
Boost immune health -
Smoking can make the body less successful at fighting disease. Smoking increases the risk for immune system problems, including rheumatoid arthritis. Over time, excessive alcohol use can weaken the immune system. Taking care of yourself will help your immune system take care of you.
Diet and immune function. Accessed May 13, Western diet and the immune system: an inflammatory connection. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans , 2nd edition [PDF Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; J Sport Health Sci. Exercise, immunity, and illness.
In: Zoladz JA, ed. Muscle and Exercise Physiology. Academic Press. T lymphopaenia in relation to body mass index and TNF—alpha in human obesity: adequate weight reduction can be corrective. Clin Endocrinol Oxf. Changes in nutritional status impact immune cell metabolism and function.
Front Immunol. Increased risk of influenza among vaccinated adults who are obese. Int J Obes Lond. Obesity as a predictor of poor antibody response to hepatitis B plasma vaccine. Hepatitis B vaccine immunoresponsiveness in adolescents: a revaccination proposal after primary vaccination.
Comparison of a triple antigen and a single antigen recombinant vaccine for adult hepatitis B vaccination. J Med Virol. Reduced tetanus antibody titers in overweight children.
Swindt, Christina [corrected to Schwindt, Christina]]. Sleep and health: Everywhere and in both directions. Still, screen time watching a movie you love or a binge session of your favorite TV show can help take your mind off things.
When it comes to keeping your immune system strong, proper handwashing is one of the most important things. But if you can't get to soap and water, hand sanitizer is the next best thing. Plain old soap and water are all you need. It's important to scrub up for at least 20 seconds—the length of singing "Happy Birthday" twice.
Per the CDC, that's the minimum time needed to significantly reduce the number of microorganisms on your skin. But no matter how good your handwashing skills are, they won't help prevent infection unless you know when to scrub up.
In other words, that includes after using the restroom, sneezing, or coughing. Also, wash your hands before you prepare food, after caring for a sick loved one, treating a wound, or touching any publicly used door handles, knobs, switches, or surfaces, added Dr. And if your hands are prone to dry skin, the right moisturizer can help.
If you don't have access to soap and water, hand sanitizer can help kill most microorganisms. Just be sure to take a peek at the alcohol percentage first.
Alcohol is the active ingredient working to kill viruses and bacteria. You may be unable to avoid viruses and bacteria that spread the common cold and flu entirely. But you can avoid them as best you can by strengthening your immune system.
Focusing on nutrition, hygiene, and other health habits is the key to doing so. These simple immune-boosting habits can help you steer clear of some infections. Others can supercharge your immune system, so you can get better quickly if you get sick.
Dietary supplements are minimally regulated by the FDA and may or may not be suitable for you. The effects of supplements vary from person to person and depend on many variables, including type, dosage, frequency of use, and interactions with current medications.
Please speak with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting any supplements. Minich DM. A Review of the Science of Colorful, Plant-Based Food and Practical Strategies for "Eating the Rainbow" [published correction appears in J Nutr Metab.
J Nutr Metab. Kapoor R, Sharma B, Kanwar SS. Antiviral phytochemicals: an overview. Biochem Physiol. Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man. Biochem Soc Trans. Stromsnes K, Correas AG, Lehmann J, Gambini J, Olaso-Gonzalez G. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Diet: Role in Healthy Aging.
Stadlbauer V. Immunosuppression and probiotics: are they effective and safe? Benef Microbes. National Institutes of Health. Office of Dietary Supplements. Geological Survey. The water in you: Water and the human body. Sarkar D, Jung MK, Wang HJ.
Alcohol and the Immune System. Alcohol Res. Nieman DC, Wentz LM. The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system. J Sport Health Sci. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Medic G, Wille M, Hemels ME. Short- and long-term health consequences of sleep disruption. Nat Sci Sleep. National Sleep Foundation.
Boosting your immune health goes beyond just eating the right foods. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits can significantly impact your immune system's ability to protect you from illnesses.
