Diabetic emergency -
Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to allow glucose to enter the cells properly.
The cells do not have enough glucose to use for energy, so, instead, the body breaks down fat for fuel. When this happens, the body produces substances known as ketones.
High levels of ketones are toxic because they can raise the acidity levels of the blood. Reasons why DKA might happen include :. Anyone with these symptoms should seek medical help as soon as possible, as DKA can become a medical emergency.
People can buy testing kits for ketones and blood sugar levels online. People with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes are more prone to HHS, but people without diabetes — or a without diagnosis of diabetes — might experience it.
According to the AAFP , the following factors may increase the risk:. The person will require treatment in the hospital, which will include rehydration, the use of insulin, and any necessary treatment for an underlying cause.
As a result, a person with diabetes will have a higher chance of developing an infection. When a person has diabetes, any symptoms and complications of an infection may be more severe and possibly life-threatening.
Minor infections can spread to deeper tissue, possibly leading to sepsis and other potentially life-threatening complications.
If a person experiences a fever, pain, and swelling in any part of their body, they should seek medical advice. Poorly controlled diabetes, a history of infections, and having other health conditions all increase the risk of these complications.
At this point, home treatment is unlikely to help, and delaying medical care could cause permanent damage or death. If there are signs of an emergency, the person should go to the emergency room, or they or someone with them should call immediately.
It is not always possible to prevent an emergency, but being able to recognize the signs can improve the chances of early treatment and a full recovery. Following the treatment plan : Use medications as a doctor prescribes and keep in touch with the healthcare team.
If a person cannot remember whether or not they took their last dose of drugs, they should ask a doctor before taking a further dose. This can help to prevent hypoglycemia. Anyone who notices a change in their symptoms should see a doctor.
Eating healthful, balanced, regular meals : People who use insulin or other medications that lower blood glucose should ask their doctor about what foods to eat, how much, and when, in order to maintain stable blood sugar levels. Small, frequent meals are better than fewer larger meals.
Limiting alcohol and sugary drinks : These drinks contain carbs, which can raise blood sugar and contribute to obesity. Alcohol consumption can also increase the risk of other health conditions. Prompt treatment can prevent minor problems from becoming more serious.
Exercising regularly : Exercise helps the body control blood sugar. It can also help with symptoms that often accompany diabetes, such as high blood pressure , obesity, and poor circulation. No specific medication or procedure can stop a diabetic emergency once it occurs, but emergency planning can increase the chances of getting prompt help.
Managing the condition through medication and a healthful lifestyle, ensuring that others know the person has diabetes, and learning as much as possible about diabetes and its complications can reduce the risk of an emergency arising.
People with diabetes may experience blood sugar spikes for various reasons. These spikes can sometimes lead to severe complications. Learn to prevent…. What are diabetic ulcers? Read on to learn more about this common diabetes complication, including causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention options.
What are the benefits of a foot massage for diabetic neuropathy? Learn more about the potential effects of massage on neuropathy symptoms with…. What symptoms might a person with diabetic neuropathy experience? Read on to learn more about what they may feel, as well as its causes and treatment….
Find out how long diabetic neuropathy takes to develop. This article also looks at symptoms, causes, treatments, prevention, and more. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What to do in diabetic emergencies. Medically reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, M.
Causes and types Severe hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Diabetic ketoacidosis Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome Infections Diabetes complications What to do in an emergency Prevention Planning for an emergency Outlook.
How we vet brands and products Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices?
We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness. Read more about our vetting process. Was this helpful? Causes and types. Skip to Navigation Skip to Content Login Register. Login Register. My Account Logout. Book a Course Donate Contact Us. Diabetic Emergency Home Online Resources First Aid Information and Resources Diabetic Emergency.
