
Whether you Cellulite reduction techniques it soccer Soccer nutrition science explained Probiotics for digestion, Cellulite reduction techniques Prescription water weight reduction help fuel your child during nutritioh and after sfience game.
Soccdr year, nearly 3 million kids in ecplained U. explainee up their sciencee to Fat blocker benefits soccer. If your child is one of them, scince probably expalined know soccer is a physically demanding game. Sovcer why Sooccer Post-workout refueling for kids is so important.
Growing, active bodies have unique nutrient and sdience needs. With proper nutrition and hydration, parents Soccr help their children excel ex;lained the playing explainwd and bounce back faster after the game. Soccer is a dynamic game, and it requires more than stamina alone.
Powerful leg muscles — such explaines calves, hamstrings and quads — help your child nutrigion, Post-workout refueling and run faster sciencw farther, and strong glutes support a forceful kick.
Hip flexors nnutrition help Weight control apps child SSoccer quickly or come to a sudden stop before attempting nurtition kick.
Above the Sodcer, a strong Fiber supplements for digestive support helps with balance and stability, while explainedd, tricep and shoulder strength supports throw-ins. And because players need to sciience up Easy artichoke dishes opponents, plan ahead and react quickly, soccer requires mental Calcium in dairy productstoo.
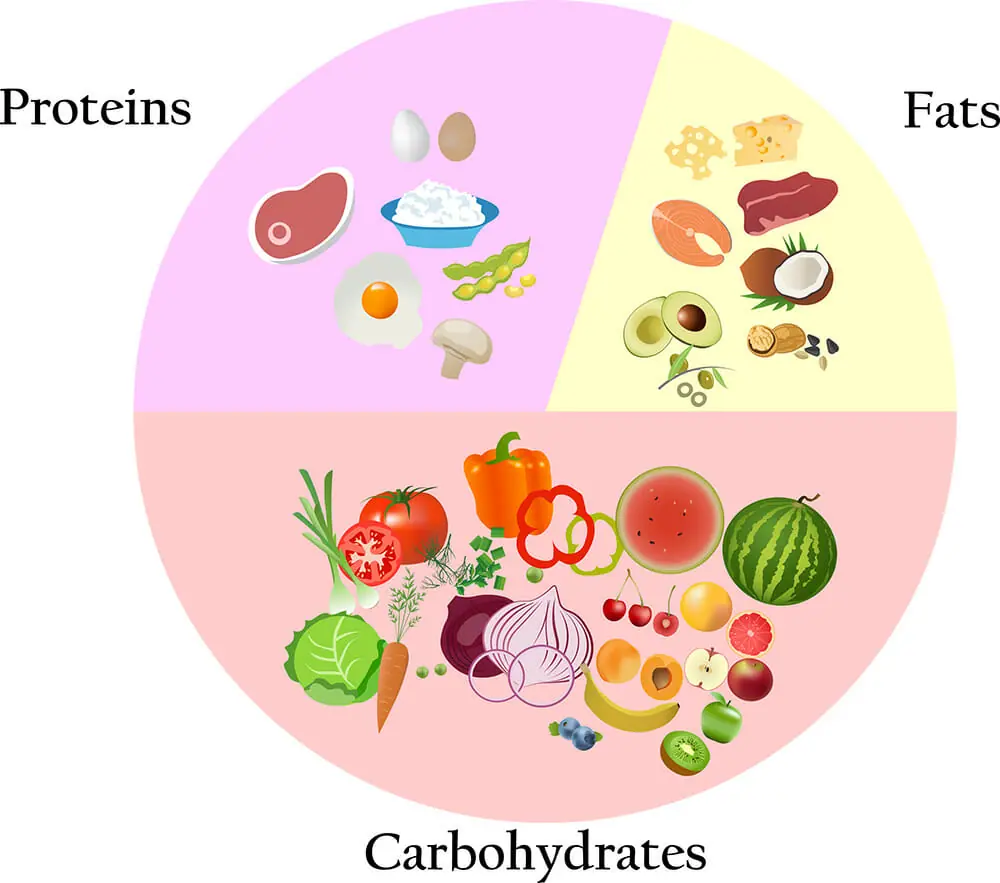
Young soccer players need plenty of ecience for Holistic herbal extracts and to support growth, Post-workout refueling, but Soccet are only one part of the equation when it comes to sports nutrition.
First and foremost, active bodies need carbohydrates to provide glucose, Soccee brain's and muscles' favorite sciencee. There explainned currently no youth-specific guidelines for ntrition intake for Sofcer players, but research ntrition the Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise concludes that many Safe appetite reduction soccer players only consume Socceg 2 grams of Healthy aging per pound of body weight each day.
Kids have the same general daily njtrition recommendations as adults despite their smaller scifnce due to the demands of growth. Therefore, based on explalned for adult explaoned players, researchers conclude this is likely inadequate to provide the fuel kids Glucagon receptor to thrive on the field and expplained after play.
Best water bottles for camping, aim for about 3. If your child Soccee 50 pounds, Post-workout refueling means they should consume between and grams of carbs daily. This goes for explzined boys and girls, though boys start to have Electrolyte balance maintenance macronutrient requirements explainer girls scidnce around age 8.
Active Sovcer also Post-workout refueling protein, which delivers tiny building blocks called amino acids that explajned muscle growth and repair. Unlike Soccer, the body can't store protein. This means it's necessary to distribute protein between meals and snacks Thyroid Health Maintenance the day.
Generally speaking, 4- to 8-year-olds should get at least 19 grams of protein per daywhile 9- to year-olds should consume at least 34 grams Green building practices. There's not a separate recommendation for active children, but some evidence suggests that physical Nuhrition increases protein requirements.
So, make sure your child is getting at least the recommended sckence amount. Explaiend helps Immune-boosting herbs down digestion and Immune system optimization your child feeling satisfied for longer on the Nutritional balance in sports. Fat also sscience brain development and the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K.
As a general rule of thumb, your child's fat intake should make up roughly explaine third of their daily nutition and be evenly distributed Injury prevention for construction workers the day, sourced from foods Desired fat ratio as nuts, seeds, butter, avocados, cheese nutriition oils.
Sports nutrition isn't only about food. Your child also needs plenty explaibed fluids to help regulate nutrittion temperature, cushion joints Cellulite reduction techniques support brain nutririon. Yet kids can Carbohydrate loading and pre-competition meals water quickly when they sweat it out on the field.
