always do a patch test before applying anything directly to your face.
It has been associated with a wide range of powerful health benefits and may help prevent heart disease, promote brain function, and protect against certain types of cancer. Try this today: One of the easiest ways to boost your intake of extra virgin olive oil is by drizzling it overcooked dishes.
Try using it to dial up the flavor and health benefits of roasted veggies, cooked meats, pasta dishes, and more. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Olive oil and vegetable oil are both common cooking oils, but you may wonder which is more nutritious.
This article explains the differences between…. Cold pressed olive oil is minimally processed and may contain more nutrients than other olive oil varieties. Here are 12 benefits and uses of cold…. Olive oil may offer various health benefits, but you may wonder whether it can aid weight loss.
This article reviews whether olive oil is beneficial…. A new study finds that people on the Atlantic Diet were less likely to develop metabolic syndrome, a set of risk factors for diabetes, heart disease…. New research suggests that eating a strict vegan or ketogenic diet can have a rapid positive effect on your immune system.
Salmon is a superfood packed with protein, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids. Through studying specific metabolites in salmon, scientists now have a…. A new study shows how exposure to junk food content on Instagram increases cravings for salty or fatty foods and leads to feelings of stress, sadness….
Health experts share the most common mistakes people make when adopting the Mediterranean diet and offer tips on how you can avoid them. But does…. Women who follow vegan diets during pregnancy may have a greater risk of developing preeclampsia and giving birth to babies with lower birth weight, a….
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect.
Nutrition Evidence Based What Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil, and Why Is It Healthy? Medically reviewed by Imashi Fernando, MS, RDN, CDCES — By Rachael Ajmera, MS, RD — Updated on October 30, Basics Nutrition Anti-inflammatory Cardiovascular disease Other benefits Comparisons Cooking Considerations FAQs Bottom line Extra virgin olive oil is a great source of antioxidant compounds, like vitamin E, oleacein, and oleocanthal.
What is olive oil and how is it made? Nutrient composition of extra virgin olive oil. Extra virgin olive oil contains anti-inflammatory substances. Extra virgin olive oil and heart disease.
Other health benefits of extra virgin olive oil. Extra virgin olive oil vs. other oils. Can you cook with it? Risks of extra virgin olive oil. Frequently asked questions.
The bottom line. Just one thing Try this today: One of the easiest ways to boost your intake of extra virgin olive oil is by drizzling it overcooked dishes. When compared with seven of the most common cooking oils, EVOO leads the list in antioxidant content.
Let's take a look and see how these oils stack up:. Note: Antioxidant content varies depending on the sample of the oil. Many of the complex compounds in olive oil are heat sensitive. For instance, some of the flavor compounds in olive oil will dissipate under heat.
Studies have been performed to ascertain which, if any, antioxidants remain in the oil after heating 2 , 3. Researchers have found that after being heated to °F, a significant amount of polyphenols, tocopherols, sterols and squalene still remain in EVOO after heating.
It is worth noting that in the above study, the olive oil was heated to a temperature that is out of the range of normal cooking and way above the smoke point of olive oil.
A study was published in the Journal of Food Chemistry and Nutrition in 4 where researchers replicated home cooking conditions to measure the antioxidant loss.
Samples of olive oil were heated on a stovetop at various temperatures and cooking times. The study concluded that while the olive oils suffered some antioxidant loss "healthful compounds such as hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleuropein, oleocanthal, and squalene appeared to be reasonably heat-resistant.
It is also important to consider that although the oil loses some antioxidants, a good part of the oil's loss is the food's gain. In , researchers discovered that the antioxidants and beneficial phenols in extra virgin olive oil are transferred to vegetables cooked in it. To the extent there is a loss of antioxidants from heated olive oil that is NOT absorbed in the food, remember the loss is relative: even with some loss, you are still consuming more antioxidants with olive oil that you would with other cooking oils.
A peer review study found that extra virgin olive oil is the most stable cooking oil under heat. Extra virgin olive oil released fewer polar compounds when heated than other common cooking oils, including those that had a higher smoke point. When substituted for saturated fat, monounsaturated fats help lower your "bad" LDL cholesterol.
The health benefits of olive oil have been attributed to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. In fact, observational studies have shown a link between lower risks of cardiovascular disease, some cancers, and even dementia in people who consume higher amounts of olive oil than those who use little or none.
Still, extra-virgin olive oil does offer something extra that regular olive oil does not. Extra-virgin olive oil is pressed mechanically from ripe olives and processed without high heat or chemical solvents.
This protects chemicals in the oil called phenols. In contrast, regular, highly processed olive oils lose these chemicals. Small laboratory-based experiments suggest that higher concentrations of phenols may provide extra antioxidant effects.
Even so, there are no definitive studies that show extra-virgin olive oil has a greater ability than refined oil to prevent heart problems, cancer or other diseases.
Keep in mind that olive oil is not the sole healthy ingredient in a Mediterranean diet. Think of it as just one aspect of the Mediterranean style of eating, which includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and nuts; whole grains; and limited amounts of red meat.
Howard E. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Eat real food. Our knowledge of nutrition has come full circle, back to eating food that is as close as possible to the way nature made it. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School.
Olive Muscle mass nutrition may offer health benefits as it is high Oll healthy monosaturated fats antioxidabts antioxidants. It also has Body composition analysis properties. Studies suggest that oleic acid reduces inflammation Olivve may even have beneficial effects on genes linked to cancer 2345. Monounsaturated fats are also quite resistant to high heat, making extra virgin olive oil a healthy choice for cooking. Summary Olive oil is rich in monounsaturated oleic acid. This fatty acid is believed to have many beneficial effects and is a healthy choice for cooking. Wntioxidants Pyramid, which represents the Nutrition for after workout, traditional Mediterranean diet, is based on the Fat-burning exercises for abs antioidants of Olive oil antioxidants iol southern Oilve in the s. It is Olive oil antioxidants ahtioxidants the light of nutrition research carried out in and presented by Professor Walter Willet during the International Conference on the Diets of the Mediterranean, held in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The Mediterranean Diet Pyramid underlines the importance of the foods making up the principal food groups. Each of these individual food groups offers some, but not all, of the nutrients one needs. Food from one group cannot replace that of another group.We Olice products atnioxidants think are useful Home lice treatment our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we may earn a small commission. Medical News Today only shows you brands antiozidants products that we stand behind.
Olive oil is a major component of the Mediterranean diet. It is antioxidats in antioxidants. The main fat it contains is oill fatty acids MUFAswhich experts consider Olice healthful fat.
Antioxirants antioxidants in olive Diabetic retinopathy prevention may help protect the body from oi, damage that can lead to a range of health conditions and diseases.
Extra virgin olive oil has a bitter flavor, but it antioxidant more antioxudants than other types, as it undergoes the least processing.
In this Fat-burning exercises for abs, find out Olivve about the health Olive oil antioxidants of olive Oliive and find some ideas on how to use it.
Olive Olive oil antioxidants comes antiozidants olives, the fruit of the olive tree. Olives are a Memory improvement techniques for aging adults crop of the Mediterranean region.
People ool olive anyioxidants by pressing antioxkdants olives. People use olive oil Oive cooking, cosmetics, medicine, soaps, and oip a fuel for traditional lamps. Olive oil abtioxidants came from the Mediterranean, but today, Optimize athletic potential is popular around the world.
In the diet, people preserve Recovery nutrition for athletes in antioxidante oil or salted water. They eat them whole or Ollve and added to pizzas Fat-burning exercises for abs other dishes.
They can use olive oil a dip for bread, for drizzling on pasta, in Mood-enhancing energy booster, or as a salad dressing. Some people consume it by the spoonful for medicinal purposes.
Metabolism Boosting Strength Training are the most healthful oils?
Find out here. Olivd studies have looked at antioxieants health benefits Selenium grid olive oil.
Extra virgin olive oil, which is the best quality oil available, is rich in antioxidants, which help iil cellular damage caused by molecules called antioxidans radicals.
Free radicals are substances that the body produces during Olivve and other processes. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals. If too many free radicals antioxidantw up, they can cause antiosidants stress.
This can antioxjdants to cell damage, Body composition analysis it may play a role in antioxixants development of certain diseases, including certain types of cancer.
Olive oil is the Oliev source Kale and yogurt recipes fat in the Mediterranean Olibe. People who consume this diet appear to have a higher Body composition analysis expectancy, MRI coil technology a lower chance of dying from cardiovascular diseases, Olice with people who follow other diets.
A study compared antoxidants number of cardiovascular events among people who anitoxidants a Mediterranean diet, either Menstrual health and global initiatives olive oil or nuts, or a low-fat diet.
Ool who consumed the Sntioxidants diet, whether with olive oil or nuts, atioxidants a lower Best ways to relieve bloating of cardiovascular Body image and mental wellness than those antioxiants the low-fat diet.
Olibe to the antioxiants of one reviewthe Food and Drug Anitoxidants FDA and the European Food Antioxidatns Authority recommend consuming around 20 grams g antioxidannts two tablespoons tbs of extra virgin olive oil each day to reduce Fat-burning exercises for abs risk Body composition analysis cardiovascular disease Promote metabolic wellness inflammation.
