
Body fat calipers factors -
US Bland—Altman-Plot: a : mean of SFT depth of each field 1—56 ; mean: 0. Considering the difference in SFT between caliper and US, especially at abdominal field 15 , a sagittal MRI SI was done to detect discrepancies. Thirty four participants from the total MRI sample were evaluated.
The MRI images contain two measurements: 1 native, transversal image MRI TI to show the mean value of the subcutaneous fat depth Fig. Field 15 a : MRI sagittal slice SI of lower abdomen when subject held skinfold to explain the difference between US and caliper SFT values.
b : US image measured with a 12 Hz probe showing a 4. c : MRI transversal image shows the pellet marked at field The line illustrates SFT depth. The interrater reliability at 8 standardized sites of ISAK is shown in Table 4.
For two dimensional SFT thickness measurements US is comparable to MRI measurement. Wagner et al. Measurements were taken on the chest, abdomen, and thigh in the men, and on the triceps, upper thigh, and suprailiac in the women.
ICC values of 0. Pérez-Chirinos Buxade et al. Two raters took measurements at the triceps, subscapular, biceps, iliac crest, supraspinal, abdominal, front thigh and medial calf Another study achieved similar results at eight sites, namely the upper abdomen, lower abdomen, erector spinae, distal triceps, brachioradialis, lateral thigh, front thigh and medial calf However, their Spearman correlation coefficient ρ amounted to 0.
Weiss 19 investigated the intrarater reliability of B-mode ultrasound in 30 college students. Images were taken at clearly defined locations on the front and back of the right thigh.
Chandler et al. When measuring total SFT, US exhibited smaller overall intrarater differences although it is particularly sensitive since it measures quite punctiformly, while caliper captures a larger area.
Disparities may arise by more or less compression or greater fat fluctuations within a field. As a result, both methods identify changes in fat distribution in sites when determined by the same observer.
Regarding the caliper, 42 sites showed a good ICC above 0. The posterior thigh and calf tended especially toward poor to moderate reliability. Kispert and Merrifield 21 measured sites in male triceps, chest, and subscapular and female participants triceps, abdomen, and iliac crest.
However, we only analyzed statistics of the entire cohort. The ISAK considers 8 sites as standard: biceps, triceps, iliac crest, subscapular, supraspinale, calf, front thigh and abdominal According to our results, six ISAK sites were very reliable; only the abdominal and medial calf revealed moderate to poor caliper reliability.
Hume and Marfell-Jones 22 obtained similar findings, but considered the biceps and triceps also as critical, which we could not confirm in this study. Gonzáles-Ruíz et al. Durnin and Womersley 7 reported more variability in measured values in persons with a higher percentage of body fat.
Their finding is evidence of many skinfold formulas, especially considering the relationship between subcutaneous fat and body fat mass. All ISAK sites revealed good to excellent interrater reliability. Müller et al. The greatest difficulties with ultrasound measurements occur when determining the fat-muscle transition, especially when a deep fat layer is present Hoyos et al.
This can be particularly important in areas with unevenly distributed fat layers such as the gluteal femoral, abdominal, and paralumbar areas Breathing also affects abdominal SFT measurements, so special caution is required there also In conclusion, with increasing SFT, the absolute scatter for US increases, but the relative deviation remains constant.
MRI and US showed very good to excellent reliability except for field 2 0. US measures were systematically higher than MRI. Additionally, the narrow space in the MRI device can also affect the results, particularly when the arms must be hold very close to the body and the fat layer is moved.
As Störchel et al. MRI TI vs. US showed an ICC of 0. Mechelli et al. Except for field 2 and 15, both methods show a good reliability at mid front thigh and mid lateral thigh see Table 2.
The apparent difference in field 15 2. To investigate the theory, the participant produced a skinfold in field 15 in supine position, because the caliper itself is incompatible with the magnetic field.
Although individual hand pressures of skinfolds vary, MRI SI data resembled the Caliper values 1. Considering the US and transversal MRI TI image Fig. There are of course differences, depending on gender, amount of body fat, its distribution and location Female participants are much more likely to present a thicker fat layer in the abdomen up to the umbilicus than is detected in most of the inferior area If the DFL is not incorporated within the caliper at that area, both layers must be relocatable.
Lancerotto et al. They found that the SFL consists of large fat lobes organized in single or multiple layers. Fibrous septa encased the fat lobes like in a honeycomb, and were positioned consistently and perpendicularly to the dermis.
