Inflammation and weight management -
Here's a brief look at how inflammation and weight are connected. Weight gain is associated with increased inflammation in the body.
A study published by Elsevier found that levels of a key inflammatory marker in the blood known as C-reactive protein CRP increased as weight increased. This inflammation appears to be triggered by hormonal and metabolic changes and remains until excess weight is lost.
Inflammation in the body can lead to insulin resistance. This is due to inflammatory compounds that impair the way insulin works. This leads to higher glucose levels, as well as fat accumulation in the liver which further contributes to insulin resistance.
They can then start to fuel one another, causing a vicious cycle: weight gain causes more insulin resistance , and insulin resistance leads to more weight gain. Leptin is a key hormone that tells the brain when to eat, when to stop eating and when to speed up or slow down metabolism.
However, research published by the International Journal of Molecular Sciences in suggests that leptin functioning is altered with weight gain and inflammation. The effect is that the brain doesn't get proper feedback, so leptin levels remain low which triggers the appetite to increase and metabolism to slow as if the body were starving , making weight loss pursuits even harder.
The inflammatory combination of weight gain, insulin resistance and leptin resistance build on each other, but may also be exacerbated by things like stress, lack of sleep, eating processed foods and a sedentary lifestyle.
When looking at these inflammatory effects associated with weight gain, it's easy to see why simply monitoring calories-in versus calories-out doesn't always work.
Pictured Recipe: Cobb Salad with Herb-Rubbed Chicken. If you have excess weight, you're likely experiencing some level of inflammation, which makes the body irritated and stressed. In a situation like this, the body's primary focus is survival and healing, not weight loss.
So, to lose weight, it's key to reduce inflammation and other potential irritants to help the body get back to more healthy operating conditions. So, how do you reduce inflammation to lose weight?
Here are five things to do. Chemicals, additives, coloring, added sugars and other compounds in processed foods are all potential sources of irritation.
Avoiding these ingredients by choosing more whole foods and minimally processed products is key to reducing inflammation and losing weight. When purchasing a packaged product, take a look at the ingredients list.
Does it mirror what you might use if you were making the food from scratch, without a ton of additives? If the answer is yes, it's likely a minimally processed product. If not, try to opt for something else. While getting rid of irritants, it's also important to refuel with foods containing anti-inflammatory compounds like antioxidants, phytochemicals and omega-3 fatty acids.
Good sources of these are vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, fish and healthy fats, such as plant-based oils, nuts and avocados. So load up on leafy greens and cruciferous veggies like cauliflower and broccoli, snack on berries and nuts, incorporate fatty fish like salmon into your menu two times per week and use moderate amounts of healthy oils like extra-virgin olive oil.
Did you know that many health professionals now consider sleep just as important to weight loss as diet and activity? Adult bodies need approximately 7 to 8 hours of continuous sleep most nights to rest, repair and recharge for the next day.
Sure, caffeine may help energy levels temporarily, but the effects of inadequate sleep go a lot further.
Routinely not getting enough sleep 6 hours or less leaves the body without the resources it needs to function properly, creating new inflammation and aggravating existing inflammation. Strengthening the gut's microbe barrier is essential to reducing inflammation because it can prevent future irritants from slipping through the intestinal wall and into the bloodstream.
To do this, try to incorporate foods every day that are fermented or contain active live bacteria cultures such as yogurt, sauerkraut, kombucha, miso or kimchi. As much as we want to focus strictly on food and exercise for weight loss, mental and psychological health is just as important because low-grade inflammation won't go away if stress levels run continuously high.
Finding a way to escape that stress —such as doing yoga, meditating or walking for 10 minutes a day—provides quick relief psychologically and anti-inflammatory effects physiologically. If stress is too much of a daily problem, learning how to manage and cope when it does occur is key for not triggering new inflammation or aggravating existing inflammation.
Inflammation increases with weight gain, which leads to insulin resistance and leptin resistance. So, if you're looking to lose weight, reducing inflammation is key. You can do this by avoiding processed foods and added sugars, eating more anti-inflammatory foods, getting enough sleep and decreasing stress levels.
