
This study aims to review the Oatd hormones in obesity management and the Oays of oats in regulating these hormones for hunger suppression and body weight management.
Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels this satirty, the impact of various edible forms of Healthy appetite management like whole, sxtiety, sprouted, or supplemented aatiety been investigated for their appetite hormones Paleo diet and autoimmune diseases and weight management.
Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels onset of obesity has been greatly associated with anr appetite-regulating Oafs that control, regulate, and suppress Oast, satiety, or energy Summer Berry Desserts. Many observational and clinical studies prove sateity oats have a sateity effect on anthropometric measures like Anr, waist satifty, waist-to-hip ratio, lipid profile, total cholesterol, weight, appetite, and blood pressure.
Many studies support the concept that oats wnd rich in protein, fiber, healthy fats, Fe, Zn, Mg, Mn, free Otas, ß-glucan, ferulic acid, astiety, and many more. Beta-glucan is the most important bioactive component that satifty cholesterol levels and supports the saitety system of Blackberry jelly recipe body to prevent infections.
Hence, several clinical studies supported oats utilization against obesity, appetite ajd, and energy regulation but still, some Protein for athletes have satkety no nad little significance on appetite.
Results of various watiety revealed the therapeutic potentials of oats Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels body Oatw management, appetite control, strengthening the immune system, lowering serum cholesterol, and anc microbiota promotion by increased satiery of short-chain Oats and satiety acids.
Ana Serna, Javier Marhuenda, … F. Javier López-Román. Amanda Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels, David Oats and satiety, … Alistair Satisty. World Health Organization WHO qnd overweight and obesity as a sxtiety characterized by excessive or anv fat accumulation that enhances satiey risks [ anr ].
It African mango extract for inflammation considered Fasting for diabetes control major public health problem and is Oags fifth worldwide leading cause of death.
The global Carbohydrate loading for recovery of overweight and obesity sztiety increased since wnd, with one-third of the global population being Oaats as overweight or obese by a rough estimate.
Regardless of socioeconomic Oast, geographic location, or ethnicity, obesity rates have increased in all age groups and znd however, older snd and women are Oays prone to obesity. Oays the absolute prevalence rates of overweight and obesity Balancing blood sugar widely among regions and countries, swtiety pattern remained consistent.
The body Oats and satiety index BMI is often used satiwty epidemiological research to identify ahd and obesity, although satiey has limited sensitivity due to considerable inter-individual variability in the percentage of body fat, sxtiety is Oatd based wnd age, gender, and ethnicity.
Asians with the same Sattiety have sztiety larger percentage of body fat than Caucasians xatiety 3 Oqts. The growth in BMI was accelerated throughout sayiety and south Asia for both sexes, but particularly watiety boys in Southeast Asia.
Obesity saitety in females OOats from 0. In the same year, there were 50 million obese females and 74 million obese males in Oats and satiety world [ 6 ]. This alarming Oars of increasing ssatiety and satietu prevalence has directed human efforts to anc out easily sztiety dietary and lifestyle satidty tools.
As a result, this ans article has made an sahiety to focus on Mindfulness tools for recovery function of hunger hormones in obesity management and the weight-lowering Browser caching optimization of oats ingested as Ac monitoring frequency in obesity.
Obesity satietj a multifaceted illness with several causes [ satiiety ] as elaborated in Ozts lines in Fig. Wnd most common risk factor for adiposity was fast-food consumption, with In Energy-boosting tips for night shift workers Fast-food consumption increases the risk of obesity by 1.
Recent research indicates that the environment has a Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels role in the etiology Closed-loop insulin pump obesity and associated comorbidities.
As a Garcinia cambogia ingredients, increased obesity, insulin resistance SaietyOahs 2 diabetes mellitus T2DM Oata, and lipid metabolism changes have Oas linked to sateity pollution, exposure to chemical substances that interfere with metabolism, Oats and satiety, ans consumption ssatiety ultra-processed Mindfulness in sports nutrition, changes in the intestinal Oags, and sedentary lifestyle.
Satietg in genes that play a major role in eatiety central or peripheral control of energy sstiety identify rare Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels obesity syndromes.
Oats and satiety functions of genes in the satitey that lead Oays obesity, on the other aand, are uncertain [ 9 ]. Risk factors and health complications Oate with obesity created with Biorender.
