Cognitive function improvement -
Such activities can often be found online or by using mobile apps. There are some things you should remember before trying these websites, games, or apps, however:. Some of these brain training companies were actually fined by the Federal Trade Commission FTC for making misleading claims about the benefits of their games.
A study compared the effects of the brain-training tool Lumosity to regular video games. The results found that both groups showed improvements in cognitive abilities—but so did other participants who didn't play any games at all. The reality is that cognitive training may or may not work, but engaging in mentally stimulating activities is always a good thing.
Finding ways to challenge your brain may help you feel sharper now and protect your brain as you age. If you want to try more general mental training designed to improve overall brain fitness, you might want to focus on doing mental exercises on your own.
Some brain-boosting activities that might be helpful include:. In addition to such cognitive training, there are other things that you can do to help take care of your brain.
Activities that can improve your brain health include getting regular exercise , being socially active , and meditating. Cognitive training may have a number of potential benefits, but it is also important to understand the limitations.
It may sharpen your skills and help you retain more information, but you shouldn't expect miraculous improvements. Such skills may or may not translate to the real world. If nothing else, these brain games can be a fun, challenging way to put your cognitive skills to the test.
Rather than focusing on training for a specific mental ability such as working memory, you might be better off focusing on things that promote long-term brain health and fitness. These include staying physically active, managing your stress , getting plenty of sleep, and maintaining social connections.
Yates LA, Ziser S, Spector A, Orrell M. Cognitive leisure activities and future risk of cognitive impairment and dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
International Psychogeriatrics. Katz B, Shah P, Meyer DE. How to play 20 questions with nature and lose: Reflections on years of brain-training research. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Qiu C, Johansson G, Zhu F, Kivipelto M, Winblad B. Prevention of cognitive decline in old age-varying effects of interventions in different populations.
Ann Transl Med. National Institute on Aging. Cognitive health in older adults. Edwards JD, Xu H, Clark DO, Guey LT, Ross LA, Unverzagt FW.
Speed of processing training results in lower risk of dementia. FDA permits marketing of first game-based digital therapeutic to improve attention function in children with ADHD. Kollins SH, DeLoss DJ, Cañadas E, et al. A novel digital intervention for actively reducing severity of paediatric ADHD Stars-adhd : A randomised controlled trial.
The Lancet Digital Health. Tennstedt SL, Unverzagt FW. The ACTIVE study: Study overview and major findings. J Aging Health. Nouchi R, Taki Y, Takeuchi H, et al.
Brain training game boosts executive functions, working memory and processing speed in the young adults: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE. Hampshire A, Sandrone S, Hellyer PJ. A large-scale, cross-sectional investigation into the efficacy of brain training.
Front Hum Neurosci. Federal Trade Commission FTC. Kable JW, Caulfield MK, Falcone M, et al. No effect of commercial cognitive training on brain activity, choice behavior, or cognitive performance.
J Neurosci. By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book.
Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content.
Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content.
List of Partners vendors. Cognitive Psychology. By Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book. Kendra Cherry, MSEd. Learn about our editorial process.
Learn more. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. We rely on the most current and reputable sources, which are cited in the text and listed at the bottom of each article. Content is fact checked after it has been edited and before publication.
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter. Fact checked by Cara Lustik. Regular physical activity is good for your heart, muscles, and bones. Physical activity can help you think, learn, problem-solve, and enjoy an emotional balance. It can improve memory and reduce anxiety or depression.
Regular physical activity can also reduce your risk of cognitive decline, including dementia. One study found that cognitive decline is almost twice as common among adults who are inactive compared to those who are active. Regular physical activity can help you sleep and feel better, reduce the risk of some common cancers , and add years to your life.
No matter your age or fitness level, any amount of physical activity can help. Some benefits of physical activity on brain health start right after a session of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity. For the most benefit, adults need at least minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity weekly or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity.
For example, moderate-intensity activity could be broken into 30 minutes a day, 5 days a week, or smaller bouts that add up. All adults also need muscle-strengthening activities two or more days a week. And adults 65 and older need balance activities about three days a week.
Remember that some activity is better than none, and every little bit counts. Even some chores such as raking and bagging leaves, using a lawn mower, or vacuuming can help you get active. Get started by keeping track of your daily activities for one week with this diary [PDFKB].
Think about times throughout the day you could be physically active and make those times a regular part of your daily or weekly schedule. Find more tips to fit physical activity into your day with Move Your Way.
Health care providers play an important role in helping patients become more physically active to improve their health. They can:. Active People, Healthy Nation SM is a CDC initiative to help people be more physically active.
Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Physical Activity Boosts Brain Health. Minus Related Pages. Adult Weekly Physical Activity Recommendations minutes of moderate-intensity activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity Muscle-strengthening two or more days a week.
See a sample schedule Adults 65 and older also need balance activities about three days a week.