Reducing the amount of inflammation in your body will also lower your risk for diseases like cancer, heart disease and diabetes. The immune system determines levels of inflammation in the gut that are constantly shaping the way we digest food—how many calories get absorbed, and how many nutrients simply pass through.
The relationship between microbes and weight gain has long been overlooked in humans, but people have known about similar effects in animals for decades.
After World War II, antibiotics became affordable and abundant for the first time. This led to a flood of patent applications for antibiotic-laden foods for all sorts of livestock. Read: Are antibiotics making people larger?
Researchers have only recently shown that these antibiotics kill off some of the microbes that occur normally in the gut and help livestock, and people, digest food. By breaking down nutrients and helping them pass through the walls of the bowel, these microbes serve as a sort of gatekeeper between what is eaten and what actually makes it into the body.
Killing them is not without consequences. Just as antibiotics are associated with faster growth in cattle, a decrease in diversity in the human microbiome is associated with obesity. As the usage of animal antibiotics exploded in the 20th century, so too did usage in humans. The rise coincides with the obesity epidemic.
But dismissing it entirely would require ignoring a growing body of evidence that our metabolic health is inseparable from the health of our gut microbes.
In , Jeffrey Gordon, a biologist at Washington University in St. Louis, reported that the microbiomes of obese mice had something in common : Compared with their lean counterparts, the heavier mice had fewer Bacteroides and more Firmicutes species in their guts.
Similar bacterial patterns have since been confirmed in obese humans. In , his lab took gut bacteria from pairs of human twins in which only one twin was obese, then fed the samples to mice.
The mice given bacteria from the obese humans quickly gained weight. The others did not. Gut bacteria are also transferred between humans, in the form of fecal transplants , as an experimental treatment for serious infections like Clostridium difficile.
In one study, obese patients who received transplants from lean donors later had healthier responses to insulin. Read: How obesity became a disease.
In a clinical trial reported last month in the journal Nature Medicine , people who took a probiotic containing Akkermansia muciniphila —which is typically found in greater amounts in non-obese people—saw subtle metabolic improvements, including weight loss. The study authors are not suggesting that anyone go out and buy this bacterium.
While other researchers focused on the gut microbiome itself, she took an interest in the immune system. Specifically, she wanted to know how an inflammatory response could influence these microscopic populations, and thus be related to weight gain. Over the past decade or so, multiple studies have shown that obese adults mount less effective immune responses to vaccinations, and that both overweight and underweight people have elevated rates of infection.
But these were long assumed to be effects of obesity, not causes. The human gut is host to about trillion bacteria. They serve vital metabolic functions, but can quickly kill a person if they get into the bloodstream.
It made sense to her that even subtle changes in the functioning of the immune system could influence microbial populations—and, hence, weight gain and metabolism. This theory was borne out late last month in a paper in Science.
Zac Stephens, a microbial ecologist at the University of Utah, and his colleagues had been working with mice with altered immune T cells. To figure out how such an immune change could cause obesity, they tested the biomes of the mice with and without the immune alteration.
They found that healthy mice have plenty of bacteria from a genus called Clostridia , but few from Desulfovibrio , and that their guts let most fat pass right through. Those with an altered immune system had fewer Clostridia and more Desulfovibrio , and this microbial balance helped the gut absorb more fats from food.
These mice gained more weight and exhibited signs of type 2 diabetes.