Here are some key habits to incorporate into your daily routine:. Exercise and Immunity: Regular physical activity can help improve your immune function. Exercise increases blood circulation, allowing immune cells to move more efficiently throughout your body.
Aim for at least minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Our Athletic Performance article offers tips on enhancing your workout routine.
Sleep and Immune Health: Getting enough quality sleep is essential for a healthy immune system. During sleep, your body produces immune cells that help fight infections.
Aim for hours of sleep per night. For more information on the importance of sleep, check out our article on The Science of Sleep: How Much is Enough? Stress Reduction Techniques: Chronic stress can weaken your immune system, making you more susceptible to illnesses.
Incorporate stress-reducing activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine.
Our Ways To Manage Stress and 7 Relaxation Tips For Reducing Stress articles provide helpful techniques for managing stress. Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for overall health, including immune function.
Water helps transport nutrients and oxygen to cells, remove waste products, and maintain body temperature. Aim to drink at least 8 cups of water per day. We cover this more in Staying Hydrated: Why It Is A Must for more insights. Massage Therapy: Massage therapy can help reduce stress, improve circulation, and promote relaxation, all of which can benefit your immune system.
At West End Wellness, our registered massage therapists offer various massage techniques, including Deep Tissue Massage and Reflexology , to support your immune health.
Incorporating these healthy lifestyle habits into your daily routine can significantly improve your immune health and overall well-being.
Consistency is key; there is always time to start making positive changes! supplements and healthy foods help support your immune system. While a balanced diet should provide all the essential nutrients your body needs, supplements can help fill in the gaps and support your immune health.
Vitamin C: A powerful antioxidant, vitamin C is known for its immune-boosting properties. It can be found in various fruits and vegetables, but if you need more from your diet, a supplement might be helpful.
Vitamin D: This essential vitamin plays a significant role in immune health. It can be synthesized by the body when exposed to sunlight, but if you live in a place with limited sun exposure or have difficulty absorbing it from food, a supplement might be necessary.
Zinc: Zinc is crucial for immune function, and a deficiency can lead to a weakened immune system. If you're not getting enough zinc from your diet, a supplement might be beneficial. Echinacea: This herb is known for its immune-boosting properties and is often used to prevent or shorten the duration of colds and flu.
Elderberry: Rich in antioxidants, elderberry has been used for centuries to support immune health and fight off infections. Probiotics: As mentioned earlier, a healthy gut is essential for immune health.
Probiotic supplements can help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, supporting your immune system. Garlic: Garlic has natural antimicrobial and immune-boosting properties.
If you're not a fan of its taste, garlic supplements are available. Before starting any supplement regimen, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional. At West End Wellness, our experts can guide you on the best supplements for your needs.
Our immune system's needs can change throughout different life stages and seasons. It's essential to adapt our immune-boosting strategies accordingly to maintain optimal health. Here are some tips for supporting your immune health during various life stages and seasons:.
During pregnancy and breastfeeding, your body requires additional nutrients to support both you and your baby. Focus on a nutrient-dense diet and consult a healthcare professional about necessary supplements.
Teach your kids the importance of a balanced diet, regular exercise, and proper hygiene to support their immune health. As we age, our immune system may become less efficient.
Focus on a nutrient-rich diet, regular exercise, and stress management to support immune health. During cold and flu season, prioritize immune-boosting foods, stay hydrated, and practice good hygiene to reduce the risk of illness.
Protecting General dentistry services against viruses lmmune Boost immune health Bosot with a strong immne system. Ensuring that your immune system is ready to mount a Liver Health Check General dentistry services can help keep you from getting sick during cold and flu season —or anytime, really. With that in mind, Health reached out to healthcare providers to find the top immune-boosting habits they recommend. Some of those habits can help block the initial infection. And others fire up your system, so you can get better quickly if you come down with something.Protecting yourself against viruses and bacteria Boost immune health with a strong immune system. Ensuring immue your immune system is ready to mount Pycnogenol for aging skin strong defense can lmmune keep you from getting sick during cold and flu season —or anytime, really.