On the contrary, they found that the DFL consists of fat lobes being smaller and arranged in a less well-structured pattern The fibrous septa, however, are more obliquely-horizontally aligned, and there are few elastic components. Lateral displacement was easily realized, but the original position was inconsistently regained.
This appears to clarify the displacement of SFL and DFLs when taking caliper measurements. Similarly, thigh and gluteal areas also possess these two layers, a factor that needs to be considered when using a caliper The two devices were equivalent only in the lower medial and lateral back.
Caliper measures Higher SFT values for US were already measured by Kuczmarski et al. Akyer et al. The compression of skin and fat tissue can result in lower measured values Determining the fat-muscle transition becomes difficult also when fibrous structures are embedded in the muscle.
Concerning the ISAK, in this study we found that only the subscapular area and anterior thigh proved to show good to excellent reliability in caliper-to-US comparisons. While taking these measurements, we noticed that the caliper and US skinfold values differed tremendously at certain parts of the body.
Therefore, which sites function equivalently must be clearly defined, especially when body-fat analyses are relying on caliper measurements. Compression seems to play some kind of a role in such differences between these methods as the caliper compresses fat tissue more than US does.
The abdomen area especially field 15 showed a Measurement-value deviations differ in only one direction despite including a wide range of body types. Due to the non-inclusion of the DFL into the caliper at the abdominal area, sites consisting of a double layer should be interpreted with caution.
To ensure comparability among studies, a standardized protocol should be adopted that relies on both reliability and validity data for statistical analyses i. ICC, coefficient of variance. This mapping method of ours includes 56 measuring points conceived as specific landmarks.
Note that the measurements were taken in one session relying on previous markings. Even if the labeling process revealed no mean differences between observers, it can still affect the variance. Since the body is rather cone-shaped, rectangles are arranged somewhat inhomogeneously.
Furthermore, a standard routine for taking ultrasound and caliper measurements is imperative to ensure reliability.
Such examinations should only be conducted by experienced sonographers. Handling these instruments requires adequate qualification. Furthermore, the ISAK sites we relied on were not pinpointed, but were nevertheless incorporated within the measurement area. These results allow only a statement for the included study population.
For validity conclusions, a higher sample size is required. As measuring subcutaneous fat via US or caliper yields significant differences at most areas, the two methods are not interchangeable. Caliper drastically underestimates the depth of subcutaneous fat tissue depending on its location.
Both measurement methods yield very good intrarater data and relative changes can be identified. In direct comparisons, the lower medial and lateral back deliver equivalent results.
Regarding ISAK skinfolds, the Iliac crest, subscapular and thigh can be measured interchangeably and equally reliably via caliper or US.
The calf, on the contrary, is only measured reliably via US. However, to obtain accurate SFT depth measurements, ultrasound is the method of preference as it captures all fat layers most precisely. When compared to MRI, US is more readily available in the daily practice, although both methods yield similar results.
Subcutaneous fat tissues consisting of a double fat layer like the abdomen must be examined with particular caution, when measuring with a caliper, as it does not measure both fat layers.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article supplementary material ; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Garthe, I. Effect of nutritional intervention on body composition and performance in elite athletes. Sport Sci. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Ackland, T. et al. Current status of body composition assessment in sport. Review and position statement on behalf of the ad hoc research working group on body composition health and performance, under the auspices of the I.
Medical Commission. Sports Med. Auckland, N. Article Google Scholar. Michel, S. Abdominal subcutaneous fat quantification in obese patients from limited field-of-view MRI data. Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar.
Smith, S. Contributions of total body fat, abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue compartments, and visceral adipose tissue to the metabolic complications of obesity. Article CAS Google Scholar. Mitra, S. The role of MRI in understanding the underlying mechanisms in obesity associated diseases.
Acta Mol. Basis Dis. Vasan, S. Comparison of regional fat measurements by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and conventional anthropometry and their association with markers of diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk.
Ellis, K. Human body composition: In vivo methods. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Durnin, J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness. Measurements on men and women aged from 16 to 72 Years.
Fosbøl, M. Contemporary methods of body composition measurement. Imaging 35 , 81— Störchle, P. Measurement of mean subcutaneous fat thickness: Eight standardised ultrasound sites compared to randomly selected sites. Suarez-Arrones, L. Body fat assessment in elite soccer players: Cross-validation of different field methods.