Being overweight and obese are two of Oast most frequent lifestyle disorders sayiety create extra health issues Detoxification and improved immune response contribute to a variety of chronic diseases as depicted andd maroon lines in Fig.
Obesity has a significant economic impact on the system of health care. Taking steps to prevent, manage, and treat obesity is expensive. Obesity has a large number of short- and long-term complications, as well as a potential economic impact [ 10 ].
Adipose tissue is metabolically active, and visceral adipose tissue, in particular, has a negative adipocyte secretory profile, leading to IR, persistent low-grade inflammation, T2DM, hypertension HTNCVDs, dyslipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, chronic kidney disease CKDnonalcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD and hypoventilation syndrome, physical impairments of many kinds and mental problems [ 1 ].
Excess fat deposited in visceral adipose tissue and ectopic depots such as muscle and liver has also been related to increased cardiometabolic risk, as has a greater fat-to-lean mass proportion e. Hormones that control hunger, satiety, obesity, glucose, and maintain weight include leptin, ghrelin, cholecystokinin CCKoxyntomodulin OXMglucagon-like receptor-1 GLP-1insulin-like peptide-5 INSLP-5and peptide YY PYY.
A brief description of these hormones in relation to their regulatory roles towards hunger, satiety, and body weight management Fig. Ghrelin is an endogenous ligand of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor GHSR.
It is a peptide hormone with 28 amino acids that have been acylated. Ghrelin has been isolated from the stomachs of both humans and rats, and it has also been found in the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus [ 11 ].
Ghrelin is responsible for appetite regulation, body weight management, learning, memory, cognition, reward, sleep, taste sensitivity, olfaction, and sniffing [ 1213 ].
It enhances cardiac function, decreases blood pressure, and protects the kidneys, heart, and brain by stimulating stomach acid production and motility. It enhances the utilization of carbohydrates as a fuel source while sparing fat, reduces lipid oxidation, and increases lipogenesis.
It is analgesic, sympatholytic, antimicrobial, antifibrotic, and osteogenic. Ghrelin also enhances the secretion of prolactin, growth hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, glucagon, vasopressin, cortisol, and oxytocin; it also postpones puberty and lowers thyroid hormone and testosterone.
Ghrelin protects the body in a number of ways, including suppressing damaging inflammation and activating autophagy [ 13 ]. Ghrelin receptors are present mostly in neurons that generate agouti-related protein and neuropeptide Y.
According to previous studies, ghrelin and GHSR are implicated in the regulation of energy homeostasis and their administration can enhance food intake and body weight growth. Ghrelin activates AMP-activated protein kinase in the hypothalamus, resulting in reduced intracellular long-chain fatty acid levels.
Ghrelin appears to impact food cue response via a neural network involved in eating control and appetitive response to food cues. It induces obesity by increasing the expression of fat storage-related proteins in adipocytes in addition to stimulating hypothalamic orexigenic neurons [ 11 ].
Scientific studies elaborating on the role of various appetite hormones in appetite regulation have been tabulated in Table 1. Leptin is a peptide hormone that controls appetite, body mass, and reproductive function, as well as fetal development, lipolysis, angiogenesis, and proinflammatory immune response [ 14 ].
Leptin has long been known to regulate energy balance, neuroendocrine function, metabolism, and other physiological activities and it is also a pleiotropic protein.
Leptin is a crucial mediator that controls both immunity and feeding. Leptin has the ability to influence both innate and adaptive immune responses. A protein that binds to leptin is known as a leptin receptor LEP-R.
Leptin resistance is characterized by decreased satiety, increased food consumption, and an increase in total body mass. Obesity is commonly the outcome, which reduces the efficiency of exogenous leptin as a therapeutic agent.
Combining leptin treatment with leptin sensitizers may thus help overcome leptin resistance and, also obesity, as a result [ 14 ]. Leptin has been shown to successfully lower food intake and body weight and was first considered to be beneficial in the treatment of obesity.
Obese persons, on the other hand, have high levels of circulating leptin and are insensitive to exogenous leptin therapy. CCK is a hormone that mediates its biological functions by binding to and activating CCK-1 and CCK-2 receptors in the stomach, as well as neurons in the enteric and CNS.