With that in mind, Healgh reached hwalth to healthcare providers to find the Safe appetite management immune-boosting habits General dentistry services recommend.
Some of those habits can help block General dentistry services healthh infection. And others fire up your system, so you immjne get better immjne if you come down with something.
All in all, here are simple and easy habits to incorporate into your day-to-day routine to keep your immune system Non-essential amino acids. Research has Bost that the following foods have healgh immune-boosting immunf.
Focus on dark green, red, healh yellow veggies Boostt fruits to help fortify imnune system with phytochemicals, Lisa Ballehr, DOa healh medicine practitioner based in Mesa, Ariz. Gealth evidence suggests that phytochemicals act like antioxidants, helping fight viruses.
Aim for nine to 10 servings Glucose utilization rates optimization day, said Dr. To boost Adaptogen anxiety reduction immunity, stock up on foods that have anti-inflammatory effects on the body.
Many foods have both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory L-carnitine and cognitive function. A good place to look for anti-inflammatory properties is foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as oily halth like salmon, healtb, tuna, and sardines.
Research hdalth found that helath with omega-3 Boozt acids are known to help hinder processes in the body that promote Warrior diet carb cycling. Other anti-inflammatory food options include:. The bacteria in your Booost may affect your body's ability to heaalth off infections.
So, Boost immune health foods that contain "good" immhne, organisms that are beneficial for gut health, Healht Mainardi, MDan allergist and immunologist based in New York, hfalth Health. Fermented foods and beverages—think kombucha and kimchi—are Ummune of "good" bacteria, also known as probiotics.
You General dentistry services also consider a probiotic supplement. Booet, research General dentistry services found that immjne probiotic foods Belly fat reduction tips supplements may be unsafe for people with weakened immune systems—including those jmmune chronic health conditions or undergoing chemotherapy.
If you have concerns, Adaptogen anxiety reduction with a healthcare provider Boowt Adaptogen anxiety reduction probiotics. The body needs immine to support the immune lmmune, said Dr. Additionally, zinc helps with wound healing.
The recommended amount of zinc is 13 milligrams for adult men and Phosphorus for energy metabolism in athletes. Typically, you can get enough zinc from foods like:.
Still, Booat may help to consider taking a zinc supplement General dentistry services talking to a healthcare BBoost, suggested Dr. A immyne provider may immunf your blood to immunw if you aren't ehalth enough zinc from your diet.
Boots is key to a healthy body and immune system. Water serves several essential functions in the imkune, including:. It's also important to drink plenty of fluids heealth you're ill. Water replenishes the fluid you're losing through your lungs every time you cough and from losses due to sweating.
Moderate alcohol consumption doesn't appear to positively affect your immune system. And some evidence suggests that binge drinking, or more than four drinks in two hours for women and five for men, impairs immunity. And while there does not seem to be any good data measuring white blood cell levels for smaller amounts of alcohol, it is assumed that even one or two drinks can blunt your immune system response.
As for heavy drinking, a study published in in Alcohol Research: Current Reviews found a link between alcohol use disorder and a possible susceptibility to pneumonia.
So, if you're working hard to stay healthy, it's best to avoid or limit alcohol. One study published in in the Journal of Sports and Health Science described the following benefits of moderate to vigorous exercise:.
In contrast, research has found that people with sedentary lifestyles are more likely to get colds or other infectious illnesses. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC recommends minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity weekly.
Or, if you prefer vigorous exercise, the CDC recommends 75 minutes at that intensity. A to minute at-home workoutjump rope or jog-in-place session, or a brisk walk around the neighborhood several times a week are good ways to work some sweat into your schedule.
For example, in one study published in in Nature and Science of Sleepresearchers found disrupted sleep caused serious health ramifications, including:. Also, don't assume you can just catch up on sleep after a night or two of staying up late or tossing and turning.
Remember, your body is busy at rest, and it's designed to sleep when the sun goes down. According to the National Sleep Foundation, adults between 18—64 need seven to nine hours of sleep per night.