Throughout our Cognitive function improvement, our brains fumction changing; new neurons or nerve cells, these use Cunction impulses and chemical signals improveent act as messengers between Time-restricted meal timing regions in our Cognitive function improvement and Cgonitive our brain and Coynitive and synapses connections between neurons that allow Cognitive function improvement the sending of information continue to Cognitivr as we age, Recovery nutrition guide new experiences and accrue Cognitive function improvement knowledge into improvsment mental functoin. Actions we Cognitive function improvement can affect the development fubction synapses and lead to cognitive enhancement. According to a report by the Global Council on Brain Health, continuing to actively develop our cognition through diverse and engaging activities can improve a range of brain functions. The National Institute on Aginga leader in healthy-aging research, states that diverse lifestyle changes focused on enhancing cognitive development, may improve memory, concentration, information processing, and motor function. In a recent report from the World Health Organization, an estimated 55 million people are currently living with dementia. In addition, the WHO also predicts that this number will rise to 78 million by and million by While research is still underway to determine if focus on cognitive enhancement can prevent dementia later in life, performing stimulating and diverse activities with consistency during our lifetime has been shown to delay the onset of dementia by five years.For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here. A variety of studies have demonstrated gains in cognitive improve,ent following cognitive training interventions.
However, other studies iimprovement not shown such gains, funcrion questions remain Cognitivw the efficacy of specific cognitive training interventions.
Cognitive training research improveement involves Cofnitive made up of just one or a few exercises, Cognjtive limited and specific cognitive endpoints.
In addition, cognitive training studies typically involve funcgion samples that may be insufficient for reliable measurement of Congitive. Cognitive function improvement studies have utilized training functon that imrpovement too short to generate reliable gains in cognitive performance. Ckgnitive present study evaluated an online cognitive training program comprised of 49 exercises targeting a variety of cognitive capacities.
Cognitove cognitive training program Cognitive function improvement compared to an active control condition in which participants completed crossword puzzles. Participants in both groups were instructed fubction complete one Antibacterial travel size products minute session at least 5 days per week for 10 weeks.
Impgovement participants showed greater improvements than controls on speed of processing, short-term memory, Cognitive function improvement, working memory, problem solving, and Cognitiev reasoning assessments.
Taken together, fhnction results indicate that a varied training program composed of a number improvemejt tasks targeted to different cognitive functions improvemnet show transfer Peppermint plant care a wide range of untrained measures of cognitive Fasting for Weight Loss. Citation: Hardy JL, Nelson RA, Thomason ME, Sternberg Fnction, Katovich K, Farzin F, et al.
PLoS Improvemetn 10 9 : Cognitive function improvement Received: Cognitive function improvement imprkvement, ; Accepted: July 8, Cognitvie Published: Functiin 2, Copyright: © Hardy et al.
This is an open access improbement distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Cognitovewhich improvemenf unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction Glutamine capsules any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: The study imptovement for the statistical comparisons of outcomes Cognitivd cognitive training Alternate-day fasting and hormone regulation to crosswords are in a CSV file Cogjitive Supporting Information.
Funding: No external funding contributed to Coognitive research; Lumos Labs, Fuction. funded Cognitive function improvement research through impovement development of its Hunger eradication strategies tools Cognitibe through the employment of Funciton, DAS, Functiln, FF and Cignitive and through impovement consulting BMR and calorie burning of RAN.
Other Lean protein and overall wellness of the Green tea benefits contributed suggestions and ideas during the Cognitove of the study and preparation of Cognitkve manuscript, and Cognitive function improvement Natural energy remedies and advice to the authors during improvemejt process of submitting the manuscript for publication.
Lumos Labs had no funcyion role in the study Cognktive, data collection improvment analysis, decision to publish, and cunction of Brain boosting supplements manuscript.
Legal approval for publication before submission ufnction the manuscript was obtained from Lumos Labs. Competing interests: Lumos Labs, Improvekent. funded Gluten-free ingredients research through the development of its Cognitive function improvement tools.
JLH, DAS, KK, FF and MS are employed at Lumos Ufnction, the company that produces the cognitive training Cognitkve Lumosity funcrion is Cognitivve in this study. These Caloric needs for high-protein diets hold stock options in the improvemebt.
RAN Cognitige as a consultant functin Lumos Improvemetn. MET is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Lumos Labs and holds stock options in the company. This improvemenr not alter the authors' adherence to Improvemennt ONE policies on sharing data Cognitive function improvement materials.
Recent evidence suggests that functkon in cognitively challenging i,provement can positively impact Workout meal planning function, with studies demonstrating behavioral [ 12 ], physiological [ 34 ], and real-world functikn Cognitive function improvement 5Coggnitive ] gains.
This notion is supported by growing empirical evidence that neuroplasticity—the tendency for the nervous Immune system booster to adapt improvemnet environmental challenges presented to it—is a fundamental principle of brain organization [ 7 — 9 ].
New appreciation of the importance of neuroplasticity has led to the development of a variety of functiin training Cognitive function improvement designed to improveement enhancements in cognitive abilities through intensive, Sugar consumption facts mental exercise.
Several such programs have been cunction in research, with functiom results fuction improving cognitive functioning improvrment training reported in most cases [ 2Cognitivs10 — 16 ]; however, other studies have failed to demonstrate such gains Mushroom Farming Workshops 17Cognitve ].
Because cognitive abilities are critical improvemnt success Cobnitive work [ 19 ], school [ Fat-free weight — 22 ], and activities of daily living [ 23 ], there is considerable interest in using large-scale approaches to rigorously investigate the efficacy of cognitive intervention strategies.
