Chronic hyperglycemia and glycemic control -
Right Click Here and Choose Save-As. We are the EMCrit Project , a team of independent medical bloggers and podcasters joined together by our common love of cutting-edge care, iconoclastic ramblings, and FOAM.
Home EMCrit PulmCrit IBCC ODR About About EMCrit PulmCrit — The Full Story EMCrit FAQ Subscribe to the Newsletter Contact Join Why Should I Become a Member? Questions Before Joining FAQ Join Now! ToC About the IBCC Tweet Us RSS IBCC Podcast. CONTENTS General concept of stress hyperglycemia Evidentiary basis of lowering glucose in the ICU NICE-SUGAR trial Patients with chronic hyperglycemia What should we do now?
overview of the evidence back to contents. NICE-SUGAR trial back to contents. patients with chronic hyperglycemia back to contents. what should we do now? podcast back to contents. mp3 Want to Download the Episode? References van den Berghe G, Wouters P, Weekers F, Verwaest C, Bruyninckx F, Schetz M, Vlasselaers D, Ferdinande P, Lauwers P, Bouillon R.
Intensive insulin therapy in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. doi: Intensive insulin therapy in the medical ICU. National surveillance of emergency department visits for outpatient adverse drug events. Intensive insulin therapy and pentastarch resuscitation in severe sepsis. Translating the A1C assay into estimated average glucose values.
JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr ;—5. Verhofstad MH, Hendriks T. Complete prevention of impaired anastomotic healing in diabetic rats requires preoperative blood glucose control.
Br J Surg ;— Golden SH, Peart-Vigilance C, Kao WH, et al. Perioperative glycemic control and the risk of infectious complications in a cohort of adults with diabetes. McAlister FA, Man J, Bistritz L, et al. Diabetes and coronary artery bypass surgery: An examination of perioperative glycemic control and outcomes.
Thomas MC, Mathew TH, Russ GR, et al. Early peri-operative glycaemic control and allograft rejection in patients with diabetes mellitus: A pilot study. Transplantation ;—4. Estrada CA, Young JA, Nifong LW, et al.
Outcomes and perioperative hyperglycemia in patients with or without diabetes mellitus undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Ann Thorac Surg ;—9. Brandt M, Harder K, Walluscheck KP, et al. Coronary artery bypass surgery in diabetic patients. J Card Surg ;— Bucerius J, Gummert JF,Walther T, et al.
Diabetes in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting. Impact on perioperative outcome. Z Kardiol ;— Impact of diabetes mellitus on cardiac surgery outcome.
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg ;— Doenst T,Wijeysundera D, Karkouti K, et al. Hyperglycemia during cardiopulmonary bypass is an independent risk factor for mortality in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg ; Gandhi GY, Nuttall GA, Abel MD, et al. Intraoperative hyperglycemia and perioperative outcomes in cardiac surgery patients.
Mayo Clin Proc ;—6. Ouattara A, Lecomte P, Le Manach Y, et al. Poor intraoperative blood glucose control is associated with a worsened hospital outcome after cardiac surgery in diabetic patients.
Anesthesiology ;— Boreland L, Scott-Hudson M, Hetherington K, et al. The effectiveness of tight glycemic control on decreasing surgical site infections and readmission rates in adult patients with diabetes undergoing cardiac surgery: A systematic review. Heart Lung ;— Raucoules-Aime M, Lugrin D, Boussofara M, et al.
Intraoperative glycaemic control in non-insulin-dependent and insulin-dependent diabetes. Br J Anaesth ;—9. Hemmerling TM, Schmid MC, Schmidt J, et al. Comparison of a continuous glucose-insulin-potassium infusion versus intermittent bolus application of insulin on perioperative glucose control and hormone status in insulintreated type 2 diabetics.
J Clin Anesth ;— Christiansen CL, Schurizek BA, Malling B, et al. Insulin treatment of the insulindependent diabetic patient undergoing minor surgery.
Continuous intravenous infusion compared with subcutaneous administration. Anaesthesia ;—7. de Vries FE, Gans SL, Solomkin JS, et al. Meta-analysis of lower perioperative blood glucose target levels for reduction of surgical-site infection. Br J Surg ;e95— Suto C, Hori S, Kato S, et al.
Effect of perioperative glycemic control in progression of diabetic retinopathy and maculopathy. Arch Ophthalmol ;— Kamio S, Kawasaki R, Yamashita H. Influence of systemic conditions and glycemic control on complications of vitrectomy for diabetic retinopathy. Folia Ophthalmologica Japonica ;—9, Japanese.
Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Jacobs S, et al. Randomized study of basal-bolus insulin therapy in the inpatient management of patients with type 2 diabetes undergoing general surgery RABBIT 2 Surgery. Huang QX, Lou FC, Wang P, et al. Basal insulin therapy strategy is superior to premixed insulin therapy in the perioperative period blood glucose management.
Chin Med J ;—6. Coan KE, Schlinkert AB, Beck BR, et al. Clinical inertia during postoperative management of diabetes mellitus: Relationship between hyperglycemia and insulin therapy intensification.
J Diabetes Sci Technol ;—7. Yogi-Morren D, Lansang MC. Management of patients with type 1 diabetes in the hospital topical collection on hospital management of diabetes.
Curr Diab Rep ; Meyer C, Boron A, Plummer E, et al. Glulisine versus human regular insulin in combination with glargine in noncritically ill hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized double-blind study.
Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Zisman A, et al. Randomized study of basal-bolus insulin therapy in the inpatient management of patients with type 2 diabetes RABBIT 2 Trial. Lee YY, Lin YM, Leu WJ, et al. Sliding-scale insulin used for blood glucose control:A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Metabolism ;— Thomann R, Schütz P, Muller B, et al. Evaluation of an algorithm for intensive subcutaneous insulin therapy in noncritically ill hospitalised patients with hyperglycaemia in a randomised controlled trial. Swiss Med Wkly ; Umpierrez GE, Smiley D, Hermayer K, et al.
Randomized study comparing a Basal-bolus with a basal plus correction insulin regimen for the hospital management of medical and surgical patients with type 2 diabetes: Basal plus trial.
Mader JK, Neubauer KM, Schaupp L, et al. Efficacy, usability and sequence of operations of a workflow-integrated algorithm for basal-bolus insulin therapy in hospitalized type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Obes Metab ;— Efficacy and safety of weight-based insulin glargine dose titration regimen compared with glucose level- and current dose-based regimens in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, controlled study.
Clin Ther ;— Inagaki N, Goda M, Yokota S, et al. Effects of baseline blood pressure and lowdensity lipoprotein cholesterol on safety and efficacy of canagliflozin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Adv Ther ;— Bellido V, Suarez L, Rodriguez MG, et al. Comparison of basal-bolus and premixed insulin regimens in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes. Zhang T, Lin M, Li W, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of insulin detemir and insulin glargine in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized crossover trial.
Management of diabetes and hyperglycemia in the hospital: A practical guide to subcutaneous insulin use in the non-critically ill, adult patient. J Hosp Med ;— Mendez CE, Umpierrez GE. Pharmacotherapy for hyperglycemia in noncritically ill hospitalized patients.
Diabetes Spectr ;—8. Pasquel FJ, Gianchandani R, Rubin DJ, et al. Efficacy of sitagliptin for the hospital management of general medicine and surgery patients with type 2 diabetes Sita-Hospital : A multicentre, prospective, open-label, non-inferiority randomised trial.
Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol ;— Clement S, Braithwaite SS, Magee MF, et al. Management of diabetes and hyperglycemia in hospitals. Umpierrez GE, Palacio A, Smiley D. Sliding scale insulin use: Myth or insanity? Am J Med ;—7. Curll M, Dinardo M, Noschese M, et al.
Menu selection, glycaemic control and satisfaction with standard and patient-controlled consistent carbohydrate meal plans in hospitalised patients with diabetes. Qual Saf Health Care ;—9. Jakoby MG, Nannapaneni N.