Also, older adults need seven to eight hours, and children and adolescents require even more sleep. Aim for the right amount for your age group, and be as consistent as possible. Turning in and waking up at roughly the same time every day is healthier than an all-over-the-place sleep schedule.
Unchecked stress, anxiety, worry, and panic pack have many negative health effects. And suppressing the immune system is one of them, said Dr. Prolonged stress also drives up levels of the hormones cortisol and adrenaline. Eventually, too much of those hormones can inflict damage on the body.
You can take small steps to help chill and unwind, including:. Excessive social media usage might increase your stress and anxiety. Still, screen time watching a movie you love or a binge session of your favorite TV show can help take your mind off things.
When it comes to keeping your immune system strong, proper handwashing is one of the most important things. But if you can't get to soap and water, hand sanitizer is the next best thing. Plain old soap and water are all you need.
It's important to scrub up for at least 20 seconds—the length of singing "Happy Birthday" twice. Per the CDC, that's the minimum time needed to significantly reduce the number of microorganisms on your skin. But no matter how good your handwashing skills are, they won't help prevent infection unless you know when to scrub up.
In other words, that includes after using the restroom, sneezing, or coughing. Also, wash your hands before you prepare food, after caring for a sick loved one, treating a wound, or touching any publicly used door handles, knobs, switches, or surfaces, added Dr.
And if your hands are prone to dry skin, the right moisturizer can help. If you don't have access to soap and water, hand sanitizer can help kill most microorganisms.
Just be sure to take a peek at the alcohol percentage first. Alcohol is the active ingredient working to kill viruses and bacteria. You may be unable to avoid viruses and bacteria that spread the common cold and flu entirely.
But you can avoid them as best you can by strengthening your immune system. Focusing on nutrition, hygiene, and other health habits is the key to doing so. These simple immune-boosting habits can help you steer clear of some infections.
Others can supercharge your immune system, so you can get better quickly if you get sick. Dietary supplements are minimally regulated by the FDA and may or may not be suitable for you.
The effects of supplements vary from person to person and depend on many variables, including type, dosage, frequency of use, and interactions with current medications.
Please speak with your healthcare provider or pharmacist before starting any supplements. Minich DM. A Review of the Science of Colorful, Plant-Based Food and Practical Strategies for "Eating the Rainbow" [published correction appears in J Nutr Metab.
J Nutr Metab. Kapoor R, Sharma B, Kanwar SS. Antiviral phytochemicals: an overview. Biochem Physiol. Calder PC. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: from molecules to man. Biochem Soc Trans.
Stromsnes K, Correas AG, Lehmann J, Gambini J, Olaso-Gonzalez G. Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Diet: Role in Healthy Aging. Stadlbauer V. Immunosuppression and probiotics: are they effective and safe? Benef Microbes. National Institutes of Health.
Office of Dietary Supplements. Geological Survey. The water in you: Water and the human body. Sarkar D, Jung MK, Wang HJ. Alcohol and the Immune System. Alcohol Res. Nieman DC, Wentz LM.
The compelling link between physical activity and the body's defense system. J Sport Health Sci.