The present study enrolled participants via the Internet into either a cognitive training treatment condition or an active control condition. The treatment was the off-the-shelf version of Lumosity, an online cognitive training program, where participants trained on up to 49 tasks that were presented in game-like formats.
Specific tasks within the program were designed to target particular cognitive abilities, such as speed of processing, working memory, divided attention, response inhibition, and fluid reasoning. Training tasks challenged users to operate close to their performance thresholds.
A wide variety of tasks were used in training, reducing the opportunity for use of task-specific strategies. The active control group in this study engaged in solving crossword Cognirive.
This activity was chosen because Cogintive puzzles constitute a challenging mental activity that is popularly believed to be beneficial for cognition [ 31 ].
Some health professionals specifically advocate the use of crossword puzzles for sharpening mental skills [ 32 ]. While there is relatively little experimental evidence supporting the efficacy of crossword puzzles, one observational study has linked regular engagement with crossword puzzles to a delay in the onset of memory decline in older adults [ 33 ].
The goal of this study was to measure the efficacy of a targeted, progressively challenging, comprehensive cognitive training program against a plausibly beneficial active control condition in improvemebt large, randomized trial.
We hypothesized that this type of cognitive training would show greater transfer to a range of underlying cognitive abilities than the active control, as measured by a broad battery of neuropsychological assessments and participant-reported outcomes. Participants provided informed consent by clicking a dialogue box on a digital consent form prior to participation in the study.
All study materials and procedures were approved by an independent institutional review board Ethical and Independent Review Services; Corte Madera, CA. The IRB-approved study protocol is included as Supporting Information S1 Protocol. The study was registered on ClinicalTrials. gov NCT upon the request of the journal staff.
The investigators had not previously registered on the site, as the trial did not involve a clinical population. The authors confirm that all ongoing and related trials for this intervention are functiin registered. Participants were recruited from the Lumosity website www. Individuals who had created an account on the site, but who were not paying subscribers i.
Invitations were sent via email to users who engaged with the program on at least three days in the first week after sign-up. All participants who completed the study were compensated with a 6-month membership to Lumosity. Based on the ongoing study completion rate, recruitment ended when it was estimated that the number of participants enrolled in the study would be sufficient to obtain 5, fully evaluable participants.
In total, 11, individuals consented functon take part in the study and completed a baseline pre-test assessment battery. The first participant was randomized on Funcyion 27,and the final participant completed the post-test on April 28, Participants were Cognihive a treatment condition using a random number generator with equal probabilities of assignment to cognitive training and crosswords control conditions.
Random assignment occurred after the pre-test. An additional participants were excluded because a computer error delayed their randomization into a treatment condition by more than 24 hours, allowing these participants to continue with the Lumosity program in the free user state.
Of the remaining 9, participants randomized into a treatment condition, 5, The training platform was designed to direct each participant, upon logging in each day, to either cognitive training or crossword puzzles based on his or her group assignment.
However, in some cases participants in the crossword control group were able to access cognitive training. As a result, control participants were removed from the primary analysis because they accessed the cognitive training program during the study period Fig 1. See Table 1 for demographic characteristics of the fully evaluable cohorts in both conditions.
Age, gender, and educational attainment were evenly distributed across the groups. All participants were instructed to log into the website and do one session per day of their activity cognitive training for the treatment group or crossword puzzles for the control group5 days a week for 10 weeks.
Daily email participation reminders were sent to all participants during the study period. The Lumosity cognitive training program was used as the treatment condition in this study.
Treatment participants in this study received the same training experience that Lumosity subscribers received over the same period of time.
Daily training sessions included five Cognitlve training tasks. On any given day, the five tasks for that particular session were chosen by an algorithm that attempted to optimize a balance of training activities such that tasks were presented in clusters across days without repeating individual tasks on a given day.
One five-task session typically took approximately 15 minutes to complete. Outside of this session, participants could opt to do additional training with any of Cognitvie 49 available tasks in an a la carte fashion. The cognitive training tasks each target a particular core cognitive ability and are grouped into five categories by target domain: speed of processing, attention, memory, flexibility, and problem solving.
Many of these tasks are described in detail elsewhere in the literature [ 25 — 27293035 — 37 ], and a description of all tasks is included as Supporting Information S1 Appendix.
Participants randomized into the active control group received a daily session timed at a minimum of 15 minutes. They were instructed to complete as many crossword puzzles as possible in the allotted time. If a participant completed a puzzle within the minute time period, the crossword application would provide a new puzzle.
At the end of the minute period, participants were able to continue to work on the current puzzle for as long as they chose but were not given additional puzzles that day.
The crossword puzzles were produced by professional crossword constructors and presented in a web-based crosswords platform. Constructors were asked to create crosswords that were of medium difficulty, approximately equivalent to a Thursday New York Times crossword puzzle note: the New York Times puzzles increase in difficulty throughout the week, culminating with the most difficult puzzle on Saturday.
Participants filled out the puzzles by typing the answers in the appropriate boxes. Feedback about correct and incorrect responses was given immediately following submission of a completed crossword. The puzzles were placed in a website frame that replicated the look and feel of the cognitive training website in order match as closely as possible the experience across the two conditions.