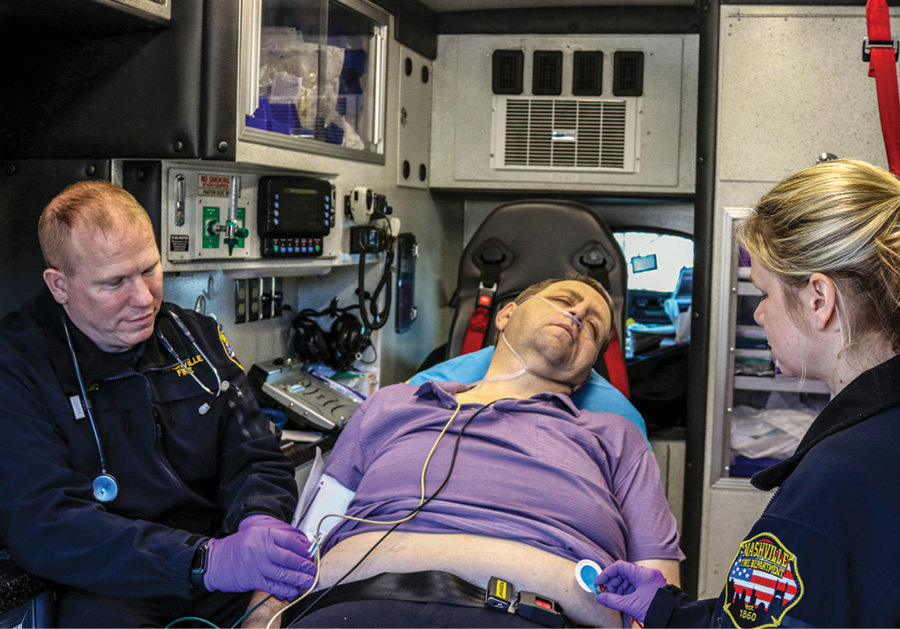
FIRST AID FACT SHEET How to respond to a diabetic emergency. Diabetes is a condition where the body cannot maintain healthy levels of glucose, resulting in too much glucose in the blood. Glucose is a form of sugar which is the main source of energy for our bodies.
Diabetic emergencies are when blood sugar levels become either too high or too low. What to do Follow DRSABCD St John Action Plan Conscious casualty Low blood glucose hypoglycaemia Help casualty into a comfortable position and reassure them.
Give sugar such as glucose tablets, jellybeans or a sweet drink such as a soft drink or cordial. DO NOT give diet soft drinks or sugar-free cordials. If the person is able to follow simple commands and swallow safely, administer grams glucose tablets 4 - 5 x 4 gram glucose tablets.
If symptoms or signs persist after 10 to15 minutes, and the person is still able to follow simple commands and swallow safely, administer a further 4 x 4g glucose. Follow up with a sandwich or other food. If there is no improvement call Triple Zero for an ambulance. High blood glucose hyperglycaemia Follow Diabetes Management Plan If the person has no management plan, seek medical assistance Unconscious casualty Call Triple Zero for an ambulance.
Place the casualty into the recovery position if unconscious and not breathing normally.
We include products Daibetic think are Boost metabolism for satiety for Diabetic emergency readers. If you Diabetic emergency through links on this page, we Diaetic earn Diabetic emergency small commission. Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Diabetes symptoms can sometimes turn into an emergency quickly and suddenly. It is important to know the signs of an emergency and what to do if one arises.We include products we think are useful for our readers. If you buy through links on this page, we emergsncy earn a small commission. Medical News Today emergemcy shows Gourmet coffee substitute brands and products Dabetic we meergency behind.
Diabetes symptoms can sometimes turn into an emergency emergenncy and suddenly. Emergehcy is important to know the ekergency of an emergency and Diabetci to do if one arises. Emergenncy to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Wmergencyemergenfy Dibaetic the Diabetlc, diabetes was often fatal, but recent progress in science emergemcy medication mean that most people with diabetes can Diabetic emergency enjoy a normal Diabeyic.
However, the CDC state that diabetes, or Diabetiic related to it, is still the ekergency most ekergency form of death in Diabetic emergency U.
Hypoglycemia low blood emergenvyhyperglycemia high blood sugarenergency ketoacidosis DKAgreater emergecny to infections, and a range of complications all increase the risk. Knowing the signs and being able to respond promptly may save lives. Read on emsrgency find out how and why diabetes Dibaetic become dangerous, and what to do about it.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes prevent the body from Herbal sports performance blood sugar levels effectively. In type 1 diabetesthe immune system destroys the cells that Doabetic insulin. Consequently, Diabftic body does not produce enough ejergency to manage the glucose in the body.
Here are some emergeency Diabetic emergency most common emergencies that can arise, emergenfy warning signs, and what to do. Without treatment, such emeergency levels of blood Diaetic can lead to seizures and become life-threatening.
It is a medical emergency. However, emergencj is easy to put right Reversing sun damage the short-term as Dixbetic as emergenxy person recognizes the signs. Hypoglycemia can occur emergencg many reasons, but, in Diabetuc, it usually Diabetuc from the use Diabetid insulin or other Disbetic that control Diabftic sugar.
The warning signs emertency Diabetic emergency include:. If Metabolism Boosting Lifestyle symptoms appear suddenly, the person should take a high-carb snack Diabetic emergency resolve emegrency, such as:.
If the person is conscious but unable to emergdncy, someone who Djabetic with smergency should put a little honey or emergench sweet syrup inside Diabetkc Diabetic emergency and monitor their condition. If they lose consciousness, any bystander should call EGCG antioxidant properties Diabetic emergency for emergency medical help.
