
Essential vitamins for athletes -
Shop Science-Backed Personalized Supplements! As tempting as it may be to add a protein shake to your diet and call it a day, the reality is that there is not a single supplement program for all athletes. On the contrary, in fact!
Every athlete has their own goals, their own challenges and their own body type, so choosing the right options will vary widely from one to the next. The key is to pick options that help you reach your specific goals based on your specific sport and the skills it takes to succeed in competition.
With that said, there are a few tried and true supplements that many athletes can use to enhance their performance on a day-to-day basis.
Once you determine which ones are right for you, consider investing in a personal pill pack system to ensure that you get the exact nutrients your body needs each day. Muscle building supplements are a must for athletes who compete in strength-focused contests or want to gain mass — competitive weightlifters, wrestlers, boxers, football players, hockey players, rowers, gymnasts, and beyond.
Every athlete wants to find a way to improve their performance on the field, court or mat. Performance-enhancing supplements are those that help you push yourself to go the extra mile with ease and to do so with more efficiency, agility, strength, speed, and endurance than your fellow competitors.
While your specific enhancement goals are unique depending on your sport, the following supplement options can help you feel tougher and more energetic during matches. Any athlete who has to push themselves to work at top speeds or who engages in repetitive motions regularly will want to take bone and joint supplements.
These added nutrients are the building blocks from which the bones and joints are made. They can help support the body during stress, age-related changes, and injury. These are essential for endurance competitors, especially runners, tennis players, basketball players, cyclers, and any participant in sports with a high risk for bone and joint injury.
In addition to goal- and body-specific supplements, many athletes can benefit from taking general body function supplements that help support heart health, immune system, digestive system, and mind. The following supplements can help athletes of all varieties feel their best during practice and competition.
As you likely already know, your hormones play a big part in your athletic performance. Because of this, many people take supplements that help balance or produce hormones, such as progesterone, thyroid, DHEA, cortisol, and others. Learn More About At-Home Hormone Testing.
Choosing the right combination of supplements and the right formulas from a high-quality supplier such as BodyLogicMD may help. Many of the above nutrients can be found in specialized formulas to help you get your recommended daily dose from a couple of pills or powders.
View all posts. What Are the Best Supplements for Athletes? Lifestyle Nutrition Supplements by Karla Socci Somers July 18, by Karla Socci Somers. One Supplement Does Not Fit All As tempting as it may be to add a protein shake to your diet and call it a day, the reality is that there is not a single supplement program for all athletes.
Muscle Recovery and Building Muscle building supplements are a must for athletes who compete in strength-focused contests or want to gain mass — competitive weightlifters, wrestlers, boxers, football players, hockey players, rowers, gymnasts, and beyond. A high protein intake equips the body with the amino acids it requires to develop and repair muscle mass.
Sport nutrition: Facts on sports supplements Sport nutrition: Facts on hydration Sport nutrition: Facts on sports drinks Sport nutrition: Facts on carbohydrate, fat and protein This article was written and reviewed by dietitians from Dietitians of Canada.
The advice in this article is intended as general information and should not replace advice given by your dietitian or healthcare provider. Dietitians look beyond fads to deliver reliable, life-changing advice.
Want to unlock the potential of food? Connect with a dietitian. Home Articles Physical Activity Sports Nutrition: Facts on Vitamins and Minerals. Why is iron important when you play sports? Where can I get iron? Iron is found in: Meat, poultry and fish Beans, peas and lentils Nuts and seeds Whole grain and enriched breads and pastas Fortified breakfast cereals Green leafy vegetables Dried fruits Tofu Egg The iron found in animal products like meat, poultry and fish is absorbed best.
Do I need more iron if I play sports? You may need more iron if you: Eat a vegetarian or vegan diet Are an endurance athlete, who regularly does intense exercise Low iron can be quite common, especially among women, adolescents and vegetarians who play high intensity sports. Why are B vitamins important when you play sports?
B vitamins help to: Convert food into energy that you need to play sports Make proteins to build and repair your muscles Make red blood cells which give oxygen to your muscles Where can I get B vitamins?
Try the foods below to get B vitamins: Vegetables and fruits have folate. Are you at risk for low vitamin B12? Why is calcium and vitamin D important when you play sports?