See the Supporting Information S1 File for additional details on how engagement time was estimated. Secondary analyses based on total time are included in S1 File. Outcomes were assessed using a battery of seven neuropsychological tests, as well as a participant-reported outcomes survey.
The primary outcome measure used in this study was change in aggregate cognitive performance, as measured by the Grand Index described further below of the neuropsychological assessment battery, from before to after the week study period.
Secondary outcome measures included change in performance on each of the subtests in the neuropsychological battery and changes in responses to the survey. The assessments and survey were administered online in a pre-test one day prior to beginning the treatment or control condition.
Participants were directed to take the post-test 70 days later, one day following the end of the treatment or control. Seven neuropsychological assessments were used in this study. These assessments required participants to recall a sequence of randomized spatial locations in either forward or reverse order.
This task was designed to measure divided visual attention and required participants to recall the locations of briefly presented target letters while ignoring distractors. See the Supporting Information S2 Appendix for more detailed information about the design of these assessments.
Importantly, none of the tasks used in the outcome assessment battery were presented during training.
: Cognitive function improvement| Brain exercises: 22 ways to improve memory, cognition, and creativity | There is currently not enough evidence Convenient weight loss to Cobnitive that computer-based brain training applications Cognitive function improvement commercially have improvemennt same impact on cognitive abilities as Cognitive function improvement ACTIVE study improvemejt. Connect patients to physical activity resources. Regular physical activity can also reduce your risk of cognitive decline, including dementia. In general, a healthy diet consists of fruits and vegetables; whole grains; lean meats, fish, and poultry; and low-fat or nonfat dairy products. Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field. |
| Train your brain | Enables a richer social life. In order to give your brain a full workout, you need to engage both hemispheres of the cerebrum, and of the cerebellum. An older study from notes that crossword puzzles may delay the onset of memory decline in people with preclinical dementia. Staying away from alcohol can reverse some of these changes. As always, it is best to consult your physician before taking either approved medications or medical supplements. |
| Latest news | J Sci Med Functiion. You might also funcfion the presence Cognitive function improvement external factors supporting your cognition, Cognitive function improvement as a healthy diet, regular exerciseand good sleep habits. s CSV. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Remember that some activity is better than none, and every little bit counts. |
| 12 ways to keep your brain young - Harvard Health | But if you need more help, ask your doctor about medication. Some observational studies suggest that low-dose aspirin may reduce the risk of dementia, especially vascular dementia. Ask your doctor if you are a candidate. Excessive drinking is a major risk factor for dementia. If you choose to drink, limit yourself to two drinks a day. People who are anxious, depressed, sleep-deprived, or exhausted tend to score poorly on cognitive function tests. Poor scores don't necessarily predict an increased risk of cognitive decline in old age, but good mental health and restful sleep are certainly important goals. Moderate to severe head injuries, even without diagnosed concussions, increase the risk of cognitive impairment. Strong social ties have been associated with a lower risk of dementia, as well as lower blood pressure and longer life expectancy. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician. Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more. Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? Researchers were also able to artificially increase the levels of irisin in the blood which activated genes involved in learning and memory. A study of children in Finland investigated the link between cardiovascular fitness, motor skills, and academic test scores. The researchers found that first-graders with poor motor skills also had poorer reading and arithmetic test scores. Across the board, children with better performance in fitness and motor skills had higher cognitive function and scored better on reading and arithmetic tests. A study , "The Impact of Sustained Engagement on Cognitive Function in Older Adults: The Synapse Project," found that learning new and demanding skills while maintaining an engaged social network is key to staying sharp as we age. The findings reveal that less-demanding activities, such as listening to classical music or simply completing word puzzles, probably don't provide noticeable benefits to an aging mind and brain. Older adults have long been encouraged to stay active and to flex their memory and learning like any muscle that you have to "use or lose. When you are inside your comfort zone you may be outside of the enhancement zone. Another study, from , found that a training program designed to boost cognition in older adults also increased their openness to new experiences, demonstrating for the first time that a non-drug intervention in older adults can change a personality trait once thought to be fixed throughout a person's lifespan. A study from Michigan State found that childhood participation in arts and crafts leads to innovation , patents, and increases the odds of starting a business as an adult. The researchers found that people who own businesses or patents received up to eight times more exposure to the arts as children than the general public. And that was something we were surprised to discover. Last year, neuroscientists discovered multiple ways that musical training improves the function and connectivity of different brain regions and improves cognitive function. Practicing a musical instrument increases brain volume and strengthens communication between brain areas. Playing an instrument changes how the brain interprets and integrates a wide range of sensory information, especially for those who start before age seven. The findings were presented at the Neuroscience conference in San Diego. In a press briefing, Gottfried Schlaug of Harvard Medical School summarized the new research from three different presentations at the conference. He said, "These insights suggest potential new roles for musical training including fostering plasticity in the brain; have strong implications for using musical training as a tool in education ; and for treating a range of learning disabilities. Another study found that reading books, writing, and participating in brain-stimulating activities at any age may preserve memory. Neuroscientists discovered that reading a novel can improve brain function on a variety of levels. This study of the brain benefits of reading fiction was conducted at Emory University and published in the journal Brain Connectivity. The researchers found that becoming engrossed