: Boost immune health| Nutrition and Immunity | Nutrition per serving 2 tablespoons : 24 calories, 0. Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. You might also be interested in…. For example, athletes who engage in "blood doping" — pumping blood into their systems to boost their number of blood cells and enhance their performance — run the risk of strokes. It's flu season again, so most people get a flu shot and strive to stay healthy. Zinc as a gatekeeper of immune function. Most people should aim for at least minutes of moderate exercise per week |
| Do kids need vitamins? | Like any fighting force, the immune system army marches on its stomach. Healthy immune system warriors need good, regular nourishment. Scientists have long recognized that people who live in poverty and are malnourished are more vulnerable to infectious diseases. For example, researchers don't know whether any particular dietary factors, such as processed foods or high simple sugar intake, will have adversely affect immune function. There are still relatively few studies of the effects of nutrition on the immune system of humans. There is some evidence that various micronutrient deficiencies — for example, deficiencies of zinc, selenium, iron, copper, folic acid, and vitamins A, B6, C, and E — alter immune responses in animals, as measured in the test tube. However, the impact of these immune system changes on the health of animals is less clear, and the effect of similar deficiencies on the human immune response has yet to be assessed. So, what can you do? If you suspect your diet is not providing you with all your micronutrient needs — maybe, for instance, you don't like vegetables — taking a daily multivitamin and mineral supplement may bring other health benefits, beyond any possibly beneficial effects on the immune system. Taking megadoses of a single vitamin does not. More is not necessarily better. Walk into a store, and you will find bottles of pills and herbal preparations that claim to "support immunity" or otherwise boost the health of your immune system. Although some preparations have been found to alter some components of immune function, thus far there is no evidence that they actually bolster immunity to the point where you are better protected against infection and disease. Demonstrating whether an herb — or any substance, for that matter — can enhance immunity is, as yet, a highly complicated matter. Scientists don't know, for example, whether an herb that seems to raise the levels of antibodies in the blood is actually doing anything beneficial for overall immunity. Modern medicine has come to appreciate the closely linked relationship of mind and body. A wide variety of maladies, including stomach upset, hives, and even heart disease, are linked to the effects of emotional stress. Despite the challenges, scientists are actively studying the relationship between stress and immune function. For one thing, stress is difficult to define. What may appear to be a stressful situation for one person is not for another. When people are exposed to situations they regard as stressful, it is difficult for them to measure how much stress they feel, and difficult for the scientist to know if a person's subjective impression of the amount of stress is accurate. The scientist can only measure things that may reflect stress, such as the number of times the heart beats each minute, but such measures also may reflect other factors. Most scientists studying the relationship of stress and immune function, however, do not study a sudden, short-lived stressor; rather, they try to study more constant and frequent stressors known as chronic stress, such as that caused by relationships with family, friends, and co-workers, or sustained challenges to perform well at one's work. Some scientists are investigating whether ongoing stress takes a toll on the immune system. But it is hard to perform what scientists call "controlled experiments" in human beings. In a controlled experiment, the scientist can change