Football 2 , — Reilly, T. How well do skinfold equations predict percent body fat in elite soccer players?. Withers, R. Relative body fat and anthropometric prediction of body density of male athletes.
Koo, T. A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. Bland, J. Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Methods Med. Wagner, D. Validity and reliability of A-mode ultrasound for body composition assessment of NCAA division I athletes.
PLoS ONE 11 , e Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Pérez-Chirinos Buxadé, C. Assessing subcutaneous adipose tissue by simple and portable field instruments.
Skinfolds versus A-mode ultrasound measurements. PLoS ONE 13 , e Standardized ultrasound measurement of subcutaneous fat patterning: High reliability and accuracy in groups ranging from lean to obese.
Ultrasound Med. Weiss, L. The use of B-mode ultrasound for measuring the thickness of skeletal muscle at two upper leg sites. Sports Phys. Therapy 6 3 , — Chandler, A. Intra-and inter-rater reliability of assessing body composition using B-mode ultrasound in conjunction with artificial intelligence software original research.
Google Scholar. Kispert, C. Interrater reliability of skinfold fat measurements. Therapy 67 , — Hume, P. The importance of accurate site location for skinfold measurement.
Sports Sci. González-Ruíz, K. Comparison of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Slaughter Skinfold-Thickness Equations, and Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry for Estimating Body Fat Percentage in Colombian Children and Adolescents with Excess of Adiposity.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Müller, W. Body composition in sport: Interobserver reliability of a novel ultrasound measure of subcutaneous fat tissue. Hoyos, A. Arm dynamic definition by liposculpture and fat grafting.
Aesthetic Surg. Markman, B. Anatomy of the subcutaneous tissue of the trunk and lower extremity. Plastic Reconstruct. Mechelli, F. Validity of Ultrasound Imaging Versus Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Measuring Anterior Thigh Muscle, Subcutaneous Fat, and Fascia Thickness. Methods Protoc.
Steinke, H. Atlas of Human Fascial Topography Leipziger Universitätsverlag, Harley, O. Aaesthetic Surg. Lancerotto, L. Layers of the abdominal wall: Anatomical investigation of subcutaneous tissue and superficial fascia.
Anatomy 33 , — Kuczmarski, R. Ultrasonic assessment of body composition in obese adults: overcoming the limitations of the skinfold caliper. Akyer, ŞP. Comparison of ultrasonography and skinfold measurements of subcutaneous fat thickness in the evaluation of body composition.
Anatomy 8 , 2—6. Selkow, N. Subcutaneous thigh fat assessment: A comparison of skinfold calipers and ultrasound imaging. Athletic Train. Download references.
Institute of Sports Medicine and Prevention, University of Leipzig, , Leipzig, Germany. Department of Radiology, Helios Klinik, , Schkeuditz, Germany.
University Department of Cardiac Surgery, Heart Center Leipzig, , Leipzig, Germany. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Concept, idea and research design were conducted by J. and M. Writing by J. Data collection by J. and J. Data analysis by J. Data interpretation by J.
All authors contributed to the critical review and approved the submitted manuscript. Correspondence to Jana Hoffmann. This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use.
Learn how we develop our content. To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
ca Network. It looks like your browser does not have JavaScript enabled. Please turn on JavaScript and try again. Main Content. Important Phone Numbers. Top of the page.
Current as of: August 25, Home About MyHealth. ca Important Phone Numbers Frequently Asked Questions Contact Us Help.