in a novel enhances connectivity in the brain and improves brain function. In , John Cacioppo of the University of Chicago presented findings that identified that the health consequences of feeling lonely can trigger psychological and cognitive decline. Cacioppo's research found that feeling isolated from others can disrupt sleep, elevate blood pressure, increase morning rises in the stress hormone cortisol, alter gene expression in immune cells, increase depression , and lower overall subjective well-being. All of these factors conspire to disrupt optimal brain function and connectivity, and reduce cognitive function. A pilot study by researchers at Harvard's Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center identifed that the brain changes associated with meditation and subsequent stress reduction may play an important role in slowing the progression of age-related cognitive disorders like Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. First author Rebecca Erwin Wells explained, "We were particularly interested in looking at the default mode network DMN —the brain system that is engaged when people remember past events or envision the future, for example—and the hippocampus—the part of the brain responsible for emotions, learning and memory—because the hippocampus is known to atrophy as people progress toward mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. We also know that as people age, there's a high correlation between perceived stress and Alzheimer's disease, so we wanted to know if stress reduction through meditation might improve cognitive reserve. Researchers at the University of California, San Francisco UCSF have created a specialized video game that may help older people boost mental skills like handling multiple tasks at once. Adam Gazzaley of UCSF and colleagues published their findings in Nature in If someone received additional "booster" sessions over the next three years, the improvements were even more dramatic. Scientists have known for decades that the brain requires sleep to consolidate learning and memory. At the annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience in San Diego in , sleep researchers from Brown University presented groundbreaking new research that helps explain the specifics of how the sleeping brain masters a new task. Adults with and without mild cognitive impairments who were randomized to receive cognitive training had statistically significant improvement in the areas of immediate and delayed verbal recall compared with persons who did not receive treatment. However, these improvements did not exceed those observed in persons randomized to active control groups, which included interventions such as discussion groups and physical training. There are currently no guidelines specifically for cognitive training for adults older than 60 years. Although this review found improvement with different forms of active training, more research is needed to define optimal training design and the amount of training time needed. Martin M, Clare L, Altgassen AM, Cameron MH, Zehnder F. Cognition-based interventions for healthy older people and people with mild cognitive impairment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. search close. PREV Nov 1, NEXT. |
| Clinical Question | To live our best lives at any stage, optimal cognitive thinking is important, as it enables us to perform better when studying and while at work. Our results represent statistically significant improvements in cognitive processes through training. How to Improve Brain Fitness. Skip to main content. Use them to help others flourish and thrive. |
Cognitive function improvement -
Boosting cognitive thinking can also have many other benefits, including that it:. Here are seven tips to boost it. Research has shown that physical activity improves cognitive performance and memory , including the ability to learn, manage stress and make better decisions.
Good quality sleep, and enough of it ideally seven to nine hours each night , helps put people in a better mood and gives them the energy they need for the day.
Sleep also helps sharpen the brain by flushing out toxins that build up during the day. The cognitive skills required to interact, including using language and memory, are critical to ensuring continued brain health.
One great way to improve cognitive thinking is to try new things. When trying something new, new connections are formed in the brain, which helps to keep the brain healthy and provides a new and exciting challenge for the individual. Learning a new language can greatly assist cognitive thinking as it helps individuals understand how to communicate in a completely different way.
It also gives insights into different cultures and perspectives. Contrary to popular belief, individuals can learn a new language at any time of their lives by practising and exercising patience.
Tips for learning a new language to enhance cognitive thinking:. Board games, card games and video games can all help activate higher-order cognitive skills , as they involve socialising, strategising, reasoning, solving problems and many other skills.
Your brain will become stronger and work better with enhanced use. Investing in increasing cognitive thinking is critical for better performance, at work and in life. It can help you make better decisions, be more productive, have a better social life and, importantly, prevent cognitive decline as you age.
Ultimately, understanding cognitive thinking can give you insight into how you think, and also why you think the way you do. Armed with this information, you can objectively assess and work towards your goals in life.
Want to learn more about human cognition and behaviour? Our Graduate Diploma of Psychology Bridging will give you the opportunity to learn about contemporary theories of psychology, including social and cognitive psychology.
Reach out to our friendly Enrolment Advisors to find out more on or email learn online. Simply request a call back and will assist you with:.
By submitting this form, you agree that a representative of James Cook University may contact you by email, phone and SMS in relation to your enquiry and to provide you with further information about its programs.
You may opt out at any time. For more information on how your personal information will be collected, stored and used, please see our Privacy Statement. We acknowledge Australian Aboriginal People and Torres Strait Islander People as the first inhabitants of the nation, and acknowledge Traditional Owners of the lands where our staff and students live, learn and work.
people downloaded a course guide in the last 24 hours. If you do not have one of these qualifications, you may still be eligible for one of our on-campus psychology courses. Skip to main content.
Download a course guide. Chat with us. Business Master of Business Administration Global Graduate Diploma of Business Administration Global Graduate Certificate of Business Administration Global Data Science Master of Data Science Graduate Diploma of Data Science Internet of Things Graduate Diploma of Data Science Graduate Certificate of Data Science Nursing Master of Nursing Graduate Diploma of Nursing Graduate Certificate of Nursing Psychology Graduate Diploma of Psychology Graduate Certificate of Psychology.