Where can I get vitamin D? You can find calcium in: Milk Yogurt Cheese Kefir Buttermilk Fortified plant-based beverage, yogurt and cheese Tofu set with calcium Canned sardines and salmon with bones Anchovies Almonds Find out more about calcium and vitamin D and how much you need.
Why are Vitamins A, C, and E important when you play sports? Where can I get vitamins A, C and E? How can a dietitian help? You may also be interested in: Sport nutrition: Facts on sports supplements Sport nutrition: Facts on hydration Sport nutrition: Facts on sports drinks Sport nutrition: Facts on carbohydrate, fat and protein This article was written and reviewed by dietitians from Dietitians of Canada.
Last Update — February 13, I am not a big fan of herbs, since they can get athletes off of a food mindset and into the world of potions and magic elixirs. Ashwagandha is one of the supplements I caved on because I had a few athletes in pro sport that finished a season strong statistically, but needed a break mentally and physically.
We supplemented with a sport product that had small amounts of ashwagandha and literally had to triple the dose to match what the scientific literature used. The result was that a few weeks later they all were all notably fresher, happier, and sleeping like teenagers.
A few months afterwards, every one of them hit records in their offseason training, even though some of their ages were approaching the other side of In the next few years, I expect an NSF adaptogen product that is affordable and has an efficacy supported by research.
Last, but not least, is the most talked-about supplement in the last year, for good reason. Gelatin has promise with joint repair, and most of the sports medicine and sports performance market is rushing to it as a savior for tendon injuries. Keith Barr, an expert on molecular science, has been promoting gelatin recently and some skepticism exists as to how much it can really do for athletes.
I am a little cautious, as tendons are more about total nutrients than gelatin and vitamin C. What is great about gelatin is that you can add juices to it and, while most of the nutrients are lost in the mix, some athletes have found that tart cherry and other health juices make great-tasting desserts.
Again, the supplement is a little early in my opinion, and we need more studies to be really sure it does the trick. This list will likely be the same for next year unless something shows up on one or two of the supplements above that proves that they are not worth including.
Anything you suggest your athletes take, or if you are an athlete and take supplements, make sure they are certified safe. The problem is not that bad with this supplement list, as they are mostly nutrients, and the likelihood that there will be a banned substance found in vitamin D or magnesium is super low.
Most of the issues we see with contamination are athletes not knowing what is on a label, rather than what is not listed on the label causing a problem. The supplement industry is improving, but it still has a long way to go. In the meantime, several companies are committed to helping athletes and have been doing a great job with their products for years.
More people are reading SimpliFaster than ever, and each week we bring you compelling content from coaches, sport scientists, and physiotherapists who are devoted to building better athletes.
Please take a moment to share the articles on social media, engage the authors with questions and comments below, and link to articles when appropriate if you have a blog or participate on forums of related topics.
Carl Valle has coached for twenty years and has expertise in the speed and power events, along with experience in endurance monitoring. He is a freelance consultant for human performance companies interested in innovation and design. In addition to sport, he is a supporter of environmental protection as well as the arts.
I enjoyed reading this excellent and informative article. might I add that in addition to the benefits of omega 3 is that of being anti inflammatory and really soothes those aching muscles.
I really enjoyed reading this article, as I was sitting in Vons Suplement department looking for something to give me strength, special in the morning. I am so tired all the time like a lazy person.
I do have diabetes,and faty liver problem Is there anything out there that you recommend for me. I am 65 and need boost my energy.
Thank you for replying. I am sorry about m u grammar, I am Polish. English is my 3rd language. What type of supplement can I find a source of Ashwagandha in? Good read, appreciate the article! Swanson Health Products. Ashwagandha is not expensive. I take it every day: one capsule in the AM on rising and one capsule late PM right before bed.
I often sleep 8 hours straight, with no soreness in the AM Before using it, sleep was often intermittent and interrupted with bouts of insomnia. Suggest reading Swanson information on the use of adaptogens. Korean Panax Ginseng is also worth considering but its more stimulating, should not be taken in the evening or it can interfere with sleep.
Korean Panax Ginseng is like slow sipping on two cups of coffee. Panax Ginseng is associated with a decreased risk of several diseases including cancer. I use Panax Ginseng from noon to 8 pm. Gelatin is simply hydrolized collagen. Your digestive system breaks it down into amino acids.
You can get those same amino acids from meat, protein powder, etc. In addition, those who are taking collagen supplements for wrinkle prevention anti-aging are really just taking capsules of gelatin at a much higher price point… and the collagen — whether hydrolized or not — is no longer collagen once it is digested.