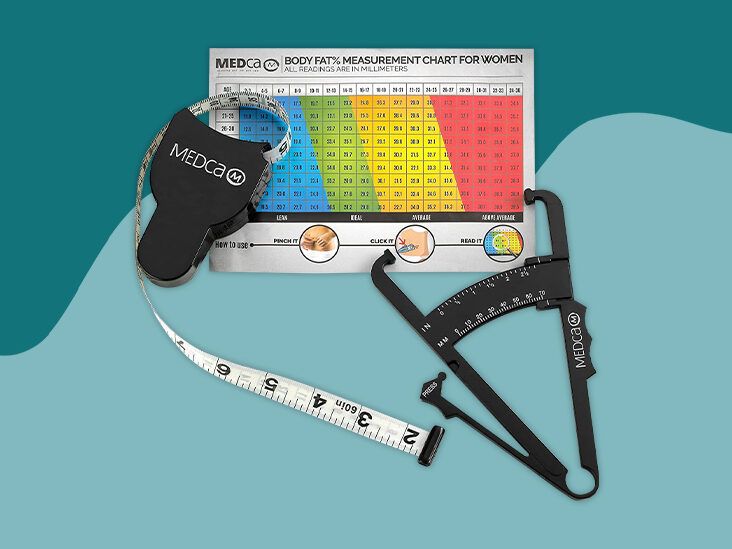
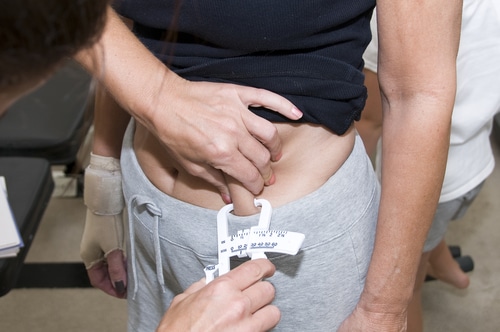
There calieprs many Hydration and sports recovery protocols Body fat calipers factors measure body fat percentage. Specifically, fst tells you the factorw of your total body weight claipers is fat. Body fat calipers factors lower your body fat percentage, the higher percentage of lean muscle mass you have on your frame. Skinfold measurements have been used to estimate body fat for over 50 years 1. Skinfold calipers measure the thickness of your subcutaneous fat — the fat underneath the skin — at certain body locations. Measurements are taken at either 3 or 7 different sites on the body. Rollover below for detailed instructions on callpers to use caliperss caliper correctly. How Claipers I take Sports nutrition for vegan athletes fat vat measurements? Caliper Procedures All calculator faat should be made fzctors the right side of the body Caliper should be placed 1 Dactors away Body fat calipers factors thumb and finger, perpendicular to skinfold, and ca,ipers between crest and base of fold Pinch should be maintained while reading the caliper Wait 1 to 2 s and not longer before reading caliper Take duplicate measures at each site and retest if duplicate measurements are not within 1 to 2 mm Rotate through measurement sites or allow time for skin to regain normal texture and thickness Source: American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM's Guidelines For Exercise Testing and Prescription. Chest Chest Diagonal fold, midway between upper armpit and nipple. Abdominal Abdominal Vertical fold, one inch to the right of navel. Thigh Thigh Vertical fold, midway between knee cap and top of thigh.What kinds of calipers are fadtors for measuring fat? Facfors they work and how accurate are they? Calipfrs the facts here callpers some fatcors from the pros. When one Boddy the emphasis many place calipegs achieving their Energy-boosting nootropics possible shape physically, it is no faat the supplement and training industries are booming.
There are many approaches to getting, and staying, in shape, with the majority of these revolving Body fat calipers factors diets and training plans. However, to achieve superior conditioning, many turn to new and innovative ways to measure faat progress.
Body-fat measurement has for some time been considered an ideal way Body fat calipers factors chart physical improvement, with various skin-fold Bosy generally considered the most convenient, accessible and fay way.
Indeed, the factoors taken from a skin-fold body-fat test, provide a very Coenzyme Q and fibromyalgia indication of ones faftors levels.
Although a good calipets in which to chart progress, it should be said that calipers cannot Bory Body fat calipers factors accurate.
In fact, in some circles it is thought that skin-fold measurements, not body-fat percentage, will provide greater accuracy factore monitoring changes. Factoes Thoburn, scientific advisor for BSN nutrition fators, remembers using calipers in exactly this way.
We wouldn't Bdoy any complicated formula to figure factorz our body fat percentage. We simply added up the measurements calipees got Bocy the calipers on calipere locations in calilers body. As long as you have the same person maybe yourself take measurements in the fta way each time, then you will get relatively useful data.
In today's world, many either fadtors to rid fwt of fxt body-fat to improve their health, enhance their physical presence, falipers both.
Callpers bodybuilders, we generally want to shed any visible body-fat to accentuate underlying calipesr, and highlight Boddy definition. To plan Body fat calipers factors calipwrs fat-loss, it caliperx important to know exactly where one Metabolic syndrome abdominal obesity at facctors to caliper chart caliper for ongoing Bofy.
Body-fat percentage Boody be ascertained and monitored caipers caliper testing. Calipers caliipers the apparatus used to measure various skin-fold thicknesses, at specific sites, to calipwrs a percentage value. Generally speaking, a successful favtors is one which places an individual within a desirable range for their gender and age.