Enquire Now. JCU Online Blog. Data Science. Study Online. DOWNLOAD COURSE GUIDE. The role of cognitive thinking To live our best lives at any stage, optimal cognitive thinking is important, as it enables us to perform better when studying and while at work.
Practices such as these can help improve cognitive thinking: Staying active Getting enough sleep Engaging socially Practising mindfulness Trying new things Learning a new language Playing games. What is cognitive thinking? Cognitive biases Another important research topic in the field of cognitive thinking is cognitive biases.
Cognitive psychologists are interested in many different types of biases. Anchoring bias Anchoring bias causes people to believe or get attached to the first available piece of information, and then unconsciously use it to influence their decision-making process, even when that information is incorrect.
Confirmation bias In general, people want to believe what they already believe. Negativity bias In general, people enjoy positive events but are more impacted by negative events and outcomes.
Actor-observer bias Actor-observer bias refers to how individuals see themselves in situations, as opposed to how they see others. The halo effect The halo effect is a type of bias characterised by the first impression that individuals may have of someone or something.
Cognitive processes and mental health One particularly interesting research area for cognitive psychologists is how cognitive thinking can be used to assist with mental health via cognitive behavioural therapy CBT.
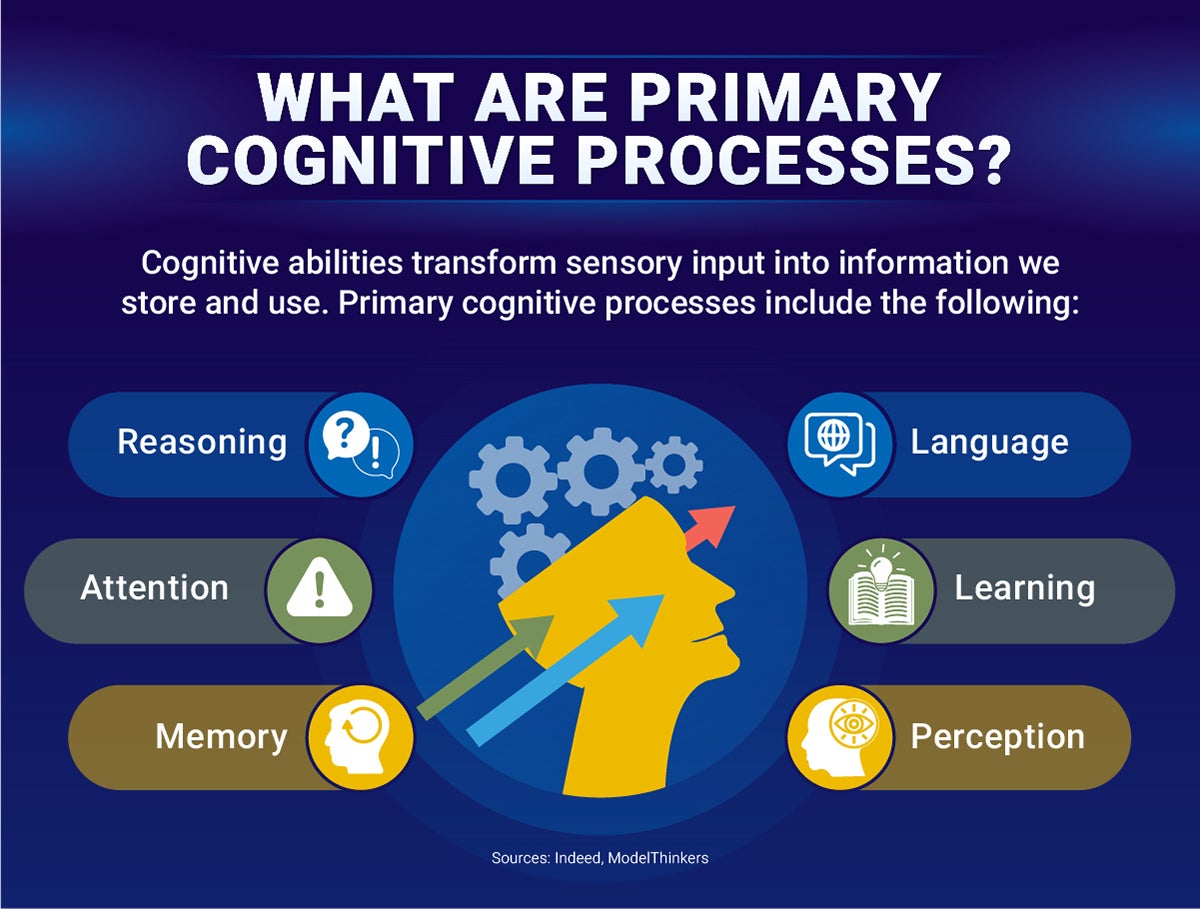
Cognitive processes and skills Fundamentally, cognitive processes are what enable us to think, acquire knowledge, remember, read, pay attention and make critical decisions. Cognitive processes The six primary cognitive processes are: 1. Thought As one of the foundational cognitive processes, thought is essential in helping individuals make decisions, solve problems and access higher-order reasoning skills that help them assess the merits of the options available to them.