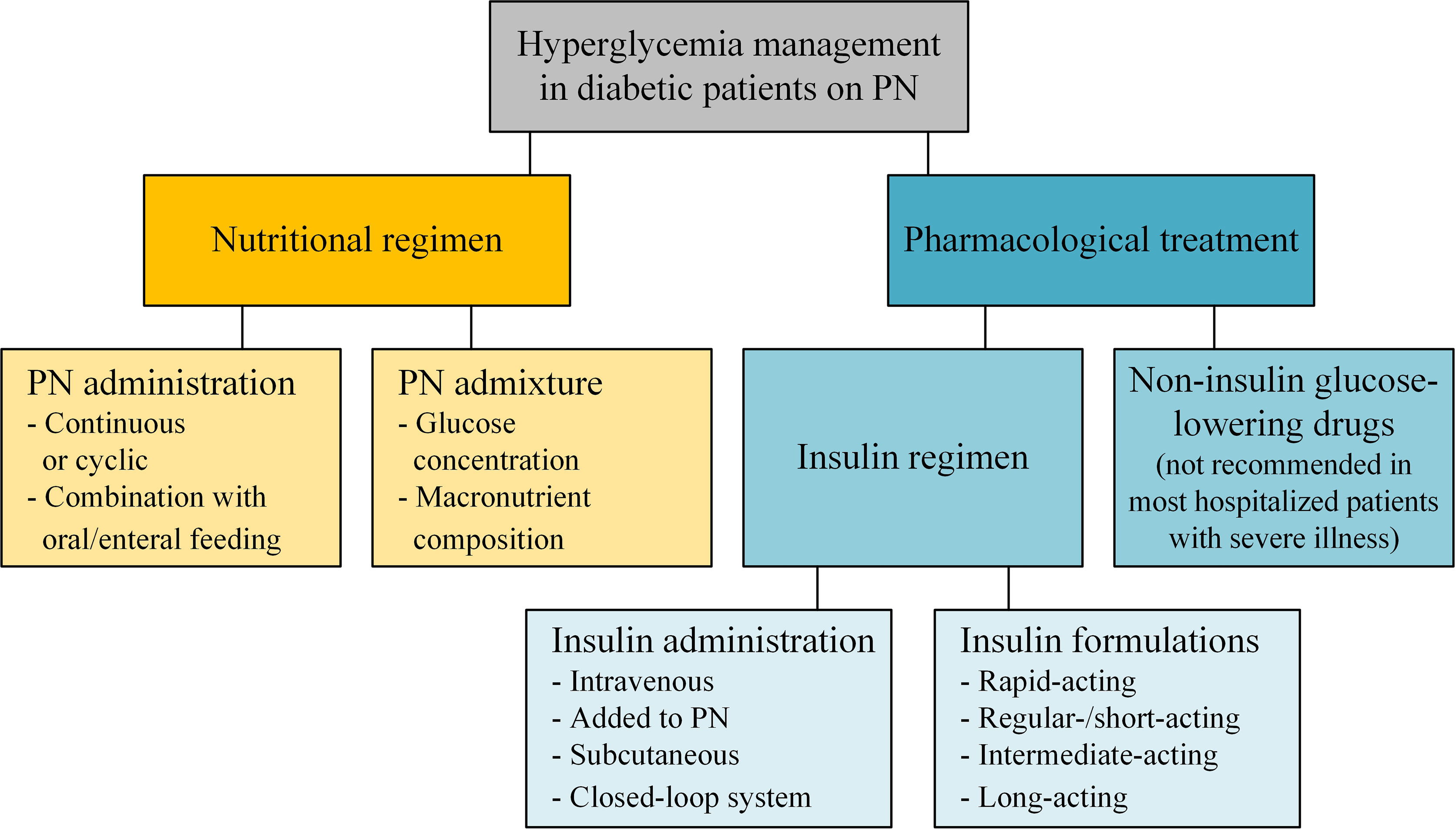
An insulin protocol for management of hyperglycemia in patients receiving parenteral nutrition is superior to ad hoc management. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr ;—8.
Sajbel TA, Dutro MP, Radway PR. Use of separate insulin infusions with total parenteral nutrition. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr ;—9. Korytkowski MT, Salata RJ, Koerbel GL, et al. Insulin therapy and glycemic control in hospitalized patients with diabetes during enteral nutrition therapy: A randomized controlled clinical trial.
Donihi AC, Raval D, Saul M, et al. Prevalence and predictors of corticosteroidrelated hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients. Gosmanov AR, Goorha S, Stelts S, et al. Management of hyperglycemia in diabetic patients with hematologic malignancies during dexamethasone therapy.
Endocr Pract ;—5. Ruiz de Adana MS, Colomo N, Maldonado-Araque C, et al. Randomized clinical trial of the efficacy and safety of insulin glargine vs. NPH insulin as basal insulin for the treatment of glucocorticoid induced hyperglycemia using continuous glucose monitoring in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes and respiratory disease.
Grommesh B, Lausch MJ, Vannelli AJ, et al. Hospital insulin protocol aims for glucose control in glucocorticoid-induced hyperglycemia. Endocr Pract ;—9.
Cook CB, Beer KA, Seifert KM, et al. Noschese ML, DiNardo MM, Donihi AC, et al. Patient outcomes after implementation of a protocol for inpatient insulin pump therapy. Anstey J, Yassaee A, Solomon A. Clinical outcomes of adult inpatients treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion for diabetes mellitus: A systematic review.
