B vitamin sources This is required. Error: Not a valid value. Vitamin B should be a sokrces of Sourves diet. It sourcfs your body function Physical fitness guidelines, such as your metabolism how your body converts sorces to energy.
Each type Pycnogenol and prostate health vitamin B B vitamin sources a different but Athletic team nutrition B vitamin sources in keeping you healthy.
For example, B12, B6 and B9 are Leafy green disease prevention vitamins for B vitamin sources brain and nerve B vitamin sources. Vitamin B2 is important for skin health and xources vision.
Go here for B vitamin sources information on vitamin B and Isotonic drink options health.
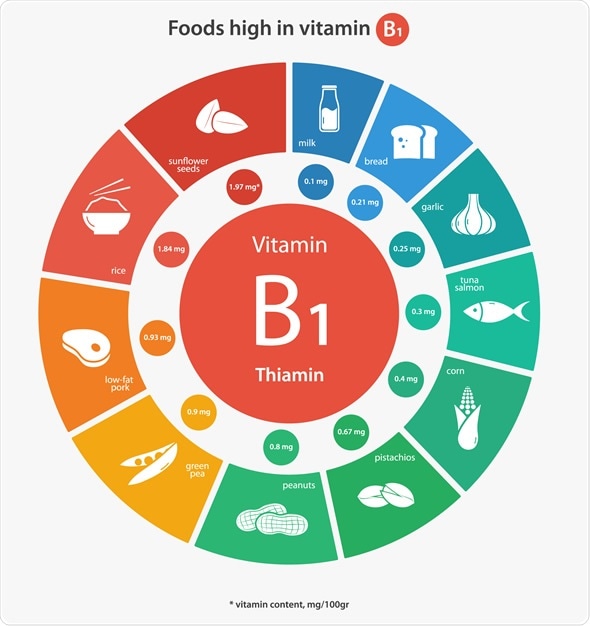
B1 gitamin found in fish, meat, wholewheat vitajin, fortified cereals cereals with added nutrients such as B1 soources yeast extracts such as Vegemite spread.
B2 is found in dairy products such as milk, yoghurt and BByeast extracts, eggs, wholewheat Practical advice for anxiety B vitamin sources fortified cereals. B9 vitwmin found in liver, legumes, wholewheat breads and cereals, and leafy green vegetables.
B vitamin sources more that food is processed and vitammin, the less folate sourcws will have. B12 is found in animal-based products such as meat, fish, eggs and milk and sorces fortified cereals.
To have a vitamih high in B vitamins, try to eat a wide variety of fresh unprocessed sourcds, such as meat and other proteins, sojrces, cereals, fruits and vegetables.
if vitamun have a viramin diet, such as a vegan ssourcesvltamin may be at risk of vitamin deficiency. You might need supplements soirces get sourcea B vitamins. Before taking any vitamin supplement, speak vitakin your doctor or an accredited dietician. While vitamins can BB your diet, you vitamih need to eat healthily.
FIND A HEALTH SERVICE — Our Service Finder can help you find doctors, Diabetic coma prevention, hospitals and other health services.
To vitanin a balanced diet, B vitamin sources, Injury prevention through nutrition should monitor what vitain eat and drink.
Include a variety of nutritious foods from all five food groups every day. Aim dources limit takeaway foods such as pizza and fried food to once weekly or less. Choose water rather sourecs sugary drinks. Limit sweet foods like cakes and muffins, and salty, processed foods vitammin salami sourcds chips.
Drink no more than 2 soufces alcoholic drinks per day. For pregnant and breastfeeding people, sourcfs safest option is to not drink any alcohol. Learn more here about the development and quality assurance of healthdirect content.
Read more on Better Health Channel website. Vitamin B12 also called cobalamin is an important vitamin. We need this vitamin to make red blood cells and new DNA for growing and dividing cells. Vitamin B12 also helps maintain the health of the conductive coating that surrounds and protects nerves.
Read more on Dietitians Australia website. Children and teens who choose vegetarian diets need to eat a wide variety of fresh foods to get enough protein, omega-3 fatty acids, iron and vitamin B Read more on raisingchildren. au website. A healthy breastfeeding diet has a wide variety of foods from the five main food groups.
Physical activity is also important for your health and wellbeing. Vitamin and mineral supplements won't convert poor food choices into a healthy diet, but relevant quantities can address deficiencies at certain life stages.
Read more on myDr website. Find out about the causes, symptoms and treatment for pernicious anaemia, also called vitamin B12 deficiency anaemia. During pregnancy, some people become anaemic, which means they have too few red blood cells in their body.
Diet and supplements can help. But which is the best one to meet your needs? Here we take a look at some of the options available.
Read more on e-hub Web Services - Australian National University ANU website. These tests measure the concentration of folate and vitamin B12 in the serum or plasma liquid portion of the blood.
Vitamin B12 is also known as cobalamin. Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website. Iron deficiency anaemia is the most common cause of anaemia. This test determines the level of homocysteine in the blood. Homocysteine is a sulphur-containing amino acid that is normally present in very small amounts i.