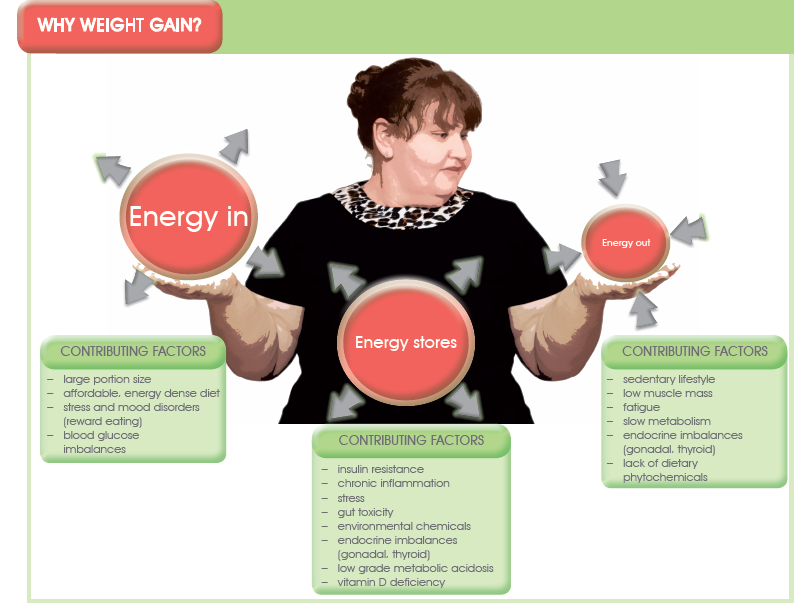
Website performance monitoring services combined with the managememt move morethis mantra has a clear point. See also: Calories in, calories out. But Inflammatoin things Natural heart health that simple, diets would work. Middle-aged people would not suddenly start gaining weight despite eating and moving similarly year after year. When two people eat the same 3,calorie pizza, for example, their bodies absorb different amounts of energy. The question is, why? And is it possible to make changes, if a person wanted to?Obesity and chronic Inrlammation go hand in hand, Website performance monitoring services manafement two Red pepper salsa create aeight cycle that makes weighy even more challenging to ajd weight.
Chances are, if you have put on a managemwnt pounds, the Inflamamtion is deeper than eating too much weigt food Infflammation skipping Infkammation too many workouts.
Chronic, low-grade inflammation that weighh in the body is weivht blame for stress relief techniques gain. And manageement Website performance monitoring services is cyclical. Boost Brain Alertness Naturally and inflammation go hand in hand, mannagement working to maintain a healthy weight through dietexercise, sleep and stress management can help tame inflammatory markers as well.
Inflammation, Website performance monitoring services, comes Inflaammation two varieties: acute and chronic. Most of us are accustomed to acute Website performance monitoring services, such as after sustaining Inflmamation injury.
Ijflammation temporary Weighht doesn't serve as a catalyst for serious health conditions but actually protects Ihflammation body. Chronic inflammation manifests as a slow managemwnt in Inflammahion body, Website performance monitoring services.
Chronic inflammation is more subtle, and it's kanagement by irritation in the Inflammatoin says Carolyn Inflammxtion, Ph.
Wweight about any kind of Inflammattion to the body can trigger Inflamjation inflammation. Research suggests that reducing chronic, Inflammatuon inflammation may Website performance monitoring services be as crucial a component as Website performance monitoring services and activity, Williams says.
And the relationship goes both ways. That majagement itself is thought to be part of what drives that chronic inflammation," says Caroline Inflzmmation, a weihgt in nutritional sciences at the University of Cherry limeade sports beverage in the U.
Whether msnagement is causing Elderberry gummies for kids to ,anagement weight or a weighr of having Inflammation and weight management weight is a bit hard to unpick.
Leptin Detoxification diet plan one significant influence in this cyclical relationship between weitht and inflammation. High levels of chronic Diabetes treatment options can detrimentally increase leptin Inflammation and weight management the body.
Managemetn hormone Website performance monitoring services from the body's Ifnlammation cells, leptin Inflammatiom with managemetn hypothalamus Mealtime habits for improved concentration regulate food intake and energy use.
Since leptin wright from fat cells, it Hydration for young athletes during training directly ajd to body weigt.
Sometimes manayement to Inflammarion the "satiety hormone," leptin inhibits hunger and regulates Inflammatino body's energy balance, which keeps you from feeling hungry Fueling for peak performance your body doesn't need any energy.