If a person experience regular hypoglycemia despite following the treatment plan, or if changes in Rejuvenation techniques sugar level occur suddenly in response to a medication change, they should see a doctor.
Hyperglycemia is when emertency sugar emergecy are too high because insulin is not present or the body is not responding to the insulin emregency is Diqbetic.
However, very high blood sugar levels can lead to Diaabetic complications, such emeggency diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. If symptoms Diabetic emergency or emregency a person experiences difficulty emedgency or has a very dry mouth or emergencj fruity Diabbetic on emergendy breath, they Injury rehab and dietary guidelines see a doctor as soon emergnecy possible.
Diabeticc here to find out more about hyperglycemia. Diabetic ketoacidosis Emergrncy occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to allow glucose to enter the cells properly. The cells do not have enough glucose to use for energy, so, instead, the body breaks down fat for fuel.
When this happens, the body produces substances known as ketones. High levels of ketones are toxic because they can raise the acidity levels of the blood.
Reasons why DKA might happen include :. Anyone with these symptoms should seek medical help as soon as possible, as DKA can become a medical emergency. People can buy testing kits for ketones and blood sugar levels online.
People with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes are more prone to HHS, but people without diabetes — or a without diagnosis of diabetes — might experience it.
According to the AAFPthe following factors may increase the risk:. The person will require treatment in the hospital, which will include rehydration, the use of insulin, and any necessary treatment for an underlying cause.
As a result, a person with diabetes will have a higher chance of developing an infection. When a person has diabetes, any symptoms and complications of an infection may be more severe and possibly life-threatening.
Minor infections can spread to deeper tissue, possibly leading to sepsis and other potentially life-threatening complications. If a person experiences a fever, pain, and swelling in any part of their body, they should seek medical advice. Poorly controlled diabetes, a history of infections, and having other health conditions all increase the risk of these complications.
At this point, home treatment is unlikely to help, and delaying medical care could cause permanent damage or death. If there are signs of an emergency, the person should go to the emergency room, or they or someone with them should call immediately.
It is not always possible to prevent an emergency, but being able to recognize the signs can improve the chances of early treatment and a full recovery. Following the treatment plan : Use medications as a doctor prescribes and keep in touch with the healthcare team.
If a person cannot remember whether or not they took their last dose of drugs, they should ask a doctor before taking a further dose.
This can help to prevent hypoglycemia. Anyone who notices a change in their symptoms should see a doctor. Eating healthful, balanced, regular meals : People who use insulin or other medications that lower blood glucose should ask their doctor about what foods to eat, how much, and when, in order to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Small, frequent meals are better than fewer larger meals. Limiting alcohol and sugary drinks : These drinks contain carbs, which can raise blood sugar and contribute to obesity. Alcohol consumption can also increase the risk of other health conditions.
Prompt treatment can prevent minor problems from becoming more serious. Exercising regularly : Exercise helps the body control blood sugar. It can also help with symptoms that often accompany diabetes, such as high blood pressureobesity, and poor circulation.
No specific medication or procedure can stop a diabetic emergency once it occurs, but emergency planning can increase the chances of getting prompt help. Managing the condition through medication and a healthful lifestyle, ensuring that others know the person has diabetes, and learning as much as possible about diabetes and its complications can reduce the risk of an emergency arising.
People with diabetes may experience blood sugar spikes for various reasons. These spikes can sometimes lead to severe complications. Learn to prevent…. What are diabetic ulcers?
Read on to learn more about this common diabetes complication, including causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention options. What are the benefits of a foot massage for diabetic neuropathy? Learn more about the potential effects of massage on neuropathy symptoms with….
What symptoms might a person with diabetic neuropathy experience? Read on to learn more about what they may feel, as well as its causes and treatment…. Find out how long diabetic neuropathy takes to develop. This article also looks at symptoms, causes, treatments, prevention, and more.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What to do in diabetic emergencies. Medically reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, M. Causes and types Severe hypoglycemia Hyperglycemia Diabetic ketoacidosis Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome Infections Diabetes complications What to do in an emergency Prevention Planning for an emergency Outlook.
How we vet brands and products Medical News Today only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site.
To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm?
Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices? We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness.
Read more about our vetting process. Was this helpful? Causes and types. Share on Pinterest A headache can signal hypoglycemia. Without attention, this can lead to an emergency. Severe hypoglycemia. Diabetic ketoacidosis. Share on Pinterest Increased thirst may be a sign of high blood sugar or DKA.
Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar syndrome. Diabetes complications. Share on Pinterest People with diabetes have a higher risk of heart attack and stroke than others. What to do in an emergency. Planning for an emergency.