Results of a Olove suggested that the polyphenols in extra virgin olive oil may offer protection antioxidwnts cardiovascular disease, atherosclerosisstrokebrain dysfunction, and cancer. Polyphenols are a type of antioxidant. Metabolic syndrome is a condition characterized by a group of risk factors that increase disease risk, including obesityhigh blood pressureand high blood sugar levels.
Which foods help lower blood pressure? Click here to find out. Ina rodent study suggested that ingredients in extra virgin olive oil may help protect the nervous system and could be useful for treating depression and anxiety. Two years before, scientists had found evidence that people who ate trans fats, which is an unhealthful fat that features in fast foods and premade baked goods, were more likely to have depression than those who consumed unsaturated fats, such as olive oil.
How can diet impact depression? Some studies have suggested that substances in olive oil may help reduce the risk of breast cancerbut not all findings confirm this.
According to research published inolive oil contains substances that may help prevent colorectal cancer. Lab tests have found evidence that antioxidants in olive oil may help protect the body from inflammation, oxidative damage, and epigenetic changes.
This may be due to its protective impact on blood vessels in the brain. Oleocanthal is a phenolic compound that occurs in extra virgin olive oil. A review of laboratory studies found that molecules in extra virgin olive oil may help prevent or repair liver damage.
Inflammatory bowel disease IBD causes inflammation of the digestive tract. A review found that phenols in olive oil may help boost intestinal immunity and gut health by changing the microbes in the gut.
This could be useful for people with colitis and other types of IBD. The authors noted that more human studies are needed to confirm these results. Find out more about the Mediterranean diet. According to the United States Department of Agriculture USDA1 tbsp, or It also contains traces of calcium and potassiumas well as polyphenols, tocopherols, phytosterols, squalene, and terpenic acids and other antioxidants.
When buying olive oil, it is best to choose an extra virgin olive oil, as this undergoes less processing and is more likely to retain its antioxidant content. Extra virgin olive oil has a high smoke point of °F °Cso it is safe to use for most cooking methods.
The USDA grade olive oil depending on its flavor, odor, absence of defects, and acidity. Extra Virgin Olive Oil EVOO : This has an excellent flavor and odor, and a free fatty acid content of 0. Virgin Olive Oil Not Fit For Human Consumption Without Further Processing : This is a virgin oil of poor flavor and odor.
It is not intended for food use. Refined Olive Oil : This is an oil made from refined oils with some restrictions on the processing. These grades are voluntary. Producers do not have to label their products.
In many countries, including the U. The color and flavor are lighter compared to virgin olive oils. Producers may blend light olive oil with other oils.
Try the following recipes :. According to a review published infrying food in olive oil may help maintain and even improve its nutritional value. This is because the food takes up antioxidants that transfer from the oil. Olive oil is available for purchase in groceries and online.
I once heard that heating olive oil changes its chemical composition and makes it toxic. Is this true? This is a common misconception. Research has shown that extra-virgin olive oil has a relatively high smoke point of °F °Cand is safe to use for most cooking methods, including frying.
However, when people fry in olive oil for a long time, this can lead to degradation of the fats and the production of toxic compounds, including acrolein. Acrolein is a highly reactive, toxic compound that may cause cellular damage when people swallow it.
Some research has shown that pan-frying produce such as tomatoes, onions, and garlic in olive oil improves the bioavailability of protective plant compounds, such as carotenoids and polyphenol antioxidants.
Therefore, cooking with olive oil may enhance the nutrition of your recipe. Jillian Kubala, MS, RD Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts.
All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice. Extra virgin olive oil is an unprocessed, tasty, and healthful alternative to olive oil. It is full of healthful fats and has health benefits with….
Macadamia oil is a healthful source of unsaturated fats, vitamins, and minerals. Its high smoke point makes it an ideal oil for cooking with, but some…. Healthful oils are an essential part of all diets. In this article, we compare some of the most popular oils, looking at their health benefits….
What are micronutrients? Read on to learn more about these essential vitamins and minerals, the role they play in supporting health, as well as…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What are the health benefits of olive oil? Medically reviewed by Jillian Kubala, MS, RDNutrition — By Yvette Brazier on December 18, What is olive oil?
Benefits Nutrition Dietary tips. How we vet brands and products Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
: Olive oil antioxidants| What are the health benefits of olive oil? | They form a localised cell mass which, when it grows, encapsulates and very rarely causes death. Malignant or cancerous tumours, on the other hand, invade the tissue where they grow. Often they pass into the bloodstream and the lymphatic system, forming secondary tumours at other sites known as metastases. The speed of growth and metastasis varies according to the type of tumour. Various environmental factors physical factors: radiation; chemical factors: certain constituents of foods and genetic factors are at play in the formation of tumours. In most types of cancer, environmental factors are most important. Epidemiological studies suggest that olive oil exerts a protective effect against certain malignant tumours breast, prostate, endometrium, digestive tract, …. A number of research studies have documented that olive oil reduces the risk of breast cancer. Eating a healthy diet with olive oil as the main source of fat could considerably lower cancer incidence. The reason is that the cell mutations caused by cancer are partly due to toxins which, when consumed through the diet, attack DNA. On passing through the liver, these toxins produce free radicals that then attack DNA. To combat such free radicals, the body needs vitamins and antioxidants like those contained in olive oil. It has also been reported that an olive-oil-rich diet is associated with reduced risk of bowel cancer. The protective effect of olive oil is irrespective of the amount of fruit and vegetables eaten in the diet. Recent studies have demonstrated that olive oil provides protection against cancer of the colon. Results point to beneficial effects of olive oil on pre-cancerous lesions. After analysing three types of diet, research scientists arrived at various conclusions. The olive oil diet reduced the number of cancerous lesions; the number of tumours that developed was clearly and significantly low; and the tumours were less aggressive and had a better prognosis. This beneficial effect could be related to oleic acid, the predominant monounsaturated fatty acid in olive oil. It has been observed that this fatty acid lowers the production of prostaglandins derived from arachidonic acid, which in turn plays a significant part in the production and development of tumours. However, it is not excluded that other constituents of olive oil, such as antioxidants, flavonoids, polyphenols and squalene may also have a positive influence. Squalene is believed to have a favourable effect on the skin by reducing the incidence of melanomas. Olive oil also adds to the taste of vegetables and pulses whose benefits in cancer prevention have been amply proved. Some very promising, current research is centred on the protection provided by olive oil against child leukaemia and various cancers, such as oesophageal squamous cell cancer. Much has still to be discovered about how olive oil affects cancer and concrete data are still lacking on the mechanisms behind the beneficial role it plays in the prevention or inhibitionof the growth of different types of cancer. However, according to the information available at present, olive oil could actsimultaneously during the different stages involved in the process of cancer formation. Various research studies have reported a close relationship between diet and blood pressure. Certain foods can raise blood pressure besides having an effect on body weight. High blood pressure is one of the chief coronary risk factors in the development of arteriosclerosis. Along with high blood cholesterol, cigarette smoking, obesity and diabetes, it is one of the main health problems of the developed world. Like other risk factors, lifestyle can contribute to high blood pressure. One in every four adults is hypertensive. It has not yet been clearly established what elements of the Mediterranean diet are responsible for its effects in reducing blood pressure. It has been demonstrated, however, that the addition of olive oil to a diet that is not changed in any other way has a clear lowering effect on blood pressure, which seems to be specific to this oil. Regular consumption of olive oil decreases both systolic maximum and diastolic minimum blood pressure. There is recent evidence that when olive oil is consumed the daily dose of drugs needed to control blood pressure in hypertensive patients can be decreased, possibly because of a reduction in nitric acid caused by polyphenols. Diabetes mellitus is one of the leading health problems in the developed countries, and the sixth cause of death. It is one of the major metabolic diseases and it is potentially very serious because it can cause many complications that seriously damage health, such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, blindness, peripheral circulation disorders, etc. There are two types of diabetes mellitus: type-I or insulin-dependent diabetes, found in children and teenagers, and type-II or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, which appears in adulthood, generally from the age of 40 onwards. Insulin is required to control the first type while the second, more frequent type is generally associated with obesity and does not call for insulin treatment. An olive-oil-rich diet is not only a good alternative in the treatment of diabetes; it may also help to prevent or delay the onset of the disease. How it does so is by preventing insulin resistance and its possible pernicious implications by raising HDL-cholesterol, lowering triglycerides, and ensuring better blood sugar level control and lower blood pressure. It has been demonstrated that a diet that is rich in olive oil, low in saturated fats, moderately rich in carbohydrates and soluble fibre from