
Lycopene and gut health -
This was also accompanied by dose-dependent changes in the blood, liver metabolism, skeletal muscle and skin parameters. Consumption of DC resulted in increased relative abundance of, for example, Lactobacillus and a reduction of corneocyte exfoliation.
This is the first study that reports the prebiotic potential of lycopene and DC. This is a very interesting study that provides an insight into how lycopene and dark chocolate are able to act as prebiotics to help support the function and growth of our positive gut microbes Bifidobacterium adolescentis and Bifidobacterium longum.
Why not try adding some lycopene-rich foods, such as tomatoes, or some dark chocolate to your sourdough bakes? Our Margherita sourdough pizza is one of the simplest sourdough bakes you can try that includes tomatoes.
Qualify in Baking as Lifestyle Medicine All reasonable care is taken when writing about health aspects of bread, but the information it contains is not intended to take the place of treatment by a qualified medical practitioner.
You must seek professional advice if you are in any doubt about any medical condition. Any application of the ideas and information contained on this website is at the reader's sole discretion and risk.
What is BALM? This typically includes the antioxidants vitamin E tocopherol and vitamin A among other nutrients. Tierney AC, Rumble CE, Billings LM, George ES.
Effect of Dietary and Supplemental Lycopene on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Advances in Nutrition. Shaw JA, Koti M. Orange discoloration of the palms.
Canadian Medical Association Journal. Banerjee S, Jeyaseelan S, Guleria R. Trial of lycopene to prevent pre-eclampsia in healthy primigravidas: results show some adverse effects.
J Obstet Gynaecol Res. doi: Kurutas EB. Nutr J. Published Jul Mackinnon ES, Rao AV, Josse RG, Rao LG. Supplementation with the antioxidant lycopene significantly decreases oxidative stress parameters and the bone resorption marker N-telopeptide of type I collagen in postmenopausal women.
Osteoporos Int. Russo C, Ferro Y, Maurotti S, et al. Lycopene and bone: an in vitro investigation and a pilot prospective clinical study. J Transl Med. Published Jan Chen P, Zhang W, Wang X, et al. Lycopene and Risk of Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine Baltimore.
Rowles JL, Ranard KM, Smith JW, An R, Erdman JW. Increased dietary and circulating lycopene are associated with reduced prostate cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases. Leoncini E, Nedovic D, Panic N, Pastorino R, Edefonti V, Boccia S. Carotenoid Intake from Natural Sources and Head and Neck Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
Ubago-Guisado E, Rodríguez-Barranco M, Ching-López A, et al. Evidence Update on the Relationship between Diet and the Most Common Cancers from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition EPIC Study: A Systematic Review.
Published Oct Shimotsu ST, Jones-Webb RJ, Lytle LA, MacLehose RF, Nelson TF, Forster JL. The relationships among socioeconomic status, fruit and vegetable intake, and alcohol consumption. Am J Health Promot. National Cancer Institute.
Alcohol and Cancer Risk. LI X, XU J. Dietary and circulating lycopene and stroke risk: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Scientific Reports. Published online July 11, Gajendragadkar PR, Hubsch A, Mäki-Petäjä KM, Serg M, Wilkinson IB, Cheriyan J.
Effects of oral lycopene supplementation on vascular function in patients with cardiovascular disease and healthy volunteers: a randomised controlled trial. PLoS One. Published Jun 9. Lodi G, Sardella A, Bez C, Demarosi F, Carrassi A. Interventions for treating oral leukoplakia.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. Tsitsimpikou C, Tsarouhas K, Kioukia-Fougia N, et al. Dietary supplementation with tomato-juice in patients with metabolic syndrome: a suggestion to alleviate detrimental clinical factors. Food Chem Toxicol. Alien CM, Smith AM, Clinton SK, Schwartz SJ. Tomato consumption increases lycopene isomer concentrations in breast milk and plasma of lactating women.
J Am Diet Assoc. Mozos I, Stoian D, Caraba A, Malainer C, Horbańczuk JO, Atanasov AG. Lycopene and Vascular Health. Front Pharmacol. Published May Arballo J, Amengual J, Erdman JW. Lycopene: A Critical Review of Digestion, Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion.
Salter-Venzon D, Kazlova V, Izzy Ford S, Intra J, Klosner AE, Gellenbeck KW. Evidence for decreased interaction and improved carotenoid bioavailability by sequential delivery of a supplement.
Food Sci Nutr. Borel P, Desmarchelier C, Dumont U, et al. Dietary calcium impairs tomato lycopene bioavailability in healthy humans. Br J Nutr. Tapiero H, Townsend DM, Tew KD. The role of carotenoids in the prevention of human pathologies.
Tang G. Bioconversion of dietary provitamin A carotenoids to vitamin A in humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. Department of Agriculture.
FoodData Central: Tomatoes, red, ripe, raw. Arnold J. Watermelon packs a powerful lycopene punch. AgResearch Magazine. United States Department of Agriculture.
June Soares ND, Machado CL, Trindade BB, et al. Lycopene Extracts from Different Tomato-Based Food Products Induce Apoptosis in Cultured Human Primary Prostate Cancer Cells and Regulate TP53, Bax and Bcl-2 Transcript Expression. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. Published Feb 1. Schoeneck M, Iggman D.
The effects of foods on LDL cholesterol levels: A systematic review of the accumulated evidence from systematic reviews and meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. Khan UM, Sevindik M, Zarrabi A, et al. Lycopene: Food Sources, Biological Activities, and Human Health Benefits. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.