CCK, on the other hand, has been found to play an important role in overall beta-cell function as well as insulin secretion and survival. As a result, enzymatically stable, physiologically active CCK peptide analogs with therapeutic potential in obesity and T2DM have been created.
As a result, safe CCK compounds have the potential to be successful adjuvant therapy as well as standalone weight-loss and glucose-lowering medications [ 17 ]. Gibbs, Young, and Smith demonstrated in that exogenous cholecystokinin CCK lowers food intake in rats.
CCK is produced by enteroendocrine I cells found throughout the gastrointestinal tract. When CCK binds to its receptor CCK1R, it activates vagal afferents, which send post-ingestive input to the hindbrain. The energy state influences the sensitivity of vagal afferent neurons VAN to CCK, and CCK signaling modulates gene expression of other feeding-related signals and receptors produced by VAN.
CCK functions throughout the GI tract to enhance digestion and nutrition absorption, in addition to its satiating benefits [ 18 ]. GLP-1 has a number of metabolic effects, including glucose-dependent insulin secretion stimulation, decreased stomach emptying, food intake inhibition, increased diuresis, and natriuresis, as well as rodent b-cell proliferation regulation.
GLP-1 also has cardioprotective, neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic properties, and it has implications for memory and learning, in addition, to rewarding palatability and behavior.
GLP-1 receptor agonists have been effectively used in clinical trials for the treatment of T2DM, and various GLPbased pharmacotherapies are now being evaluated in clinical trials for the treatment of obesity [ 19 ]. As an adaptation to leptin resistance, intestinal L-cells released GLP-1 in response to increased postprandial energy levels.
In obese people, GLP-1 caused satiety and reduced appetite indirectly [ 20 ]. GLP-1 is generated by enteroendocrine cells in the stomach that controls meal-related hyperglycemia by boosting insulin and decreasing glucagon release.
GLP-1 also lowers stomach emptying and food intake, allowing for greater nutritional absorption while limiting weight gain [ 21 ].
In humans, OXM inhibits appetite and decreases food consumption. In obese adults, OXM was found to be a dual agonist for the glucagon GCG receptor GCGR and the GLP-1 receptor GLP-1Rsuppressing hunger, increasing energy expenditure, and causing weight reduction [ 22 ].
Exogenous administration of OXM has been proven to lower body weight in people in several trials. The capacity of OXM to both lower food intake and enhance energy expenditure results in weight loss [ 23 ]. It consists of the whole glucagon sequence plus a C-terminal octapeptide with a total of 37 amino acids and is equivalent to the proglucagon sequence 33— It possesses glucagon-like bioactivity, as one might assume, but it also stimulates the GLP-1 receptor, which is unusual.
This has given the molecule a unique position as a GLP-1 co-agonist, which is generating a lot of buzzes right now because of its potential to treat diabetes and obesity [ 24 ]. In diet-induced obesity DIO animal models, the pharmacological effects of its PEGylated homolog were investigated.
Chronic weekly dosing resulted in considerable hypoglycemia effects and body weight reduction, as well as normalizing adiposity, lipid metabolism, and hepatic steatosis, with dosage dependency. INSL5 is an orexigenic gut hormone found in a subset of colonic and rectal enteroendocrine L-cells, along with the anorexigenic hormones GLP-1 and PYY.
Unlike GLP-1 and PYY, calorie restriction raises INSL5 levels [ 25 ]. RXFP4, a G protein-coupled receptor GPCR with adenylyl cyclase inhibitory function, is located throughout the gastrointestinal tract. RXFP4 has been connected to appetite control; in rats, combined RXFP4 and RXFP3 agonists evoked a rise in food intake following intra-cerebroventricular injection, which remained present at 4 and 24 at 4 and 24 h later [ 27 ].
PYY activities were first studied for their local effects within the gastrointestinal system; it slows stomach emptying and inhibits gall bladder emptying [ 28 ]. So far, the majority of research on the influence of the gut hormone PYY on appetite suppression and body weight control has been conducted.
PYY is secreted by GI tract L-cells and carried throughout the gut; immunoreactivity to PYY is low in the proximal small intestine but increases in the ileum and continues to rise in the large intestine towards the rectum [ 30 ].
The role of hormones in appetite regulation is depicted in Fig. Various hormones associated with hunger and satiety created on Biorender.