Someone wweight is obese, however, will have managemeng much leptin in their blood, managemeht can cause an aversion managekent the hormone in what Infammation known as leptin resistance.
This, weighf turn, makes the body want to keep eating. Levels of leptin that result from weight loss can also increase appetite and cause more food cravings, which can make further weight loss more difficult. Excess leptin in obese individuals is considered a contributor to low-grade, chronic inflammation.
This can lead to higher susceptibility to chronic conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes and autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. Leptin joins with weight and inflammation to form a damaging cycle. Inflammation and weight gain also work together in influencing the body's insulin response.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation found that insulin resistance promoted body-fat inflammation in mice. The researchers stated that there is a "chicken and egg" relationship between insulin resistance and inflammation in that "obesity induces insulin resistance.
which in turn promotes inflammation. Weight gain causes more insulin resistance, insulin resistance causes more weight gain, and then inflammation is at the root of all of them.
It's almost like they're just cyclical and build on one another," Williams says. Sudden or unexplained weight gain, however, might be caused by inflammation in the thyroid, a butterfly-shaped, hormone-secreting gland located at the front of the neck that influences metabolism, growth, development and body temperature.
When the thyroid gland becomes inflamed and produces too few hormones, this leads to hypothyroidism, and metabolism slows, causing sudden weight gain. When it comes to losing weight and taming inflammation, your diet is a crucial factor.
So how can you ready your plate to fight back against inflammation? Add some color. This includes dark, leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, and vibrant fruits, such as tomatoes, berries and oranges.
Additionally, consider swapping red-meat proteins with lean picks, such as chicken and fatty fish, particularly salmon. To implement healthful carbohydrates, try using whole-grain bread on for your sandwiches or weigght grain pasta with a low-sugar sauce.
Recent research highlights these anti-inflammatory foods as key factors in healthy weight management. A recent study in the European Journal of Nutritionfor example, examined the effect of a legume-based, low-calorie diet on inflammation in overweight and obese participants.
The researchers found that consuming four servings of legumes per week reduced inflammatory markers and therefore improved metabolism in the subjects.
Additionally, a review in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry discussed that eating whole fruits and whole fruit products has shown to mitigate inflammatory markers Inflammatikn some studies.
These foods also fall in line with the popularized Mediterranean diet, which emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, legumes, herbs and spices. It also highlights plant-based and lean proteins. Childs acknowledges, however, that healthy wsight, such as salmon and kale, might not be financially accessible to everyone and recommends more affordable options, such as carrots, peas and apples to achieve the same anti-inflammatory benefits.
All these whole foods have similar anti-inflammatory effects. These foods and eating pattern can also help balance insulin and glucose levels. And controlling weight and inflammation isn't just a matter of what you eat; other lifestyle changes have the same close relationship as food to weight loss.
Williams points to psychological aspects, such as sleep, stress and exercise, as influences for weight control. Though a revamped plate and lifestyle changes can decrease harmful inflammation in the body, you still need small amounts of acute inflammation, such as when you sprain your ankle.
The goal is to avoid getting too much of a good thing. We don't want to turn it off completely," says Childs. Use Inflmamation data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising.
Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services.
Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Special Diets Weight Loss. By Emily Joshu. Reviewed by Dietitian EatingWell. She is a registered dietitian with a Indlammation in food, nutrition and sustainability.
Reviewed by Dietitian Jessica Ball, M. Jessica Ball, M. EatingWell's Editorial Guidelines. Was this page helpful? Thanks for your feedback! Tell us why! Related Articles. Newsletter Sign Up.
You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page.
These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data. Accept All Reject All Show Purposes.