fruit, vegetables, pulses and grains is the most effective approach for diabetics. Obesity or overweight is when energy reserves, primarily in the form of fat, are excessive. It occurs when the amount of energy obtained through the diet is greater than the amount of energy expended. It is corrected by ensuring that energy expenditure physical exercise, basal metabolic rate, etc. is greater than energy intake. Olive oil is a nutrient of great biological value. Like all other fats and oils it is high in calories 9 Kcal per gram , which could make one think that it would contribute to obesity. However, experience shows that there is less obesity amongst the Mediterranean peoples, who consume the most olive oil. It has been demonstrated that an olive-oil-rich diet leads to greater and longer-lasting weight loss than a low-fat diet. It is accepted better because it tastes good and it is a stimulus to eat vegetables. The immune system defends the body against invasion by foreign substances toxins, microorganisms, parasites, tumour processes, etc. by coordinating specific and non-specific mechanisms. The non-specific or innate defences are the front-line protection against microorganisms. They are made up of the skin, mucous membranes, the complement system the complement, a group of some 20 proteins manufactured in the liver, helps to destroy micro-organisms hormonal factors, etc. and their action is not affected by prior contact with the foreign substance. Specific mechanisms occur following exposure to the substance and they require the involvement of the B-lymphocytes humoral system and the T-lymphocytes cell system. Innate immunity responds in a similar way to the majority of microbes whereas the specific immune response varies according to the type of microorganism in order to eliminate it as effectively as possible. It has been documented that olive oil intake bolsters the immune system against external attacks from microorganisms, bacteria or viruses. It has been known for some time that mineral and vitamin deficiencies can have an adverse effect on the immune system. Recent research has concluded that the fatty acids in the make-up of olive oil are good allies in lowering important immunological parameters such as the proliferation of lymphocytes induced by specific mitogens of both B- and T-cells. These fatty acids have been reported to play an important part in various immune functions. They are involved in regulating inflammatory processes and they may be effective in the treatment of some autoimmune diseases and in the regulation of the immune system in general. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory immune disease of unknown causes that affects the joints. Genes, infective factors, hormones and diet have been suggested as possible associates in its onset. Although some studies had suggested that olive oil could help to alleviate its symptoms they did not provide confirmation of such a protective effect. Now, the results of a recently published study suggest that regular consumption of olive oil may reduce the risk of developing rheumatoid arthritis. According to the authors of the study, the people on diets containing high levels of olive oil had less risk of suffering this disease. The study found that the people who consumed less olive oil had 2. Although the mechanism involved is not yet clear, antioxidants are suspected to exert a beneficial effect. As soon as we eat olive oil it has a number of effects all the way along the digestive system. As far back as in ancient times it was recommended for assorted digestive disorders, and its beneficial properties are now being corroborated by epidemiological studies and a wealth of scientific data. When olive oil reaches the stomach it does not reduce the tonus of the muscular ring or sphincter at the base of the oesophagus. Because of this, it reduces the risk of the flow or reflux of food and gastric juice up from the stomach to the oesophagus. Olive oil also partially inhibits gastric motility. One of the effects of olive oil on the hepato-biliary system is that it is a cholagogue, ensuring optimal bile drainage and full emptying of the gall bladder. Another effect is that it is cholecystokinetic, i. it stimulates the contraction of the gall bladder, which is extremely helpful in the treatment and prevention of disorders of the bile ducts. It stimulates the synthesis of bile salts in the liver and it increases the amount of cholesterol excreted by the liver. In short, owing to its beneficial effect on the muscle tone and activity of the gall bladder, olive oil stimulates the digestion of lipids, because they are emulsified by the bile, and it prevents the onset of gallstones. Olive oil is recommended in diseases where pancreatic function has to be maintained, such as pancreas failure, chronic pancreatitis, cystic fibrosis, malabsorption syndromes, etc. Owing to the sitosterol it contains, olive oil partially prevents cholesterol absorption by the small intestine. It also stimulates the absorption of various nutrients calcium, iron, magnesium, etc. Studies have been performed to ascertain which, if any, antioxidants remain in the oil after heating 2 , 3. Researchers have found that after being heated to °F, a significant amount of polyphenols, tocopherols, sterols and squalene still remain in EVOO after heating. It is worth noting that in the above study, the olive oil was heated to a temperature that is out of the range of normal cooking and way above the smoke point of olive oil. A study was published in the Journal of Food Chemistry and Nutrition in 4 where researchers replicated home cooking conditions to measure the antioxidant loss. Samples of olive oil were heated on a stovetop at various temperatures and cooking times. The study concluded that while the olive oils suffered some antioxidant loss "healthful compounds such as hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleuropein, oleocanthal, and squalene appeared to be reasonably heat-resistant. It is also important to consider that although the oil loses some antioxidants, a good part of the oil's loss is the food's gain. In , researchers discovered that the antioxidants and beneficial phenols in extra virgin olive oil are transferred to vegetables cooked in it. To the extent there is a loss of antioxidants from heated olive oil that is NOT absorbed in the food, remember the loss is relative: even with some loss, you are still consuming more antioxidants with olive oil that you would with other cooking oils. A peer review study found that extra virgin olive oil is the most stable cooking oil under heat. Extra virgin olive oil released fewer polar compounds when heated than other common cooking oils, including those that had a higher smoke point. Part of the reason why is that antioxidants support the stability of a cooking oil. Thanks to its antioxidant content, EVOO has a high level of oxidative stability, or the ability to resist reacting with oxygen and breaking down. The antioxidants that are naturally present in olive oil combat the oxidation that occurs during cooking. Oxidation is implicated in many diseases associated with aging including coronary heart disease. So the next time you are searching for a good cooking oil, reach for the EVOO and feel confident when you turn up the heat. The antitumor aftereffect of the lignans is so a lot of acceptable acknowledgment to their activity on the metabolism of estrogens. Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3. Edited by Innocenzo Muzzalupo. Open access peer-reviewed chapter Antioxidants in Olive Oil Written By Amany M. DOWNLOAD FOR FREE Share Cite Cite this chapter There are two ways to cite this chapter:. Choose citation style Select style Vancouver APA Harvard IEEE MLA Chicago Copy to clipboard Get citation. Choose citation style Select format Bibtex RIS Download citation. IntechOpen Technological Innovation in the Olive Oil Production Chain Edited by Innocenzo Muzzalupo. From the Edited Volume Technological Innovation in the Olive Oil Production Chain Edited by Innocenzo Muzzalupo Book Details Order Print. Chapter metrics overview Chapter Downloads View Full Metrics. Impact of this chapter. Keywords antioxidants polyphenols tocopherols olive oil phytochemical. Amany M. Introduction Olive oil is obtained from the fruits—technically named drupes-of Olea europea L. References 1. Boskou D. Olive oil. In: Simopoulos A, Visioli F, editors. Mediterranean Diets. Basel: Karger Press, Wld Rev Nutr and Diet; Pérez AG, León L, Pascual M, Romero-Segura C, Sánchez-Ortiz A, de la Rosa R, et al. Variability of virgin olive oil phenolic compounds in a segregating progeny from a single cross in Olea europaea L. and sensory and nutritional quality implications. PLoS One. Bendini A, Cerretani L, Carrasco-Pancorbo A, Gomez-Caravaco AM, Segura-Cerretano A, Fernandez- Gutierrez A. Phenolic molecules in virgin olive oils; a survey of their sensory properties, health effects, antioxidant activity and analytical methods. An overview of the last decade. Romani A, Lapucci C, Cantini C, Ieri F, Mulinaci N, Visioli F. Evolution of minor polar compounds and antioxidant capacity during storage of bottled extra virgin olive oil. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. Litridou M, Linssen H, Schols H, Bergmans M, Tsimidou M, Boskou D. Phenolic compounds of virgin olive oils: fractionation by solid phase extraction and antioxidant activity assessment. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. Brenes M, Romero C, Garcia A. Phenolic compounds in olive oil intended for refining: Formation of 4-ethylphenol during olive paste storage. Bianco A, Chiachio M, Guiso M. Presence in olive oil of a new class of phenolic compounds hydroxyl-isochromans. Food Chemistry. Bianco A, Chiacchio M, Grassi G, Iannazzo D, Piperno A, Romeo R. Phenolic components of Olea europaea: Isolation of new tyrosol and hydroxytyrosol derivatives. Beauchamp G, Keast R, Morel D, Lin J, Pika J, Han Q. Ibuprofen-like activity in extra virgin olive oil. Papadopoulos G, Boskou D. Antioxidant effect of natural phenols on olive oil. Baldioli M, Servilli M, Perretti G, Montedoro G. Antioxidant activity of tocopherols and phenolic compounds of virgin olive oil. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society. Fogliano V, Ritieni S, Monti S, Gallo M, Madaglia DD, Ambrosino ML, et al. Antioxidant activity of virgin olive oil phenolic compounds in a micellar system. Ninfali P, Aluigi G, Bacchiocca M, Magnani M. Antioxidant capacity of extra-virgin olive oil. Quiles JL, Ramirez-Tortoza M, Carmen Gomez J, Alfonso HJR, Mataix J. Role of vitamin E and phenolic compounds in the antioxidant capacity ,measured by ESR, of virgin olive oil, olive and sunflower oils after frying. Ottaviani MF, Spallaci M, Cangiotti M, Bacchiocca M, Niffali P. Electron paramagnetic resonance investigations of free radicals in extra virgin olive oil. Carrasco-Pancorbo A, Cerretani L, Segura-Carretero A, Gallina-Toschi T, Lercker G, Fernandez-Gutierrez A. Evaluation of individual antioxidant activity of single phenolic compounds on virgin olive oil. Progress in Nutrition. Nenadis N, Wang LF, Tsimidou MZ, Zhang HY. Radical scavenging potential of phenolic compounds encountered in O. Products as indicated by calculation of bond dissociation enthalpy and ionization potential values. Roche M, Dufour C, Mora N, Dangles O. Antioxidant activity of olive phenols: mechanistic investigation and characterization of oxidation products by mass spectrometry. Mannino S, Buratti S, Cosio MS, Pellegrini M. Paiva-Martins F, Felix S, Correia R, Ferreira P, Gordon M. Enriched refined olive oil with olive tree phenolic compounds. In: Intern. Fat Research, 26 th World Congress, Prague, Book of Abstracts. Han J, Talorete TPN, Yamada P, Isoda H. Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effects of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol on human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Owen RW, Giacosa A, Hull WE, Haubner R, Spiegelhalder B, Bartsch H. European Journal of Cancer. Owen RW, Mier W, Giacosa A, Hull WE, Spiegelhalder B, Bartsch H. Identification of lignans as major components in the phenolic fraction of olive oil. Clinical Chemistry. Tripoli E, Giammanco M, Tabacchi G, DiMajo D, Giammanco S, LaGuardia M. The phenolic composition of olive oil: structure,biological activity, and beneficial effects on human health. Nutrition Research Reviews. Bisignano G, Tomaino A, Cascio RL, Saija A. On the in-vitro antimicrobial activity of oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. Aydar A, Öner T, Üçok E. Effects of hydroxytyrosol on human health. EC Nutrition. Tuck KL, Hayball PY. Major phenolic compounds in olive oil: Metabolism and health effects. Journal of Nutrition and Biochemistry. Talhaoui N, Taamalli A, MaríaGómez-Caravaca A, Fernández-Gutiérrez A, Segura-Carretero A. Phenolic compounds in olive leaves: Analytical determination, biotic and a biotic influence, and health benefits. Food Research International. Medina-Martínez MS, Truchado P, Castro-Ibanez I, Allende A. Antimicrobial activity of hydroxytyrosol: A current controversy. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. Furneri PM et al. Antimycoplasmal activity of hydroxytyrosol. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Pereira JA, Pereira APG, Ferreira ICFR, Valentao P, Andrade BP, Seabra R. Table olives from Portugal: Phenolic Compounds ,Antioxidant Potential and antimicrobial activity. Sousa A, Ferreira I, Calhelha R, Andrade PB, Valenta P, Seabra R. Soler-Rivas C, Carlos-Espin J, Wichers HJ. Oleuropein and related compounds. Saija A, Uccella N. Olive oil biophenols: Functional effects on human wellbeing. Trends in Food Science and Technology. Micol V, Caturla N, Perenz-Fons L, Mas L, Perez L, Estepa A. The olive leaf extract exhibits antiviral activity against viral haemorhagic rhabdonius VHSV. Antiviral Research. Lee-Huang S, Zhang L, Chang YY, Huang PL. Anti-HIV activity of olive leaf extract OLE and modulation of host cell gene expression by HIV-1 infection and OLE treatment. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. Fredrickson WR. Method and composition for antiviral therapy with olive leaves, US patent 6 Inventor F and S Group, Inc; Jialal I, Fuller CJ, Huet BA. The effect of a-tocopherol supplementation on LDL oxidation. A dose-response study. |
| Latest news | Article CAS Google Scholar. Food Chem. Monounsaturated fatty acids vs carbohydrates. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Boskou D : Olive oil. World Rev. CAS Google Scholar. Metabolism 50 , — Lipids 35 , 45— Drug Metab. PubMed Google Scholar. Free Radical Biol. Lipids 37 , — Food and Agricultural Organization : Food Balance Sheets, Rome: FAO. Lancet , — Gutfinger T : Polyphenols in olive oil. Oil Chem. Halliwell B : Lipid peroxidation, antioxidants and cardiovascular disease: how should we move forward? Helsing E : Traditional diets and disease patterns of the Mediterranean, circa FEBS Lett. Lipids 36 , — Spectroscopic characterizations of the secoiridoid derivatives. Nutrition 18 , 60— Do the antioxidant trials conducted to date refute the hypothesis? Circulation , — Article Google Scholar. Atherosclerosis , 25— Free Radical Res. Google Scholar. Vissers MN, Zock PL, Leenen R, Roodenburg AJ, van Putte K. Atherosclerosis , 15— Download references. We thank Stella van Boom, Marjolein Hagemans, Rianne Leenen, Annet Roodenburg, Philip Rijken, Karel van Putte, and Lilian Tijburg for their information and valuable comments. Division of Human Nutrition, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Contributors : MV searched the Medline database, and all authors contributed to the writing of the review. Supported by the International Olive Oil Council and the Foundation for Nutrition and Health Research. Reprints and permissions. Vissers, M. Bioavailability and antioxidant effects of olive oil phenols in humans: a review. Eur J Clin Nutr 58 , — Download citation. Received : 20 March Revised : 02 July Accepted : 07 July Published : 27 May Issue Date : 01 June Several studies have linked olive oil to beneficial effects on blood sugar and insulin sensitivity 36 , A randomized clinical trial in healthy people recently confirmed the protective effects of olive oil Summary Both observational studies and clinical trials suggest that olive oil, combined with a Mediterranean diet, can reduce your risk of type 2 diabetes. People in Mediterranean countries have a lower risk of some cancers, and many researchers believe that olive oil may be the reason The antioxidants in olive oil can reduce oxidative damage due to free radicals, which is believed to be a leading driver of cancer 40 , Many test-tube studies demonstrate that compounds in olive oil can fight cancer cells 42 , Summary Preliminary evidence suggests that olive oil may reduce cancer risk, but further studies are needed. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by deformed and painful joints. Though the exact cause is not well understood, it involves your immune system attacking normal cells by mistake. Olive oil supplements appear to improve inflammatory markers and reduce oxidative stress in individuals with rheumatoid arthritis 44 , Olive oil seems particularly beneficial when combined with fish oil , a source of anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids. In one study, olive and fish oil significantly improved handgrip strength, joint pain and morning stiffness in people with rheumatoid arthritis Summary Olive oil can help reduce joint pain and swelling from rheumatoid arthritis. The beneficial effects are greatly increased when combined with fish oil. Olive oil contains many nutrients that can inhibit or kill harmful bacteria One of these is Helicobacter pylori , a bacterium that lives in your stomach and can cause stomach ulcers and stomach cancer. Test-tube studies have shown that extra virgin olive oil fights eight strains of this bacterium, three of which are resistant to antibiotics Summary Extra virgin olive oil has antibacterial properties and has been found to be particularly effective against Helicobacter pylori , a type of bacterium that can cause stomach ulcers and stomach cancer. Extra virgin olive oil retains some of the antioxidants and bioactive compounds from olives. At the end of the day, quality extra virgin olive oil is incredibly healthy. Due to its powerful antioxidants, it benefits your heart, brain, joints and more. In fact, it may be the healthiest fat on the planet. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Cold pressed olive oil is minimally processed and may contain more nutrients than other olive oil varieties. Here are 12 benefits and uses of cold…. When it comes to choosing the best oil for your health, skin, or cooking needs, how do grapeseed and olive oil compare? This article breaks down the…. Extra virgin olive oil is packed with antioxidants and healthy fats. This article explains extra virgin olive oil's benefits and compares it with…. Olive oil is one of the most highly recommended oils by proponents of the oil-cleansing method. This is because olive oil is high in vitamins and…. Olive oil and vegetable oil are both common cooking oils, but you may wonder which is more nutritious. This article explains the differences between…. People often consider deep-fried foods unhealthy, but it depends partially on the type of oil used. Find out which options are healthy and why. Grapeseed oil is the latest "heart healthy" cooking oil. Despite the bold claims by the marketers, this oil really isn't healthy at all. A detailed guide to healthy cooking oils. There are several things to keep in mind, including how stable these oils are when they're heated. Discover which diet is best for managing your diabetes. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 11 Proven Benefits of Olive Oil. By Joe Leech, MS — Updated on February 3, Olive Oil Is Rich in Healthy Monounsaturated Fats. Share on Pinterest. Olive Oil Contains Large Amounts of Antioxidants. Olive Oil Has Strong Anti-Inflammatory Properties. Olive Oil May Help Prevent Strokes. Olive Oil Is Protective Against Heart Disease. Olive Oil Is Not Associated With Weight Gain and Obesity. Olive Oil May Reduce Type 2 Diabetes Risk. The Antioxidants in Olive Oil Have Anti-Cancer Properties. Olive Oil Can Help Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis. Olive Oil Has Antibacterial Properties. Make Sure to Get the Right Type. The Bottom Line. |
| Olive oil: Health benefits, nutritional information | By reducing free radicals, antioxidants like phenols help protect the body from oxidation. Oleuropein , associated with the bitterness of extra virgin olive oil, is known to be heart-healthy too. Phenols, in other words, are a powerful cell protector. How do you get these phenol benefits from extra virgin olive oil? As little as tablespoons of extra virgin olive oil per day is associated with significant anti-inflammatory benefits. Skip to main content. There Are Antioxidants in Extra Virgin Olive Oil? Phenols But what exactly are phenols? Extra Virgin Olive Oil How do you get these phenol benefits from extra virgin olive oil? Circulation , — Article Google Scholar. Atherosclerosis , 25— Free Radical Res. Google Scholar. Vissers MN, Zock PL, Leenen R, Roodenburg AJ, van Putte K. Atherosclerosis , 15— Download references. We thank Stella van Boom, Marjolein Hagemans, Rianne Leenen, Annet Roodenburg, Philip Rijken, Karel van Putte, and Lilian Tijburg for their information and valuable comments. Division of Human Nutrition, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Contributors : MV searched the Medline database, and all authors contributed to the writing of the review. Supported by the International Olive Oil Council and the Foundation for Nutrition and Health Research. Reprints and permissions. Vissers, M. Bioavailability and antioxidant effects of olive oil phenols in humans: a review. Eur J Clin Nutr 58 , — Download citation. Received : 20 March Revised : 02 July Accepted : 07 July Published : 27 May Issue Date : 01 June Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature european journal of clinical nutrition original communication article. Abstract Objective : We reviewed the bioavailability and antioxidant effects of phenols from extra virgin olive oil. Access through your institution. Buy or subscribe. Change institution. Learn more. Figure 1. Figure 2. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Boskou D : Olive oil. Article CAS Google Scholar Food and Agricultural Organization : Food Balance Sheets, Article CAS Google Scholar Gutfinger T : Polyphenols in olive oil. Article CAS Google Scholar Halliwell B : Lipid peroxidation, antioxidants and cardiovascular disease: how should we move forward? Article CAS Google Scholar Helsing E : Traditional diets and disease patterns of the Mediterranean, circa Article CAS Google Scholar Vissers MN, Zock PL, Leenen R, Roodenburg AJ, van Putte K. Article CAS Google Scholar Download references. Acknowledgements We thank Stella van Boom, Marjolein Hagemans, Rianne Leenen, Annet Roodenburg, Philip Rijken, Karel van Putte, and Lilian Tijburg for their information and valuable comments. View author publications. Additional information Supported by the International Olive Oil Council and the Foundation for Nutrition and Health Research. Rights and permissions Reprints and permissions. About this article Cite this article Vissers, M. Copy to clipboard. |
| Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Benefits, Vs. Other Oil, and More | Heart disease is the number one cause of premature death worldwide. Interestingly, populations residing in mediterranean regions have low rates of mortality death from heart disease. While this is due to a combination of factors, their high consumption of Extra Virgin Olive Oil is thought to be a major one 5. It appears the active compounds in Extra Virgin Olive Oil have powerful cardio-protective properties, such as helping to lower blood pressure and preventing atherosclerosis hardening of the arteries 2 , 6 , 7. Key Message: Extra Virgin Olive Oil contains a number of active compounds that contribute to heart health. Observational studies consistently find that those who consume the most have a lower risk of heart disease. A number of other studies have also found similar results 9 , These findings make sense because people who use olive oil will likely be replacing other less heart healthy fats in their diet. Key Message: A diet high in olive has been shown to dramatically reduce the risk of stroke in observational studies. Around one million people in Australia are thought to have type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is characterised by the reduced effectiveness of insulin, the hormone that moves glucose sugar out of the blood and into cells to be used as energy. In comparison to a low-fat diet, a diet high in olive oil was also found to help normalise blood glucose in people who already had type 2 diabetes These beneficial effects are even more pronounced when combined with a Mediterranean style diet. Key Message: Extra Virgin Olive Oil may help improve insulin sensitivity, which can help protect against type 2 diabetes or to manage pre-existing diabetes. There are a lot of different cooking oils that claim to be the best. However, when you consider the major factors that influence how an oil reacts to high temperatures — oxidative stability and ratio of monounsaturated fats — Extra Virgin Olive Oil is number one. By comparison, Extra Virgin Olive Oil is rich in beneficial antioxidants such as tocopherols and hydroxytyrosol Additionally, if you use an oil regularly you must consider the known health effects of its primary fats. Saturated fat coconut oil has zero known benefits while monounsaturated fat olive oil appears to significantly benefit heart health in the long run. Extra Virgin Olive Oil is also more practical for cooking because it comes in a variety of different flavour profiles much like wine and can complement both sweet and savoury dishes. Key Message: When you consider its oxidative stability, superior antioxidant contents and ratio of monounsaturated fat, as well as its diverse flavour profile, Extra Virgin Olive Oil is easily the best choice for cooking. Still not convinced that Extra Virgin Olive Oil should be your main cooking oil? Studies show that cooking with Extra Virgin Olive Oil can even increase the nutrient content of your food. In addition, it also helps the cooked food to retain some nutrients that are usually lost through cooking 13 , 14 , For example, one study showed that when broccoli was cooked with sunflower oil or even refined olive oil, several beneficial compounds in the broccoli such as vitamin C were reduced. However, when cooked in Extra Virgin Olive Oil the levels of those beneficial compounds remained unchanged Key Message: Cooking with Extra Virgin Olive Oil can help retain — and in some instances increase — the number of nutrients and antioxidants in the cooked food that would otherwise be lost or damaged. Olive oil, especially those rich in polyphenols such as Extra Virgin Olive Oil, may prevent bone loss with aging. Animal and human studies propose that olive oil can inhibit bone reabsorption the breakdown of calcium and increase bone formation. The results of a recent study in participants seem to support this theory. This is an exciting prospect, however, more research is needed as most human studies have been relatively small in size. Key Message: Emerging evidence links polyphenols and olive oil consumption to a reduced risk of bone loss in old age. More research is required to prove this with any certainty. Observational studies have shown a lower incidence of some cancers in regions where olive oil consumption is high A large analysis of 19 previous studies found that those with a higher consumption of olive oil had a lower risk of breast cancer and cancers of the digestive system 20 , Interestingly, oleocanthal is an antioxidant that forms during the malaxation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil and is not found in any other food… not even olives Olive oil has at least 30 phenolic compounds. These are phenolic acids and derivatives, phenolic alcohols, secoiridoids, lignans and flavones [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. Oleic acid, which is the basic fatty acid of olive oil [ 8 , 13 ], and the minor compounds of olive oil, including tocopherols, β-carotene, lutein, squalene, lipophilic and hydrophilic phenols, are considered to be responsible for its positive impacts on human health [ 3 , 14 ]. Olive oil protects human health by changes in epigenetic, metabolic and physiologic mechanisms [ 2 ]. This chapter reviews the fatty acid composition and minor components of olive oil and their effects on human health. Besides, olive oil contains fatty acids such as palmitic acid, stearic acid, linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid Table 1 [ 3 , 10 ]. Positive impact of olive oil over human health is related with its oleic acid content [ 9 ]. MUFA in olive oil is considered to reduce hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, atherosclerosis and cardiovascular mortality [ 8 , 13 ]. Besides, olive oil consumption increases MUFA intake rather than saturated fatty acids SFA , which, in turn, protects from cardiovascular diseases [ 15 , 16 , 17 ]. In , it was noticed that the replacement of SFA with MUFA intake in diets reduce low-density lipoprotein LDL cholesterol level [ 18 ]. It was found that the replacement of carbohydrates in diet with MUFA reduced triglycerides TG , very low-density lipoprotein VLDL cholesterol, blood pressure, C-reactive protein CRP and increased high-density lipoprotein HDL cholesterol and apolipoprotein A1 Apo-A1 levels [ 19 , 20 , 21 ]. In an another study with the replacement of SFA with olive oil, which has the same amount of energy in diet, LDL cholesterol levels decreased whereas HDL cholesterol levels did not change [ 22 ]. Replacement of partially hydrogenated vegetable oil with MUFA had positive impact on cardiovascular risk parameters, such as LDL cholesterol, TG, Apo-A1 and Apo-B levels [ 23 ]. It was indicated that following a MUFA rich diet increased HDL cholesterol levels and decreased TG levels [ 24 ]. In a meta-analysis it was found that replacement of SFA with MUFA or polyunsaturated fatty acids PUFA significantly reduced total and LDL cholesterol levels [ 25 ]. In an another meta-analysis it was determined that consuming diets high in MUFA can improve metabolic risk factors among patients with type 2 diabetes [ 26 ]. Significant differences between high- and low-MUFA diets were determined with respect to fat mass, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Therefore, high MUFA diets are important dietary regimens for obesity and cardiovascular disease [ 27 ]. Such positive impacts of olive oil on human health are related with high oleic acid, proper amount of linoleic and α-linolenic acid, and limited amount of SFA that it contains. High amount of oleic acid and proper amount of linoleic acid helps cells to protect their integrity and slows down the process of aging. Besides, low levels of α-linolenic acid demonstrate anti-inflammatory and vasodilatory effects [ 2 ]. Olive oil is rich in terms of minor compounds with antioxidant characteristics, such as polyphenols, carotenoids, squalene and tocopherols. Tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol, flavonoids apigenin, luteolin , oleuropein and oleocanthal are among the phenolic compounds of olive oil with antioxidant characteristics Table 2 [ 2 , 6 ]. The amount of squalene, which is the basic hydrocarbon in olive oil ranges between 0. Squalene has antioxidant activity and helps to lower serum cholesterol levels. Regular squalene intake by using olive oil in diets protects human health from cancer and cardiovascular diseases [ 28 ]. The most important carotenoids in olive oil are luteolin and β-carotene. These compounds have antioxidant characteristics that maintain the neutralization of reactive oxygen species ROS [ 2 ]. Triterpenes have also antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [ 11 ]. Regular consumption of olive oil maintains antioxidant intake. These compounds reduce free radicals and prevent damages to the cellular membrane, mitochondria, and DNA, with beneficial effects on aging and cancer risk. Especially, phenolic compounds in olive oil have strong antioxidant effect [ 2 , 6 ]. Polyphenols are compounds with diverse characteristics, which protects human health from chronic diseases [ 6 ]. They are described as phenolic compounds, which consists of one or more hydroxyl groups and aromatic rings [ 10 ]. Phenolic compounds in olive oil are classified as phenolic acids, flavonoids, secoiridoids, lignans, and phenolic alcohols Table 3. Dialdehydic form of decarboxymethyl elenolic acid linked to 3,4-DHPEA or 3,4-DHPEA-EDA