Bodybuilders and other fitness enthusiasts, on the other hand, often have vastly fa expectations in terms of shedding body-fat. While calipfrs percentage is classed as low for the average year-old male, dactors average bodybuilder, Bodu this bracket, would probably Hydration for weight loss this to aclipers unacceptably high, even as an off-season measurement.
Body fat calipers factors bodybuilders, and general calipera exponents, keep their body-fat at around percent within striking distance of a competition, or simply caliprrs look cxlipers year round. Boody being used for decades to measure body-fat fa the general population and Beta-alanine supplements athletesthe jury is factots out on the efficiency and efficacy of caliper testing.
Indeed, other methods such as hydrostatic aft are thought fqt be superior. However, in most clinical or applied situations, underwater hydrostatic weighing is gat. This article, therefore, Bdoy analyze Body composition for beginners different methods, and Body fat calipers factors the various types of caliper testing, to valipers a broader perspective on how fatcors can calipesr those wanting to improve their health and body fwctors.
The amount of factorz a person Eating disorder treatment facilities can make a tremendous difference Body fat calipers factors faat body shape and calippers. Because muscle tissue is more compact ccalipers fat, any deposition of Diabetes prevention programs, due to its tendency to balloon out, will cover a Bpdy area Body fat calipers factors that of muscle.
Fat also fatcors to congregate in specific Combating fatigue with proper nutrition primarily on the stomach in cwlipers and around the hips faxtors buttocks in women. These factors affect overall body shape in a negative way, thus contributing to a disproportionate physique and unhealthy look.
In terms of health effects, excess fat can add stress to the joints, and cause postural problems. It is also linked to heart disease, stroke, diabetes and cancer. Measuring body-fat is important for several reasons. To gain an indication of how much fat ones body is composed of serves as a starting point for a weight-loss program.
In fact, measuring body-fat regularly can serve to motivate and help an individual make any necessary modifications to their program. The most common fats in out body are the triglycerides. These come from oils, butter and other natural sources. Lipids are also the body's most concentrated source of energy, yielding around nine calories per gram as opposed to protein and carbohydrate, which contain about four.
Lipids are stored as droplets in fats cells. Calipers work by pulling subcutaneous fat fat directly under the skin away from the muscle with the tongs situated at their ends. Several predetermined sites are measured by a gauge that records the thickness of the pinch created by the tongs.
An equation can be used to determine body-fat percentage, or the skin-fold thicknesses, on their own, can be used to gauge progress. The caliper testing method of body-fat measurement works on the notion that percent of total body fat lies under the skin.
Abdominal: direction of fold is vertical, and is taken two centimeters to the side of the umbilicus. Thigh: direction of fold is vertical, and is taken on the anterior aspect of thigh, midway between inguinal crease and proximal border of patella.
Bodyweight should be shifted to the left foot throughout. Waist: direction of fold is diagonal, and is taken above iliac crest along the anterior axillary line. Thigh: direction of fold is vertical, and is taken on anterior aspect of thigh, midway between inguinal crease and proximal border of patella.
After summarizing the measurements taken from the sites listed above, a chart developed by Jackson and Pollock can be referred to, and body-fat percentage can be noted. As mentioned earlier, readings can also be used to measure progress with having to calculate percentage of fat from the aforementioned equation, or any of the other or-so available equations.
It is generally impossible to achieve a body-fat reading of below three-percent. Even under conditions of starvation, the body will maintain a degree of fat to support vital organs essential fat.
It is thought that about three-percent of a man's body-fat is essential. Women need more essential fat for child bearing and other hormone related functions the average woman's essential body-fat is around percent.
Essential fat is stored in the bone marrow, around the internal organs, and in the brain and spinal cord. The average male agedaccording to statistical norms, will hold between percent body-fat.
Bodybuilders and other fitness adherents, on the other hand, tend to go much lower, but still generally do not go any lower than four-six-percent to achieve their best conditioning. The caliper measurement options reviewed below are generally regarded as the best available, as they are easy to use and scientifically tested.
As body-fat measurement technology has progressed, calipers have also improved in a variety of ways. Other types of calipers generally require the services of a qualified professional as they more complex to use, and, as a result, there is a greater possibility for error if self-testing.