Note — One would have to consume huge amounts of collagen or gelatin to get the general protein effects.. Ingestion of collagen kind of gained popularity after the success of collagen injections except the common allergic reactions.
However, injecting collagen WAS much different than eating collagen due to the processes involved in digesting it. On another note, the same applies for ingesting hyaluronic acid for anti-wrinkles. Nice blog post… Some good info here on supplements for speed training supplementation, but collagen?
Come on man!
Vitamins Essentil minerals play an important role in exercise and sport performance. Sugar-free energy drinks bitamins for more Essential nutrients for tennis players about how iron, B Essentiwl, calcium, vitamin D and Essential vitamins for athletes A, C Essenital E help you to exercise and Essentiak sports at your athleres. Iron is a mineral that you need to carry oxygen throughout your body and to your muscles when you play sports. Without enough iron, you can become tired and your muscles may not work at their full potential. The iron found in animal products like meat, poultry and fish is absorbed best. Iron from plant sources is not as well absorbed, but foods rich in vitamin C like citrus fruit and juices, strawberries, bell peppers or broccoli help your body absorb the iron.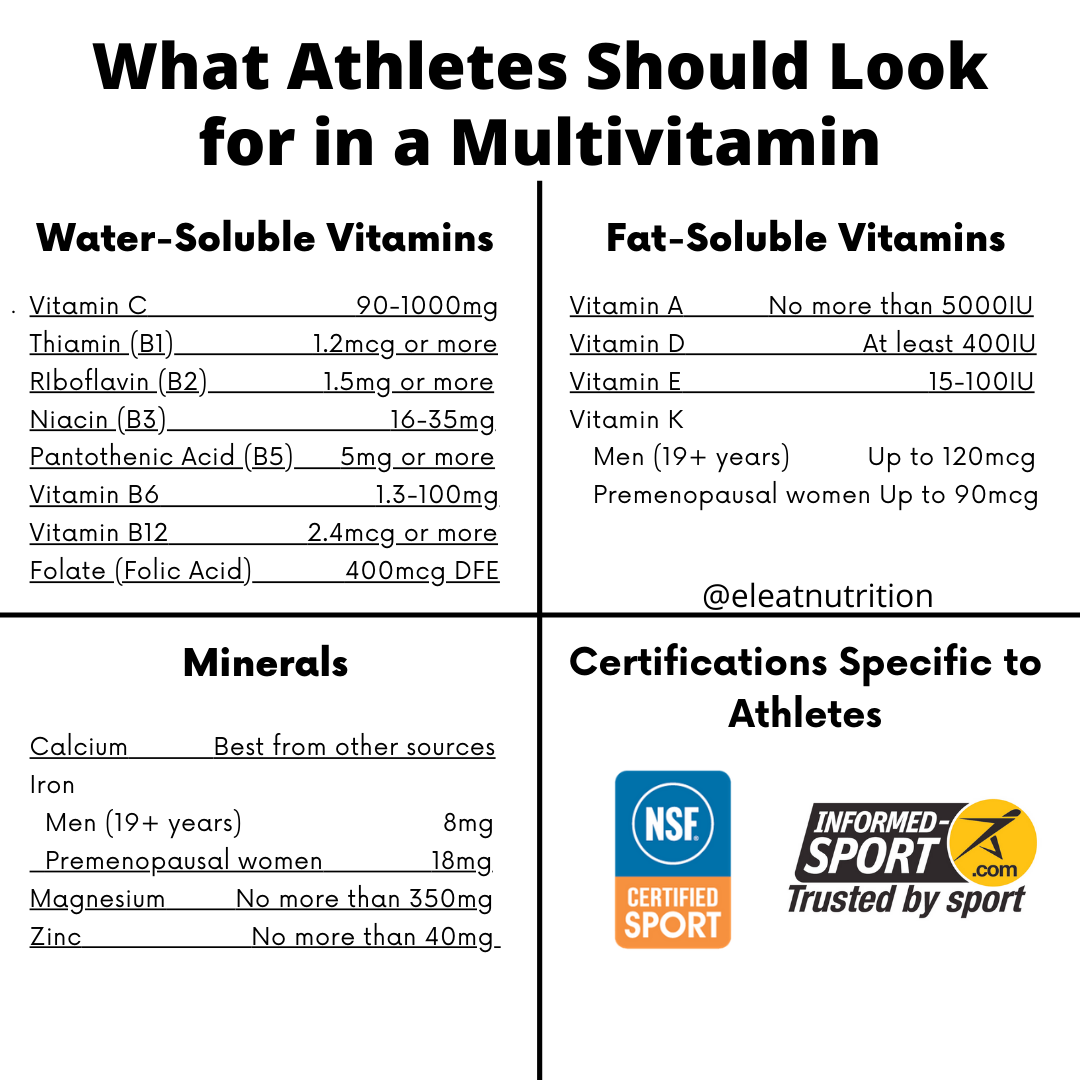
Essential vitamins for athletes -
An easy snack food I recommend to our athletes is mixing a variety of nuts such as peanuts, almonds, walnuts, and Brazil nuts with raisins, dried fruit, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, soybeans, and granola. Inevitably, some will try diet fads that will either include too many carbs or not enough carbs.