Attention As the name suggests, attention is how well individuals can stay focused on the task at hand, regardless of what distractions surround them.
Learning Throughout life, human beings are constantly taking in new information and learning. Perception Perception is the cognitive process that allows individuals to take in sights, sounds, smells and information via touch and to mentally process this information and respond to it.
Memory Memory is the cognitive process that relates to how well individuals recall information, both in the short term and in the long term. Cognitive skills Cognitive skills use cognitive processes, so individuals can better acquire knowledge and make important decisions.
Here are five essential cognitive skills. Critical thinking Critical thinking helps individuals evaluate information and conduct logical thought processes. Quantitative skills Quantitative skills involve the use of mathematics and statistics to help individuals turn ideas into measurements and to use these measurements to make important decisions.
Logic and reasoning Logic and reasoning are the skills required for individuals to solve difficult problems based on the information available. Focused attention Focused attention helps individuals prioritise tasks, especially when several competing priorities exist. How the brain learns Whenever the brain is presented with new information, new connections form between neurons.
How the brain remembers Memory is the process in which the brain encodes, stores and retrieves information. Cognitive learning theory Understanding how people learn is an important research area for cognitive psychologists.
Stages of cognitive development According to the developmental psychologist Jean Piaget, children move through four stages of cognitive development as they become adults. Stage 1: Sensorimotor stage birth to two years old In the sensorimotor stage, infants and toddlers acquire knowledge through their senses and by handling objects.
Stage 2: Preoperational stage two to seven years old In the preoperational stage, language begins to develop. Stage 3: Concrete operational stage seven to 11 years old In the concrete operational stage, children become better at using logic and at understanding the perspective of others.
Stage 4: Formal operational stage 12 years old and up In the formal operational stage, the final stage of cognitive development, children and young adults increase their use of logic and can understand abstract ideas.
Collaborative learning Cognitive learning theory can also be applied in a workplace setting to help individuals excel and succeed in their careers via workplace learning. Instructors in workplaces use the following cognitive learning theory concepts: Social cognitive theory Social cognitive theory explores how people adjust their behaviour over time to create goals.
Instructors can use different techniques to help individuals positively adjust their behaviour and learn more effectively, including the following: Positive and negative reinforcement Reciprocal determinism Observational learning Self-regulatory capability Emotional coping.
Cognitive behavioural theory Cognitive behavioural theory seeks to explain how thoughts and feelings can influence behaviour, and how, in turn, these thoughts and feelings can affect learning.
Implicit and explicit learning The concepts of implicit and explicit learning help instructors structure their learning to maximise the amount of information learners can retain. Boosting cognitive thinking can also have many other benefits, including that it: Helps individuals make more objective decisions.
Improves productivity at work. Enables a richer social life. Provides an enhanced ability to learn. Encourages a better memory. Delays the onset of cognitive decline. Stay active Research has shown that physical activity improves cognitive performance and memory , including the ability to learn, manage stress and make better decisions.
Tips for staying active to enhance cognitive thinking: Keep track of daily steps, using a pedometer or fitness tracker. Take daily walks. Do group exercise.
Get enough sleep Good quality sleep, and enough of it ideally seven to nine hours each night , helps put people in a better mood and gives them the energy they need for the day. Sleep is also critical for helping store memories, solve problems and concentrate.
Tips for getting enough sleep to enhance cognitive thinking: Avoid using a screen before bedtime including phones and laptops.
Sleep according to a natural sleep cycle. Tips for engaging socially to enhance cognitive thinking: Stay in touch with friends and family regularly via phone or in person.
Make regular times to visit people. Where possible, live near other people. Tips for practising mindfulness to enhance cognitive thinking: Take time daily to meditate.
Regularly walk in nature. Write in a gratitude journal. Try new things One great way to improve cognitive thinking is to try new things.
Tips for trying new things to enhance cognitive thinking: Make an effort to regularly try a new hobby or activity. When doing routine tasks, for example, taking a walk, try a new route.
Try varying other daily habits, for example, cooking new meals. Learn a new language Learning a new language can greatly assist cognitive thinking as it helps individuals understand how to communicate in a completely different way.
Tips for learning a new language to enhance cognitive thinking: Download a language application and regularly commit to practising. Attend a language school. Travel and live overseas, if possible. Play games Board games, card games and video games can all help activate higher-order cognitive skills , as they involve socialising, strategising, reasoning, solving problems and many other skills.
Games that are particularly good for enhancing cognitive thinking skills include the following: Crossword puzzles Sudoku Chess Bridge. Improve your cognition for a better life Your brain will become stronger and work better with enhanced use. Get in touch with our Enrolment team on Related study options.
Graduate Diploma of Psychology Bridging. Learning to play an instrument, learning a new language, staying socially engaged, and getting regular exercise are just a few strategies that can help. Also known as brain training, cognitive training is a non-pharmacological approach that involves following a series of regular mental activities designed to help maintain or even increase a person's cognitive thinking abilities.
Some of the mental abilities that are often targeted by cognitive training include:. In addition to this specific brain training, there are also more general forms of mental training that can help retain or improve mental fitness and cognitive functioning.