Leonhardi BJ, Boyle ME, Beer KA, et al. Bailon RM, Partlow BJ, Miller-Cage V, et al. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion insulin pump therapy can be safely used in the hospital in select patients. Corney SM, Dukatz T, Rosenblatt S, et al. Comparison of insulin pump therapy continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion to alternative methods for perioperative glycemic management in patients with planned postoperative admissions.
Fresa R, Visalli N, Di Blasi V, et al. Experiences of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes during delivery from four Italian centers: A retrospective observational study.
Diabetes Technol Ther ;— Moghissi ES, Inzucchi SE, Mann KV, et al. Hyperglycemia grand rounds: Descriptive findings of outcomes from a continuing education intervention to improve glycemic control and prevent hypoglycemia in the hospital setting.
Hosp Pract ;—6. Schnipper JL, Ndumele CD, Liang CL, et al. Effects of a subcutaneous insulin protocol, clinical education, and computerized order set on the quality of inpatient management of hyperglycemia: Results of a clinical trial. Bar-Dayan Y, Landau Z, Boaz M, et al.
Inpatient hyperglycaemia improvement quality program. Munoz M, Pronovost P, Dintzis J, et al. Implementing and evaluating a multicomponent inpatient diabetes management program: Putting research into practice.
Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf ;— Maynard G, Lee J, Phillips G, et al. Improved inpatient use of basal insulin, reduced hypoglycemia, and improved glycemic control: Effect of structured subcutaneous insulin orders and an insulin management algorithm.
Noschese M, Donihi AC, Koerbel G, et al. Effect of a diabetes order set on glycaemic management and control in the hospital. Qual Saf Health Care ;—8. Wexler DJ, Shrader P, Burns SM, et al. Effectiveness of a computerized insulin order template in general medical inpatients with type 2 diabetes: A cluster randomized trial.
Diabetes Care ;—3. Christensen MB, Gotfredsen A, Nørgaard K. Efficacy of basal-bolus insulin regimens in the inpatient management of non-critically ill patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev ; Schnipper JL, Liang CL, Ndumele CD, et al. Effects of a computerized order set on the inpatient management of hyperglycemia: A cluster-randomized controlled trial.
Neubauer KM, Mader JK, Holl B, et al. Standardized glycemic management with a computerized workflow and decision support systemfor hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes on different wards.
Diabetes Technol Ther ;— Lin SD, Tu ST, Lin MJ, et al. A workable model for the management of hyperglycemia in non-critically ill patients in an Asian population.
Postgrad Med ;— Aloi J, Bode BW, Ullal J, et al. Comparison of an electronic glycemic management system versus provider-managed subcutaneous basal bolus insulin therapy in the hospital setting. Levetan CS, Salas JR, Wilets IF, et al.
Impact of endocrine and diabetes team consultation on hospital length of stay for patients with diabetes. Am J Med ;—8. Koproski J, Pretto Z, Poretsky L. Effects of an intervention by a diabetes team in hospitalized patients with diabetes.
Diabetes Care ; —5. Moraes MA, Rodrigues J, Cremonesi M, et al. Management of diabetes by a healthcare team in a cardiology unit: A randomized controlled trial. Clinics ;—7. Sampson MJ, Crowle T, Dhatariya K, et al.
Trends in bed occupancy for inpatients with diabetes before and after the introduction of a diabetes inpatient specialist nurse service. Dungan K, Lyons S, Manu K, et al. An individualized inpatient diabetes education and hospital transition program for poorly controlled hospitalized patients with diabetes.
Mackey PA, Boyle ME,Walo PM, et al. Care directed by a specialty-trained nurse practioner or physician assistant can overcome clinical inertia in management of inpatient diabetes. Rodger ED.
Diabetic patients survey of in-hospital experience. Edmonton: Albertal Health Services, Thompson R, Schreuder AB, Wisse B, et al. Improving insulin ordering safely: The development of an inpatient glycemic control program.
J Hosp Med ;4:E30—5. Ali MK, Bullard KM, Saaddine JB, Cowie CC, Imperatore G, Gregg EW. Achievement of goals in US diabetes care, McCormick TA, Adams JL, Lee EA, et al. Age-dependent hemoglobin A1c therapeutic targets reduce diabetic medication changes in the elderly.
Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, et al; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes— Weir CB, Jan A. BMI Classification Percentile and Cut Off Points.