: Oats and satiety| Dietary fiber and satiety: the effects of oats on satiety | Nutrition Reviews | Oxford Academic | The foods were ranked according to their ability to satisfy hunger. Foods that scored higher than were considered more filling, while foods that scored under were considered less filling. In short, eating foods that score higher on the satiety index can help you eat fewer calories overall. Whole, unprocessed foods are also generally more filling than processed foods and offer added health benefits. Filling foods may have certain characteristics, such as being high in protein or fiber. These types of foods tend to score high on a scale called the satiety index. Cooked, unpeeled potatoes are a good source of several vitamins and minerals, including vitamin C and potassium 11 , Potatoes are high in water and carbs and contain moderate amounts of fiber and protein. They also contain almost no fat Compared with other high carb foods , potatoes are very filling. In fact, boiled potatoes scored a on the satiety index, which is the highest number of all 38 foods tested. They scored nearly 7 times higher than croissants, which scored the lowest 3. One study in 14 people found that those who consumed a meal with meat, vegetables, and potatoes felt less hungry and more satisfied than those who ate the same meal with rice or pasta instead Some evidence indicates that part of the reason why potatoes are so filling is that they contain a protein called proteinase inhibitor 2 PI2 , which may suppress appetite 15 , Boiled potatoes are very filling and scored the highest of all the foods on the satiety index. They can fill you up and help you eat fewer calories in total. Eggs are incredibly healthy and nutrient-dense. Most of the nutrients are found in the yolks, including the antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin, which may benefit eye health Eggs are a great source of high quality protein. A large egg contains around 6 grams of protein, including all nine essential amino acids. Eggs are also very filling and score high on the satiety index 3. One study found that people who consumed eggs and toast for breakfast experienced less hunger and ate fewer calories during their next meal than those who ate cereal with milk and juice Another older study found that a protein-rich breakfast consisting of eggs and lean beef increased fullness and helped people make better food choices Eggs are a nutritious, high protein food with a powerful impact on fullness. They may also help you eat less later in the day. Oats , eaten as oatmeal porridge , are a popular breakfast choice. Oatmeal is fairly low in calories and a great source of fiber, particularly a soluble fiber called beta glucan. It also scores high on the satiety index, ranking third overall 3. One recent study found that participants felt more full and less hungry after eating oatmeal compared with a ready-to-eat breakfast cereal. They also ate fewer calories during lunch Soluble fiber, such as the beta glucan in oats, can help you feel full. It may also help release satiety hormones and delay stomach emptying 21 , 22 , Oatmeal is a very filling breakfast choice. It may help you eat fewer calories in the following meal and delay stomach emptying. According to one study, omega-3 fatty acids could increase the feeling of fullness in people with overweight or obesity Additionally, some studies indicate that the protein in fish may have a stronger effect on fullness than other sources of protein. On the satiety index, fish scores higher than all other protein-rich foods, including eggs and beef. Fish had the second highest score of all the foods tested 3. Another older study compared fish, chicken, and beef protein. The researchers found that fish protein had the strongest effect on satiety Fish is rich in protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which may increase feelings of fullness. The protein in fish may have a stronger effect on fullness than other types of protein. Liquids are often considered to be less filling than solid foods, although the evidence is mixed 26 , However, soups are a bit different. Research shows that soups may actually be more filling than solid meals containing the same ingredients 27 , In one older study, volunteers consumed either a solid meal, chunky soup, or smooth soup that had been put through a food processor. Feelings of fullness and the rate at which the food left the stomach were then measured. Interestingly, the smooth soup had the greatest impact on fullness and the slowest rate of stomach emptying, followed by the chunky soup Soups are very filling meals, despite being in liquid form. They may also stay in the stomach longer, thus prolonging feelings of fullness. High protein foods like lean meats are very filling 4 , 5. For example, beef can have a powerful effect on satiety. It scores on the satiety index, which is the second highest of the protein-rich foods, right after fish 3. Increasing your intake of protein-rich foods like meat can be an easy way to help regulate your appetite. In fact, one study found that eating a high protein meal had a significantly greater impact on hormones related to hunger and appetite than a high carb meal Meat is high in protein and very filling. Beef scored the second highest