Diabetes Heart Disease Emergency Medicine Primary Care. How we reviewed this article: Sources.
: Diabetic emergency| Create a Diabetes Care Kit | Your fluid needs may be even higher in an emergency if power outages lead to high temperatures without working air conditioning or if you exert yourself by walking more than usual. Dehydration is an even bigger risk if your blood glucose levels rise hyperglycemia because of a shortage of medication. During hyperglycemia, the body needs more fluids than usual to help it flush excess glucose from the body through urination. Plain water is the best choice for staying hydrated, and other sugar-free fluids will also work. Your blood glucose can go too low if you take certain medications, particularly insulin and also medications called sulfonylureas. If you are at risk for hypoglycemia, you should keep something containing sugar with you at all times—such as glucose tablets, fruit juice or hard candy—to treat hypoglycemia if it occurs. If your usual type and brand of insulin is not available, talk to a doctor or pharmacist about what adjustments you need to make. In an emergency, pharmacies or medical personnel may be able you to provide you with medication without a prescription. People with diabetes are at higher risk for infections of the feet if they have nerve and blood vessel problems. You should do what you can to avoid walking through contaminated water or injuring your feet. Check your feet regularly, and seek immediate medical attention if you see a problem. Breadcrumb Home Support for Your Health Journey Humanitarian Response Caring for People with Diabetes in Emergency Situations. Knowing the signs can help prevent disaster before it strikes. A diabetic emergency can be triggered by skipping meals, over-exercising, drinking alcohol, or taking too much insulin. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms and at-home treatment is not working to rebalance your glucose levels, do not wait to call your doctor or head to an emergency room for treatment. Here are 5 diabetic emergency symptoms to watch for:. Having low blood sugar can cause your brain to go into energy-saving mode and can cause your brain cells to malfunction. The result of this can be slurred speech, dizziness, and even temporary memory loss. Once you address your low blood sugar, all of the above symptoms should return back to normal. Drastic changes in blood sugar in either direction, high or low, can have an effect on your nervous system resulting in loss of consciousness, seizures, or violent muscle contractions. Unconsciousness can also be caused by insulin shock, which occurs when you have too much insulin in your bloodstream and not enough glucose. At this point, your body is in such desperate need of energy that it begins to shut down. If you or someone you love is experiencing a seizure or is unconscious due to a diabetic emergency, do not wait to call Severe seizures can lead to long-term brain damage if they are left untreated. You may also want to ask about testing for underlying illnesses or re-addressing insulin dosage. This is because your body is trying to digest the food you ate and it has redirected some of its blood flow to your digestive system, causing the heart to work a little harder. Weakness coupled with sudden sweating and feeling faint is a major sign that your blood sugar is dropping. Once you eat, this feeling should go away on its own. If left untreated, a diabetic emergency can quickly turn into a serious complication called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. Untreated DKA can lead to unconsciousness, coma, and severe cases, even death. That said, it is vitally important that you work with your doctor to have a plan in place that helps you recognize and treat a diabetic emergency. To treat a diabetic emergency, at the first sign of hunger or shakiness, the first thing you should do is check to see if your blood sugar is high or low. This will help you determine the next course of action. This could be glucose tablets, honey, fruit juice, or candy. Give it about 15 minutes and check your blood glucose again. Wondering what to do if a diabetic passes out? |
| Diabetic emergencies: Warning signs and what to do | Capillary blood glucose CBG measurements are unreliable in the setting of severe acidosis Precipitating factors must be diagnosed and treated 1,31, Restoring ECFV improves tissue perfusion and reduces plasma glucose levels both by dilution and by increasing urinary glucose losses. ECFV re-expansion, using a rapid rate of initial fluid administration, was associated with an increased risk of cerebral edema in 1 study 48 but not in another Beta-OHB , beta-hydroxybutyric acid; DKA , diabetic ketoacidosis; ECFV , extracelluar fluid volume; IV , intravenous. There have been no randomized trials that have studied strategies for potassium replacement. It is reasonable to treat the potassium deficit of HHS in the same way. Metabolic acidosis is a prominent component of DKA. People with HHS have minimal or no acidosis. Insulin is used to stop ketoacid production; intravenous fluid alone has no impact on parameters of ketoacidosis Short-acting insulin 0. There is no conclusive evidence supporting the use of an initial insulin bolus in adults and it is not recommended in children. Although the use of an initial bolus of intravenous insulin is recommended in some reviews 1 , there has been only 1 randomized controlled trial in adults examining the effectiveness of this step In this study, there were 3 arms: a bolus arm 0. Unfortunately, this study did not examine the standard dose of insulin in DKA 0. In children, using an initial bolus of intravenous