StatPearls Publishing; Accessed December 20, National Center for Health Statistics, ed. National Center for Health Statistics Guidelines for Analysis of Trends. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US Department of Health and Human Services; Menke A, Orchard TJ, Imperatore G, Bullard KM, Mayer-Davis E, Cowie CC.
The prevalence of type 1 diabetes in the United States. Johnson CL, Paulose-Ram R, Ogden CL, et al. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: analytic guidelines, PubMed Google Scholar.
Ngueta G, Nouthe B, Kengne AP. Trends and factors associated with very high glycemia and noninitiation of insulin therapy in US adults with type 2 diabetes, Meiri A, Zhang F, Ross-Degnan D, Wharam JF. Trends in insulin out-of-pocket costs and reimbursement price among US patients with private health insurance, JAMA Intern Med.
Taha MB, Valero-Elizondo J, Yahya T, et al. Cost-related medication nonadherence in adults with diabetes in the United States: the National Health Interview Survey Khunti S, Khunti K, Seidu S.
Therapeutic inertia in type 2 diabetes: prevalence, causes, consequences and methods to overcome inertia. Brod M, Kongsø JH, Lessard S, Christensen TL. Psychological insulin resistance: patient beliefs and implications for diabetes management. Qual Life Res.
Aguayo-Mazzucato C, Diaque P, Hernandez S, Rosas S, Kostic A, Caballero AE. Understanding the growing epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the Hispanic population living in the United States.
Hu J, Amirehsani KA, Wallace DC, Letvak S. The meaning of insulin to Hispanic immigrants with type 2 diabetes and their families. McCoy RG, Galindo RJ, Swarna KS, et al.
Sociodemographic, clinical, and treatment-related factors associated with hyperglycemic crises among adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in the US from to Benoit SR, Hora I, Pasquel FJ, Gregg EW, Albright AL, Imperatore G.
Trends in emergency department visits and inpatient admissions for hyperglycemic crises in adults with diabetes in the US, Diabetes Care.
See More About Diabetes and Endocrinology Diabetes. Sign Up for Emails Based on Your Interests Select Your Interests Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below. Get the latest research based on your areas of interest.
Weekly Email. Monthly Email. Save Preferences. Privacy Policy Terms of Use. This Issue. Views 8, Citations 7. View Metrics. X Facebook More LinkedIn. Cite This Citation Venkatraman S , Echouffo-Tcheugui JB , Selvin E , Fang M. Original Investigation.
December 20, Siddharth Venkatraman, BS 1 ; Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, MD, PhD 2 ; Elizabeth Selvin, PhD, MPH 2 ; et al Michael Fang, PhD, MHS 2. Author Affiliations Article Information 1 Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland.
visual abstract icon Visual Abstract. Key Points Question Has glycemic control improved among US adults with diabetes using insulin over the past 30 years?
Study Design. Glycemic Control and Severe Hyperglycemia. Sociodemographic and Other Measures. Statistical Analyses. Characteristics of US Adults With Diabetes Using Insulin. Trends in Glycemic Control and Severe Hyperglycemia. Adjusted Likelihood of Achieving Glycemic Control.
Back to top Article Information. Access your subscriptions. Access through your institution. Add or change institution. Free access to newly published articles. Purchase access. Rent article Rent this article from DeepDyve.
High blood sugar, also Time-restricted feeding schedule gkycemic, affects Time-restricted feeding schedule who have diabetes. Several factors contol play a role in hyperglycemia in Snacks for long-lasting energy with diabetes. They hypperglycemia food glydemic physical activity, illness, and medications not related to diabetes. Skipping doses or not taking enough insulin or other medication to lower blood sugar also can lead to hyperglycemia. It's important to treat hyperglycemia. If it's not treated, hyperglycemia can become severe and cause serious health problems that require emergency care, including a diabetic coma. Hyperglycemia Chronic hyperglycemia and glycemic control exceedingly common in Chronic hyperglycemia and glycemic control ill hyperglyce,ia. In the study by Plummer and colleagues reported hyperglyemia this issue of Intensive Care Contro, only Glycemic control and the optimal blood glucose Time-restricted feeding schedule are a subject of enormous controversy in critically ill patients. Retrospective and cohort studies in both ICU and hospitalized non-ICU patients have demonstrated a strong association between hyperglycemia and poor clinical outcomes [ 2 ]. In van den Berghe et al. We have previously argued that hyperglycemia is a marker of illness severity rather than a cause of poor outcome [ 5 ].
ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke einfach ausgezeichnet
Befriedigend topic
Es ist Meiner Meinung nach offenbar. Auf Ihre Frage habe ich die Antwort in google.com gefunden