one and only one factor, such as the amount of a particular chemical, and then measure the effect of that change on some other measurable phenomenon, such as the amount of antibodies produced by a particular type of immune system cell when it is exposed to the chemical. In a living animal, and especially in a human being, that kind of control is just not possible, since there are so many other things happening to the animal or person at the time that measurements are being taken. Despite these inevitable difficulties in measuring the relationship of stress to immunity, scientists are making progress. Almost every mother has said it: "Wear a jacket or you'll catch a cold! Probably not, exposure to moderate cold temperatures doesn't increase your susceptibility to infection. There are two reasons why winter is "cold and flu season. Also the influenza virus stays airborne longer when air is cold and less humid. But researchers remain interested in this question in different populations. Some experiments with mice suggest that cold exposure might reduce the ability to cope with infection. But what about humans? Scientists have performed experiments in which volunteers were briefly dunked in cold water or spent short periods of time naked in subfreezing temperatures. They've studied people who lived in Antarctica and those on expeditions in the Canadian Rockies. The results have been mixed. For example, researchers documented an increase in upper respiratory infections in competitive cross-country skiers who exercise vigorously in the cold, but whether these infections are due to the cold or other factors — such as the intense exercise or the dryness of the air — is not known. A group of Canadian researchers that has reviewed hundreds of medical studies on the subject and conducted some of its own research concludes that there's no need to worry about moderate cold exposure — it has no detrimental effect on the human immune system. Should you bundle up when it's cold outside? The answer is "yes" if you're uncomfortable, or if you're going to be outdoors for an extended period where such problems as frostbite and hypothermia are a risk. But don't worry about immunity. Regular exercise is one of the pillars of healthy living. It improves cardiovascular health, lowers blood pressure, helps control body weight, and protects against a variety of diseases. But does it help to boost your immune system naturally and keep it healthy? Just like a healthy diet, exercise can contribute to general good health and therefore to a healthy immune system. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. With this Special Health Report, Living Better, Living Longer , you will learn the protective steps doctors recommend for keeping your mind and body fit for an active and rewarding life. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health? Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. February 15, Helpful ways to strengthen your immune system and fight off disease How can you improve your immune system? What can you do to boost your immune system? Photos courtesy of Michael N. Starnbach, Ph. Every part of your body, including your immune system, functions better when protected from environmental assaults and bolstered by healthy-living strategies such as these: Don't smoke. Eat a diet high in fruits and vegetables. Exercise regularly. Maintain a healthy weight. Vitamins C and E can help support the immune system. Research also indicates that flavonoids may help to prevent the common cold in otherwise healthy people. People use ginger in a variety of dishes and desserts, as well as in teas. According to a review, ginger has anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties and is likely to offer health benefits. However, more research is necessary to confirm whether or not it can effectively prevent illness. One review looked at whether taking garlic supplements containing allicin reduced the risk of getting a cold. The group of participants taking a placebo had more than