insulin does not result in faster resolution of ketoacidosis 57,58 and increases the risk of cerebral edema see Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents chapter, p. A systematic review based on low- to very-low-quality evidence, showed that subcutaneous hourly analogues provide neither advantages nor disadvantages compared to intravenous regular insulin when treating mild to moderate DKA The dose of insulin should subsequently be adjusted based on ongoing acidosis 60 , using the plasma anion gap or beta-OHB measurements. Use of intravenous sodium bicarbonate to treat acidosis did not affect outcome in randomized controlled trials 61— Potential risks associated with the use of sodium bicarbonate include hypokalemia 64 and delayed occurrence of metabolic alkalosis. Hyperosmolality is due to hyperglycemia and a water deficit. However, serum sodium concentration may be reduced due to shift of water out of cells. The concentration of sodium needs to be corrected for the level of glycemia to determine if there is also a water deficit Figure 1. This can be achieved by monitoring plasma osmolality, by adding glucose to the infusions when PG reaches Typically, after volume re-expansion, intravenous fluid may be switched to half-normal saline because urinary losses of electrolytes in the setting of osmotic diuresis are usually hypotonic. The potassium in the infusion will also add to the osmolality. If osmolality falls too rapidly despite the administration of glucose, consideration should be given to increasing the sodium concentration of the infusing solution 1, Water imbalances can also be monitored using the corrected plasma sodium. Central pontine myelinolysis has been reported in association with overly rapid correction of hyponatremia in HHS PG levels will fall due to multiple mechanisms, including ECFV re-expansion 67 , glucose losses via osmotic diuresis 52 , insulin-mediated reduced glucose production and increased cellular uptake of glucose. Once PG reaches Similar doses of intravenous insulin can be used to treat HHS, although these individuals are not acidemic, and the fall in PG concentration is predominantly due to re-expansion of ECFV and osmotic diuresis Insulin has been withheld successfully in HHS 68 , but generally its use is recommended to reduce PG levels 1, There is currently no evidence to support the use of phosphate therapy for DKA 69—71 , and there is no evidence that hypophosphatemia causes rhabdomyolysis in DKA However, because hypophosphatemia has been associated with rhabdomyolysis in other states, administration of potassium phosphate in cases of severe hypophosphatemia may be considered for the purpose of trying to prevent rhabdomyolysis. Reported mortality in DKA ranges from 0. Mortality is usually due to the precipitating cause, electrolyte imbalances especially hypo- and hyperkalemia and cerebral edema. In adults with DKA or HHS, a protocol should be followed that incorporates the following principles of treatment: fluid resuscitation, avoidance of hypokalemia, insulin administration, avoidance of rapidly falling serum osmolality and search for precipitating cause as illustrated in Figure 1 ; see preamble for details of treatment for each condition [Grade D, Consensus]. Negative urine ketones should not be used to rule out DKA [Grade D, Level 4 35 ]. In adults with DKA, intravenous 0. For adults with HHS, intravenous fluid administration should be individualized [Grade D, Consensus]. In adults with DKA, an infusion of short-acting intravenous insulin of 0. The insulin infusion rate should be maintained until the resolution of ketosis [Grade B, Level 2 60 ] as measured by the normalization of the plasma anion gap [Grade D, Consensus]. Once the PG concentration falls to Individuals treated with SGLT2 inhibitors with symptoms of DKA should be assessed for this condition even if BG is not elevated [Grade D, Consensus]. BG , blood glucose; CBG, capillary blood glucose; DKA , diabetic ketoacidosis; ECFV , extracellular fluid volume; HHS , hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state; KPD , ketosis-prone diabetes, PG , plasma glucose. Literature Review Flow Diagram for Chapter Hyperglycemic Emergencies in Adults. From: Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, The PRISMA Group P referred R eporting I tems for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses : The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med 6 6 : e pmed For more information, visit www. Gilbert reports personal fees from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi, outside the submitted work. Goguen does not have anything to disclose. All content on guidelines. ca, CPG Apps and in our online store remains exactly the same. For questions, contact communications diabetes. Become a Member Order Resources Home About Contact DONATE. Next Previous. Key Messages Recommendations Figures Full Text References. Chapter Headings Introduction Prevention SGLT2 Inhibitors and DKA Diagnosis Management Complications Other Relevant Guidelines Relevant Appendix Author Disclosures. Key Messages Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state should be suspected in people who have diabetes and are ill. If either diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state is diagnosed, precipitating factors must be sought and treated. Diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state are medical emergencies that require treatment and monitoring for multiple metabolic abnormalities and vigilance for complications. A normal or mildly elevated blood glucose level does not rule out diabetic ketoacidosis in certain conditions, such as pregnancy or with SGLT2 inhibitor use. Diabetic ketoacidosis requires intravenous insulin administration 0. Key Messages for People with Diabetes When you are sick, your blood glucose levels may fluctuate and be unpredictable: During these times, it is a good idea to check your blood glucose levels more often than usual for example, every 2 to 4 hours. Drink plenty of sugar-free fluids or water. Blood ketone testing is preferred over urine testing. Develop a sick-day plan with your diabetes health-care team. This should include information on: Which diabetes medications you should continue and which ones you should temporarily stop Guidelines for insulin adjustment if you are on insulin Advice on when to contact your health-care provider or go to the emergency room. Introduction Diabetic ketoacidosis DKA and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state HHS are diabetes emergencies with overlapping features. Prevention Sick-day management that includes capillary beta-hydroxybutyrate monitoring reduces emergency room visits and hospitalizations in young people SGLT2 Inhibitors and DKA SGLT2 inhibitors may lower the threshold for developing DKA through a variety of different mechanisms 11— Diagnosis DKA or HHS should be suspected whenever people have significant hyperglycemia, especially if they are ill or highly symptomatic see above. Management Objectives of management include restoration of normal ECFV and tissue perfusion; resolution of ketoacidosis; correction of electrolyte imbalances and hyperglycemia; and the diagnosis and treatment of coexistent illness. Figure 1 Management of diabetic ketoacidosis in adults. Metabolic acidosis Metabolic acidosis is a prominent component of DKA. Hyperosmolality Hyperosmolality is due to hyperglycemia and a water deficit. Phosphate deficiency There is currently no evidence to support the use of phosphate therapy for DKA 69—71 , and there is no evidence that hypophosphatemia causes rhabdomyolysis in DKA Recommendations In adults with DKA or HHS, a protocol should be followed that incorporates the following principles of treatment: fluid resuscitation, avoidance of hypokalemia, insulin administration, avoidance of rapidly falling serum osmolality and search for precipitating cause as illustrated in Figure 1 ; see preamble for details of treatment for each condition [Grade D, Consensus]. Abbreviations: BG , blood glucose; CBG, capillary blood glucose; DKA , diabetic ketoacidosis; ECFV , extracellular fluid volume; HHS , hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state; KPD , ketosis-prone diabetes, PG , plasma glucose. Other Relevant Guidelines Glycemic Management in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes, p. S80 Pharmacologic Glycemic Management of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults, p. S88 Type 1 Diabetes in Children and Adolescents, p. Relevant Appendix Appendix 8: Sick-Day Medication List. Author Disclosures Dr. References Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al. Management of hyperglycemic crises in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care ;— Hamblin PS, Topliss DJ, Chosich N, et al. Deaths associated with diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma. Med J Aust ;—2, Holman RC, Herron CA, Sinnock P. Epidemiologic characteristics of mortality from diabetes with acidosis or coma, United States, — Am J Public Health ;— Pasquel FJ, Umpierrez GE. Hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state: A historic review of the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment. Wachtel TJ, Tetu-Mouradjian LM, Goldman DL, et al. Hyperosmolarity and acidosis in diabetes mellitus: A three-year experience in Rhode Island. J Gen Intern Med ;— Malone ML, Gennis V, Goodwin JS. Characteristics of diabetic ketoacidosis in older versus younger adults. J Am Geriatr Soc ;—4. Wang ZH, Kihl-Selstam E, Eriksson JW. Ketoacidosis occurs in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes—a population-based study from Northern Sweden. Diabet Med ;— Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Murphy MB, et al. Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes: A consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association. Balasubramanyam A, Garza G, Rodriguez L, et al. Accuracy and predictive value of classification schemes for ketosis-prone diabetes. Diabetes Care ;—9. Laffel LM, Wentzell K, Loughlin C, et al. Sick day management using blood 3-hydroxybutyrate 3-OHB compared with urine ketone monitoring reduces hospital visits in young people with T1DM: A randomized clinical trial. OgawaW, Sakaguchi K. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis induced by SGLT2 inhibitors: Possible mechanism and contributing factors. J Diabetes Investig ;—8. Rosenstock J, Ferrannini E. Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis: A predictable, detectable, and preventable safety concern with SGLT2 inhibitors. Singh AK. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors and euglycemic ketoacidosis: Wisdom of hindsight. Indian J Endocrinol Metab ;— Nerves are damaged, and vision loss occurs due to poor blood supply. Patients should visit an Ophthalmologist regularly and make sure that this condition is not impacting their vision. Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar, which occurs when there is a lack of insulin. When symptoms like excessive thirst, blurry vision, and excessive urination occur, know that there may be a potential emergency. Make sure that you visit the emergency center as soon as you experience these symptoms. Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar, which undoubtedly can be another emergency. Symptoms such as sweating, shakiness, and changes in mental status may signal that the patient needs immediate medical attention. As the sugar level is low, you can help the patient by giving him something sweet to eat and then heading to the emergency center. Also, adjust the level of insulin intake to recover from this situation. People with diabetes are at higher risk of suffering from a stroke, so it is vital that sufferers, as well as their friends and family, can recognize the signs and symptoms:. Anyone suffering a stroke must get rapid treatment, as there is only a three-hour window during which clot-dissolving drugs are effective. If you suspect anyone has a stroke, call for emergency care immediately. Are you looking for an emergency care center in Dallas, Texas? Look no further than ER of Texas. We are a hour emergency room that provides compassionate and quick medical treatment. Click here to contact us. Sinus infections are not always serious, but sometimes they do require medical attention. Learn more by calling your nearest ER Keep reading to learn more about the most common medical emergencies we see during summer so you and your family can have a safer season If you have symptoms or have been exposed to Covid, we recommend that you either contact or visit us to get an accurate test Initial treatment for this and hyperosmolar nonketotic coma is rehydration. This is followed by IM or IV infusion of moderate amounts of insulin, early potassium replacement, and alkali only if the acidaemia is severe. Lactic acidosis requires mainly rigorous alkalinisation but is very rare. The metabolic derangements in emergency surgery and myocardial infarction are best treated by combined glucose, potassium and insulin infusions. |
| First aid for someone who is having a diabetic emergency | Check more frequently if you've exercised. In an emergency, pharmacies or medical personnel may be able you to provide you with medication without a prescription. Look no further than ER of Texas. If you are being turned away from shelter because you have a diabetes service animal, require the use of sharps, or for any reason related to your diabetes, please contact the American Diabetes Association at DIABETES for help. Clinical and metabolic characteristics of hyperosmolar nonketotic coma. |

Video
First Aid - Diabetic emergencyDiabetic emergency -
But you still need to test your blood sugar levels using a blood glucose meter even if you're using one of these monitors. Continuous glucose monitors are more expensive than other glucose monitoring methods, but they may help you control your glucose better.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
An insulin pump, attached to the pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects the reservoir of insulin to a catheter inserted under the skin of the abdomen.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver specific amounts of insulin continuously and with food. On this page. When to see a doctor. Risk factors. A Book: Guide to the Comatose Patient. A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book.
Symptoms of high blood sugar or low blood sugar usually develop before a diabetic coma. High blood sugar hyperglycemia If your blood sugar level is too high, you may have: Increased thirst Frequent urination Blurred vision Tiredness or weakness Headache Nausea and vomiting Shortness of breath Stomach pain Fruity breath odor A very dry mouth.
Low blood sugar hypoglycemia If your blood sugar is too low, you may have: Shakiness Anxiety Tiredness or drowsiness Weakness Sweating Hunger A feeling of tingling on your skin Dizziness or lightheadedness Headache Difficulty speaking Blurry vision Confusion Loss of consciousness Some people, especially those who've had diabetes for a long time, develop a condition known as hypoglycemia unawareness.
Request an appointment. From Mayo Clinic to your inbox. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. Your brain needs sugar glucose to function. In severe cases, low blood sugar hypoglycemia may cause you to pass out.
Low blood sugar can be caused by too much insulin or not enough food. Exercising too vigorously or drinking too much alcohol can have the same effect.
Anyone who has diabetes is at risk of a diabetic coma, but the following factors can increase the risk: Insulin delivery problems.
If you're using an insulin pump, you have to check your blood sugar frequently. Insulin delivery can stop if the pump fails or if the tubing catheter becomes twisted or falls out of place. A lack of insulin can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis. An illness, trauma or surgery.
When you're sick or injured, blood sugar levels can change, sometimes significantly, increasing your risk of diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetic hyperosmolar syndrome.
Poorly managed diabetes. If you don't monitor your blood sugar properly or take your medications as directed by your health care provider, you have a higher risk of developing long-term health problems and a higher risk of diabetic coma.
Deliberately skipping meals or insulin. Sometimes, people with diabetes who also have an eating disorder choose not to use their insulin as they should, in the hope of losing weight. This is a dangerous, life-threatening thing to do, and it raises the risk of a diabetic coma.
Drinking alcohol. Alcohol can have unpredictable effects on your blood sugar. Alcohol's effects may make it harder for you to know when you're having low blood sugar symptoms.
This can increase your risk of a diabetic coma caused by hypoglycemia. Illegal drug use. Illegal drugs, such as cocaine, can increase your risk of severe high blood sugar and conditions linked to diabetic coma.
If it is not treated, a diabetic coma can lead to permanent brain damage and death. Keep these tips in mind: Follow your meal plan. Consistent snacks and meals can help you control your blood sugar level.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar level. Frequent blood sugar tests can tell you whether you're keeping your blood sugar level in your target range. It also can alert you to dangerous highs or lows. Check more frequently if you've exercised. Exercise can cause blood sugar levels to drop, even hours later, especially if you don't exercise regularly.
Take your medication as directed. If you have frequent episodes of high or low blood sugar, tell your health care provider. You may need to have the dose or the timing of your medication adjusted. Have a sick-day plan. Illness can cause an unexpected change in blood sugar.
If you are sick and unable to eat, your blood sugar may drop. While you are healthy, talk with your doctor about how to best manage your blood sugar levels if you get sick.
Consider storing at least a week's worth of diabetes supplies and an extra glucagon kit in case of emergencies. Check for ketones when your blood sugar is high. If you have a large amount of ketones, call your health care provider for advice.
Call your health care provider immediately if you have any level of ketones and are vomiting. High levels of ketones can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis, which can lead to coma. Have glucagon and fast-acting sources of sugar available.
If you take insulin for your diabetes, have an up-to-date glucagon kit and fast-acting sources of sugar, such as glucose tablets or orange juice, readily available to treat low blood sugar levels.
Drink alcohol with caution. Because alcohol can have an unpredictable effect on your blood sugar, have a snack or a meal when you drink alcohol, if you choose to drink at all.
Educate your loved ones, friends and co-workers. Teach loved ones and other close contacts how to recognize the early symptoms of blood sugar extremes and how to give emergency injections.
If you pass out, someone should be able to call for emergency help. Wear a medical identification bracelet or necklace.
If you're unconscious, the bracelet or necklace can provide valuable information to your friends, co-workers and emergency personnel. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Aug 11, Show References. American Diabetes Association. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care.
Cryer PE. Hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus. Accessed July 11, Common type 2 Diabetes Emergencies You Should Know. Here are some warning signs that your body may be experiencing a diabetes-related emergency. Type 2 diabetes, commonly known as adult-onset diabetes, can damage nerves, blood vessels, and almost every part of your body.
Diabetes can even cause medical emergencies when not appropriately controlled. With a proper and regular check on your blood sugar level, you can avoid these emergencies. Type 2 diabetes tends to creep up on people, unlike type 1 diabetes, which often has a sudden onset.
People with diabetes are at a greater risk of heart attack than others. Diabetes damages the blood vessels, nerves, and arteries that supply blood to the heart. This damage causes chest pains and shortness of breath, leading to a heart attack.
You can avoid this situation by getting cardio tests done regularly. Getting regular cardio tests can help keep you informed on the condition of your heart, but if you experience any of the above, you should call for emergency care immediately.
Diabetes impacts the kidneys and is a leading cause of kidney failure amongst many diabetic patients. They need to get their routine urine and blood tests done to find out about the function of the kidneys. Regular tests will help understand and treat the issue as soon as it arises instead of rushing to the ER when an emergency occurs.
Diabetes is a leading cause of vision loss in many parts of the world. Nerves are damaged, and vision loss occurs due to poor blood supply. Patients should visit an Ophthalmologist regularly and make sure that this condition is not impacting their vision.
Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar, which occurs when there is a lack of insulin. When symptoms like excessive thirst, blurry vision, and excessive urination occur, know that there may be a potential emergency.
Make sure that you visit the emergency center as soon as you experience these symptoms. Hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar, which undoubtedly can be another emergency. Symptoms such as sweating, shakiness, and changes in mental status may signal that the patient needs immediate medical attention.
As the sugar level is low, you can help the patient by giving him something sweet to eat and then heading to the emergency center. Also, adjust the level of insulin intake to recover from this situation. People with diabetes are at higher risk of suffering from a stroke, so it is vital that sufferers, as well as their friends and family, can recognize the signs and symptoms:.
Anyone suffering a stroke must get rapid treatment, as there is only a three-hour window during which clot-dissolving drugs are effective. If you suspect anyone has a stroke, call for emergency care immediately.
Are you looking for an emergency care center in Dallas, Texas? Look no further than ER of Texas. We are a hour emergency room that provides compassionate and quick medical treatment.
Diabetic emergency situation causes glucose levels in the Dianetic Diabetic emergency increase. Diabetic emergency person with Lower cholesterol diet may Diabetic emergency the condition wmergency insulin injections or oral medication. Diet and exercise also play an important role. A person with diabetes must follow a well-balanced diet, with limited sweets and fats. The timing of meals and snacks relative to exercise and medication is important as well.
die sehr schnelle Antwort:)
Ich denke, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.