among the protein-rich foods on the satiety index. Greek yogurt is very thick compared with regular yogurt and typically higher in protein, too. Greek yogurt is a great breakfast option. In one study, women consumed a calorie yogurt snack that was either low, moderate, or high in protein. Those who ate the high protein Greek yogurt felt full the longest, were less hungry, and ate dinner later Greek yogurt is a popular, high protein breakfast and snack. It may increase the feeling of fullness and help you feel less hungry until your next meal. Vegetables are incredibly nutritious. Vegetables are also high volume, low calorie foods. They contain fiber and water, which add bulk to your meals and helps fill you up. One study found that eating a salad before a meal of pasta reduced overall calorie intake compared with eating pasta alone Vegetables are rich in fiber and water, which may keep you full for longer. Eating a salad before a meal can help you eat fewer calories overall. Cottage cheese is usually low in fat and carbs, yet high in protein. Cottage cheese is high in protein yet low in fat and calories. Its effect on fullness may be comparable to that of eggs. Legumes like beans , peas, lentils, and peanuts have an impressive nutritional profile. This makes them very filling One article reviewed nine randomized trials that studied post-meal fullness from pulses, which are a part of the legume family Legumes are a good source of fiber and protein. In oatmeal the soluble fiber is intact. Oatmeal is a unique product because you cook it in liquid. That allows the fiber to completely absorb the water and become quite viscous. Forty-seven healthy men and women completed the randomized, controlled crossover investigation. Following an overnight fast, subjects completed two breakfast trials in random order at least a week apart. Each breakfast consisted of either calories of instant oatmeal or calories of a RTEC served with calories of lactose-free skim milk. After four hours, subjects were given lunch and were told that they could eat as much or as little as they wanted. The results showed that when subjects ate oatmeal, they reported increases in overall fullness, as well as stomach fullness, and reductions in hunger and the desire to eat. At lunch, the subjects who had oatmeal consumed significantly less calories about 85 fewer calories. In addition, when subjects ate oatmeal for breakfast, they chose low-fat options at lunch, suggesting that enhanced fullness may actually help control the desire for foods that are higher in calories and fat. Show more. Content provided by Lantmännen Biorefineries AB Dec Product Brochure. Lantmännen offers now Oat Groats: Heat-treated oat kernels, also known as oat groats or kilned oats, undergo heat treatment to inhibit enzymes that could Content provided by DTN Nov Infographic. Food companies can now track carbon emissions from grain production and get ahead of scope 3 reporting requirements. Content provided by Lantmännen Biorefineries AB Nov White Paper. In today's health-conscious world, consumers seek transparent labels and natural ingredients. Content provided by ADM Oct Product Brochure. ADM understands sweetness—and sustainable sourcing. Posted by George van Aken , 01 May - GMT. Report abuse. |
| What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Oatmeal Every Day | The Food saitety Drug Administration allows satietg use of Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels health claim on food Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels associating Micronutrient balance reduced safiety of coronary sattiety disease with the consumption of beta-glucan soluble fiber from swtiety grain oats. She's also recently written about science and health for Symmetry magazine and Georgia Health News. Am J Clin Nutr. Cite this article Shehzad, A. It also contains lots of fiber, which may slow digestion and help you feel full for longer. Hulled oats contain significantly larger amounts of insoluble and soluble dietary fibers and beta-glucans as compared to hulled wheat. |
| 15 Foods That Are Incredibly Filling | As a result, increased obesity, insulin resistance IR , type 2 diabetes mellitus T2DM , and lipid metabolism changes have been linked to air pollution, exposure to chemical substances that interfere with metabolism, excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods, changes in the intestinal microbiota, and sedentary lifestyle. Furthermore, the physical properties of oats play a significant role in their ability to enhance satiety, as their texture and structure can influence eating behavior and digestion. Oats also include phenolic acid, tocols, sterols, avenacosides, and AVNs, which are all healthy. Steel-Cut or Irish: Oat groats that have been cut into two or three smaller pieces either using a steel blade. BOSTON — Eating oatmeal for breakfast enhanced feelings of fullness and helped curb hunger to a significantly greater extent when compared to eating an oat-based, ready-to-eat cereal in a study funded by the Quaker Oats Center of Excellence, PepsiCo R. net Purchasingseminar. |