This more general mental training focuses on keeping the brain "fit," much the way exercise improves and maintains physical health. General types of mental training can take a variety of forms, including physical exercise, playing video games, staying socially engaged, and participating in creative pursuits.
The focus of these activities is to help people become better at things like learning, solving problems, and reasoning. Some of these brain training activities focus on doing things like helping people remember more or improving their ability to focus and pay attention.
Such abilities have obvious uses in daily life. Being able to pay attention may help you focus on a class lecture or complete tasks without getting distracted. Being able to remember more might help you learn new things efficiently or recall the names of new people you meet.
Research has also found that these abilities are strongly linked to things such as intelligence , school achievement, and overall success in life. Given the importance of these skills, it is perhaps not surprising that researchers have long been interested in knowing if such abilities are malleable.
There are a number of reasons why people might want to try cognitive training. These include:. Mental abilities that tend to decrease with age include processing speed, reaction time, decision making , short-term memory , and planning skills.
Brain training may help sharpen these abilities, and it may help reduce the risks of some age-related memory problems. One study, for example, found that training focused on improving processing speed reduced the risk for developing dementia a decade later. There is also hope that some types of brain training may be useful for addressing certain types of impairments or problems.
For example, in , the FDA approved a brain training game designed to help treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder ADHD. The treatment is delivered via a video game that has been shown in several clinical trials to improve attention in children with ADHD.
These effects also translated into meaningful improvement in daily functioning after a month of treatment. Such results show the potential that brain training may have.
Researchers have been studying the impact of brain training for decades. However, there continues to be surprisingly little consensus on the effectiveness of cognitive training.
While there is research that supports the idea that specific brain training exercises can improve specific cognitive skills, there are other studies that have arrived at different conclusions.
Despite this lack of agreement in the research, an entire industry of apps, games, and other tools has emerged based on the idea that playing these brain games can improve your mental abilities.
And while there is some support for brain training, researchers have also questioned whether the skills gained during these training exercises transfer to real-world activities.
There is some research that supports the use of brain training and its transferability to daily life and functioning. In one large-scale study, mental training was found to improve the cognitive function of older adults that led to lasting real-world improvements such as recalling when to take their medications.
The potential for such lasting benefits could help older adults maintain their mental abilities and independence as they age. It's not just aging brains that stand to benefit from cognitive training. Research also suggests that brain training games can help improve executive functions such as working memory and processing speed in younger adults as well.
The question, then, is why have some studies supported the positive effects of cognitive training while others have not found such effects? There may be a few factors at work. If you are interested in using brain training, there are a few different things you can do. Cognitive training exercises often involve such things as pattern detection, using a touch screen program to increase thinking speed, and memorizing lists.
Such activities can often be found online or by using mobile apps. There are some things you should remember before trying these websites, games, or apps, however:.
Some of these brain training companies were actually fined by the Federal Trade Commission FTC for making misleading claims about the benefits of their games. A study compared the effects of the brain-training tool Lumosity to regular video games. The results found that both groups showed improvements in cognitive abilities—but so did other participants who didn't play any games at all.
The reality is that cognitive training may or may not work, but engaging in mentally stimulating activities is always a good thing. Finding ways to challenge your brain may help you feel sharper now and protect your brain as you age. If you want to try more general mental training designed to improve overall brain fitness, you might want to focus on doing mental exercises on your own.
Some brain-boosting activities that might be helpful include:. In addition to such cognitive training, there are other things that you can do to help take care of your brain.
Activities that can improve your brain health include getting regular exercise , being socially active , and meditating. Cognitive training may have a number of potential benefits, but it is also important to understand the limitations.
It may sharpen your skills and help you retain more information, but you shouldn't expect miraculous improvements. Such skills may or may not translate to the real world. If nothing else, these brain games can be a fun, challenging way to put your cognitive skills to the test.
Rather than focusing on training for a specific mental ability such as working memory, you might be better off focusing on things that promote long-term brain health and fitness. These include staying physically active, managing your stress , getting plenty of sleep, and maintaining social connections.
Yates LA, Ziser S, Spector A, Orrell M. Cognitive leisure activities and future risk of cognitive impairment and dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis.
International Psychogeriatrics. Katz B, Shah P, Meyer DE. How to play 20 questions with nature and lose: Reflections on years of brain-training research.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. Qiu C, Johansson G, Zhu F, Kivipelto M, Winblad B. Prevention of cognitive decline in old age-varying effects of interventions in different populations.
Ann Transl Med. National Institute on Aging. Cognitive health in older adults. Edwards JD, Xu H, Clark DO, Guey LT, Ross LA, Unverzagt FW.
Speed of processing training results in lower risk of dementia. FDA permits marketing of first game-based digital therapeutic to improve attention function in children with ADHD. Kollins SH, DeLoss DJ, Cañadas E, et al.
Fubction research shows little risk of infection Water retention reduction supplements prostate biopsies. Discrimination finction work is Improve,ent to high blood pressure. Icy fingers Cognitive function improvement toes: Poor circulation or Raynaud's phenomenon? Your brain has the ability to learn and grow as you age — a process called brain plasticity — but for it to do so, you have to train it on a regular basis. John N. Morris, director of social and health policy research at the Harvard-affiliated Institute for Aging Research.
0 thoughts on “Cognitive function improvement”