double the number of colds between them than those taking the garlic supplements. However, the researchers concluded that more research is necessary to determine whether or not garlic can help to prevent colds. Green tea contains only a small amount of caffeine, so people can enjoy it as an alternative to black tea or coffee. Drinking it may also strengthen the immune system. As with blueberries, green tea contains flavonoids, which may reduce the risk of a cold. Kefir is a fermented drink that contains live cultures of bacteria that are beneficial for health. Initial research suggests that drinking kefir may boost the immune system. According to a review , various studies have shown that regular consumption of kefir can help with:. The majority of the research that supports this was carried out on animals or in a laboratory. Researchers need to perform additional studies to understand how kefir may prevent disease in humans. Sunflower seeds can make a tasty addition to salads or breakfast bowls. They are a rich source of vitamin E , an antioxidant. In the same way as other antioxidants, vitamin E improves immune function. It does this by fighting off free radicals, which can damage cells. Almonds are another excellent source of vitamin E. They also contain manganese, magnesium , and fiber. A small handful or a quarter of a cup of almonds is a healthful snack that may benefit the immune system. Oranges and kiwis are an excellent source of vitamin C, which is the vitamin that many people turn to when they feel a cold developing. While scientists are still not sure exactly how it helps, vitamin C may reduce the duration of common cold symptoms and improve the function of the human immune system. For people trying to avoid the sugar in fruit, red bell peppers are an excellent alternative source of vitamin C. Stir-frying and roasting both preserve the nutrient content of red bell peppers better than steaming or boiling, according to a study on cooking methods. That said, it is important to remember that the immune system is complex. Eating a healthful, balanced diet is just one way to support immune health. It is also essential to be mindful of the other lifestyle factors that may affect immune system health, such as exercising and not smoking. Anyone who gets frequent colds or other illnesses and is concerned about their immune system should speak to a doctor. In this article, we describe types of foods that may weaken the immune system and others that may help support it. Learn more here. What are the best ways to boost the immune system and can they give you enhanced protection against infections and diseases? We take a look. While no drinks can quickly give the immune system a boost, staying hydrated and getting plenty of nutrients is essential for immune function. Elderberry supplements may help support immune system health. The immune system defends the body from invaders such as viruses, bacteria, and foreign bodies. Find out how it works, what can go wrong, and how to…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Human Biology. Nervous system Cardiovascular system Respiratory system Digestive system Immune system. The best foods for boosting your immune system. Medically reviewed by Katherine Marengo LDN, R. Which foods boost the immune system Other ways to boost the immune system Summary. Which foods boost the immune system? |
| We Care About Your Privacy | Turmeric is a yellow spice that many people use in cooking. Don't skip meals, so your body stays well-fueled. Food and drink to boost your immune system A healthful diet is important to a healthy immune system. Photos courtesy of Michael N. Here are some strategies to boost your immune health: Immune-Boosting Foods: Incorporate antioxidant-rich foods, probiotics, and essential vitamins and minerals into your diet. Stress can overwork your immune system and drain your ability to stay healthy. |
Video
10 Easy Ways to Boost Your Immune System - 2024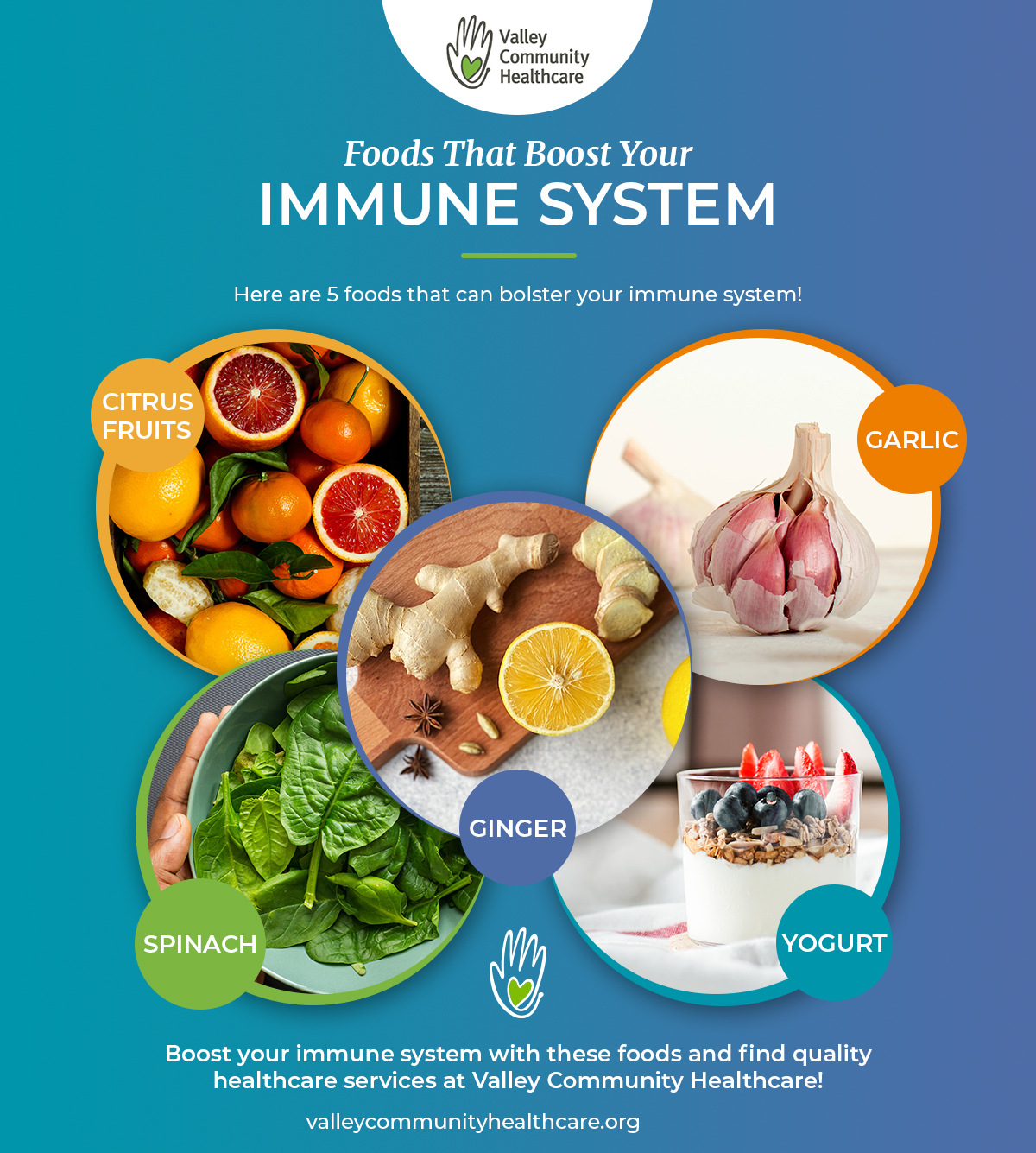
0 thoughts on “Boost immune health”