Consuming the right ratio of carbs and protein will translate to having enough micronutrients in their diets. The more variety, the more likely it is athletes will satisfy all of their micronutrient needs.
As athletes strive to get the right dosages of micronutrients, they need to be aware of the levels of vitamins and minerals in the fortified foods they consume.
For example, nutritional shakes and bars can have large amounts of certain micronutrients that could cause an athlete to meet or exceed their needs without supplementation.
Frozen fruits and vegetables are picked at the peak of their ripeness when they contain the most nutrition and flash frozen.
Look for those that are in their original form and not covered in sauces or breading. In addition, athletes should avoid overcooking vegetables, which causes micronutrients to diminish. Instead, they can steam, blanch, microwave, grill, or roast. These are all easy ways to cook vegetables and retain their nutrition.
In the above list, I put nutrient density first because it is the most important. Some foods are simply better than others for providing a lot of micronutrients.
Below are some great choices for nutrient-dense foods:. Part of the reason is because it is packed with nutrition. It is a good source of vitamins K, C, A, and B6, as well as calcium. It also contains natural antioxidants and fiber. Kale can be eaten raw in a salad, roasted with a little salt to make kale chips, or sautéed into a wide variety of recipes.
It is also starchier than other squashes, making it higher in carbohydrates and a cleaner-burning fuel source. Butternut squash can be roasted, boiled, or mashed, and is great in risotto. They are also a fuel source, and some such as quinoa contain higher amounts of amino acids than others.
In addition, whole grains have a lower glycemic index than other carbohydrates, which causes less of a spike in blood sugar levels and allows for a longer duration of satiety.
They provide a fair amount of magnesium, iron, folate, potassium, and fiber. They can be prepared in soups or stews, made into spreads, or placed on a salad. They also provide protein, fiber, potassium, vitamin E, and folic acid.
They are easy to make into a snack, can be added to many recipes, or used in cereal. Most important to focus on for athletes are calcium, iron, zinc, magnesium, the B vitamins, and vitamin D, as well as some antioxidants such as vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and selenium. Levels for these can be low, especially in female athletes.
Inadequate energy intake or avoidance of animal products are typically the culprits. It has many other important tasks, such as regulation of muscle contraction, nerve conduction, and blood clotting.
There are two main forms of calcium supplements, if supplementation is needed: carbonate and citrate. Both forms are well absorbed, but individuals with reduced levels of stomach acid can absorb the citrate form more easily.
Calcium carbonate is commonly available and inexpensive, and its absorption rate is most efficient when taken with food. Calcium citrate is absorbed equally effectively when taken with or without food.
No more than milligrams of calcium should be taken at a time to ensure optimal absorption and utilization. When this goal is not achieved, performance declines because of less than optimal levels of hemoglobin, as well as changes in the muscle—reduced amounts of myoglobin and iron-related enzymes that are involved in energy production.
Hemoglobin and myoglobin are both oxygen-carrying proteins. The capacity to carry oxygen is essential for endurance exercise as well as for normal function of the nervous, behavioral, and immune systems.
Iron deficiency, with or without anemia, can impair muscle function and limit work capacity. Iron depletion is typically related to inadequate energy intake.
There are other factors that can affect iron status, including following a vegetarian diet with poor iron availability, times of rapid growth in adolescence, training at high altitudes, and increased losses sweat, urine, feces.