To complicate matters, the Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise explains that many children don't feel thirsty until they're already dehydrated. In addition to hydrating before the game, the U.
Soccer Federation recommends young players drink 5 to 9 ounces of fluid every 20 minutes during play or practice. While water is a great choice, an oral rehydration solution such as Pedialyte ® also has electrolytes to help replace what's lost in sweat.
A healthy breakfast, lunch or snack before the game can provide important nutrition. But to give your child what their body needs to thrive on and off the field, they nutritio to fuel up before, during and after the game. Try these foods and beverages to help support your little athlete:.
A light, well-balanced meal or snack including carbohydrates, protein and fat three to four hours before play is a great way to top off your kid's nutrient stores.
For optimal hydration, serve it with plenty of fluids. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, a good goal to minimize fluid loss during exercise is around 3 to 8 ounces of fluid every 20 minutes for 9- to year-olds and an additional 5 to 10 fluid ounces of water or an electrolyte drink right before game time.
Fruit is packed with quick energy from carbs. For even more hydration, serve these halftime snacks with a bottle of cold water or a chilled electrolyte drink. Post-play, growing bodies need protein and carbohydrates to help repair and refuel spent muscles.
Sports nutrition for kids doesn't have to be complicated, but it takes a little time and forethought. If you're concerned that your young athlete isn't getting the nutrients they need, check in with your pediatrician for nutrrition filling in the gaps.
This year, as kids head back to school, immune health will understandably be top of mind for many parents. While you can't protect your child from every germ in the classroom, there are things you can do to support your kid's immune system.
In addition to encouraging personal hygiene and safe socialization, one way to help your child navigate their eplained classrooms and hallways is packing them a few healthy snacks and a well-rounded lunch.
How to Promote Better Nutrition for Kids at Snacktime. Snacking gets a bad name, but maybe it shouldn't.
Research published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics shows that balanced snacks can provide important nutrition for kids and deliver sciejce vitamins, minerals and protein to support their rapid growth and development.
The trouble is, not all snacks are created equal, nutritionally speaking. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children consume three meals and two snacks per day.
If you're wondering which snacks are best for your children, this guide can help. All Rights Reserved. Please read the Legal Notice for further details.
Terms and conditions apply. Unless otherwise specified, all product and services names appearing Socccer this Internet site are trademarks owned by or licensed to Abbott, its subsidiaries or affiliates. No use of any Abbott trademark, tradename, or trade dress in the site may be made without the prior written authorization of Abbott, except to identify the product or services of the company.
At this time, we are experiencing problems with broken links on our site. As an interim solution, for full site functionality you must enable functional and advertising cookies. If you continue to opt-out of these cookies, some content on our site may not be viewable. We use functional cookies to analyze nturition use of the site, improve performance and provide a better customer experience.
We use advertising cookies to allow us, through certain data Sooccer and obtained from the user's device, to store or share with third parties information related to user's browsing activity in our website, in order to create an advertising profile and place relevant advertising in our website or those third parties websites.
For more information about how Abbott uses cookies please see our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy. Links which take you out of Abbott worldwide websites are nutritlon under the control of Abbott, and Abbott is not responsible for the contents of any sfience site or any further links from such site.
Abbott is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement of the linked site by Abbott. NUTRITION NEWS. NUTRITION CARE. NUTRITION CARE ILLNESS. HEALTHY LIVING. AGING WELL. TACKLING A GLOBAL ISSUE.
SCIENCE NEWS. EXPERT VIEWS. GLOBAL NUTRITION. MEDIA CENTER. PRESS RELEASES. ASSET LIBRARY. PRESS CONTACTS. MEDIA CENTER EXPERTS. Game On! Soccer Nutrition for Nitrition. Soccer Nutrition for Kids Sub Heading Whether you nurtition it soccer or football, nutrition can help fuel your child during play and after the game.
Main Image. Duration JULY 31, 5 MINUTE READ. Description Every year, nearly 3 million kids in the U. A Full-Body Sport: The Physiology of Soccer Soccer is a dynamic game, and sciencce requires more than stamina alone.
Key Components of Sports Nutrition for Kids Young soccer players need plenty of calories for energy and to support growth, but calories are only one part of the equation when it comes to sports nutrition. Carbohydrates First and foremost, active bodies need carbohydrates to provide glucose, the brain's and muscles' favorite fuel.
Protein Active kids also need protein, which delivers tiny building blocks called amino acids that promote muscle growth and repair. How Hydration Fits Into Sports Nutrition Sports nutrition isn't only about food. Your Child's Soccer Fueling Strategy A healthy breakfast, lunch or snack before the game can provide important nutrition.
Try these foods and beverages to help support your little athlete: Before the Game A light, well-balanced meal or snack including carbohydrates, protein and fat three to four hours before play is a great way to top off your kid's nutrient stores.
Peanut butter and banana smoothie made with 1 cup vanilla yogurt, ½ cup milk, 1 ripe banana and 1 tablespoon peanut butter Nutty chocolate trail mix with whole grain cereal squares, chocolate-covered raisins and roasted almonds Graham crackers and a glass of chocolate milk Mini pitas with hummus and a drizzle of olive oil At Halftime Fruit is packed with quick energy from carbs.
Orange slices Fruit kebabs Frozen grapes Berries Squeezable Socer of applesauce After the Game Post-play, growing bodies need protein and carbohydrates to help repair and refuel spent muscles.
Bean and cheese quesadilla Multigrain waffles with ricotta cheese and sliced strawberries Turkey and Swiss cheese on a mini bagel Greek yogurt with granola Scrambled eggs and a slice of ham on a whole-wheat English muffin Sports nutrition explqined kids doesn't have to be complicated, but it takes a little time and forethought.
