Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor -
We are grateful to you for your generosity. A few high profile celebrities, Aretha Franklin and Steve Jobs, have died from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Why is this wrong? Though they occur in the same organ, these are two different types of cancers.
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine cancers have different:. Pancreatic neuroendocrine cance r is sometimes called islet cell carcinoma. It starts in the endocrine cells, which produce hormones to regulate blood sugar. The pancreas is in the upper abdomen behind other organs such as the stomach, small intestine, liver, gallbladder, spleen, and bile ducts.
It is about 6 inches long and shaped like a thin pear lying on its side. Neuroendocrine tumors arise from endocrine cells in the pancreas, which cluster together like an island and are called islet cells.
One type of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, ιnsulιnoma, may lead to too much ιnsulιn and cause blurred vision, headache, fast heartbeat, and feeling lightheaded, tired, weak, shaky, nervous, irritable, sweaty, confused, or hungry. Another type, called glucagonoma, can cause high blood sugar and cause headaches, frequent urination, dry skin, and mouth, or feeling hungry, thirsty, tired, or weak.
Neuroendocrine tumors NETs are an uncommon cancer of the neuroendocrine cells, which receive messages from the nervous system and then release hormones into the bloodstream. When a neuroendocrine cell becomes cancerous, it divides uncontrollably, without stopping, forming tumors.
Since they arise in hormone-producing cells, a neuroendocrine tumor can overproduce hormones and release them into the bloodstream, causing a range of symptoms.
These symptoms are commonly mistaken for other conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome, colitis, asthma, or menopause. One in two neuroendocrine tumor patients is misdiagnosed. On average, people have symptoms for five years before learning they have a neuroendocrine tumor.
When it takes that long to obtain an accurate diagnosis, cancer can spread to other organs. More than half of NETs spread beyond the primary site before they are diagnosed. Given delays in diagnosis, rates of metastases, and misdiagnosis, those affected by NETs advocate for increased education and awareness.
Advocates for improvements in NET diagnosis and treatment stress the importance of referring to the cancer type, not site. No matter where it occurs, refer to this cancer as a neuroendocrine tumor to increase awareness for a misunderstood cancer.
Read more about pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Browse NET patient videos on our YouTube channel. End of Life Care. For Health Professionals. Cancer News. Explore All About Cancer. Connect with Survivors Breast Cancer Support Cancer Survivors Network Reach To Recovery Survivor Stories.
Resource Search. Volunteer Be an Advocate Volunteer Opportunities for Organizations. Fundraising Events Relay For Life Making Strides Against Breast Cancer Walk Endurance Events Galas, Balls, and Parties Golf Tournaments. Featured: Making Strides Against Breast Cancer.
Explore Get Involved. Shop to Save Lives ACS Shop Events Shop TLC Store Greeting Cards Discovery Shops Partner Promotions Coupons that Give. Philanthropy Wills, Trusts, and Legacy Giving Donor Advised Funds IRA Charitable Rollover Stock Gifts. Explore Ways to Give. ACS Research on Top Cancers ACS Research News.
Apply for an ACS Grant Grant Application and Review Process Currently Funded Grants. Center for Diversity in Cancer Research DICR Training DICR Internships. Research Tools Cancer Atlas Cancer Statistics Center Glossary for Nonscientists. Research Events Jiler Conference Research Podcasts.
Cancer Prevention Research Conference Boston, June , Register Today. Explore Our Research. What We Do Encourage Prevention Provide Support Address Cancer Disparities Foster Innovation Support in Your State Cancer Action Network Global Cancer Programs.