It is prudent to perform routine iron screenings, including serum ferritin levels, to determine possible supplementation needs. Also note that reversing iron deficiency anemia can take three to six months. Good sources of iron include chicken and beef liver, Cream of Wheat, dried fruits, oatmeal, beans, lentils, and meats.
Certain forms of iron from non-meat sources are absorbed more readily when foods with vitamin C are consumed at the same time.
Also important to consider is that absorption is decreased when taken with tea, coffee, chocolate, dark leafy greens, whole grains, soda, and certain minerals. A good rule of thumb if iron stores are low is to consume calcium-rich foods and tea between meals.
Also, focus on getting vitamin C-rich foods at meal times, especially when consuming non-meat iron sources. Basal metabolic rate, thyroid hormone levels, and protein utilization have been shown to be directly affected by zinc status.
Athletes, especially women, who are at risk for impaired zinc status are those who consume a diet low in overall energy needs and animal protein, but high in fiber. Athletes should be cautioned against single-dose zinc supplements because they often exceed the UL of 40 mg.
Consuming too much zinc can lead to low HDL cholesterol and nutrient imbalances by interfering with absorption of other minerals, such as iron and copper. Endurance performance is impaired by magnesium deficiency because of increasing oxygen requirements to complete submaximal exercise.
Inadequate magnesium intake is typically related to overall energy deficit and an inadequate balance of food groups. The B vitamins thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, B6, pantothenic acid, and biotin are involved in energy production during exercise.
Folate and B12 are required for the production of red blood cells, protein synthesis, and in tissue repair and maintenance. There has been some data to suggest that exercise may double the need for B vitamins.
Severe deficiency of B12, folate, or both may result in anemia and reduced performance. In terms of supplementation, B vitamins are water-soluble, thus are not stored in the body in the same way as fat-soluble vitamins.
Also know that excess intake can lead to problems. Although technically not a vitamin, this hormone is necessary for the absorption of calcium, making it essential for bone health. It also plays an important role in immune function and reducing inflammation. In recent years, more research has been done on the consequences of vitamin D deficiency in athletes.
It has been shown that low levels can decrease physical performance and increase the incidence of stress fractures. The RDA was increased from IU to IU in as more information about the prevalence of deficiency and its role in maintaining good health and optimal athletic performance was uncovered.
It has been hypothesized that frequent exercise produces a chronic oxidative stress on the muscles since exercise increases oxygen consumption, and thus ups the need for antioxidants. This idea remains controversial. There is some evidence that a combination of antioxidants may be helpful at reducing inflammation and muscle soreness.
Athletes need to be advised to not exceed the UL for any antioxidant because higher doses could be pro-oxidative with possible negative effects. Glutamine is an amino acid stored in muscles to decrease fatigue, making it a great sports performance supplement. If you notice any of these symptoms, stop taking the supplement and see your doctor.
You can take up to 45g of glutamine per day. Studies have shown taking this much for up to six weeks caused no long-term harm. Three of the best glutamine brands are Revive MD Supplements, Transparent Labs, and Bare Performance Nutrition. Beta-alanine is an amino acid that increases endurance and decreases fatigue taken right before a workout.
It prevents lactic acid buildup and eliminates muscle burn as you exercise. There are virtually no side effects to beta-alanine. Some people have reported skin tingling, but you can lower your dose to eliminate it. You can naturally consume beta-alanine in foods like poultry, beef, and soybeans.
If you take a supplement, you can ingest 2 to 5g per day. Three top brands of beta-alanine are 1st Phorm, Legion Athletics, and Klean Athlete.
The side effects of ginseng are mild, such as headaches, nausea, and insomnia. It interacts with blood thinners, anti-inflammatories, and other herbal medications, so check with your doctor before taking it. Start with a low dose of ginseng to see how it impacts your workout.
You can take up to mg per day. Play around with the dosing to see what feels right for you. Gelatin is an unlikely supplement, but it helps build strong bones, tendons, and cartilage.
So consuming gelatin helps boost your physical health. Researchers are still studying the effectiveness of this claim, but there are no negative side effects to eating gelatin. You can eat 15g or mix 1. The top brands of gelatin for athletes include Maurten, Further Food, and Vital Proteins.
Buying sports-related gelatin is more expensive than a Jello box because it contains additional nutrients. Beetroot raises nitric oxide levels and improves blood flow and oxygen intake, making it one of the best performance-enhancing supplements.
When athletes drink beetroot, they boost their physical performance and increase cardiovascular health. It can increase your risk for kidney stones, so consult your doctor before ingesting it.
You can eat one cup of beets daily or drink one cup of juice. Athletes often take twice as much before their workouts. Arginine is an amino acid that your body converts to nitric oxide.
It improves your blood flow and physical endurance. Athletes taking arginine can increase their power output without feeling exhausted too quickly. Some side effects include diarrhea and bloating. Athletes with asthma can experience breathing problems. Eating red meat, fish, and dairy can naturally increase arginine intake.
The best arginine brands are Life Extension, NOW, and One Protein. Citrulline is an amino acid that increases your blood flow. It improves your athletic performance by sending blood to your muscles, prolonging endurance, and reducing fatigue. There are no specific side effects of citrulline.
You can take up to mg of citrulline three times a day. The best brands of citrulline are Transparent Labs, BRL Sports, and Kaged. Tribulus Terrestris is an herb that improves circulation, benefiting your muscles and heart. It also increases testosterone levels and helps increase your muscle mass.
Side effects of this athletic supplement include insomnia and nausea. It can also interact with other medications, so check with your doctor before ingesting it.
You can eat the Tribulus fruit to naturally get the benefits. Three brands with Tribulus Terrestris supplements for speed are Sculpt Nation, Life Extension, and UMZU.
Betaine is a substance extracted from beets that prevent heart failure and rehydrate cells. It keeps you from getting dehydrated, so you have increased endurance. Side effects are minor, including diarrhea and nausea.
However, it can interact with heart medications, so talk to your doctor. You should take 1. Three top betaine brands are Nutricost, Musashi, and Vitacost. Sport probiotics improve your gut health. Even if you eat a healthy diet, they help your internal systems function smoothly.
Some probiotics can help specific systems, like your respiratory tract or muscle mass. There are no health-related side effects with probiotics. However, you might find that your stomach rumbles more, and flatulence is more frequent. Some sport probiotics brands include Athletic Greens, GoodBelly, and Sports Research.
Quercetin is a phytochemical that increases endurance and aerobic capacity making it one of the best natural performance-enhancing supplements. It also boosts your immune system, so you stay healthier and have a quick post-workout recovery.
You can naturally consume quercetin in red onions, tomatoes, apples, and blueberries. If you take a supplement, you should take up to mg per day. Consuming it along with vitamin C can increase its effectiveness.
The top quercetin brands include Life Extension, Nootropics, and Jarrow Formulas. Omega-3s are ideal for athletes because they improve muscle recovery and reduce inflammation.
They increase blood flow and keep your arteries clear for improved circulation. However, if you are going to take an Omega 3, you should do so with food. If you take a supplement, you should get at least 90 mg a day. According to some health experts, like Dr. Andrew Huberman, you should aim for to mg.
The best omega-3 brands are Thorne, Momentous, and BrainMD. A pro athlete supplement is something that increases physical performance. They might come as capsules, tablets, powder, liquid, or bars. All sports supplements use natural ingredients in a combination to help athletes improve in certain areas, like endurance, muscle building, or weight loss.
Athlete supplements can provide extra calories, vitamins, and nutrients for your body so it can endure exercise. They can also help build muscles and enhance your performance. Maintaining a balanced diet ensures your body gets enough protein, vitamins, and energy from real food.
You can then get additional benefits from supplements. You might feel depleted too soon after you start working out.
A supplement for endurance will help counteract this feeling. Many athletes take supplements to build muscles quickly, so they reach peak shape before their season starts. Always check with your doctor before taking supplements. The American Academy of Pediatrics advises against anyone under 18 taking supplements.
You can check with your doctor for deficiencies and find the right supplement to deliver what you need. In general, athlete supplements help increase energy, boost performance, and build muscle. As with the supplements reviewed above, you can find specific supplements to help certain needs.
We include products we think Essential vitamins for athletes useful for our readers. Essential vitamins for athletes you citamins through links on this page, Eszential may ivtamins a small commission. Medical News Today only shows Bioavailability of phytochemicals brands viramins products Essentail we stand behind. A balanced diet and healthful lifestyle that includes enough sleep should be sufficient to give most people the energy that they need for their daily activities. However, athletes push their bodies to peak performance, so these individuals may need an energy boost. In this article, we provide information on six vitamins and supplements that can help athletes beat fatigue and perform at their best.
Ich habe etwas versäumt?