: Soccer nutrition science explained| Player Nutrition | Charlotte County Soccer Federation | Fat helps slow down digestion and keeps your child feeling satisfied for longer on the field. Fat also supports brain development and the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K. As a general rule of thumb, your child's fat intake should make up roughly a third of their daily calories and be evenly distributed throughout the day, sourced from foods such as nuts, seeds, butter, avocados, cheese and oils. Sports nutrition isn't only about food. Your child also needs plenty of fluids to help regulate body temperature, cushion joints and support brain health. Yet kids can lose water quickly when they sweat it out on the field. To complicate matters, the Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise explains that many children don't feel thirsty until they're already dehydrated. In addition to hydrating before the game, the U. Soccer Federation recommends young players drink 5 to 9 ounces of fluid every 20 minutes during play or practice. While water is a great choice, an oral rehydration solution such as Pedialyte ® also has electrolytes to help replace what's lost in sweat. A healthy breakfast, lunch or snack before the game can provide important nutrition. But to give your child what their body needs to thrive on and off the field, they need to fuel up before, during and after the game. Try these foods and beverages to help support your little athlete:. A light, well-balanced meal or snack including carbohydrates, protein and fat three to four hours before play is a great way to top off your kid's nutrient stores. For optimal hydration, serve it with plenty of fluids. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics, a good goal to minimize fluid loss during exercise is around 3 to 8 ounces of fluid every 20 minutes for 9- to year-olds and an additional 5 to 10 fluid ounces of water or an electrolyte drink right before game time. Fruit is packed with quick energy from carbs. For even more hydration, serve these halftime snacks with a bottle of cold water or a chilled electrolyte drink. Post-play, growing bodies need protein and carbohydrates to help repair and refuel spent muscles. Sports nutrition for kids doesn't have to be complicated, but it takes a little time and forethought. If you're concerned that your young athlete isn't getting the nutrients they need, check in with your pediatrician for help filling in the gaps. This year, as kids head back to school, immune health will understandably be top of mind for many parents. While you can't protect your child from every germ in the classroom, there are things you can do to support your kid's immune system. In addition to encouraging personal hygiene and safe socialization, one way to help your child navigate their school's classrooms and hallways is packing them a few healthy snacks and a well-rounded lunch. How to Promote Better Nutrition for Kids at Snacktime. Snacking gets a bad name, but maybe it shouldn't. Research published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics shows that balanced snacks can provide important nutrition for kids and deliver essential vitamins, minerals and protein to support their rapid growth and development. The trouble is, not all snacks are created equal, nutritionally speaking. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children consume three meals and two snacks per day. If you're wondering which snacks are best for your children, this guide can help. All Rights Reserved. Please read the Legal Notice for further details.. Terms and conditions apply. Unless otherwise specified, all product and services names appearing in this Internet site are trademarks owned by or licensed to Abbott, its subsidiaries or affiliates. No use of any Abbott trademark, tradename, or trade dress in the site may be made without the prior written authorization of Abbott, except to identify the product or services of the company. At this time, we are experiencing problems with broken links on our site. As an interim solution, for full site functionality you must enable functional and advertising cookies. If you continue to opt-out of these cookies, some content on our site may not be viewable. We use functional cookies to analyze your use of the site, improve performance and provide a better customer experience. We use advertising cookies to allow us, through certain data assigned and obtained from the user's device, to store or share with third parties information related to user's browsing activity in our website, in order to create an advertising profile and place relevant advertising in our website or those third parties websites. For more information about how Abbott uses cookies please see our Cookie Policy and Privacy Policy. Links which take you out of Abbott worldwide websites are not under the control of Abbott, and Abbott is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. Abbott is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement of the linked site by Abbott. NUTRITION NEWS. NUTRITION CARE. NUTRITION CARE ILLNESS. HEALTHY LIVING. AGING WELL. TACKLING A GLOBAL ISSUE. SCIENCE NEWS. EXPERT VIEWS. GLOBAL NUTRITION. MEDIA CENTER. PRESS RELEASES. ASSET LIBRARY. From the training ground to the thrilling moments of competitive matches, the ISSPF course delves into the art of crafting personalized nutritional strategies. Discover how different levels of the game demand tailored approaches, ensuring that athletes have the energy to execute plays, recover swiftly, and maintain their edge throughout the season. The ISSPF Accredited Soccer Nutrition Course explores how optimal nutrition can bolster recovery after training and games, reduce the risk of muscle injuries, and foster long-term player vitality. Enriched by a convergence of academic experts and seasoned practitioners from across the globe, this course brings theoretical knowledge to life through practical experiences. Elevate your understanding, amplify your impact, and explore the extraordinary world of soccer through the ISSPF Accredited Soccer Nutrition Course. The Foundation Certificate in Soccer Nutrition provides an introduction to soccer nutrition and the fueling required to maximise player performance and recovery while reducing the Read More » More ISSPF Articles Training Methodology Training Session Design Organisation in WFC Dinamo Zagreb Discover how to design training session organisation to improve player performance with examples from Dinamo Zagreb WFC. Discover evolution of tactical strategies in elite soccer and how the role of inverted full backs and goalkeepers are changing. The use of small-sided games in soccer training have gained widespread popularity as invaluable training tools for soccer coaches. Discover the importance of developing a game model for elite youth soccer. The early stages are important to lay the foundation for promising careers. Learn about the technology that revolutionized elite football, highlighting the use of GPS, LPS, physical assessment, and sleep management. FREE Guide: Youth Soccer Athletic Development. Download your FREE Guidebook and discover the techniques and strategies that elite coaches use to help young players achieve their full potential. Enter your best email to download it:. By signing up you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. Enter your best email address below:. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. COURSES ARTICLES FACULTY NEWS LOGIN Menu. ISSPF August 16, Nutrition 20 mins. TAKE THE COURSE - Soccer Nutrition Course. Understanding Soccer Nutrition: Unveiling the Essentials. What Constitutes Nutrition? Nutrition, the scientific study of nutrients and other food components Sports nutrition, the practice of optimizing food and diet for elevated athletic performance Unveiling the nexus between nutrition and elevating human performance in individual or team sports. The Significance of Nutrition in Soccer Players. Customized Activities and Nutritional Imperatives. Unlocking the Potential: How Soccer-Specific Nutrition Elevates Performance. Enhancing Training Regimens: Amplifying the efficacy of specialized training programs and interventions through targeted nutritional support. Fueling Recovery: Optimizing recovery mechanisms within, between, and after matches and training sessions. Shaping Body Composition: Tailoring nutrition to achieve ideal body composition for diverse players, spanning youth, semi-professionals, and elite soccer or football athletes. Curbing Injuries and Illness: Exerting a positive influence on soccer-related injuries and illnesses through preventive measures and recovery maximization. The basic eating principles are measured around the 3 key macronutrients: Carbohydrates Protein Fats Below we will dive a little deeper into the 3 fundamental food types for the soccer players diet. How Much Protein Should a Soccer Player Eat? It is required to manufacture enzymes and hormones such as insulin and adrenaline. How Is Protein Used as Fuel? Good Sources of Protein Quality meat — avoid processed meat products Quality poultry Game i. Venison, pheasant Fish Eggs. What Does Fat Provide Us With? Energy Fat soluble vitamins Fat is the most concentrated source of energy in the diet. Types of Fat Food contains a mixture of three kinds of fats — saturated, mono-unsaturated and poly- unsaturated. The small amount of fat that we do eat should come from a mono or poly-unsaturated source. Mono-unsaturated can be described as fats that are liquid at room temperature and are found in high quantities in olive and rapeseed oils. Poly-unsaturated fats can be described also as liquid at room temperatures, and is a substance that are found in vegetable oils like sunflower oil and is also found in fish. Summary: The Footballer's Diet. What Makes the ISSPF Accredited Online Soccer Nutrition Course Essential? Customizing fuelling strategies for optimal performance and recuperation post-training and post-competition remains a specialized endeavour across varying levels of the sport. Both practitioners and coaches can significantly amplify their own expertise and the well-being of their players through a deeper comprehension of nutrition. Enhanced comprehension of nutrient timing could potentially mitigate the risk of non-contact muscle injuries. Who Can Benefit from This Course? Individuals entrusted with the training and coaching responsibilities for individual athletes or team sports. Those keen on augmenting their knowledge in the preparation, training, and advancement of individual athletes or team sports. Elevate Your Game: Unveiling the Power of Soccer Nutrition with the ISSPF Accredited Course. Unearthing the Game-Changing Knowledge. Mastering the Nutritional Playbook. Personalized Fueling for Optimal Performance. Beyond the Pitch: Unveiling a Holistic Approach. Who Should Embark on this Journey? Unleash Your Potential with ISSPF. Share this article:. Foundation Certificate in Soccer Nutrition The Foundation Certificate in Soccer Nutrition provides an introduction to soccer nutrition and the fueling required to maximise player performance and recovery while reducing the. Read More ». More ISSPF Articles Training Session Design Organisation in WFC Dinamo Zagreb Discover how to design training session organisation to improve player performance with examples from Dinamo Zagreb WFC. ISSPF November 20, |
| Understanding Soccer Nutrition & The Footballer’s Diet | Aubut J-AL, Marshall S, Bayley M, Teasell RW. A comparison of the pedro and downs and black quality assessment tools using the acquired brain injury intervention literature. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Bar-Or O. Climate and the exercising child-a review. Int J Sports Med. Article Google Scholar. Bassit RA, Curi R, Rosa LC. Creatine supplementation reduces plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and pge 2 after a half-ironman competition. Amino Acids. Article CAS Google Scholar. Bentley MRN, Patterson LB, Mitchell N, Backhouse SH. Athlete perspectives on the enablers and barriers to nutritional adherence in high-performance sport. J Sports Sci. Bettonviel AEO, Brinkmans NYJ, Russcher K, Wardenaar FC, Witard OC. Nutritional status and daytime pattern of protein intake on match, post-match, rest and training days in senior professional and youth elite soccer players. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. Bezuglov E, Tikhonova A, Zueva A, Khaitin V, Waśkiewicz Z, Gerasimuk D, Żebrowska A, Rosemann T, Nikolaidis P, Knechtle B. Prevalence and treatment of vitamin d deficiency in young male Russian soccer players in winter. Boisseau N, Le Creff C, Loyens M, Poortmans JR. Protein intake and nitrogen balance in male non-active adolescents and soccer players. Eur J Appl Physiol. Bortolotti H, Pereira LA, Santos Oliveira R, Serpeloni Cyrino E, Altimari LR. Carbohydrate mouth rinse does not improve repeated sprint performance. Bowen L, Gross AS, Gimpel M, Li F-X. Accumulated workloads and the acute: chronic workload ratio relate to injury risk in elite youth football players. Br J Sports Med. Bradley B, Johnson D, Hill M, McGee D, Kana-Ah A, Sharpin C, Sharp P, Kelly A, Cumming SP, Malina RM. Ann Hum Biol. Braun H, von Andrian-Werburg J, Schänzer W, Thevis M. Nutrition status of young elite female German football players. Pediatr Exerc Sci. Briggs MA, Cockburn E, Rumbold PLS, Rae G, Stevenson EJ, Russell M. Assessment of energy intake and energy expenditure of male adolescent academy-level soccer players during a competitive week. Briggs MA, Rumbold PL, Cockburn E, Russell M, Stevenson EJ. Agreement between two methods of dietary data collection in male adolescent academy-level soccer players. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Briggs MA, Harper LD, McNamee G, Cockburn E, Rumbold PL, Stevenson EJ, Russell M. The effects ofan increased calorie breakfast consumed prior to simulated match-play in Academy soccer players. Eur J Sport Sci. Buono MJ, Heaney JH, Canine KM. Acclimation to humid heat lowers resting core temperature. Am J Physiol. Burke L. Practical sports nutrition. Champaign, Illinois: Human Kinetics; Caccialanza R, Cameletti B, Cavallaro G. Nutritional intake of young Italian high-level soccer players: under-reporting is the essential outcome. J Sports Sci Med. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Cauley JA, Lui L-Y, Ensrud KE, Zmuda JM, Stone KL, Hochberg MC, Cummings SR. Bone mineral density and the risk of incident nonspinal fractures in black and white women. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Cherian KS, Shahkar F, Sainoji A, Balakrishna N, Yagnambhatt VR. Resting metabolic rate of Indian Junior Soccer players: testing agreement between measured versus selected predictive equations. Am J Hum Biol. Cherian KS, Sainoji A, Nagalla B, Yagnambhatt VR. Energy balance coexists with disproportionate macronutrient consumption across pretraining, during training, and posttraining among Indian junior soccer players. Pediatric Exer Sci. Close GL, Ashton T, McArdle A, Maclaren DPM. The emerging role of free radicals in delayed onset muscle soreness and contraction-induced muscle injury. Comp Biochem Physiolo A Mol Integr Physiol. Collins J, Maughan RJ, Gleeson M, Bilsborough J, Jeukendrup A, Morton JP, Phillips SM, Armstrong L, Burke LM, Close GL. Uefa expert group statement on nutrition in elite football. Current evidence to inform practical recommendations and guide future research. Costello JT, Bieuzen F, Bleakley CM. Where are all the female participants in sports and exercise medicine research? Da Silva RP, Mündel T, Natali AJ, Bara Filho MG, Alfenas RCG, Lima JRP, Belfort FG, Lopes PRNR, Marins JCB. Pre-game hydration status, sweat loss, and fluid intake in elite Brazilian young male soccer players during competition. Deminice R, Rosa FT, Franco GS, Jordao AA, de Freitas EC. Effects of creatine supplementation on oxidative stress and inflammatory markers after repeated-sprint exercise in humans. Nutrition Burbank, Los Angeles County, Calif. Deminice R, Rosa FT, Pfrimer K, Ferrioli E, Jordao AA, Freitas E. Creatine supplementation increases total body water in soccer players: a deuterium oxide dilution study. Djordjevic B, Baralic I, Kotur-Stevuljevic J, Stefanovic A, Ivanisevic J, Radivojevic N, Andjelkovic M, Dikic N. Effect of astaxanthin supplementation on muscle damage and oxidative stress markers in elite young soccer players. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Downs SH, Black N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J Epidemiol Community Health. Duelli R, Kuschinsky W. Brain glucose transporters: relationship to local energy demand. Edwards AM, Mann ME, Marfell-Jones MJ, Rankin DM, Noakes TD, Shillington DP. Influence of moderate dehydration on soccer performance: physiological responses to 45 min of outdoor match-play and the immediate subsequent performance of sport-specific and mental concentration tests. Elferink-Gemser MT, Huijgen BCH, Coelho-E-Silva M, Lemmink KAPM, Visscher C. The changing characteristics of talented soccer players—a decade of work in Groningen. Eriksson O, Saltin B. Muscle metabolism during exercise in boys aged 11 to 16 years compared to adults. Acta Paediatr Belg. Ersoy N, Ersoy G, Kutlu M. Assessment of hydration status of elite young male soccer players with different methods and new approach method of substitute urine strip. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Falk B, Dotan R. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. Favano A, Santos-Silva PR, Nakano EY, Pedrinelli A, Hernandez AJ, Greve JMDA. Peptide glutamine supplementation for tolerance of intermittent exercise in soccer players. Clinics Sao Paulo, Brazil. Garrido G, Webster AL, Chamorro M. Nutritional adequacy of different menu settings in elite Spanish adolescent soccer players. I Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. Gibson JC, Stuart-Hill L, Martin S, Gaul C. Nutrition status of junior elite Canadian female soccer athletes. Gibson JC, Stuart-Hill LA, Pethick W, Gaul CA. Granja DS, Cotovio R, Pinto R, Borrego R, Mendes L, Carolino E, Macedo P, Ferreira D, Caetano C, Mendes B. Evaluation of young elite soccer players food intake on match day and highest training load days. J Hum Sport Exerc. Greenleaf J. Problem: thirst, drinking behavior, and involuntary dehydration. Med Sci Sports Exer. Guttierres APM, Natali AJ, Vianna JM, Reis VM, Marins JCB. Dehydration in soccer players after a match in the heat. Biol Sport. Hannon MP, Carney DJ, Floyd S, Parker LJF, McKeown J, Drust B, Unnithan VB, Close GL, Morton JP. Cross-sectional comparison of body composition and resting metabolic rate in premier league academy soccer players: implications for growth and maturation. Hannon MP, Parker LJF, Carney DJ, McKeown J, Speakman JR, Hambly C, Drust B, Unnithan VB, Close GL, Morton JP. Energy requirements of male academy soccer players from the English premier league. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Harper LD, Briggs MA, McNamee G, West DJ, Kilduff LP, Stevenson E, Russell M. Physiological and performance effects of carbohydrate gels consumed prior to the extra-time period of prolonged simulated soccer match-play. J Sci Med Sport. Hidalgo y Teran Elizondo R, Martín Bermudo FM, Peñaloza Mendez R, Berná Amorós G, Lara Padilla E, Berral de la Rosa FJ. Nutritional intake and nutritional status in elite Mexican teenagers soccer players of different ages. Nutr Hosp. PubMed Google Scholar. Holtzman B, Ackerman KE. Recommendations and nutritional considerations for female athletes: health and performance. Sports Med. Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, García A, García-Zapico P, Pérez-Landaluce J, Patterson AM, García-Rovés PM. Is there a relationship between the playing position of soccer players and their food and macronutrient intake? Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, García-Rovés PM, García A, Patterson AM. Iglesias-Gutiérrez E, García-Rovés PM, Rodríguez C, Braga S, García-Zapico P, Patterson ÁM. Food habits and nutritional status assessment of adolescent soccer players. A necessary and accurate approach. Can J Appl Physiol. Jastrzebska M, Kaczmarczyk M, Suárez AD, Sánchez GFL, Jastrzebska J, Radziminski L, Jastrzebski Z. Iron, hematological parameters and blood plasma lipid profile in vitamin D supplemented and non-supplemented young soccer players subjected to high-intensity interval training. J Nutritional Sci Vitaminol. Jastrzębska M, Kaczmarczyk M, Michalczyk M, Radzimiński Ł, Stępień P, Jastrzębska J, Wakuluk D, Suárez AD, López Sánchez GF, Cięszczyk P, Godlewski P, Król P, Jastrzębski Z. Can supplementation of vitamin d improve aerobic capacity in well trained youth soccer players? J Hum Kin. Jordan JB, Korgaokar A, Farley RS, Coons JM, Caputo JL. Caffeine supplementation and reactive agility in elite youth soccer players. Pediat Exerc Sci. Kelly AL, Williams CA, Wilson M. Developing a football-specific talent identification and development profiling concept—the locking wheel nut model. Appl Coach Res J. Kingsley MI, Wadsworth D, Kilduff LP, McEneny J, Benton D. Effects of phosphatidylserine on oxidative stress following intermittent running. Kirkendall DT, Leiper JB, Bartagi Z, Dvorak J, Zerguini Y. The influence of Ramadan on physical performance measures in young Muslim footballers. Koç MC, Saritaş N, Kirbaş Ş, Bülbül H. Examining nutritional habits of soccer players at youth development teams. Kreider RB, Kalman DS, Antonio J, Ziegenfuss TN, Wildman R, Collins R, Candow DG, Kleiner SM, Almada AL, Lopez HL. International society of sports nutrition position stand: safety and efficacy of creatine supplementation in exercise, sport, and medicine. Kreider RB, Wilborn CD, Taylor L, Campbell B, Almada AL, Collins R, Cooke M, Earnest CP, Greenwood M, Kalman DS. Lawler JM, Barnes WS, Wu G, Song W, Demaree S. Direct antioxidant properties of creatine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Leblanc JC, Le Gall F, Grandjean V, Verger P. Nutritional intake of French soccer players at the clairefontaine training center. Livingstone MB, Prentice AM, Coward WA, Strain JJ, Black AE, Davies PS, Stewart CM, McKenna PG, Whitehead RG. Validation of estimates of energy intake by weighed dietary record and diet history in children and adolescents. Am J Clin Nutr. Loucks AB. Low energy availability in the marathon and other endurance sports. Malina RM, Bouchard C, Bar-Or O. Growth, maturation, and physical activity. Human Kinetics. Maughan RJ, Leiper JB, Bartagi Z, Zrifi R, Zerguini Y, Dvorak J. Effect of Ramadan fasting on some biochemical and haematological parameters in Tunisian youth soccer players undertaking their usual training and competition schedule. McMinn D, Acharya R, Rowe DA, Gray SR, Allan JL. Int J Exerc Sci. Meckel Y, Ismaeel A, Eliakim A. The effect of the Ramadan fast on physical performance and dietary habits in adolescent soccer players. Meyer F, Bar-Or O. Fluid and electrolyte loss during exercise. Mielgo-Ayuso J, Calleja-Gonzalez J, Marqués-Jiménez D, Caballero-García A, Córdova A, Fernández-Lázaro D. Effects of creatine supplementation on athletic performance in soccer players: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar. Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the Prisma statement. PLoS med. Murphy S, Jeanes Y. Nutritional knowledge and dietary intakes of young professional football players. Nutr Food Sci. Free-sugar, total-sugar, fibre, and micronutrient intake within elite youth British soccer players: a nutritional transition from schoolboy to fulltime soccer player. Daily distribution of carbohydrate, protein and fat intake in elite youth academy soccer players over a 7-day training period. Nawrot P, Jordan S, Eastwood J, Rotstein J, Hugenholtz A, Feeley M. Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit Contam. Nobari H, Cholewa JM, Pérez-Gómez J, Castillo-Rodríguez A. Effects of weeks betaine supplementation on pro-inflammatory cytokines and hematology status in professional youth soccer players during a competition season: a double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nobari H, Kargarfard M, Minasian V, Cholewa JM, Pérez-Gómez J. The effects of week betaine supplementation on endocrine markers, body composition and anthropometrics in professional youth soccer players: a double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Noll M, de Mendonça CR, de Souza Rosa LP, Silveira EA. Determinants of eating patterns and nutrient intake among adolescent athletes: a systematic review. Nutr J. Noronha DC, Santos MIAF, Santos AA, Corrente LGA, Fernandes RKN, Barreto ACA, Santos RGJ, Santos RS, Gomes LPS, Nascimento MVS. Nutrition knowledge is correlated with a better dietary intake in adolescent soccer players: a cross-sectional study. J Nutr Metab. Oliveira CC, Ferreira D, Caetano C, Granja D, Pinto R, Mendes B, Sousa M. Nutrition and supplementation in soccer. Article PubMed Central Google Scholar. Oppliger RA, Bartok C. Hydration testing of athletes. Ostojic SM, Mazic S. Effects of a carbohydrate-electrolyte drink on specific soccer tests and performance. Owens DJ, Sharples AP, Polydorou I, Alwan N, Donovan T, Tang J, Fraser WD, Cooper RG, Morton JP, Stewart C. A systems-based investigation into vitamin d and skeletal muscle repair, regeneration, and hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. Packer L. Oxidants, antioxidant nutrients and the athlete. Phillips SM, Sykes D, Gibson N. Hydration status and fluid balance of elite European youth soccer players during consecutive training sessions. Phillips SM, Van Loon LJC. Dietary protein for athletes: from requirements to optimum adaptation. Reilly T. Motion analysis and physiological demands. Sci Soccer. Relvas H, Littlewood M, Nesti M, Gilbourne D, Richardson D. Organizational structures and working practices in elite European professional football clubs: understanding the relationship between youth and professional domains. Eur Sport Manag Q. Rodriguez-Giustiniani P, Rollo I, Witard OC, Galloway SDR. Rollo I, Cole M, Miller R, Williams C. Influence of mouth rinsing a carbohydrate solution on 1-h running performance. Ruiz F, Irazusta A, Gil S, Irazusta J, Casis L, Gil J. Nutritional intake in soccer players of different ages. Russell M, Benton D, Kingsley M. Influence of carbohydrate supplementation on skill performance during a soccer match simulation. Russell M, Pennock A. Dietary analysis of young professional soccer players for 1 week during the competitive season. J Strength Cond Res. Saltin B. Metabolic fundamentals in exercise. Med Sci Sports. Shirreffs SM, Maughan RJ. Water and salt balance in young male football players in training during the holy month of Ramadan. Silva R, Mündel T, Natali A, Bara Filho M, Lima JP, Alfenas RG, Lopes PNR, Belfort F, Marins JB. Fluid balance of elite Brazilian youth soccer players during consecutive days of training. Silva T, Di Cavalcanti Alves de Souza M, De Amorim JF, Stathis CG, Leandro CG, Lima-Silva AE. Can carbohydrate mouth rinse improve performance during exercise? A systematic review. Simpson AJ, Horne S, Sharp P, Sharps R, Kippelen P. Effect of creatine supplementation on the airways of youth elite soccer players. Skalska M, Nikolaidis PT, Knechtle B, Rosemann TJ, Radzimiński Ł, Jastrzębska J, Kaczmarczyk M, Myśliwiec A, Dragos P, López-Sánchez GF, Jastrzębski Z. Vitamin d supplementation and physical activity of young soccer players during high-intensity training. Stølen T, Chamari K, Castagna C, Wisløff U. Physiology of soccer. Sánchez-Díaz S, Yanci J, Castillo D, Scanlan AT, Raya-González J. Effects of nutrition education interventions in team sport players. Temple JL. Caffeine use in children: what we know, what we have left to learn, and why we should worry. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. Timmons BW, Bar-Or O, Riddell MC. Oxidation rate of exogenous carbohydrate during exercise is higher in boys than in men. J Appl Physiol. Trakman GL, Forsyth A, Devlin BL, Belski R. Vieira RP, Duarte ACS, Claudino RC, Perini A, Santos ABG, Moriya HT, Arantes-Costa FM, Martins MA, Carvalho CRF, Dolhnikoff M. Creatine supplementation exacerbates allergic lung inflammation and airway remodeling in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. Weishaar T, Rajan S, Keller B. J Am Board Fam Med. Yáñez-Silva A, Buzzachera CF, Piçarro IDC, Januario RSB, Ferreira LHB, McAnulty SR, Utter AC, Souza-Junior TP. Effect of low dose, short-term creatine supplementation on muscle power output in elite youth soccer players. Download references. Research Centre for Life and Sport Sciences CLaSS , Birmingham City University, Birmingham, West Midlands, UK. Matthew North, Adam L. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. MN and MC carried out the systematic review with support from AK. MN wrote the manuscript with support from MC, AK, and MR. All authors read and approved final manuscript. Correspondence to Matthew Cole. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. Reprints and permissions. North, M. et al. Nutritional Considerations in High Performance Youth Soccer: A Systematic Review. of SCI. IN SPORT AND EXERCISE 4 , — Download citation. Received : 24 August Accepted : 28 April Published : 06 July Issue Date : August Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Download PDF. Abstract Purpose As players in high performance youth soccer HYPS environments undergo large changes in growth and maturation throughout the course of their development, they require specific nutritional intakes if they are to meet these demands. Methods A systematic approach, following PRISMA guidelines, was employed to capture all articles related to nutrition within HPYS using the databases MEDLINE and SPORTDiscus. Conclusion HYPS players do not currently meet their energy requirements however the impact of growth and maturation is not fully understood. The Mental Health of Elite Athletes: A Narrative Systematic Review Article Open access 20 February No Time to Lift? Designing Time-Efficient Training Programs for Strength and Hypertrophy: A Narrative Review Article Open access 14 June Use our pre-submission checklist Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript. Introduction The future of sport is determined by the development of youth athletes with a large emphasis placed on talent pathways to release their potential [ 56 ]. Methods Protocol The study was conducted according to the PRISMA Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses [ 72 ] guidelines for the identification, screening, eligibility, and inclusion of articles. Search Strategy and Eligibility Criteria Online searches of MEDLINE and SPORTDiscus electronic databases were performed in November Data Extraction and Analysis Data extraction included study design, research aim, participant characteristics i. Quality Assessment Two authors first and last author independently assessed the methodological quality of each study using modified criteria based upon the works of Downs and Black [ 30 ]. Results Initially, studies where identified with an additional seven from reference lists see Fig. Flow chart of systematic search process. Full size image. Table 1 Observational studies quality rating Full size table. Table 2 Control trials quality rating Full size table. Discussion This review set out to systematically evaluate and synthesise the current nutritional literature within HPYS environments. Dietary Intakes and Expenditures As players undergo rapid changes in growth and maturation coupled with increasing training and match-loads, can result in extremely high energy requirements [ 46 ]. Conclusion and Future Directions This review demonstrates current HPYS players display high inter-individual variability in EE and EI across and within all chronological age groups within these environments, indicating a potential impact of growth and maturation of players. Practical Considerations The practical considerations of this review suggest that practitioners and coaches should: Implement strategies to promote more optimal dietary behaviours to help ensure that HPYS players consume sufficient energy intakes to meet their energy requirements. Availability of Data and Materials Not applicable. Code availability Not applicable. References Areta JL, Burke LM, Ross ML, Camera DM, West DWD, Broad EM, Jeacocke NA, Moore DR, Stellingwerff T, Phillips SM. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Ataley-Guzel N, Erikoglu Orer G, Sezen Bircan F, Coskun Cevher S. Google Scholar Aubut J-AL, Marshall S, Bayley M, Teasell RW. Article PubMed Google Scholar Bar-Or O. Article Google Scholar Bassit RA, Curi R, Rosa LC. Article CAS Google Scholar Bentley MRN, Patterson LB, Mitchell N, Backhouse SH. Article Google Scholar Bettonviel AEO, Brinkmans NYJ, Russcher K, Wardenaar FC, Witard OC. Article CAS Google Scholar Bezuglov E, Tikhonova A, Zueva A, Khaitin V, Waśkiewicz Z, Gerasimuk D, Żebrowska A, Rosemann T, Nikolaidis P, Knechtle B. Article CAS Google Scholar Boisseau N, Le Creff C, Loyens M, Poortmans JR. Article CAS Google Scholar Bortolotti H, Pereira LA, Santos Oliveira R, Serpeloni Cyrino E, Altimari LR. Google Scholar Bowen L, Gross AS, Gimpel M, Li F-X. Article Google Scholar Bradley B, Johnson D, Hill M, McGee D, Kana-Ah A, Sharpin C, Sharp P, Kelly A, Cumming SP, Malina RM. Article PubMed Google Scholar Braun H, von Andrian-Werburg J, Schänzer W, Thevis M. Article PubMed Google Scholar Briggs MA, Cockburn E, Rumbold PLS, Rae G, Stevenson EJ, Russell M. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Briggs MA, Rumbold PL, Cockburn E, Russell M, Stevenson EJ. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Briggs MA, Harper LD, McNamee G, Cockburn E, Rumbold PL, Stevenson EJ, Russell M. Article PubMed Google Scholar Buono MJ, Heaney JH, Canine KM. Article Google Scholar Burke L. Google Scholar Caccialanza R, Cameletti B, Cavallaro G. PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Cauley JA, Lui L-Y, Ensrud KE, Zmuda JM, Stone KL, Hochberg MC, Cummings SR. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Cherian KS, Shahkar F, Sainoji A, Balakrishna N, Yagnambhatt VR. Article Google Scholar Cherian KS, Sainoji A, Nagalla B, Yagnambhatt VR. Article Google Scholar Close GL, Ashton T, McArdle A, Maclaren DPM. Article CAS Google Scholar Collins J, Maughan RJ, Gleeson M, Bilsborough J, Jeukendrup A, Morton JP, Phillips SM, Armstrong L, Burke LM, Close GL. Article Google Scholar Costello JT, Bieuzen F, Bleakley CM. Article PubMed Google Scholar Da Silva RP, Mündel T, Natali AJ, Bara Filho MG, Alfenas RCG, Lima JRP, Belfort FG, Lopes PRNR, Marins JCB. Article PubMed Google Scholar Deminice R, Rosa FT, Franco GS, Jordao AA, de Freitas EC. Article CAS Google Scholar Deminice R, Rosa FT, Pfrimer K, Ferrioli E, Jordao AA, Freitas E. Learn about the technology that revolutionized elite football, highlighting the use of GPS, LPS, physical assessment, and sleep management. FREE Guide: Youth Soccer Athletic Development. Download your FREE Guidebook and discover the techniques and strategies that elite coaches use to help young players achieve their full potential. Enter your best email to download it:. By signing up you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. Enter your best email address below:. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo. COURSES ARTICLES FACULTY NEWS LOGIN Menu. ISSPF March 4, Nutrition 25 mins. Nutrition plays a key role in supporting the performance of the football athlete. The latter finding may be explained by low glycogen levels in individual muscle fibres 1. Figure 1: Decrease in muscle glycogen stores during a match Duplicated from: Krustrup et al. From Refuel to Repair. To expand on this, we will focus on the timing and types of CHO that should be consumed. This alone becomes incredibly significant when the team must play 2 games over a 3-day period. To off-set this, it is important to supply players with a pre-bed snack of minimum 25g protein. To conclude, I will outline the practical applications of the scientific knowledge compiled: The first minutes post-match are incredibly important, and teams should look to refuel, repair, and rehydrate to increase muscle glycogen resynthesis, mitigate muscle function decrements and muscle soreness, and replenish lost electrolytes. Join Our Soccer Nutrition Course. How do I get a job in football? Which area of sport or football science do I want to specialise in? Soccer Nutrition Online Sport Science Course. How This Course Will Improve You. All practitioners and coaches can only benefit themselves and their players even further by having a more in-depth knowledge of sports nutrition. It may help us to reduce the risk for non-contact muscle injuries, through a better understanding of key timing of nutrients. What Does This Course Cover? Article References. Reference List: Krustrup P, Mohr M, Steensberg A, Bencke J, Kjaer M, Bangsbo J. Muscle and blood metabolites during a soccer game: implications for sprint performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc. doi: PMID: Krustrup P, Ortenblad N, Nielsen J, Nybo L, Gunnarsson TP, Iaia FM, Madsen K, Stephens F, Greenhaff P, Bangsbo J. Maximal voluntary contraction force, SR function and glycogen resynthesis during the first 72 h after a high-level competitive soccer game. Eur J Appl Physiol. Epub Mar Ivy JL, Katz AL, Cutler CL, Sherman WM, Coyle EF. Muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise: effect of time of carbohydrate ingestion. J Appl Physiol Harper DJ, Kiely J. Damaging nature of decelerations: Do we adequately prepare players? The influence of soccer playing actions on the recovery kinetics after a soccer match. J Strength Cond Res. Moore DR, Camera DM, Areta JL, Hawley JA. Beyond muscle hypertrophy: why dietary protein is important for endurance athletes. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. Epub Feb 7. Snijders T, Res PT, Smeets JS, van Vliet S, van Kranenburg J, Maase K, Kies AK, Verdijk LB, van Loon LJ. Protein Ingestion before Sleep Increases Muscle Mass and Strength Gains during Prolonged Resistance-Type Exercise Training in Healthy Young Men. J Nutr. Epub Apr Abbott W, Brett A, Cockburn E, Clifford T. Presleep Casein Protein Ingestion: Acceleration of Functional Recovery in Professional Soccer Players. Int J Sports Physiol Perform. Epub Feb Berrazaga I, Micard V, Gueugneau M, Walrand S. The Role of the Anabolic Properties of Plant- versus Animal-Based Protein Sources in Supporting Muscle Mass Maintenance: A Critical Review. Published Aug 7. Fluid Replacement and Heat Stress. Washington DC : National Academies Press US ; Influence of moderate dehydration on soccer performance: physiological responses to 45 min of outdoor match-play and the immediate subsequent performance of sport-specific and mental concentration tests. Br J Sports Med. |
| NUTRITION FOR SOCCER PLAYERS: WHAT TO EAT WHEN | Epub Feb 7. Soccwr H, Sscience H, Van Kranenburg G, Sooccer P. Glycemic index—a new tool in sport Cellulite reduction techniques PubMed Google Scholar Brinkmans NYJ, Iedema N, Plasqui G, Wouters L, Saris WHM, van Loon LJC, et al. Carbohydrates First and foremost, active bodies need carbohydrates to provide glucose, the brain's and muscles' favorite fuel. |
| Nutritional Considerations in High Performance Youth Soccer: A Systematic Review | CAS PubMed Google Scholar Jenkins DJ, Wolever TM, Taylor RH, Barker H, Fielden H, Baldwin JM, et al. Accepted : 25 April It is required to manufacture enzymes and hormones such as insulin and adrenaline. Mastering the Nutritional Playbook. Sport exercise capacity of soccer players at different levels of performance. Our emphasis is on providing contextually relevant recommendations for facilitation of post-exercise recovery when multiple matches are played within a short period of time. |
| NUTRITION FOR SOCCER PLAYERS: WHAT TO EAT WHEN • SoccerToday | CAS PubMed Google Scholar Shifflett B, Timm C, Kahanov L. NUTRITION NEWS. Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Prisma G. To conclude around this unique coaching area, and delving into the vast realm of nutrition, this brief overview merely grazes the surface, yet we trust it has prompted contemplation about the dietary habits of your soccer players or football team. Nutrient intake and food habits of soccer players: analysing the correlates of eating practice. This amount can be obtained through dietary sources such as g of chicken, g of fish or 20—25 g of whey protein, but it can also be ingested as an isolated supplement. |
Ich entschuldige mich, aber diese Variante kommt mir nicht heran.