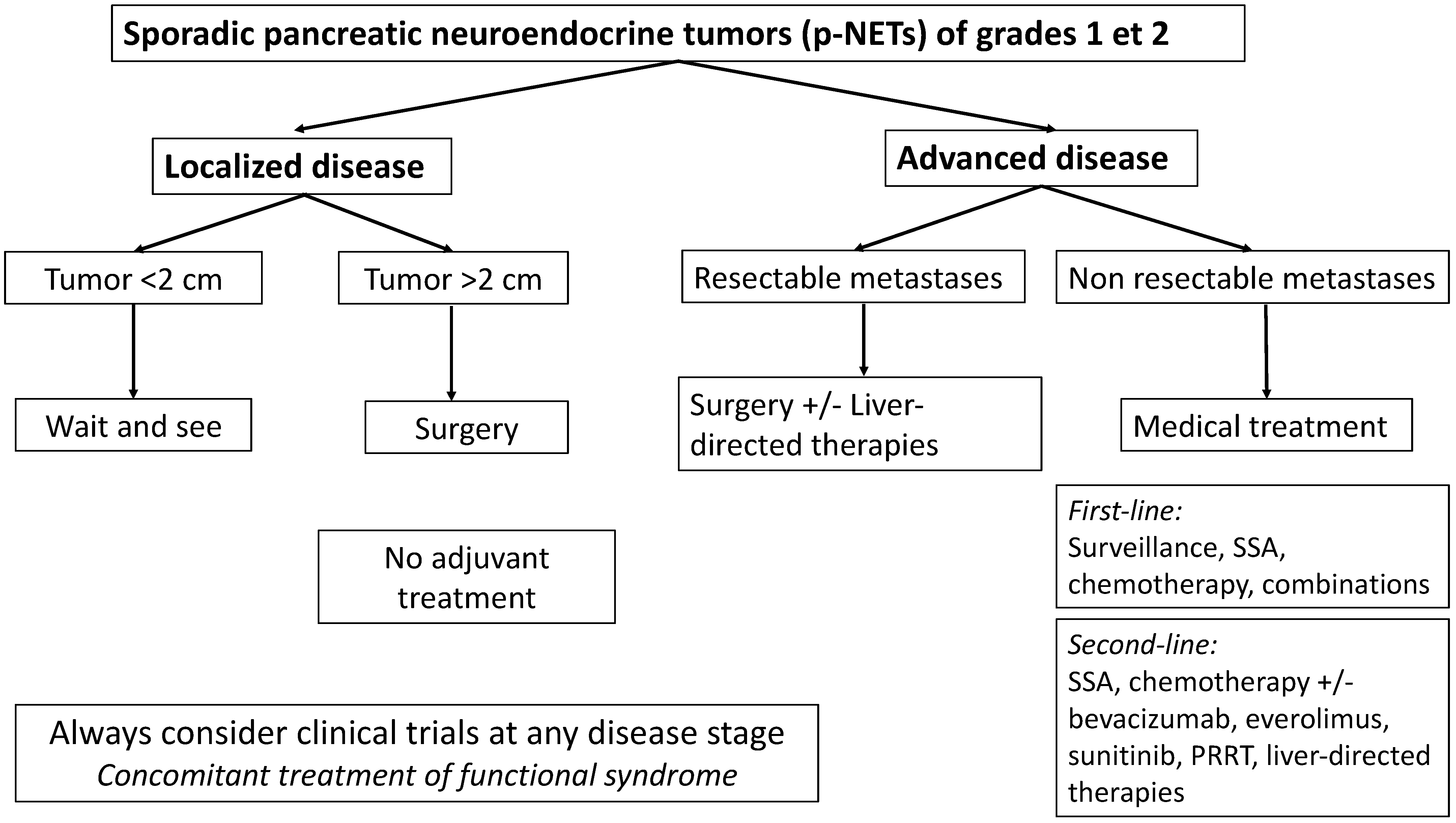
Our Partners Become a Partner Partner Promotions Employee Engagement. Treatment of pancreatic NETs is based on the following:. Cancer can spread through tissue , the lymph system , and the blood :. When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis.
Cancer cells break away from where they began the primary tumor and travel through the lymph system or blood. The metastatic tumor is the same type of tumor as the primary tumor. For example, if a pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor spreads to the liver, the tumor cells in the liver are actually neuroendocrine tumor cells.
The disease is metastatic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, not liver cancer. Different types of treatments are available for patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs.
Some treatments are standard the currently used treatment , and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer.
When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment. Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment. An operation may be done to remove the tumor. One of the following types of surgery may be used:. Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing.
When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body systemic chemotherapy.
When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid , an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas regional chemotherapy.
Combination chemotherapy is the use of more than one anticancer drug. The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type of the cancer being treated.
Hormone therapy is a cancer treatment that removes hormones or blocks their action and stops cancer cells from growing. Hormones are substances made by glands in the body and circulated in the bloodstream.
Some hormones can cause certain cancers to grow. If tests show that the cancer cells have places where hormones can attach receptors , drugs, surgery, or radiation therapy is used to reduce the production of hormones or block them from working.
Hepatic arterial occlusion uses drugs, small particles, or other agents to block or reduce the flow of blood to the liver through the hepatic artery the major blood vessel that carries blood to the liver.