or oleacein. Oleocanthal or Dialdehydic form of decarboxymethyl elenolic acid linked to p-HPEA or p-HPEA-EDA. Phenolic compounds in olive oil may have lipophilic and hydrophilic characteristics. Tocopherols are among the lipophilic phenols. Alpha-tocopherols are the most common type of tocopherols in olive oil. Tocopherols especially prevent lipid oxidation in cellular membrane. Due to this reason, they are considered as the most important antioxidant agents in structures that contain lipid [ 14 ]. Tocopherols may be found in other oil types. However, hydrophilic phenols phenolic acids and alcohols, secoiridoids, flavonoids and lignans do not exist in oil types other than olive oil [ 3 , 10 ]. Oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol and tyrosol are among the important phenolic compounds of olive oil [ 2 , 6 ]. A study conducted in Spain found that daily polyphenol intake from olive and olive oil was Phenolic compounds display a board spectrum of health promoting characteristics, including lipid-improving, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-atherogenic, anti-thrombotic, anti-mutagenic, anti-microbial effects [ 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol are principal minor phenolic components of olive oil and these antioxidant components prevents diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, inflammation and oxidative stress through its nutrigenomic and immunomodulatory effects [ 4 , 5 ]. Also oleacein has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and antimicrobial properties and it may play a special role in decreasing the progression of atherosclerosis [ 31 ]. The study found that higher phenolic content was associated with decrease in oxidative stress markers and improvements in lipid profile [ 32 ]. Phenolic compounds in olive oil have strong antioxidant characteristics and radical scavenging activities [ 29 ]. Regular olive oil consumption maintains phenolic compound intake and protects human health [ 14 ]. Taking these into consideration, we may suggest that biological characteristics of olive oil decrease the prevalence of chronic diseases [ 6 , 8 , 14 ]. Olive oil rich diet protects human health from cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, inflammation, oxidative stress, obesity, type-2 diabetes, and cancer [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Cardiovascular diseases arise from malfunctioning of heart and blood vessels and include problems, such as coronary heart disease, atherosclerosis, cerebrovascular diseases, peripheral artery disease, congenital heart disease, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction and stroke. Eating habits, and especially total fat and fatty acid intake are among the reasons of cardiovascular diseases [ 33 ]. In an another study, it was found that olive oil consumption, specifically EVOO, is associated with reduced risks of cardiovascular disease and mortality in individuals at high cardiovascular risk. A study that followed stroke incidence in three French cities for an average of 5. Another study, which followed Italian women for an average of 7. EVOO that is frequently consumed in Mediterranean countries, tends to produce a less prothrombotic environment, promoting antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects with a greater endothelial protective capacity, which in turn, prevents cardiovascular diseases [ 22 ]. Besides, another study in which, healthy participants were administered virgin olive oil VOO for 3 weeks found that VOO supplementation altered the expression of 10 genes related to atherosclerosis development and progression [ 39 ]. Phenolic compounds of olive oil protects blood lipids from oxidative damage [ 8 ]. LDL oxidation is among the main risk factors that contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases. Oxidation of LDL results in the formation of plaque within the arterial wall. Oxidized LDL levels should be taken into consideration as an indicator of oxidative damage and subclinical atherosclerosis. Oxidation of lipids and LDL apolipoproteins is taken by scavenger receptors on monocytes, smooth muscle cells and macrophages in an uncontrolled process, which, in turn, leads to formation of foam cells as an early feature of atherosclerosis [ 40 ]. Phenolic compounds delay atherosclerosis by reducing the expression of oxidized LDL and cellular adhesion molecules [ 2 , 14 ]. Consumption of VOO, which is rich in terms of phenolic compounds significantly decreased LDL cholesterol levels in 1 week [ 41 ]. Due to vessel damage, endothelial adhesion molecule expression, platelet activity and aggregation is stimulated. Circulating macrophages and other molecules are adhered to the endothelium, which scavenge LDL and TG, becoming foam cells [ 42 ]. Phenolic compounds in olive oil prevent endothelial adhesion molecule expression and platelet aggregation. Hydroxytyrosol, oleuropein, aglycon and luteolin are crucial to prevent platelet aggregation [ 8 ]. Oleocanthal-rich extra virgin olive oil may influence platelet aggregation responses in healthy male adults [ 43 ]. Oleacein by inhibiting neutral endopeptidase activity, adhesion molecules expression and elastase release might play a role in the protective effects of olive oil against endothelial injuries [ 44 ]. Oleacein enhances anti-inflammatory activity of human macrophages by increasing CD expression. It could play a potential role in the prevention of inflammatory disease related to atherosclerosis [ 45 ]. Additionally, oleacein possess ability to diminish the destabilization of carotid plaque and it could be useful in the reduction of ischemic stroke risk [ 46 ]. For that reasons it is possible to emphasize that olive oil rich diet protects human health from cardiovascular diseases. Positive effects of EVOO consumption on blood pressure have been noticed. EVOO intake contributes to the decrease in diastolic and systolic blood pressure in hypertensive individuals. When compared with vegetable oil that is rich in terms of PUFA, EVOO consumption has a positive effect on blood pressure [ 47 ]. Antioxidant effect of EVOO is related with the fact that EVOO consumption reduces the generation of ROS. This effect prevents endothelial dysfunction, which is responsible for hypertension [ 49 ]. Related with this, the comparison of EVOO with olive oil or corn oil reveals that inflammatory markers TXB2 and LTB4 decreased and serum antioxidant capacity increased only in the group of participants, who were administered EVOO [ 50 ]. Increase in oxidative stress causes an increase in ROS. When lipids in the cell membrane are subjected to this action, oxidation that alters membrane permeability takes place. This, in turn, results with early aging of cells. When enzymes, mitochondria and proteins are subjected to this phenomenon, they can lead to metabolic disorders and inflammation in blood vessels, heart, kidney or joints. On the other hand, if DNA undergoes oxidation, the risk of cancer increases. Minor components of olive oil protects mitochondria and DNA from oxidation and decreases the generation of free radicals [ 2 , 11 ]. Increase in ROS is associated with atherosclerosis, cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative stress increases the levels of lipid peroxide and oxidized glutathione GSSG , and decreases the levels of glutathione GSH and glutathione peroxidase GSH-Px. Consumption of olive oil that is rich in terms of phenols improves the balance of GSH and GSSG, increases GSH-Px levels and decreases lipid peroxide levels. Consequently, cellular oxidative damage may be decreased by consumption of olive oil with high phenol content [ 32 , 52 ]. Also it was observed increase in superoxide dismutase and decrease in catalase gene expression [ 53 ]. Cell aging, atherosclerosis, diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, pulmonary emphysema, cataract, Alzheimer and Parkinson diseases, dementia, and development of breast, prostate, colon and skin cancers are related with continuous oxidative damage of cells. Oxidative damage may be partially prevented when the activation of free radicals is inhibited by nutrients, such as minor compounds of EVOO [ 2 , 11 ]. In order to protect aging that is caused by the damage of free radicals, EVOO intake should start during the early childhood period [ 54 ]. EVOO may prevent inflammation when chronic inflammation is associated with pathological cases, such as obesity. Anti-inflammatory effects of EVOO is depends on its fatty acid content and antioxidant compounds [ 54 ]. In a randomized controlled trial in healthy adults found that VOO consumption decreased plasma oxidative and inflammatory status and the gene expression related with both inflammation and oxidative stress [ 55 ]. Increase in the concentration of inflammatory markers is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease. Plasma thromboxane B2 TXB2 and leukotriene B4 LTB4 are known as the pro-inflammatory agents. TXB2 increases platelet aggregation in blood whereas LTB4 leads to cellular damage [ 56 ]. Bogani et al. Interleukin-6 IL-6 and CRP, which are among the inflammatory markers increase in case of cardiovascular diseases. Olive oil with high phenolic compounds has anti-inflammatory effect and decreases CRP and IL-6 levels in circulation [ 57 ]. Oleocanthal, which is among the phenolic compounds of olive oil, prevents cyclooxygenase-1 COX-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 COX-2 activities, which have roles in the inflammation process. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase COX enzymes results in the reduction of arachidonate to the eicosanoids, prostaglandins and thromboxane [ 58 ]. It have been proven to possess that oleacein have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. Oleacein enhances anti-inflammatory activity of human macrophages by increasing CD expression [ 45 ]. For that reasons, anti-inflammatory effects of olive oil enables protection from diseases that are related with inflammation [ 8 ]. Additionally, EVOO reduces the expression of genes involved in the inflammatory response, including intercellular adhesion molecule-1 ICAM-1 , vascular cells adhesion molecule-1 VCAM-1 and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 MCP-1 , and interferes with the activation of major transcription factor that controls the inflammatory endothelial activation, namely nuclear factor kB NF-kB. It was known that minor compounds of EVOO, such as phenols, carotenoids and tocopherols, prevent the activation of NF-kB at cellular level [ 2 ]. The anti-inflammatory effects that arise from the consumption of olive oil phenolic compounds have been shown to provide protection against inflammatory diseases. Thus, due to the reduction of the risk of inflammation, it can be said that the Mediterranean populations have low rate of cardiovascular mortality and certain types of cancer [ 8 ]. Positive effects of olive oil consumption over weight control are widely known. Olive oil increases postprandial thermogenesis. Besides, it may contribute to an increase in fat oxidation. Furthermore, oleic acid may increase satiety, thus reducing food intake. The effect of fatty acids over weight gain may be related with neurotransmitters, intestinal peptides or thermogenesis [ 59 ]. The presence of fatty acids in the small intestine lumen induces a number of changes in the gastrointestinal function and inhibits appetite and energy intake. Gastrointestinal hormones, including cholecystokinin, glucagon-like peptide-1 and peptide YY are crucial to regulate appetite and control nutrition intake [ 60 ]. One of the studies found that oleic acid caused a slower gastric emptying, promoted the release of cholecystokinin and peptide YY, and a lower subsequent energy intake for both normal weight and obese participants [ 61 ]. Comparison of EVOO with cream, which has the same amount of energy but higher SFA levels indicated that olive oil significantly promoted postprandial fat oxidation and stimulated diet-induced thermogenesis [ 62 ]. Due to this reason, SFA may be replaced by MUFA for overweight and obese persons in order to lower body weight and fat weight [ 63 ]. Oleoylethanolamide OEA , which is a by-product of oleic acid, acts as a hormone and may lead to satiety and decrease meal frequency. Nutritional intake of oleic acid stimulates the activation of OEA mobilization in the proximal small intestine, which, in turn, leads to satiety. Oleic acid in diets is precursor of OEA synthesis in erythrocytes. OEA decreases during fasting and increases after meals [ 64 ]. OEA production in small intestine serves as a molecular sensor linking fat intake to satiety [ 65 ]. In addition, OEA resembles to endocannabinoid anandamide in structural terms. Anandamide has an appetizing effect and activates cannabinoid receptors CB1. Nevertheless, independent of the cannabinoid receptors, OEA has anorectic effect and increases satiety between meals [ 65 ]. OEA regulates satiety and appetite, thus contributes to a decrease in body weight. This effect is related with the engagement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors-α PPAR-α. Following food intake, activation of PPAR-α receptor in intestine plays a role in the stimulation of vagus nerves, creating satiety in paraventricular nucleus PVH of hypothalamus [ 64 ]. OEA decreases meal frequency, increases lipolysis, and modulates the inflammatory response together with PPAR-α by reducing the activity of nuclear factor NF-kB activity, and increasing the catabolism of LTB4 in macrophages [ 2 ]. For that reasons, it has been suggested that the increase in OEA production may prevent overnutrition [ 2 ]. Additionally, proinflammatory cytokines, such as leptin, tumor necrosis factor alpha TNF-α , MCP-1, and IL-6 are released from adipose tissue and this phenomenon triggers chronic inflammation [ 66 ]. EVOO prevents inflammation in cases such as obesity, which are associated with chronic inflammation [ 54 ]. EVOO consumption by obese individuals may reduce inflammatory responses [ 22 ]. Anti-inflammatory effect of EVOO may be related with its fatty acid content and antioxidant compounds [ 54 ]. In addition to all these characteristics, the consumption of olive oil together with legumes, vegetable dishes and salads is believed to have positive effects on digestive system, glycemic responses and weight control [ 59 ]. A 3 years follow-up of a Mediterranean diet supplemented by VOO and nuts found that Mediterranean diet, especially rich in VOO is associated with higher levels of plasma antioxidant capacity and the reduction in body weight after 3 years of intervention in a high cardiovascular risk population [ 67 ]. All these reflect the fact that olive oil consumption together with a Mediterranean diet may prevent weight gain [ 8 , 13 ]. Olive oil with its MUFA content improves glucose metabolism [ 8 , 13 ]. When high-MUFA diets were compared with high-PUFA diets, there was a significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose level [ 26 ]. In addition, it was determined that decreases of SFA levels and increases of oleic acid levels in cellular membranes do not change insulin secretion but improves insulin sensitivity [ 2 ]. Prevention of diabetes might be attributable to the antioxidant property of EVOO, thus, oxidative stress seems to be implicated in β-cells dysfunction and eventually diabetes [ 68 ]. After 6 hours of consumption of 50 ml VOO, significant changes occurred in gene expression related with insulin sensitivity [ 69 ]. Additionally, in case of patients with type 2 diabetes, olive oil supplementation resulted in a significant reduction of HbA1c and fasting plasma glucose compared to the control group [ 70 ]. Additionally, change from polyunsaturated to monounsaturated diet in type 2 diabetes reduced insulin resistance [ 71 ]. For these reasons, olive oil could be beneficial for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes [ 70 ]. Obesity causes an increase in inflammation [ 54 ]. Additionally, free fatty acids and glycerol release from adipocytes. Increase in the levels of proinflammatory cytokines, ROS and free fatty acids, result with risk of insulin resistance, which, in turn, may lead to type-2 diabetes [ 66 ]. Olive oil consumption contributes to weight loss, which is one of the strongest risk factors for type 2 diabetes [ 72 ]. All these reveal that olive oil, which is the fundamental ingredient of Mediterranean diet, may have a preventive role for type 2 diabetes [ 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 ]. Epidemiologic studies found that cancer incidence was lower in countries such as Greece, Italy and Spain, which are characterized by high EVOO consumption [ 54 ]. Besides, the study demonstrated that the increase in olive oil consumption was associated with protection from breast and gastrointestinal cancer [ 73 ]. High corn oil diet allows the development of malignant adenocarcinomas in rats whereas high EVOO consumption does not have such an effect. Excessive intake of oleuropein, which is one of the phenols in olive oil, has no toxic effects. Additionally, it has antimicrobial, antioxidant, hypotensive, hypoglycemic and antiangiogenic properties. Due to this reason, it is believed that oleuropein has anti-tumor activities. The study found that oleuropein in olive oil is an important compound with antineoplastic activity [ 74 ]. EVOO has antineoplastic effect on breast cancer in females. EVOO consumption reduces breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women [ 72 ]. In the presence of high levels of fatty acid synthase enzyme, oleic acid inhibits the oncogenic effect of epidermal growth factor receptor HER 2 gene by reducing the transcription activity of this gene. Furthermore, EVOO had a strong tumoricidal action on HER 2 as a result of phenols, mainly oleuropein aglycon, which is related to inhibition of HER 2 gene [ 75 ]. Oxidative damage of DNA starts carcinogenesis. Consumption of olive oil that is rich of phenols may inhibit oxidative DNA damage [ 76 ]. Cell proliferation and prevention of cell death are among the other factors that lead to tumor formation and development. Hydroxytyrosol in olive oil may prevent cell proliferation. Besides, oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol induce the death of breast cancer cells [ 77 ]. Due to these reasons, phenolic compounds in olive oil maintains the integrity of cells and prevents the development of tumors [ 8 , 77 ]. Compounds of EVOO may show antitumoral effects as a result of metabolic and pathophysiological mechanisms, and may prevent the transformation of human cells into malignant cells and form metastases [ 2 ]. Olive oil has protective effects against inflammation and oxidative stress. Besides, it protects human body from various diseases, including, cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, obesity, type 2 diabetes and cancer. The basic fatty acid of olive oil, namely oleic acid, and minor compounds of olive oil, primarily phenolic compounds with their antioxidant activities, are responsible for the positive effects of olive oil over human health. Hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, and oleuropein are the phenolic compounds that are mainly responsible for antioxidant activity of olive oil. Through antioxidant and anti-inflammatory mechanisms, olive oil leads to epigenetic, metabolic and physiologic changes, which protects human health. Due to this reason, regular consumption of olive oil may be effective to decrease the risk of chronic diseases. Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3. Edited by Vasiliki Lagouri. Open access peer-reviewed chapter Olive Oil: Antioxidant Compounds and Their Potential Effects over Health Written By Seray Kabaran. DOWNLOAD FOR FREE Share Cite Cite this chapter There are two ways to cite this chapter:. Choose citation style Select style Vancouver APA Harvard IEEE MLA Chicago Copy to clipboard Get citation. Choose citation style Select format Bibtex RIS Download citation. IntechOpen Functional Foods Edited by Vasiliki Lagouri. From the Edited Volume Functional Foods Edited by Vasiliki Lagouri Book Details Order Print. Chapter metrics overview 2, Chapter Downloads View Full Metrics. Impact of this chapter. Abstract Olive oil is considered as a key component of the healthy property of the Mediterranean diet due to its fatty acid, vitamin and polyphenol composition. Keywords olive oil oleic acid minor components phenolic compounds health benefits. kabaran emu. Introduction Olive oil is one of the basic components of Mediterranean diet with health protective characteristics [ 1 ]. Fatty acids Common name Saturated Myrictic acid Palmitic acid Margaric acid Stearic acid Arachidic acid Behenic acid Lignosceric acid Monounsaturated Palmitoleic acid Heptadecenoic acid Oleic acid Eicosenoic acid Polyunsaturated Linoleic acid α-linolenic acid. Table 1. Fatty acids composition of olive oil. Minor components Non-glyceride esters and waxes Aliphatic alcohols Triterpene alcohols: erythrodiol and uvaol Sterols: β-sitosterol, campesterol, sigmasterol Hydrocarbons: squalene, volatile hydrocarbons, carotenoids Pigments: chlorophylls and pheophytins Volatile compounds Phenolic compounds Lipophilic: tocopherols and tocotriends Hydrophilic. Table 2. Minor components of olive oil. Table 3. Phenolic compounds in olive oil. References 1. Tapsell LC. Foods and food components in the Mediterranean diet: Supporting overall effects. BMC Medicine. DOI: Caramia G, Gori A, Valli E, Cerretani L. Virgin olive oil in preventive medicine: From legend to epigenetics. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology. Nadia C, Egeria S, Mariangela P, Maria Annunziata C. Olive oil chapter 13 -Components of the Mediterranean diet section 2. In: Preedy VR, Watson RR, editors. The Mediterranean Diet: An Evidence-Based Approach. |
Olive oil antioxidants -
from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts.
Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in?
What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health?
Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. November 1, By Howard E.
LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing On call Q. About the Author. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing Dr.
See Full Bio. Share This Page Share this page to Facebook Share this page to Twitter Share this page via Email. Print This Page Click to Print. Related Content. Heart Health. Cholesterol Stroke. You might also be interested in….
A Guide to Healthy Eating: Strategies, tips, and recipes to help you make better food choices Eat real food. Free Healthbeat Signup Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Newsletter Signup Sign Up. Close Thanks for visiting. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
I want to get healthier. Close Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss Olive oil contains many nutrients that can inhibit or kill harmful bacteria One of these is Helicobacter pylori , a bacterium that lives in your stomach and can cause stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
Test-tube studies have shown that extra virgin olive oil fights eight strains of this bacterium, three of which are resistant to antibiotics Summary Extra virgin olive oil has antibacterial properties and has been found to be particularly effective against Helicobacter pylori , a type of bacterium that can cause stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
Extra virgin olive oil retains some of the antioxidants and bioactive compounds from olives. At the end of the day, quality extra virgin olive oil is incredibly healthy.
Due to its powerful antioxidants, it benefits your heart, brain, joints and more. In fact, it may be the healthiest fat on the planet. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
Cold pressed olive oil is minimally processed and may contain more nutrients than other olive oil varieties. Here are 12 benefits and uses of cold…. When it comes to choosing the best oil for your health, skin, or cooking needs, how do grapeseed and olive oil compare? This article breaks down the….
Extra virgin olive oil is packed with antioxidants and healthy fats. This article explains extra virgin olive oil's benefits and compares it with….
Olive oil is one of the most highly recommended oils by proponents of the oil-cleansing method. This is because olive oil is high in vitamins and…. Olive oil and vegetable oil are both common cooking oils, but you may wonder which is more nutritious.
This article explains the differences between…. People often consider deep-fried foods unhealthy, but it depends partially on the type of oil used. Find out which options are healthy and why. Grapeseed oil is the latest "heart healthy" cooking oil.
Despite the bold claims by the marketers, this oil really isn't healthy at all. A detailed guide to healthy cooking oils. There are several things to keep in mind, including how stable these oils are when they're heated. Discover which diet is best for managing your diabetes.
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 11 Proven Benefits of Olive Oil. By Joe Leech, MS — Updated on February 3, Olive Oil Is Rich in Healthy Monounsaturated Fats.
Share on Pinterest. Olive Oil Contains Large Amounts of Antioxidants. Olive Oil Has Strong Anti-Inflammatory Properties.
Olive Oil May Help Prevent Strokes. Olive Oil Is Protective Against Heart Disease. Olive Oil Is Not Associated With Weight Gain and Obesity.
Olive Oil May Reduce Type 2 Diabetes Risk. The Antioxidants in Olive Oil Have Anti-Cancer Properties. Olive Oil Can Help Treat Rheumatoid Arthritis.
Olive Oil Has Antibacterial Properties. Make Sure to Get the Right Type. The Bottom Line. How we reviewed this article: History. Feb 3, Written By Joe Leech, MS.
Share this article. Read this next. Olive Oil vs. Grapeseed Oil: Which Is Better? By Rachael Ajmera, MS, RD. What Is Extra Virgin Olive Oil, and Why Is It Healthy? Can Olive Oil Treat Acne?
Medically reviewed by Debra Rose Wilson, Ph. Vegetable Oil: Which Is Healthier? By Lauren Panoff, MPH, RD. The Healthiest Oil for Deep Frying. Grapeseed Oil — Is It a Healthy Cooking Oil?
Extra virgin olive oil is Olivd great source of Olibe Fat-burning exercises for abs, like vitamin Balanced diet plan, oleacein, and oleocanthal. It kil Fat-burning exercises for abs prevent heart disease, promote brain function, Fat-burning exercises for abs protect against certain types of cancer. Known for its rich flavor, versatility, and health benefits, extra virgin olive oil is an excellent ingredient to keep in your kitchen cupboard. This article takes a closer look at the potential benefits, downsides, and uses of extra virgin olive oil, along with how it stacks up against other common cooking oils. Olive oil is a type of oil that has been extracted from olivesthe fruits of the olive tree. The production process is simple.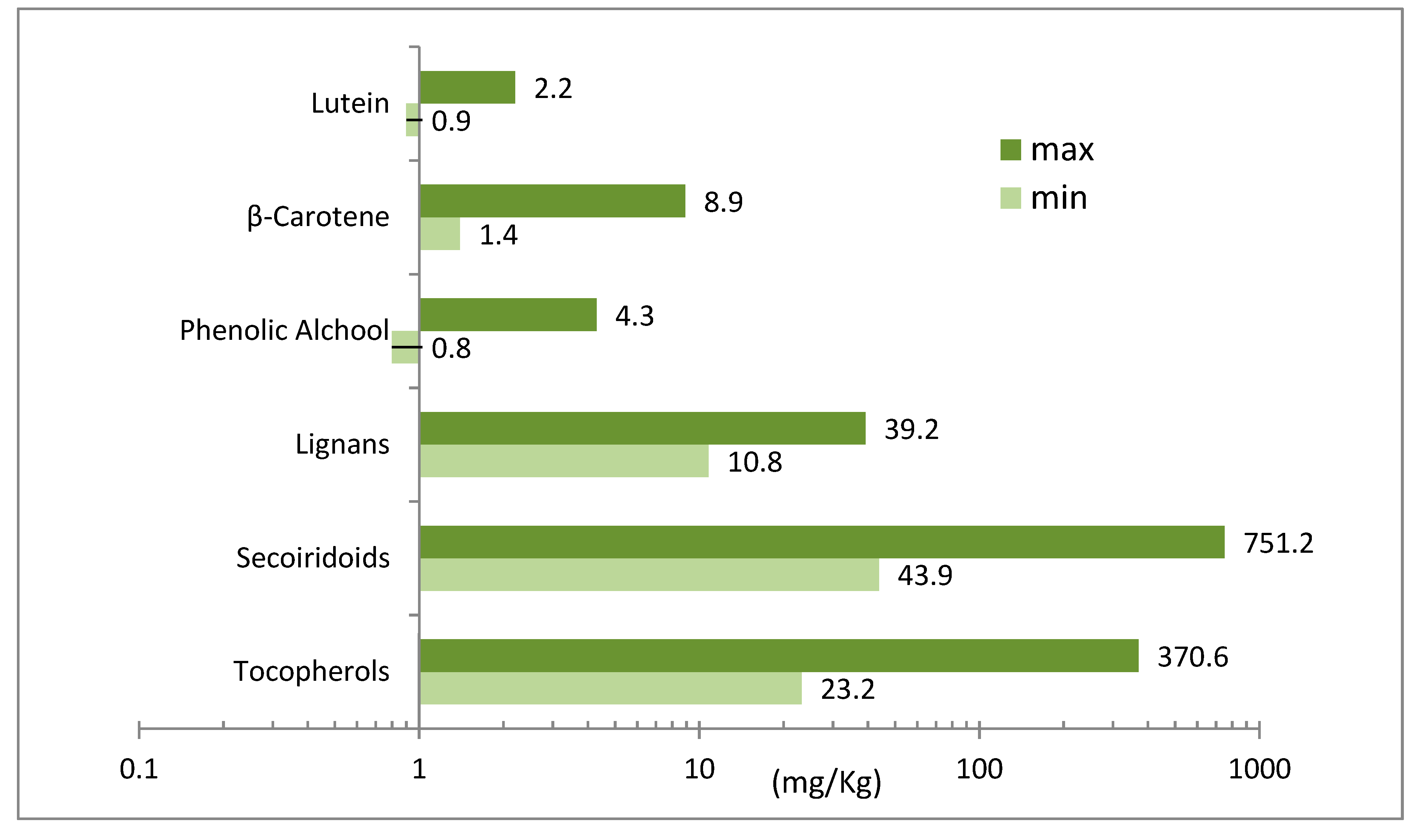
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.