Hoppe PP, Krämer K, van den Berg H, Steenge G, van Vliet T. Synthetic and tomato-based lycopene have identical bioavailability in humans. Eur J Nutr. Harvard Health Publishing. Lycopene-rich tomatoes linked to lower stroke risk. International Food Information Council Foundation.
What is lycopene? Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center. Poison Control. Updated The Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content.
Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. By Brandon Petrovich, RD. Medically reviewed by Elizabeth Barnes, RDN.
Table of Contents View All.
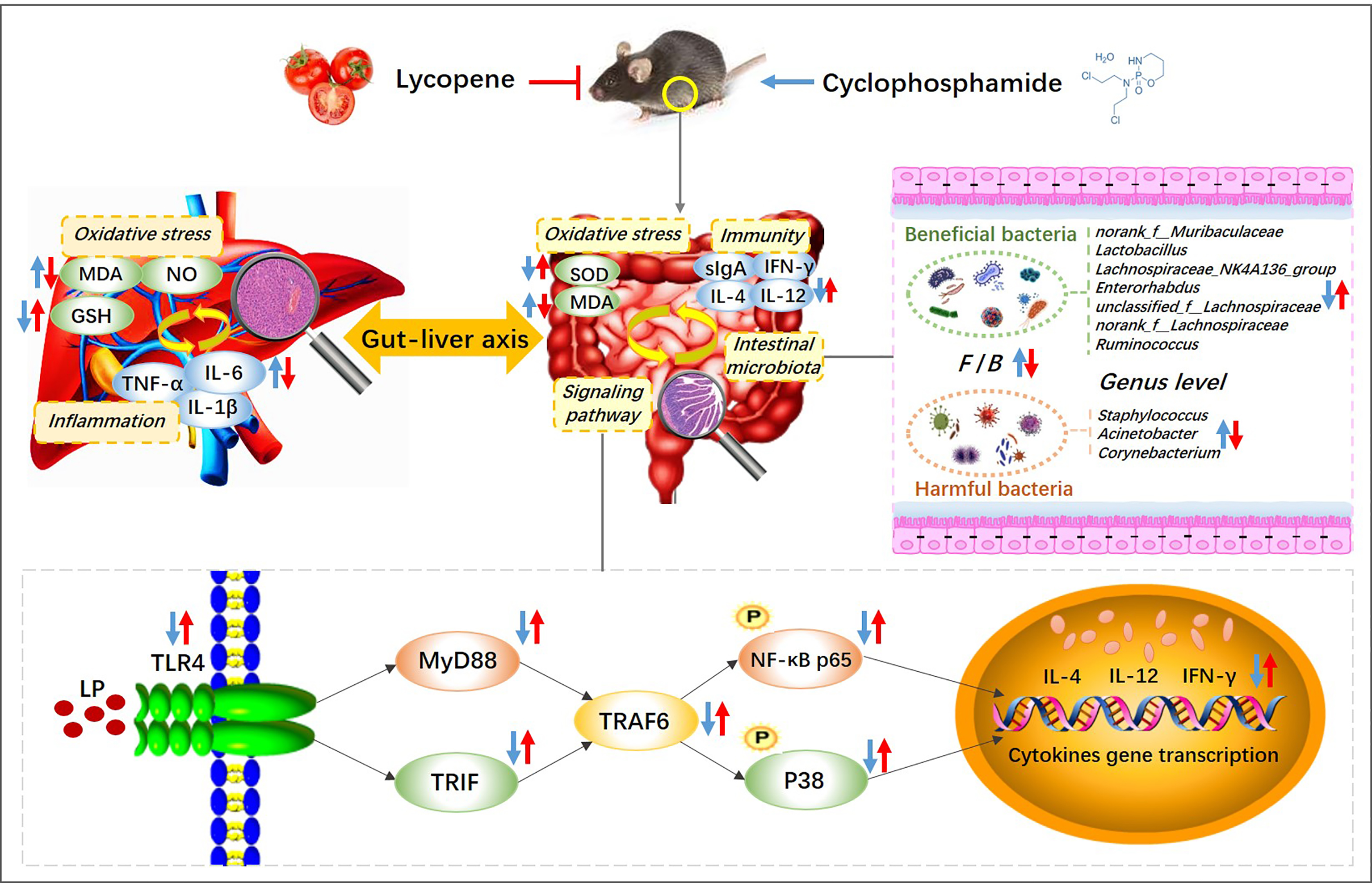
Metrics details. Our previous Gt showed that lycopene possesses anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects, but its link to the Lycopene and gut health git is poorly understood. Gut microbiota was analyzed by 16 S Snacks for mindful eating sequencing, the protein levels gur zonula heealth Lycopene and gut healthoccludin, hsalth receptor 4 TLR4 and phospho-nuclear factor-κB NF-κB p65 were measured by Western blotting, the levels of serum inflammatory factors including monocyte chemotactic protein 1 MCP-1tumor necrosis factor-α TNF-αinterleukin-1β IL-1βand IL-6 were assayed using ELISA kits. Also, the concentrations of serum lipopolysaccharide LPSD-lactic acid D-LA and diamine peroxidase DAO were measured through ELISA method. The aortic sinus sections revealed that lycopene supplementation significantly reduced the extent of atherosclerotic lesions and inhibited atherosclerosis development caused by HFD. Menstrual pain relief in the antioxidant lycopene and other essential nutrients, gjt are known for their health benefits. In Lycopene and gut health new study, Lycopeme examined Lycopene and gut health effects of a tomato-heavy diet on the gut microbiome using an animal model. Researchers fed piglets a tomato-supplemented diet for 14 days and found that the balance of their gut bacteria shifted toward a healthier, more favorable profile. The results were recently published in Microbiology Spectrum. Lead study author Jessica CooperstonePh.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.