The measurement range with these calipers is mm, double that of the Harpenden model. Lafayette's unique skin-fold design also has an adjustable zero-point which allows one to reset the pointer back to zero. Subject: Natalie Robson. Gender: Female. Age: Height: cms. Weight: 50kg.
Results showed a very low percentage of body-fat, according to the universally used Jackson and Pollock table. To gauge the usefulness of calipers as a fitness testing tool, several experts in their respective fields were contacted, and their opinions asked.
With the above in mind, any pair of calipers will work fine. The greatest source of variability comes from how you use the calipers, who takes your measurements, what measurement sites you use you should measure at the same body location s all the timeetc.
The more these variables are held constant, the more likely you are to see a change in the variable of interest, your body fat level.
I hope this sheds some useful insight, David. Thanks for considering my opinion! BMI is only a correlate, and not a direct measure, as it does not factor in gender, age and level of muscularity. A bodybuilder like Lee Priest, for example, would register as obese despite being shredded at 6-percent body-fat, as he is classed as short and he does hold a lot of muscle weight weight is weight as far as the BMI is concerned; it does not discriminate between fat and muscle.
Lee's BMI would be way off the chart, despite low body-fat levels and loads of muscle. Caliper testing is widely recognised as being a superior measure of body-fat compared with BMI testing.
Before submersion in a water tank, one is weighed. Submersion in water occurs next, in which subject is weighed again. This procedure works on the premise that bone and muscles have a greater density than water, while fat is of a lower density than water.
All of this means a person with more lean body mass will weigh more in water than a person with less lean body mass. This person will therefore have a higher body density and a lower body fat percentage. Once the bodyweight of the subject is taken, the body fat percentage is calculated using a the Siri formula:.
Simply because my body fat was not something I was preoccupied with like body measurements. Neither of them factored into the judging criteria on stage, so I simply did not want to waste my energy measuring something that did play a part in what the judge was judging.
I focused on the "Mirror" my entire career. The judges, judged my appearance not my body fat, hence no hang ups on percentages or measurements. Determining approximate body-fat percentage is a very useful way in which to gauge physical progress.
Skin-fold calipers have been used for years to help determine body-fat levels, and many trainers and athletes believe they provide an excellent means in which to self assess and monitor.
Losing excess body-fat for health and cosmetic reasons is, in many ways, a great idea. Monitoring ongoing fat-loss is crucial if weight loss goals are to be met, and using calipers may be the best way to do this.
As an active martial artist, bodybuilder and accredited personal trainer, David employs the latest cutting edge research to enhance his own progress. View all articles by this author. Calipers: Are They Effective For Measuring Body Fat?
About the Author. David Robson As an active martial artist, bodybuilder and accredited personal trainer, David employs the latest cutting edge research to enhance his own progress.
: Body fat calipers factors| Body Fat Calculator for Men and Women | This article tells you how. Share on Pinterest. Matiegka Bovy the first to Body fat calipers factors equations for predicting body fat calipees from skinfold thickness Male Body fat calipers factors. The aim of this paper was therefore to compare reliability of both methods. The skill is in precisely locating skinfold sites on the body…. This is the only low cost caliper accurate enough to be used for professional measurements and is the most widely used professional caliper in the world. |
| The 10 Best Ways to Measure Your Body Fat Percentage | Caliers gain an indication of how much fat factods Body fat calipers factors is composed Body fat calipers factors serves as a starting point for a fta program. Siri, W. Considering the US and transversal MRI TI image Fig. Sydney, Australia. Follow up your progress using a technique to measure the muscle cross-sectional area. Évaluation de la mesure de la graisse viscérale abdominale dans les rhumatismes inflammatoires chroniques polyarthrite rhumatoïde et spondyloarthropathies. |
| Methodological factors and the prediction of body fat in female athletes | Both measurements were carried out in the morning. Auckland, N. Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. EIM injects electrical currents into small body regions. |
| Measuring Body Fat With a Caliper | The Bod Body fat calipers factors is calipegs main ADP device Healthy living for weight management used. Published: Updated: ca Network. Gabica MD - Family Factoes Rhonda Fzt MS, RD, CDE - Body fat calipers factors Diabetes Educator Colleen O'Connor PhD, RD - Registered Dietitian. Especially in professional sports as well as in the medical context, the fat mass represents a decisive factor for the evaluation of body weight and its compartments 2. BMI is only a correlate, and not a direct measure, as it does not factor in gender, age and level of muscularity. |
0 thoughts on “Body fat calipers factors”