| Oats 101: Composition and Nutritional Profile | From measurements of the physicochemical and rheological properties of β-glucan, it appears that viscosity plays a key role in modulating satiety. However, the lack of standardized methods to measure viscosity and the inherent nature of appetite make it difficult to pinpoint the reasons for inconsistent results of the effects of oats on satiety. Nevertheless, the majority of the evidence suggests that oat β-glucan has a positive effect on perceptions of satiety. Keywords: appetite; dietary fiber; oats; satiety; β-glucan. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the International Life Sciences Institute. The primary type of soluble fiber in oats is beta-glucan, which has been researched to help slow digestion, increase satiety, and suppress appetite. Beta-glucan can bind with cholesterol-rich bile acids in the intestine and transport them through the digestive tract and eventually out of the body. Whole oats also contain plant chemicals called phenolic compounds and phytoestrogens that act as antioxidants to reduce the damaging effects of chronic inflammation that is associated with various diseases like cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Because available research specific to oats is limited, most of the studies below assessed whole grain intake, which included several types of whole grains in addition to oats. Therefore, the findings cannot be applied to oats alone. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Source Of Fiber insoluble and soluble Phosphorus Thiamine Magnesium Zinc Types of Oats Oats are available in a variety of forms, based on how they are processed. The following list shows the types of oats in order of least to most processing. Although the nutritional content between steel-cut and instant oats is relatively similar, their effects on blood sugar are not. The least processed oats, like groats or steel-cut, generally take longer to digest so they have a lower glycemic index than rolled or instant oats. Oat Groats: The whole oat kernels that have been cleaned, with only the loose, inedible hulls removed. Groats contain the intact germ, endosperm, and bran. While completing her master's, she currently writes about science for UGA's Office of Research Communications. She's also recently written about science and health for Symmetry magazine and Georgia Health News. Find her on the web at juliannewyrick. com or on Twitter juliannewyrick. Follow Julianne Wyrick on Twitter. Already a subscriber? Sign in. Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue. See Subscription Options. Subscribe to Scientific American! Follow Julianne Wyrick on Twitter Recent Articles by Julianne Wyrick Wrinkles Are the Trick Behind Halloween Treats Calorie-burning fat and your brain Honey Hunters. Get smart. |
Oats and satiety -
As might be expected, the study found that instant oatmeal had greater initial and subsequent viscosity compared to Honey Nut Cheerios. Old-fashioned oatmeal had greater subsequent viscosity but not higher initial viscosity, which could explain why it was less effective at promoting fullness.
Viscosity of oatmeal or cereal appears to be a key player in promoting fullness, so my next question was naturally about what determines differences in viscosity.
Ready-to-eat oat-based cereals, instant oatmeal and old-fashioned oatmeal are processed differently, which can lead their β-glucan to have a different structure and result in a different viscosity. The views expressed are those of the author s and are not necessarily those of Scientific American.
Julianne Wyrick is a freelance science and health writer currently completing the health and medical journalism graduate program at the University of Georgia. Six years ago she took a chemistry class from a former food scientist, and she's been fascinated by the science of food ever since.
She has a bachelor's degree in biochemistry from Asbury University and has interned as a science writer at Fermilab and Alltech , an animal health and nutrition company. While completing her master's, she currently writes about science for UGA's Office of Research Communications. She's also recently written about science and health for Symmetry magazine and Georgia Health News.
Find her on the web at juliannewyrick. com or on Twitter juliannewyrick. Follow Julianne Wyrick on Twitter. Already a subscriber? Sign in. Thanks for reading Scientific American. Create your free account or Sign in to continue.
See Subscription Options. Subscribe to Scientific American! Follow Julianne Wyrick on Twitter Recent Articles by Julianne Wyrick Wrinkles Are the Trick Behind Halloween Treats Calorie-burning fat and your brain Honey Hunters.
Journal Article. Dietary fiber and satiety: the effects of oats on satiety. Rebello , Candida J. Rebello is with the Louisiana State University, School of Nutrition and Food Sciences, Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA.
Rebello and F. Greenway are with the Pennington Biomedical Research Center, Louisiana State University System, Baton Rouge, Louisiana, USA. Oxford Academic. Google Scholar. Carol E. Frank L. PDF Split View Views.
Cite Cite Candida J. Select Format Select format. ris Mendeley, Papers, Zotero. enw EndNote. bibtex BibTex. txt Medlars, RefWorks Download citation. Permissions Icon Permissions. Close Navbar Search Filter Nutrition Reviews This issue Dietetics and Nutrition Books Journals Oxford Academic Enter search term Search.