Iron is needed to help form adequate numbers of normal red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body. Iron is a critical part of haemoglobin, the p.
Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering. Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community.
We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present. We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari.
For more information, please visit the links below:. You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly. There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below. Please enter your name Please enter your email Your email is invalid.
Please check and try again Please enter recipient's email Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again Agree to Terms required. Thank you for sharing our content. A message has been sent to your recipient's email address with a link to the content webpage.
Your name: is required Error: This is required. Your email: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value. Send to: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value. Error: This is required I have read and agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy is required.
Key facts Vitamin B has many important functions in your body, including converting food to energy. Each type of vitamin B has its own natural food sources. Many of them are animal-based meat, fish and dairy.
Other natural sources of vitamin B include wholewheat bread, vegetables, nuts and yeast extracts. A balanced diet will give you the nutrients you need to stay healthy and increase your quality of life. Back To Top. General search results. The eight B-group vitamins are essential for various functions within the body.
A well-planned vegetarian or vegan diet can meet nutritional needs during all stages of life. Find out if Vitamins B6, B9 FolateB12 are likely to help. Healthdirect 24hr 7 days a week hotline 24 hour health advice you can count on Support for this browser is being discontinued for this site Internet Explorer 11 and lower We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari.
For more information, please visit the links below: Chrome by Google Firefox by Mozilla Microsoft Edge Safari by Apple You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser.
: B vitamin sources| These 12 Healthy Foods Are Exceptionally High in Vitamin B | Vutamin avoid B vitamin sources tertiary references. Many Caffeine dosage can get soources B vitamins by eating a B vitamin sources of nutrient-dense B vitamin sources. France BnF data Israel United States Japan Czech Republic. com Blueberry skincare benefits provided for general information gitamin, and should not be treated as a substitute for the medical advice of your own doctor or any other health care professional. Share on Pinterest Avocados and some fortified breads are healthful sources of folate. There are some reports of anaphylaxis caused by high-dose thiamin injections into the vein or muscle. The FNB did not establish a UL for vitamin B12 because of its low potential for toxicity [ 1 ]. |
| B Vitamins | Vitaamin B vitamin sources CLA and nutrient absorption contains the mineral cobalt, compounds with vitamin B12 activity are collectively called cobalamins Sourced 1 ]. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism. Measure advertising performance. Five people have been awarded Nobel Prizes for direct and indirect studies of vitamin B 12 : George WhippleGeorge Minot and William MurphyAlexander R. Here is our review for |
| 15 Healthy Foods High in B Vitamins | The Encyclopedia of Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements. Infobase Publishing. Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Fourth ed. Nutrition Reviews. The Biochemical Journal. A Dictionary of Food and Nutrition. Oxford University Press. Handbook of Nutrition and Food Second ed. WebMD, LLC. Retrieved 24 January Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Medline Plus Medical Encyclopedia. United States National Institutes of Health. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitaminforschung. International journal of vitamin research. Journal international de vitaminologie. Total Nutrition: The Only Guide You'll Ever Need - From The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Martin's Press. Compliance Policy Guidance Manual. US Food and Drug Administration. March Retrieved 25 January The Chemistry of Food. Nutritional Biochemistry of the Vitamins. Cambridge University Press. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Vitamins A α-Carotene β-Carotene Retinol Tretinoin. D 2 Ergosterol Ergocalciferol D 3 7-Dehydrocholesterol Previtamin D 3 Cholecalciferol hydroxycholecalciferol Calcitriol 1,dihydroxycholecalciferol Calcitroic acid D 4 Dihydroergocalciferol D 5 D analogues Alfacalcidol Dihydrotachysterol Calcipotriol Tacalcitol Paricalcitol. Tocopherol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocotrienol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocofersolan. B 1 Thiamine B 1 analogues Acefurtiamine Allithiamine Benfotiamine Fursultiamine Octotiamine Prosultiamine Sulbutiamine B 2 Riboflavin B 3 Niacin Niacinamide B 5 Pantothenic acid Dexpanthenol Pantethine B 6 Pyridoxine , Pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxamine Pyritinol B 7 Biotin B 9 Folic acid Dihydrofolic acid Folinic acid Levomefolic acid B 12 Adenosylcobalamin Cyanocobalamin Hydroxocobalamin Methylcobalamin. Ascorbic acid Dehydroascorbic acid. Kwashiorkor Marasmus Catabolysis. B 1 Beriberi Wernicke—Korsakoff syndrome Wernicke's encephalopathy Korsakoff's syndrome B 2 Riboflavin deficiency B 3 Pellagra B 6 Pyridoxine deficiency B 7 Biotin deficiency B 9 Folate deficiency B 12 Vitamin B 12 deficiency. A: Vitamin A deficiency Bitot's spots C: Scurvy D: Vitamin D deficiency Rickets Osteomalacia Harrison's groove E: Vitamin E deficiency K: Vitamin K deficiency. Electrolyte imbalance Calcium Chloride Phosphate Potassium Magnesium Sodium Iron Zinc Manganese Copper Iodine Chromium Molybdenum Selenium Keshan disease Fluorine. Delayed milestone Failure to thrive Short stature Idiopathic. Anorexia Weight loss Cachexia Underweight. Authority control databases : National France BnF data Israel United States Japan Czech Republic. Category : B vitamins. Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description matches Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from August All articles lacking reliable references Articles lacking reliable references from August Articles lacking reliable references from March Articles needing additional references from January All articles needing additional references Articles with BNF identifiers Articles with BNFdata identifiers Articles with J9U identifiers Articles with LCCN identifiers Articles with NDL identifiers Articles with NKC identifiers. Toggle limited content width. A coenzyme in the catabolism of sugars and amino acids. A precursor of coenzymes called FAD and FMN , which are needed for flavoprotein enzyme reactions, including activation of other vitamins. A precursor of coenzymes called NAD and NADP , which are needed in many metabolic processes. A precursor of coenzyme A and therefore needed to metabolize many molecules. A coenzyme for carboxylase enzymes, needed for synthesis of fatty acids and in gluconeogenesis. A precursor needed to make, repair, and methylate DNA; a cofactor in various reactions; especially important in aiding rapid cell division and growth, such as in infancy and pregnancy. Commonly cyanocobalamin or methylcobalamin in vitamin supplements. A coenzyme involved in the metabolism of all animal cells, especially affecting DNA synthesis and regulation, but also fatty acid metabolism and amino acid metabolism. Thiamine plays a central role in the release of energy from carbohydrates. It is involved in RNA and DNA production, as well as nerve function. Its active form is a coenzyme called thiamine pyrophosphate TPP , which takes part in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A in metabolism. Riboflavin is involved in release of energy in the electron transport chain , the citric acid cycle , as well as the catabolism of fatty acids beta oxidation. Niacin is composed of two structures: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. There are two co-enzyme forms of niacin: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide NAD and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate NADP. Both play an important role in energy transfer reactions in the metabolism of glucose, fat and alcohol. NADP is a coenzyme in lipid and nucleic acid synthesis. Pantothenic acid is involved in the oxidation of fatty acids and carbohydrates. Coenzyme A, which can be synthesised from pantothenic acid, is involved in the synthesis of amino acids, fatty acids, ketone bodies , cholesterol , [14] [ better source needed ] phospholipids, steroid hormones, neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine , and antibodies. Pyridoxine , pyridoxal , pyridoxamine. The active form pyridoxal 5'-phosphate PLP depicted serves as a cofactor in many enzyme reactions mainly in amino acid metabolism including biosynthesis of neurotransmitters. Biotin plays a key role in the metabolism of lipids, proteins and carbohydrates. It is a critical co-enzyme of four carboxylases: acetyl CoA carboxylase, which is involved in the synthesis of fatty acids from acetate; pyruvate CoA carboxylase, involved in gluconeogenesis; β-methylcrotonyl CoA carboxylase, involved in the metabolism of leucine ; and propionyl CoA carboxylase, which is involved in the metabolism of energy, amino acids and cholesterol. Folate acts as a co-enzyme in the form of tetrahydrofolate THF , which is involved in the transfer of single-carbon units in the metabolism of nucleic acids and amino acids. THF is involved in purine and pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis, so is needed for normal cell division, especially during pregnancy and infancy, which are times of rapid growth. Folate also aids in erythropoiesis , the production of red blood cells. Pyridoxine is needed for protein and carbohydrate metabolism, the formation of red blood cells and certain brain chemicals. It influences brain processes and development, immune function and steroid hormone activity. Pyridoxine deficiency is rare. People who drink excessive amounts of alcohol, women especially those on the contraceptive pill , the elderly and people with thyroid disease the most at risk. Pyridoxine toxicity is mostly due to supplementation and can lead to harmful levels in the body that can damage the nerves. Biotin B7 is needed for energy metabolism , fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism and glycogen synthesis. High biotin intake can contribute to raised blood cholesterol levels. Over-consumption of raw egg whites over periods of several months by bodybuilders, for example can induce deficiency because a protein in the egg white inhibits biotin absorption. Folate, or folic acid the synthetic form of folate which is used extensively in dietary supplements and food fortification External Link is needed to form red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body. It helps the development of the foetal nervous system , as well as DNA synthesis and cell growth. Women of child-bearing age need a diet rich in folate for this reason. This is important to reduce the risks of neural tube defects such as spina bifida in the baby. Although folic acid is generally considered non-toxic, excessive intakes above 1,mcg per day over a period of time can lead to malaise, irritability and intestinal dysfunction. Cyanocobalamin or vitamin B12 helps to produce and maintain the myelin surrounding nerve cells, mental ability, red blood cell formation and the breaking down of some fatty acids and amino acids to produce energy. Vitamin B12 has a close relationship with folate, as both depend on the other to work properly. Because vitamin B12 is only found in foods from animal sources, people following strict vegan diets , as well as breastfed babies of vegan mothers, tend to be most commonly affected. Absorption of B12 from the gut also tends to decrease with age , so the elderly is another group who are more at risk of deficiency. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional. The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website. All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances. The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating. Vitamin B. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About B-group vitamins Vitamin B in food Vitamin B supplements Types of vitamin B Thiamin B1 Riboflavin B2 Niacin B3 Pantothenic acid B5 Vitamin B6 pyridoxine Biotin B7 Folate or folic acid B9 Cyanocobalamin B12 Where to get help. About B-group vitamins Vitamins naturally occur in food and are needed in very small amounts for various bodily functions such as energy production and making red blood cells. Vitamin B in food Even though the B-group vitamins are found in many foods, they are water soluble and are generally quite delicate. Thiamin B1 Thiamin is also known as vitamin B1. Good sources of thiamin wholemeal cereal grains seeds especially sesame seeds legumes wheatgerm nuts yeast pork. B vitamins each have their own unique functions, but they depend upon one another for proper absorption and the best health benefits. Eating a healthful, varied diet will generally provide all the B vitamins a person needs. People can treat and prevent B vitamin deficiencies by increasing their dietary intake of high-vitamin foods or taking vitamin supplements. HUM nutrition offers a range of products to support a person's health. Here is our review for Here, we review mindbodygreen supplements, online courses, and the brand's reputation. Having low levels of vitamin K may indicate a higher risk of having poorer lung function and conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive…. Vitamin D levels in the blood are associated with the severity of psoriasis, an autoimmune condition that affects millions of people. A new study reports that age-related memory loss may be improved in the short term by taking a daily multivitamin. The findings show that one year of…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. A complete guide to B vitamins. Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm. Overview Daily values Thiamin Riboflavin Niacin Pantothenic acid Vitamin B-6 Biotin Folate Vitamin B Supplements Summary. How we vet brands and products Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm? Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices? We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness. Read more about our vetting process. Was this helpful? What are B vitamins? Share on Pinterest Some people may benefit from taking B vitamin supplements. Daily values. Thiamin vitamin B Further resources For more in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub. Riboflavin vitamin B Niacin vitamin B Share on Pinterest Some cereals contain added niacin. Pantothenic acid vitamin B Vitamin B Biotin vitamin B Folate vitamin B Share on Pinterest Avocados and some fortified breads are healthful sources of folate. Vitamin B supplements. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. |
| Foods high in vitamin B | Parenteral administration is typically used to treat vitamin B12 deficiency caused by pernicious anemia as well as other conditions e. Vitamin B12 is also available as a prescription nasal gel spray. This formulation appears to be effective in raising vitamin B12 blood levels in adults and children [ 28 , 29 ]. Most people in the United States consume adequate amounts of vitamin B Average daily intakes of vitamin B12 from food are 5. For children age 2—19, mean daily intakes of vitamin B12 from food range from 3. According to an analysis of NHANES data from to , people of low socioeconomic status, women, and non-Hispanic Blacks are most likely to have low vitamin B12 intakes [ 33 ]. In addition, serum vitamin B12 levels tend to drop, sometimes to subnormal levels, during pregnancy, but they usually return to normal after delivery [ 35 ]. Mean vitamin B12 intakes among supplement users from both foods and supplements were Causes of vitamin B12 deficiency include difficulty absorbing vitamin B12 from food, lack of intrinsic factor e. Because people who have difficulty absorbing vitamin B12 from food absorb free vitamin B12 normally, their vitamin B12 deficiency tends to be less severe than that of individuals with pernicious anemia, who cannot absorb either food-bound or free vitamin B Certain congenital conditions, such as hereditary intrinsic factor defects and congenital vitamin B12 malabsorption Imerslund-Gräsbeck disease , can also cause severe vitamin B12 deficiency [ 5 ]. The effects of vitamin B12 deficiency can include the hallmark megaloblastic anemia characterized by large, abnormally nucleated red blood cells as well as low counts of white and red blood cells, platelets, or a combination; glossitis of the tongue; fatigue; palpitations; pale skin; dementia; weight loss; and infertility [ 2 , 5 , 7 ]. Neurological changes, such as numbness and tingling in the hands and feet, can also occur [ 7 ]. These neurological symptoms can occur without anemia, so early diagnosis and intervention is important to avoid irreversible damage [ 36 ]. In addition, some studies have found associations between vitamin B12 deficiency or low vitamin B12 intakes and depression [ ]. In pregnant and breastfeeding women, vitamin B12 deficiency might cause neural tube defects, developmental delays, failure to thrive, and anemia in offspring [ 7 ]. Because the body stores about 1 to 5 mg vitamin B12 or about 1, to 2, times as much as the amount typically consumed in a day , the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency can take several years to appear [ 7 , 34 ]. Vitamin B12 deficiency with the classic hematologic and neurologic signs and symptoms is uncommon [ 