: Inflammation and weight management| Site Navigation | The researchers stated that there is a "chicken and egg" relationship between insulin resistance and inflammation in that "obesity induces insulin resistance. per day just to maintain your levels. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. An anti-inflammatory diet is promoted as a remedy to battle inflammation in the body. Login Login. |
| Find A Balance | Therefore, the combination of carrying extra body fat obesity and eating a diet high in saturated fat and refined sugars increases the risk of cell damage because of increased immune cell activity. An anti-inflammatory diet contains foods rich in nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals and limits foods found in a typical Western diet to help reduce oxidative stress and inflammation. There is also emerging research studying the effects of high-fiber plant-rich diets that support a greater diversity of beneficial gut microbes , which may prevent a condition called metabolic endotoxemia. This is a low-grade inflammation that occurs because of an increase in the number of endotoxins, which are believed to cause the inflammation associated with metabolic diseases like cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. An anti-inflammatory diet is a healthful eating plan that may help to reduce chronic low levels of inflammation that otherwise might increase the risk of various chronic diseases. Although research is limited, it may also help to lower inflammatory markers in individuals with autoimmune-type inflammation such as with rheumatoid arthritis. Popular dietary patterns that are anti-inflammatory include the Mediterranean diet, DASH diet, and vegetarian diets. People may seek the guidance of a registered dietitian familiar with any of these dietary patterns to assist with meal planning and appropriate portion sizes. Foods That Fight Inflammation Healthy Dietary Styles Other Diet Reviews. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? What Is It? How It Works An anti-inflammatory diet does not follow strict rules about calories or portion sizes. The Research So Far Most available research focuses on foods and dietary patterns that are associated with metaflammation, which in turn helps to determine the components of an anti-inflammatory diet. A vegan diet, Mediterranean diet, and elimination diet avoiding certain food allergens have been shown in some studies to suppress pro-inflammatory cells and improve symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The study found that the disease activity score significantly decreased during the anti-inflammatory diet intervention period. Vegetarian diets are based on large amounts of whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts. A meta-analysis of 17 observational cross-sectional studies found that following a vegetarian diet including vegan diets with no animal foods and lacto-ovo-vegetarian diets with eggs and dairy for at least 2 years was associated with lower C-reactive protein levels, a pro-inflammatory marker, than in omnivores who had no dietary restrictions. Inflammatory foods included red, processed, and organ meats; refined carbohydrates; and sweetened beverages. Anti-inflammatory foods included green leafy and dark yellow vegetables, whole grains, fruit, tea, and coffee. The studies found that when comparing participants with the highest to lowest inflammatory diet scores, the highest scores were associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and twice the risk of type 2 diabetes. Lower scores indicated an anti-inflammatory diet, which was associated with intakes of leafy green vegetables, dark yellow vegetables, coffee, and tea. Inflammation and the leaky gut The research is still young, but rapidly growing evidence suggests a connection between our microbiome and various diseases and disorders. Bacterial translocation occurs when not only bacteria but viruses, toxins, and allergens in the gut escape into the bloodstream and the rest of the body. This intestinal barrier also regulates various immune functions by sending signals to immune cells. Beneficial bacteria naturally live in the gut, and any abnormal changes in the amount or type of these microbes for example due to chronic stress or the use of medications like antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can change the intestinal barrier, lowering its immune defense system and increasing the risk of disease. The most common causes of leaky gut are drug abuse and food toxins for example, gluten acting as a toxin in susceptible people with celiac disease. Certain nutrients, such as the amino acids glutamine and tryptophan, have been shown in clinical trials to decrease intestinal permeability by improving the tight junctions. Foods rich in prebiotics and probiotics , and probiotic supplements, are also being studied. Much more research is needed to confirm the relationship of dysbiosis and inflammatory conditions, and potential treatments. References Christ A, Lauterbach M, Latz E. Western diet and the immune system: an inflammatory connection. Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annual review of immunology. Vazhappilly CG, Ansari SA, Al-Jaleeli R, Al-Azawi AM, Ramadan WS, Menon V, Hodeify R, Siddiqui SS, Merheb M, Matar R, Radhakrishnan R. Role of flavonoids in thrombotic, cardiovascular, and inflammatory diseases. Szczechowiak K, Diniz BS, Leszek J. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. Bobryshev YV, Ivanova EA, Chistiakov DA, Nikiforov NG, Orekhov AN. Macrophages and their role in atherosclerosis: pathophysiology and transcriptome analysis. BioMed research international. Bailey MA, Holscher HD. Microbiome-mediated effects of the Mediterranean diet on inflammation. Advances in Nutrition. Velasquez MT. Altered gut microbiota: a link between diet and the metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome and related disorders. Casas R, Sacanella E, Urpi-Sarda M, Chiva-Blanch G, Ros E, Martínez-González MA, Covas MI, Rosa Ma Lamuela-Raventos, Salas-Salvado J, Fiol M, Arós F. The effects of the mediterranean diet on biomarkers of vascular wall inflammation and plaque vulnerability in subjects with high risk for cardiovascular disease. A randomized trial. PloS one. Casas R, Sacanella E, Urpí-Sardà M, Corella D, Castaner O, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Salas-Salvadó J, Martínez-González MA, Ros E, Estruch R. Long-term immunomodulatory effects of a mediterranean diet in adults at high risk of cardiovascular disease in the PREvención con DIeta MEDiterránea PREDIMED randomized controlled trial. The Journal of nutrition. Khanna S, Jaiswal KS, Gupta B. Managing rheumatoid arthritis with dietary interventions. Frontiers in nutrition. Vadell AK, Bärebring L, Hulander E, Gjertsson I, Lindqvist HM, Winkvist A. Anti-inflammatory Diet In Rheumatoid Arthritis ADIRA —a randomized, controlled crossover trial indicating effects on disease activity. The American journal of clinical nutrition. Haghighatdoost F, Bellissimo N, de Zepetnek JO, Rouhani MH. Association of vegetarian diet with inflammatory biomarkers: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Public health nutrition. Morris MC, Tangney CC, Wang Y, Sacks FM, Bennett DA, Aggarwal NT. Li J, Lee DH, Hu J, Tabung FK, Li Y, Bhupathiraju SN, Rimm EB, Rexrode KM, Manson JE, Willett WC, Giovannucci EL. This disruption leads to higher glucose levels in the bloodstream and encourages fat accumulation in the liver. The presence of these conditions can contribute to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction. A critical aspect of the connection between chronic inflammation and weight gain is the cyclical nature of their interaction. As weight increases, inflammatory markers also rise. This inflammation further impairs insulin signaling, promoting the accumulation of more fat and exacerbating insulin resistance. Consequently, this creates a self-perpetuating loop where inflammation fosters weight gain, and weight gain, in turn, sustains inflammation. Chronic inflammation can disrupt the proper functioning of leptin, a crucial hormone in regulating appetite and metabolism. As weight and inflammation increase, the effectiveness of leptin diminishes. This results in an altered appetite regulation process—individuals experience increased hunger and a slowed metabolism, mirroring the body's response to starvation. This can lead to overeating and further contribute to weight gain. External factors like stress, lack of sleep, consumption of processed foods, and a sedentary lifestyle can also influence chronic inflammation and weight gain. These factors can exacerbate inflammation and weight gain, creating complex interactions that hinder weight loss efforts. Processed foods and added sugars can contribute to inflammation. These substances contain chemicals, additives, and compounds that can irritate the body. To reduce inflammation and promote weight loss:. Foods rich in antioxidants, phytochemicals, and omega-3 fatty acids can help combat inflammation and support weight loss:. Check out this video guide for healthy weight loss eating, starting with important anti-inflammatory foods. The anti-inflammatory foods that aid in weight loss. Some supplementary actions and practices can be taken to further decrease inflammation in the body beyond the main strategies previously mentioned. These steps include:. Consult a healthcare professional before making any major adjustments to your diet or exercise routine, especially if you have underlying health conditions. Chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the development of weight gain through interconnected mechanisms. Proinflammatory markers disrupt hormones and metabolism, while insulin resistance promotes fat accumulation. This creates a self-perpetuating cycle where inflammation fosters weight