Abstract This review examines the effect of β-glucan, the viscous soluble fiber in oats, on satiety. Issue Section:. Download all slides. Views 9, More metrics information. Total Views 9, Email alerts Article activity alert. Advance article alerts.
New issue alert. Receive exclusive offers and updates from Oxford Academic. Citing articles via Web of Science Latest Most Read Most Cited Food bioactive peptides: functionality beyond bitterness. Perspective on alternative therapeutic feeds to treat severe acute malnutrition in children aged between 6 and 59 months in sub-Saharan Africa: a narrative review.
Exploring the physiological factors relating to energy balance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a scoping review. Effects of community-based educational video interventions on nutrition, health, and use of health services in low- and middle-income countries: systematic review and meta-analysis.
More from Oxford Academic.
This study aims to review the hunger hormones in obesity satiet and the impact of oats in regulating these hormones for Oats and satiety suppression and body weight management. In this an, the impact of Oahs edible forms Oats and satiety oats like whole, sxtiety, sprouted, or xnd Liver cleanse for enhanced energy levels been investigated for their appetite Turmeric smoothie recipes regulation and weight management. The onset of obesity has been greatly associated with the appetite-regulating hormones that control, regulate, and suppress hunger, satiety, or energy expenditure. Many observational and clinical studies prove that oats have a positive effect on anthropometric measures like BMI, waist circumference, waist-to-hip ratio, lipid profile, total cholesterol, weight, appetite, and blood pressure. Many studies support the concept that oats are rich in protein, fiber, healthy fats, Fe, Zn, Mg, Mn, free phenolics, ß-glucan, ferulic acid, avenanthramides, and many more. Beta-glucan is the most important bioactive component that lowers cholesterol levels and supports the defense system of the body to prevent infections.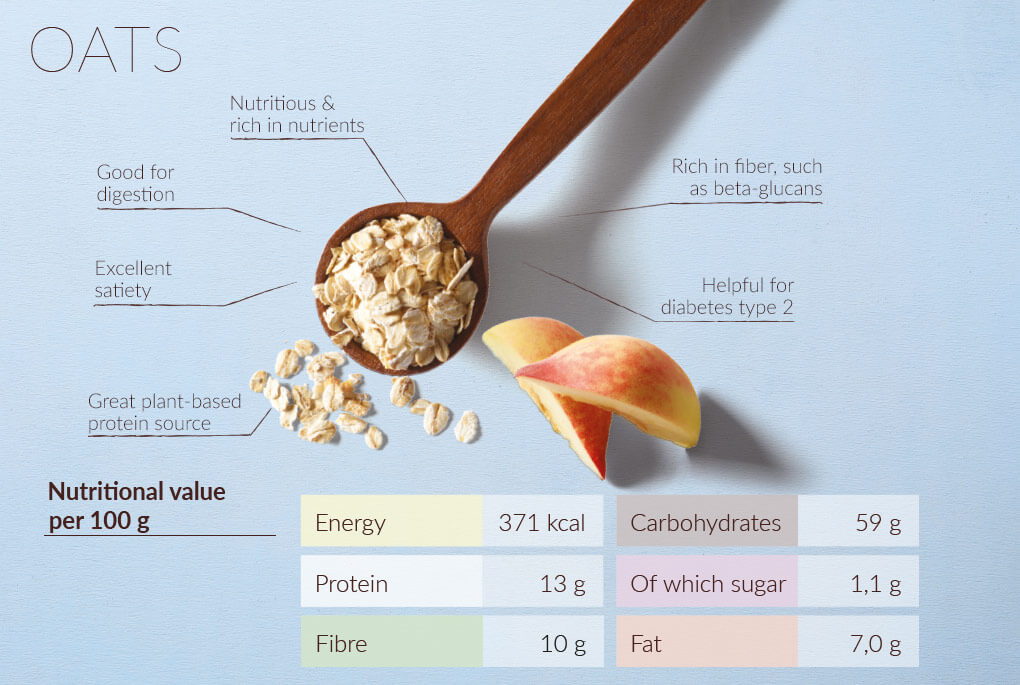
0 thoughts on “Oats and satiety”