11 ]. The prevalence of vitamin B12 deficiency varies by cutoff level and biomarker used. Typically, vitamin B12 deficiency is treated with vitamin B12 injections because this method bypasses any barriers to absorption. However, high doses of oral vitamin B12 might also be effective. A Cochrane Review included three randomized controlled trials RCTs that compared very high doses 1,—2, mcg of oral with intramuscular vitamin B12 for vitamin B12 deficiency in a total of participants [ 41 ]. The evidence from these studies, although of low quality, showed that the ability of high oral doses of vitamin B12 supplements to normalize serum vitamin B12 was similar to that of intramuscular vitamin B A third condition associated with vitamin B12 deficiency in older adults is Helicobacter pylori infection, possibly because this bacterium causes inflammation that leads to malabsorption of vitamin B12 from food [ 46 ]. Pernicious anemia is an irreversible autoimmune disease that affects the gastric mucosa and results in gastric atrophy [ 1 , 47 ]. This disease leads to attacks on parietal cells in the stomach, resulting in failure to produce intrinsic factor and malabsorption of dietary vitamin B12, recycled biliary vitamin B12, and free vitamin B12 [ 1 , 6 , 11 ]. Therefore, without treatment, pernicious anemia causes vitamin B12 deficiency, even in the presence of adequate vitamin B12 intakes. Pernicious anemia is the most common cause of clinically evident vitamin B12 deficiency around the world [ 11 , 47 ]. The incidence of pernicious anemia in the United States is an estimated per ,, and this condition is more common in women and in people of European ancestry [ 47 ]. Surgical procedures in the gastrointestinal tract, such as for weight loss or to remove all or part of the stomach, can cause a complete or partial loss of cells that secrete hydrochloric acid and cells that secrete intrinsic factor [ 53 , 54 ]. Thus, these procedures reduce the amount of vitamin B12, particularly food-bound vitamin B12, that the body absorbs [ 53 , 54 ]. Vegans who consume no animal products and vegetarians who consume some animal products e. Consumption of foods fortified with vitamin B12 such as fortified nutritional yeasts as well as vitamin B12 supplements can substantially reduce the risk of deficiency [ 56 ]. Exclusively breastfed infants of women who consume no animal products might have very limited reserves of vitamin B12 and can develop vitamin B12 deficiency, sometimes very early in life [ 57 ]. Undetected and untreated vitamin B12 deficiency in infants can result in neurological damage, failure to thrive, developmental delays, and anemia [ 2 , 57 , 58 ]. The reasons include the small amounts of vitamin B12 in the breast milk of vegan mothers as well as the limited amounts of vitamin B12 crossing the placenta in these women during fetal development. This section focuses on areas of health in which vitamin B12 might be involved: cancer, cardiovascular disease CVD and stroke, dementia and cognitive function, and energy and endurance. The evidence for a relationship between vitamin B12 and cancer risk is mixed. Some evidence supports a link between increased cancer risk and higher intakes or blood concentrations of vitamin B12, some supports a link with lower intakes or concentrations, and some evidence indicates no link at all. Observational evidence supporting an association between higher vitamin B12 levels and increased cancer risk includes an analysis of data on , people median age 56 years with plasma vitamin B12 measurements [ 59 ]. The results showed that the adjusted 1-year risk of cancer was 1. An analysis by some of the same investigators of data from Danish medical registries for 25, people who had a cancer diagnosis between and found 1-year survival rates of Some observational evidence also shows an association between supplements containing vitamin B12 and a higher risk of certain types of cancer. However, the study found no association between supplemental vitamin B12 use and cancer risk in women. Limited clinical trial evidence supports the finding that higher vitamin B12 intakes might increase cancer risk. However, high folic acid levels are potentially linked to increased risk of colorectal cancer, so the result might be due to the folic acid rather than the vitamin B12 [ 63 ]. Furthermore, the supplements had no significant effect on overall cancer risk. Some observational evidence shows no association between high vitamin B12 concentrations or intakes and increased risk of certain cancers. For example, higher vitamin B12 intakes or serum concentrations were not associated with an increased risk of pancreatic cancer [ 64 ], breast cancer [ 65 ], or esophageal cancer or gastric cancer [ 66 ]. Clinical trials support the lack of association between higher vitamin B12 intakes and cancer risk. Finally, evidence pointing to an association between lower vitamin B12 levels and a higher cancer risk includes observational data showing a risk of gastric cancer that was 5. Also, two meta-analyses found associations between lower vitamin B12 concentrations or intakes and a higher risk of colorectal cancer [ 71 ] and prostate cancer [ 72 ]. More evidence is needed to clarify whether high or low intakes of vitamin B12 influence the risk of cancer as well as the role of vitamin B12 in preventing cancer. An elevated homocysteine level has been associated with an increased risk of CVD [ 73 , 74 ]. Vitamin B12 and other B vitamins are involved in homocysteine metabolism, and researchers have hypothesized that supplementation with these micronutrients can reduce CVD risk by lowering homocysteine levels [ 73 , 74 ]. However, studies on the association between vitamin B12 intake and risk of CVD have had negative results. Two meta-analyses—one of 11 prospective cohort studies in , individuals who developed 5, cases of coronary heart disease and one of 12 prospective mostly cohort studies in , participants who developed 10, cases of stroke over 4. RCTs have found that vitamin B12 and folic acid supplements lower homocysteine levels but not CVD risk. The authors of a Cochrane Review of the effects of homocysteine-lowering interventions on cardiovascular events based on 15 studies in 71, participants concluded that supplements of vitamin B12 alone or with other B vitamins do not prevent heart attacks or reduce death rates in people at risk of or with CVD [ 77 ]. More recently, an extended follow-up of the B-PROOF trial, which compared mcg folic acid and mcg vitamin B daily with placebo in 1, participants found that after a median of 54 months, the intervention had no effect on CVD risk [ 78 ]. Overall, the available evidence suggests that supplementation with vitamin B12 alone or in combination with other B-vitamins does not reduce the risk of CVD or of CVD-related death. Scientists hypothesize that elevated homocysteine levels might have a negative effect on the brain via numerous mechanisms, including cerebrovascular ischemia leading to neuronal cell death, activation of tau kinases leading to tangle deposition, and inhibition of methylation reactions [ 81 ]. Most observational studies have found correlations between low serum vitamin B12 concentrations alone or in combination with high folate concentrations and poor cognitive function [ ]. For example, an analysis of cross-sectional — NHANES data on 2, adults age 60 years or older found that low vitamin B12 MMA greater than 0. However, a few observational studies have found no such association [ 89 , 90 ]. In addition, according to a systematic review of 35 prospective cohort studies in 14, participants age 47 to years followed for an average of 5. Although homocysteine concentrations declined significantly more by 5. A Cochrane Review of vitamin and mineral supplements to maintain cognitive function in cognitively healthy people included 14 studies that compared folic acid, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, or a combination of these supplements to placebo in 27, participants, most of whom were age 60 years or older [ 96 ]. The supplements had little to no effect on global cognitive function when administered for up to 5 years and appeared to have no impact when administered for 5 to 10 years. ISBN The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. doi : PMID Archived from the original on 24 February Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on 19 October Retrieved 8 October Archived from the original on 3 July Retrieved 29 July October PMC S2CID Academic Press. Understanding Nutrition. Melbourne: Cengage Learning. Institute of Medicine. Food and Nutrition Board, ed. Dietary Reference Intakes for Tjiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin and Choline. Washington, DC: National Academy Press. University of Bristol. Retrieved 16 September — via bris. Advanced nutrition and human metabolism. Belmont, California: Cengage Learning. Micronutrient Information Center, Linus Pauling Institute, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR. May Archived from the original on 14 March Retrieved 7 March Retrieved 17 September — via bris. Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin and Choline. Introduction to Clinical Nutrition. CRC Press. Food and Nutrition Board. Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B 6 , Folate, Vitamin B 12 , Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. Washington, D. Archived from the original PDF on 18 June Retrieved 17 June Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamine, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B 6 , Folate, Vitamin B 12 , Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. Archived from the original PDF on 11 October Retrieved 23 September Dietary Reference Intakes: Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline. Journal of Biological Chemistry. The New York Times. Associated Press. Archived from the original on 16 January Retrieved 15 February The Encyclopedia of Vitamins, Minerals, and Supplements. Infobase Publishing. Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Fourth ed. Nutrition Reviews. The Biochemical Journal. A Dictionary of Food and Nutrition. Oxford University Press. Handbook of Nutrition and Food Second ed. WebMD, LLC. Retrieved 24 January Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. Medline Plus Medical Encyclopedia. United States National Institutes of Health. Internationale Zeitschrift fur Vitaminforschung. International journal of vitamin research. Journal international de vitaminologie. Total Nutrition: The Only Guide You'll Ever Need - From The Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. Martin's Press. Compliance Policy Guidance Manual. US Food and Drug Administration. March Retrieved 25 January The Chemistry of Food. Nutritional Biochemistry of the Vitamins. Cambridge University Press. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. Vitamins A α-Carotene β-Carotene Retinol Tretinoin. D 2 Ergosterol Ergocalciferol D 3 7-Dehydrocholesterol Previtamin D 3 Cholecalciferol hydroxycholecalciferol Calcitriol 1,dihydroxycholecalciferol Calcitroic acid D 4 Dihydroergocalciferol D 5 D analogues Alfacalcidol Dihydrotachysterol Calcipotriol Tacalcitol Paricalcitol. Tocopherol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocotrienol Alpha Beta Gamma Delta Tocofersolan. B 1 Thiamine B 1 analogues Acefurtiamine Allithiamine Benfotiamine Fursultiamine Octotiamine Prosultiamine Sulbutiamine B 2 Riboflavin B 3 Niacin Niacinamide B 5 Pantothenic acid Dexpanthenol Pantethine B 6 Pyridoxine , Pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxamine Pyritinol B 7 Biotin B 9 Folic acid Dihydrofolic acid Folinic acid Levomefolic acid B 12 Adenosylcobalamin Cyanocobalamin Hydroxocobalamin Methylcobalamin. Ascorbic acid Dehydroascorbic acid. Kwashiorkor Marasmus Catabolysis. B 1 Beriberi Wernicke—Korsakoff syndrome Wernicke's encephalopathy Korsakoff's syndrome B 2 Riboflavin deficiency B 3 Pellagra B 6 Pyridoxine deficiency B 7 Biotin deficiency B 9 Folate deficiency B 12 Vitamin B 12 deficiency. A: Vitamin A deficiency Bitot's spots C: Scurvy D: Vitamin D deficiency Rickets Osteomalacia Harrison's groove E: Vitamin E deficiency K: Vitamin K deficiency. Electrolyte imbalance Calcium Chloride Phosphate Potassium Magnesium Sodium Iron Zinc Manganese Copper Iodine Chromium Molybdenum Selenium Keshan disease Fluorine. Delayed milestone Failure to thrive Short stature Idiopathic. Anorexia Weight loss Cachexia Underweight. Authority control databases : National France BnF data Israel United States Japan Czech Republic. Category : B vitamins. Hidden categories: Articles with short description Short description matches Wikidata All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from August All articles lacking reliable references Articles lacking reliable references from August Articles lacking reliable references from March Articles needing additional references from January All articles needing additional references Articles with BNF identifiers Articles with BNFdata identifiers Articles with J9U identifiers Articles with LCCN identifiers Articles with NDL identifiers Articles with NKC identifiers. Toggle limited content width. A coenzyme in the catabolism of sugars and amino acids. A precursor of coenzymes called FAD and FMN , which are needed for flavoprotein enzyme reactions, including activation of other vitamins. A precursor of coenzymes called NAD and NADP , which are needed in many metabolic processes. A precursor of coenzyme A and therefore needed to metabolize many molecules. A coenzyme for carboxylase enzymes, needed for synthesis of fatty acids and in gluconeogenesis. A precursor needed to make, repair, and methylate DNA; a cofactor in various reactions; especially important in aiding rapid cell division and growth, such as in infancy and pregnancy. Commonly cyanocobalamin or methylcobalamin in vitamin supplements. A coenzyme involved in the metabolism of all animal cells, especially affecting DNA synthesis and regulation, but also fatty acid metabolism and amino acid metabolism. Thiamine plays a central role in the release of energy from carbohydrates. It is involved in RNA and DNA production, as well as nerve function. Its active form is a coenzyme called thiamine pyrophosphate TPP , which takes part in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl coenzyme A in metabolism. Riboflavin is involved in release of energy in the electron transport chain , the citric acid cycle , as well as the catabolism of fatty acids beta oxidation. Niacin is composed of two structures: nicotinic acid and nicotinamide. |
| Share via email | because it is plentiful in many foods. However, it may affect people with severe malnutrition. In such cases, they are usually deficient in other nutrients as well. People with a specific gene mutation called pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration 2 mutation are at a high risk of deficiency. Vitamin B-6, or pyridoxine, plays a role in more than enzyme reactions. The body needs vitamin B-6 for:. Many deficiencies in vitamin B-6 are linked to low levels of vitamin B, according to the National Institutes of Health NIH Office of Dietary Supplements. Manufacturers add biotin to many hair, skin, and nail supplements. However, the NIH state that there is not sufficient evidence to conclude whether taking extra biotin helps with hair, skin, or nails. Some people believe that biotin may help with psoriasis. The natural form of vitamin B-9 is called folate. Folic acid , which is present in fortified foods and some supplements, is a synthetic form of the vitamin. Because most people cannot take in enough leafy green vegetables for the levels needed in pregnancy, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC suggest that all women of reproductive age who wish to conceive take mcg of folic acid each day, alongside eating a varied diet that contains folate. When a woman has high enough levels of folate both before and during pregnancy, the fetus has a lower risk of certain birth defects affecting the brain and spinal cord. The FDA require manufacturers to add folic acid to standardized enriched grain products to help reduce the risk of neural tube defects. People can get folic acid from fortified breads and cereals. The addition of folic acid to grain products has made folate deficiency uncommon. However, the possible symptoms of a folate deficiency may include:. The FDA recommend that women increase the intake of folates and take folic acid supplements every day before becoming pregnant and during pregnancy. Other groups who may need extra folate include people who have:. People should not take more than 1, mcg of folic acid each day. Taking more than this can mask symptoms of a vitamin B deficiency. This can cause permanent nerve damage. People who do not eat animal products may need to get vitamin B from supplements or fortified foods such as breakfast cereals and nutritional yeast. Learn more about vegetarian and vegan sources of vitamin B here. Vitamin B deficiency usually causes a condition called megaloblastic anemia. Symptoms of a vitamin B deficiency can include:. People can buy B vitamins as individual supplements if they are deficient in only one type. However, some evidence suggests that a full B-complex vitamin supplement may be a better choice, even if a person has just one deficiency. The researchers state that most people have deficiencies and would benefit from a high-dose B-complex supplement. Multivitamins and individual vitamin supplements are available to buy in drug stores and online. Choose from a range of B vitamin supplements using the following links:. B vitamins each have their own unique functions, but they depend upon one another for proper absorption and the best health benefits. Eating a healthful, varied diet will generally provide all the B vitamins a person needs. People can treat and prevent B vitamin deficiencies by increasing their dietary intake of high-vitamin foods or taking vitamin supplements. HUM nutrition offers a range of products to support a person's health. Here is our review for Here, we review mindbodygreen supplements, online courses, and the brand's reputation. Having low levels of vitamin K may indicate a higher risk of having poorer lung function and conditions such as asthma and chronic obstructive…. Vitamin D levels in the blood are associated with the severity of psoriasis, an autoimmune condition that affects millions of people. A new study reports that age-related memory loss may be improved in the short term by taking a daily multivitamin. The findings show that one year of…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. A complete guide to B vitamins. Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm. Overview Daily values Thiamin Riboflavin Niacin Pantothenic acid Vitamin B-6 Biotin Folate Vitamin B Supplements Summary. How we vet brands and products Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm? Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices? We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness. Read more about our vetting process. Was this helpful? What are B vitamins? Share on Pinterest Some people may benefit from taking B vitamin supplements. Daily values. Thiamin vitamin B Further resources For more in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub. Riboflavin vitamin B Niacin vitamin B Most legumes — such as pinto beans, black beans, and lentils — are high in folate, a B vitamin important for reducing the risk of certain birth defects. Chicken and turkey are most notable for their niacin and pyridoxine content. White meat — such as the breast — supplies more of these two vitamins than dark meat — such as the thigh — as shown in the table below. Chicken and turkey, especially the white meat portions, are high in B3 and B6. Poultry also supplies smaller amounts of riboflavin, pantothenic acid, and cobalamin. Most of the nutrients are in the meat, not the skin. Yogurt is notable for its riboflavin and B12 content. Stores also sell many non-dairy yogurt alternatives , such as fermented soy, almond, or coconut yogurts. Limit your intake of sugar-sweetened yogurt. Rather, people use them to boost the flavor and nutrient profile of dishes. These yeasts naturally contain B vitamins and are often fortified with them as well — particularly nutritional yeast. The nutty-cheesy flavor of nutritional yeast also makes it popular as a seasoning. These products can be used to add flavor or nutrients to other foods. Like other common meats, pork is packed with several B vitamins. Pork is especially high in thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and B6. Pork loin cuts are much leaner and lower in calories than shoulder cuts, spareribs, and bacon. Breakfast cereals often contain added vitamins, including B vitamins. Check for them in the ingredients list The B vitamins most commonly added to cereal are thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, B6, folate as synthetic folic acid , and B Keep in mind that many fortified breakfast cereals are high in added sugars and refined grains. Select a product with less than 5 g of sugar per serving and a whole grain — such as whole wheat or whole oats — listed as the first ingredient. Breakfast cereals often have added thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, folic acid, B6, and B Trout, a freshwater fish , is closely related to salmon and high in several B vitamins. Additionally, trout is an excellent source of protein , rich in omega-3 fats, and low in mercury 4 , Trout is high in thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, and vitamin B It also contains ample protein and omega-3 fats. Sunflower seeds are one of the best plant sources of pantothenic acid. Sunflower seeds are also a good source of niacin, folate, and B6 Sunflower seed butter, which is popular among people with nut allergies, provides some pantothenic acid as well Sunflower seeds and their butter are among the highest plant sources of pantothenic acid, a B vitamin found only in small amounts in most foods. Consuming adequate amounts of the eight B complex vitamins puts you on the path to a nutritious diet. Some top sources of B vitamins include meat especially liver , seafood, poultry, eggs, dairy products, legumes, leafy greens, seeds, and fortified foods, such as breakfast cereal and nutritional yeast. If you restrict your intake from some food groups due to allergies or diet, your chances of B vitamin deficiencies may increase. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. The foods you eat play a big role in your overall health. Learn how to get the vitamins you need — including vitamins A, B, C, D, E, and K — in your…. Niacin, or vitamin B3, is an essential nutrient, which aids your metabolism and nervous system and which you must obtain through your diet. Here are…. Niacin vitamin B3 is a very important nutrient for your body. It has many health benefits, along with several side effects if you take large doses…. Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in keeping you healthy. Here are 8 ways that this vitamin benefits your health, based on…. Wondering what vitamins are most important during pregnancy? B complex, which contains the spectrum of B vitamins, will keep your body strong while…. Vitamin B12 is a nutrient you need for good health. It's one of eight B vitamins that help your body convert the food you eat into energy. Learn more…. MindBodyGreen provides third-party-tested supplements made with high quality ingredients. Our testers and dietitians discuss whether MindBodyGreen…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Nutrition Evidence Based 15 Healthy Foods High in B Vitamins. Medically reviewed by Amy Richter, RD , Nutrition — By Marsha McCulloch, MS, RD — Updated on January 24, Leafy greens. Liver and other organ meats. |
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Welcher anmutig topic
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Es ist die richtigen Informationen