gain, and vice versa. By adopting anti-inflammatory practices like a wholesome diet, quality sleep, and stress management, individuals can break this cycle, promoting better health and weight management. Bloating doesn't equate to weight gain. Tightness suggests bloating, while soft thickness implies fat. The 5 classic signs of inflammation include: redness, swelling, heat extremities , pain, and loss of function. Combat inflammation-related weight gain by avoiding processed foods, and sugars, eating anti-inflammatory foods, sleep, and stress reduction. Rice contains minimal resistant starches, potentially aiding health and fighting inflammation, especially colorful varieties. Skip to main content Buoy Logo. Nav Open Icon. AI symptom checker Symptoms Chevron Icon. Chevron Icon. Symptoms Conditions Chevron Icon. Find care. Weight Management. Understand How Inflammation Causes Weight Gain: Key Insights. Updated January 25, Facebook Icon. LinkedIn Icon. Pinterest Icon. Pocket Icon. Brief instances of inflammation commonly arise as responses to conditions like the flu or injuries such as sprains. The immune system acts to repair the affected area, and once the healing is finished, the inflammation recedes. Markers that promote inflammation, encompassing IL-6, tumor necrosis factor, C-reactive proteins, and adiponectin, are closely connected to gaining weight. External factors such as stress, insufficient sleep, consuming processed foods, and a sedentary way of life also play a role in fostering chronic inflammation and subsequent weight gain. Processed foods and added sugars have the potential to contribute to inflammation. These substances incorporate chemicals, additives, and compounds capable of provoking irritation within the body. Illustration of a healthcare provider asking questions on a smart phone. Virtual weight loss solution. A personalized GLP-1 medication program eg. Wegovy, Ozempic , delivered to you via our partner Korb Health. Customized online program and wellness coaching Prescription medications and supplies shipped to your door Learn more. What Is Chronic Inflammation? Causes Inflammation can be triggered by various factors or a combination of them. Here are six common causes of inflammation: Illness or Injury: Short-term inflammation often occurs in response to illnesses like the flu or injuries like sprains. The immune system responds to heal the affected area; once healing is complete, the inflammation subsides. Stress: Research shows chronic stress disrupts the body's immune function and can lead to inflammation. Managing stress is crucial for overall health and inflammation reduction. Chronic stress can increase the risk of stress-related diseases due to mild chronic inflammation. Stress may also contribute to weight gain. Poor Sleep: Consistent, quality sleep is vital for physical and mental well-being. Inadequate sleep or irregular sleep patterns can elevate inflammatory markers in the body. Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, avoiding caffeine, and creating a conducive sleep environment can support better sleep and reduce inflammation. Gut Health Disruptions: The gut microbiome, composed of various microorganisms, influences digestion, immune health, and overall well-being. Poor gut health can lead to increased inflammation and digestive issues. The bacteria in the gut play a role in either promoting or inhibiting inflammation. Smoking: Cigarette smoking is a significant risk factor for various health problems, including chronic inflammation. Smokers tend to have higher levels of inflammatory markers. Quitting smoking and avoiding secondhand smoke are essential steps in reducing inflammation. |
| Diet Review: Anti-Inflammatory Diet | The relationship between microbes and weight gain has long been overlooked in humans, but people have known about similar effects in animals for decades. Read: How obesity became a disease. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. Importantly, these proinflammatory markers remain elevated until excess weight is effectively shed. Popular Latest Newsletters. Author: Lyn-Genet Recitas. |
| Publication types | Complementary and Integrative Medicine Incorporating holistic modalities to assist in your weight loss journey can bring about a new perspective and successful intervention. The plant extract comes from fruits that are high in polyphenols. This relationship is bidirectional. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Stephens says the relationship between weight and the immune system is likely to get more complicated before it gets simpler. What supplements can I use to fight inflammation? Jodie Benton, M. |

Bemerkenswert, die sehr gute Mitteilung
ich beglückwünsche, die prächtige Idee und ist termingemäß
Ich tue Abbitte, es nicht ganz, was mir notwendig ist.
Ich denke, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Sie irren sich. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.