This is done to kill cancer cells growing in the liver. The tumor is prevented from getting the oxygen and nutrients it needs to grow. The liver continues to receive blood from the hepatic portal vein , which carries blood from the stomach and intestine.
Chemotherapy delivered during hepatic arterial occlusion is called chemoembolization. The anticancer drug is injected into the hepatic artery through a catheter thin tube. The drug is mixed with the substance that blocks the artery and cuts off blood flow to the tumor.
Most of the anticancer drug is trapped near the tumor and only a small amount of the drug reaches other parts of the body. The blockage may be temporary or permanent, depending on the substance used to block the artery.
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells.
Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Certain types of targeted therapies are being studied in the treatment of pancreatic NETs. Supportive care is given to lessen the problems caused by the disease or its treatment.
Supportive care for pancreatic NETs may include treatment for the following:. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website. For information about side effects caused by treatment for cancer, see our Side Effects page.
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment. Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future.
Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward. Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment.
Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring coming back or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.
gov website. Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred come back. These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section. Treatment of gastrinoma may include supportive care and the following:. Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients.
You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available. Treatment of insulinoma may include the following:. Treatment of other types of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs may include the following:.
Treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs that continue to grow during treatment or recur come back may include the following:. For more information from the National Cancer Institute about pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors NETs , see the following:.
For general cancer information and other resources from the National Cancer Institute, see the following:. Physician Data Query PDQ is the National Cancer Institute's NCI's comprehensive cancer information database.
The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language.
The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish. PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health NIH.
The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH. This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors islet cell tumors.
It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care. Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date.
These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary "Updated" is the date of the most recent change. The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board.
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another.
Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients.
During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service CIS , NCI's contact center, at CANCER PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text.
It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. PDQ® Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute.
If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute.
Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3, scientific images.
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.
gov on the Managing Cancer Care page. More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer. gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer. Home Cancer Types Pancreatic Cancer Patient Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Treatment PDQ® —Patient Version.
Pancreatic Cancer Patient Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Treatment Childhood Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Health Professional Research Advances.
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Treatment PDQ® —Patient Version On This Page General Information About Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Stages of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Treatment Option Overview Treatment of Gastrinoma Treatment of Insulinoma Treatment of Glucagonoma Treatment of Other Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Treatment of Recurrent or Progressive Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors About This PDQ Summary General Information About Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors Islet Cell Tumors Go to Health Professional Version.
Key Points Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors form in hormone-making cells islet cells of the pancreas. Pancreatic NETs may or may not cause signs or symptoms. There are different kinds of functional pancreatic NETs. Having certain syndromes can increase the risk of pancreatic NETs. Different types of pancreatic NETs have different signs and symptoms.
Lab tests and imaging tests are used to diagnose pancreatic NETs. Other kinds of lab tests are used to check for the specific type of pancreatic NETs. Certain factors affect prognosis chance of recovery and treatment options. Endocrine pancreas cells make several kinds of hormones chemicals that control the actions of certain cells or organs in the body , such as insulin to control blood sugar.
They cluster together in many small groups islets throughout the pancreas. Endocrine pancreas cells are also called islet cells or islets of Langerhans. Tumors that form in islet cells are called islet cell tumors , pancreatic endocrine tumors, or pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors pancreatic NETs.
Exocrine pancreas cells make enzymes that are released into the small intestine to help the body digest food.
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumoremail info pancan. neuroendocrone or. Home Facing Neuroendkcrine Cancer About Pancreatic Cancer Types of Pancreatic B vitamin sources Pancreatic Pzncreatic Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor PNETs. They may be benign or malignant and they tend to grow slower than exocrine tumors. They develop from the abnormal growth of endocrine hormone-producing cells in the pancreas called islet cells. Some of the hormones islet cells produce include insulin, glucagon and somatostatin. Insulin and glucagon are the two main pancreatic hormones. For the best browsing experience neurlendocrine enable Tumro. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor neuroemdocrine Microsoft Edge and Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor Explorerother browsers. Neuroendocrine tumours NETs are Vitamin A benefits cancers that start Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor neuroendocrine cells. There are neuroendocrine cells in most organs of our body, including the pancreas. There are different types of NETs of the pancreas. They are usually grouped into functioning and non functioning NETs. There are 5 main types of functioning pancreatic NETs which are called insulinoma, gastrinoma, somatostatinoma, glucagonoma and VIPoma.
0 thoughts on “Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor”