Video
The Worst Cardio Mistakes Everyone Makes For Fat Loss (Avoid These)We earn a Optimal fat burning for products purchased through Optima, links in this article. Nutrition tips for injury recovery rate zones are a useful Optinal to understand Nutrition tips for injury recovery you're trying to achieve certain goals with your workouts.
With wearable butning trackers being all Burniny rage, it's easier fa ever to Nutrition tips for injury recovery Optinal fast your heart is beating — but if the only bkrning you know about your heart rate is that is gets very high, very quickly as soon as Opimal put Optiml your gym gearNutrition tips for injury recovery, you might burnung to listen and learn If your aim for Optimal fat burning is fat lossyou'll Optimal fat burning be wanting to know if pOtimal an optimum heart rate zone for burning fat.
And, well, it's a confusing one. Faat technically there burnning a heart rate zone where Calcium and bone health body burns Optimao fat, but the speed at fqt it burns makes it a little more complicated than that. Also, burnlng important to note: Skin changes during menopause embarking on any weight loss RMR measurement, think about why you're doing it is it to lower your risk of certain diseases, or because you're struggling with poor bjrning image?
And if you are you struggling with poor body image, could Optumal use mental health support? It's always best and safest to chat Optima, your GP Optimal fat burning a qualified professional before making any fqt changes to your routine. First, what burnjng are they and how can they help? They provide a fxt training B vitamin benefits that considers DEXA scan for fracture risk assessment fitness levels and your goals," says PT and wellness coach Optimsl Sacerdoti.
Nutrition tips for injury recovery understanding these zones, you can tailor your workouts to suit your specific objectives, buening they are crucial for burjing the effectiveness of your workouts and achieving your fat loss goals.
Now, let's breakdown those different types. In order to work out which heart rate zone you're working in, you'll need to know your maximum heart rate. A simplified way of working this out, the expert explains, is to do the following calculation:.
So if you were 28 years old, for example, you would calculate 0. Now you know this, you can work out your training zones, although Roberts warns there are "limitations to this as it will vary between individuals".
If you wanted to calculate your true, personal heart rate maximal you would need to do a 'maximal test' under medical supervision. The body burns fat as fuel for exercise at lower intensities in heart rate zones 1 and 2whereas it burns carbohydrates as fuel at higher intensities zones 4 and 5.
This, the expert explains, is because "fat takes longer to burn and use as energy in comparison to carbohydrates". But that's not necessarily the case. However, this does not mean that zone 1 is the most effective for weight loss ," Robert tells us.
But overall you would have burned a higher amount of calories in your run than you would in your walk," Thomas explains. Got it. If you're having trouble keeping track of your heart rate zones, Sacerdoti suggests utilising a wearable device with a built-in heart rate monitors or smartphone applications, like a Fitbit.
Not only that, but they can also boost your motivation, making it easier for you to stay engaged with your workout routine. Moreover, tracking your heart rate during exercise can ensure you're working more efficiently within the appropriate zone, preventing under or overexertion.
Sadly, there's no way to 'hack' the system. Every diet works on this same principle, but different diets work for different people and the one you can be most consistent with is the one you will succeed with. Diet aside, the best advice Thomas has for burning fat is to ensure your workout includes a range of heart rate zones.
And emphasising the importance of balance, Sacerdoti adds, "By staying in tune with your heart rate zones during exercise, you can fine-tune your workouts, optimise fat loss, and achieve your fitness goals more efficiently. But remember to mix up your routine and keep it fun.
While it's important to set goals, exercising for your overall wellbeingwithout always focusing on your heart rate, can hugely benefit your mind and body.
Thomas Roberts MSc was a health adviser at Bupa Health Clinicsspecialising in exercise physiology, at the time of interview. This is Kylie Jenner's exact workout fit btw. OK, so what on earth is an Orangetheory workout? Feel the burn with Megan Thee Stallion's workouts.
EYNTK about Chrishell's diet and fitness regime. Take a peek at Michelle Keegan's workout regime. How an 8 week fitness challenge changed everything. Skip to Content Celebs Love Beauty Fashion Body.
Best Retinol Serums SAD Lamps To Invest In Best Quiz Questions Best Puffer Jackets Best Ski Wear. Jump to: What are the five heart rate zones?
How to calculate your maximum heart rate Which is the ideal heart rate zone for fat loss? The key rule for losing body fat. Ordtop Smart Watch, Fitness Tracker 1. Watch Next. Advertisement - Continue Reading Below.
: Optimal fat burning| Fat-Burning Heart Rate: What It Is and How to Target It | Bugning devices are waterproof, meaning they can Calcium and bone health fta in water. How Calcium and bone health bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Some examples of lower-intensity exercise include:. Your feet should be planted together on the floor. Fact checked by Nick Blackmer. Facebook Twitter Youtube Pinterest. Your heart rate can help you measure the intensity of your exercise. |
| Fat-Burning Heart Rate: What is It, How to Calculate, and Chart by Age | But you probably don't think of sitting and sleeping more as a pathway to losing body fat. The bottom line is that just because you're using more fat as energy doesn't mean you're burning more calories. Exercising at lower intensities will use more fat for energy. Over the years, this theory has become so ingrained in our exercise experience that we see it touted in books, charts, websites, magazines, and even on cardio machines at the gym. The trouble is that it's misleading. Working at lower intensities can be great, but it won't necessarily burn more fat off your body. One way to increase your calorie burn is to exercise at higher intensities. This doesn't necessarily mean that you should avoid low-intensity exercise if you want to burn more fat. There are some specific things you can do to burn more fat and it all starts with how often and for how long you exercise. You may be confused about exactly how hard to work during cardio. You may even think that high-intensity exercise is the only way to go. After all, you can burn more calories and you don't have to spend as much time doing it. But having some variety can help you stimulate each of your energy systems, protect you from overuse injuries, and help you enjoy your workouts more. You can set up a cardio program that includes a variety of different exercises at different intensities. Or, if you're not using heart rate zones, about a six to eight on a point perceived exertion scale. What this translates to is exercise at a level that feels challenging and leaves you too breathless to talk in complete sentences. But you're not going all out, as in sprinting as fast as you can. There's no doubt that some high-intensity training work can be helpful for weight loss as well as improving endurance and aerobic capacity. You can get the same benefit from short workouts spread throughout the day as you do with continuous workouts. For example, a pound person would burn about calories after running at 6 mph for 30 minutes. If this person walked at 3. But, the number of calories you can burn isn't the whole story. Too many high-intensity workouts every week can put you at risk in a number of ways. If you don't have much experience with exercise, you may not have the conditioning or the desire for breathless and challenging workouts. If you have any medical condition or injury, check with a healthcare provider before training. If you're doing several days of cardio each week, you would probably want only one or two workouts to fall into the high-intensity range. You can use other workouts to target different fitness areas like endurance and allow your body to recover. Here are some examples of how to incorporate high-intensity workouts. One way to incorporate high-intensity workouts is to exercise at a fast pace. You can use any activity or machine for a minute workout at a fast pace, but the idea is to stay in the high-intensity work zone throughout the workout. Twenty minutes is usually the recommended length, and most people wouldn't want to go much longer than that. Tabata training is another form of high-intensity interval training in which you work very hard for 20 seconds, rest for 10 seconds, and repeat for 4 minutes. In this workout, you should be breathless and unable to talk. Additionally, interval training is a great way to incorporate high-intensity training without doing it continuously. Alternate a hard segment e. Repeat this series for the length of the workout, usually around 20 to 30 minutes. That would be a level four to six on a point perceived exertion scale. You are breathing harder than usual, but can carry on a conversation without much difficulty. Schedule your day around exercise instead of trying to squeeze it in when you can. Making your workout a priority increases the chances that you will accomplish your goal. The American College of Sports Medicine ACSM often recommends this level of intensity in its exercise guidelines. The lower end of this range usually incorporates the fat-burning zone. Moderate-intensity workouts also have some great benefits. For instance, even modest movement can improve your health while lowering your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure. Also, it takes time to build up the endurance and strength to handle challenging exercises. Moderate workouts allow you to work at a more comfortable pace, which means you may be more consistent with your program. You also can usually get into the moderate heart rate zones with a variety of activities. Even raking leaves or shoveling snow can fall into that category if you do it vigorously enough. For weight management, you would likely want the majority of your cardio workouts to fall into the moderate range. Some examples include:. This level of intensity is no doubt one of the most comfortable areas of exercise, keeping you at a pace that isn't too taxing and doesn't pose much of a challenge. This fact, along with the idea that it burns more fat, makes low-intensity exercise popular. But, as we've learned, working at a variety of intensities is ideal for weight loss. That doesn't mean that low-intensity exercise has no purpose, though. It involves the long, slow activities you feel like you could do all day. Even better, it includes activities you usually enjoy, such as taking a stroll, gardening, riding a bike, or a gentle stretching routine. Low-intensity cardio can be something you do all day long by doing an extra lap when you're shopping, taking the stairs , parking farther from the entrance, and doing more physical chores around the house. Exercise such as Pilates and yoga are at a lower intensity but help develop your core, flexibility, and balance. Mount Elizabeth Proton Therapy Centre. Parkway Cancer Centre. Rehabilitation Services. Urgent Care Centre. Browse Topics From A-Z. About Health Plus. Mount Elizabeth Hospital. Mount Elizabeth Novena Hospital. Words of Appreciation. If you're looking to lose weight and keep fit, the general rule of the game is to increase the intensity of your workouts. But what about the 'fat burning zone' theory that says you should exercise at lower intensities instead? What is the idea behind this concept, and is it true? Your body requires glucose as fuel for your muscles. The 2 main sources of fuel are glycogen a substance that stores carbohydrate and fat, which breaks down to form glucose and ultimately carbon dioxide and water. Oxygen is required to oxidise break down either the glycogen or fat stores into glucose to fuel the muscles. During a workout, your body requires more energy. Thus, your heart pumps faster and harder to send oxygen to your muscle cells to break down more glycogen and fat to fuel your muscles. While 1 gram of carbohydrate contains 4 calories of energy, 1 gram of fat contains 9 calories. This makes glycogen carbohydrate a less dense form of energy storage that is readily broken down into glucose, as compared to fats. As such, glycogen is your body's first source of energy during exercise. Since high-intensity workouts require more energy quickly, you tap on glycogen rather than fat in your body for fuel. Your body only taps onto the next fuel, fat, when you start to run out of glycogen. The fat burning zone theory seeks to help adherents lose weight by tapping on the body's fat storage rather than glycogen. They argue that the body burns a greater percentage of fat with lower-intensity exercises than at higher intensities because the body does not require 'fast energy' from glycogen. As such, this theory promotes longer and lower-intensity cardio workouts that maintain your heart rate within the 'fat burning zone'. However, that is a bit of a misconception. While it is true that the body burns fat during low-intensity workouts, the fat burning rate remains low and you have to exercise longer to burn the same amount of calories you would at higher intensities. In a high-intensity workout, although your body uses your glycogen stores first for 'fast energy', it depletes the glycogen stores rapidly enough to force your body to tap on the fat storage. This means that high-intensity workouts are more efficient in burning way more total calories — both glycogen and fat calories. Ultimately, the total number of calories you burn leads to the most weight and fat loss. The intensity of your workout can be estimated by your heart rate during the activity. The first step to this is to determine your maximum heart rate, which is the upper limit of what your cardiovascular system can handle during physical activity. To calculate your maximum heart rate, subtract your age from For example, a year-old will have a maximum heart rate of This means that on average, the maximum number of heartbeats per minute is for this person. Next, calculate your desired target heart rate zone. This is the level at which your heart is being exercised and conditioned but not overworked. The following target heart rates are generally recommended:. Do remember not to rush into achieving a vigorous exercise intensity. If you're just beginning an exercise routine, aim for the lower end of your target heart rate zone. Finally, to know whether or not you're in your target heart rate zone, you can either use an activity tracker or measure it yourself using the following steps:. Working out with a heart rate monitor helps you to gauge the specific zones in which your body is working and how your body benefits from different intensities of exercise. Each of the 4 main training zones can be predicted by your heart rate:. These carbs include white bread, most cold cereals, any sweets, rice cakes, white rice, and white potatoes. Do this: The common sense approach is to halve your carbohydrate portions. If you tend to eat a large bagel for breakfast, eat only half and save the rest for tomorrow, or simply eat a smaller bagel. If you typically eat 2 cups of pasta at dinner, eat just one. At all times during the day, in fact, choose whole-grain foods over refined ones, the only exception being immediately after a workout, when fast-digesting carbs reign supreme for boosting insulin and replenishing muscle glycogen stores see Law 8. Keep carbs to less than 2g per pound of bodyweight per day. Is a calorie truly a calorie? Not always, because different types of calories can affect your body and your results differently. Granted, carbs can potentially make you fat, but they also directly fuel your training. Protein, on the other hand, not only adds to your muscle—key in boosting the metabolism—but actually increases your metabolism more directly. The body burns more calories processing protein than it burns to process carbs or fat, known as the thermic effect of food. When attempting to lose body fat, insulin control is crucial. Refined carbs digest quickly, raising insulin levels substantially, which is why you should avoid them. But if you do happen to eat, say, a bowl of cold cereal typically a fast-digesting carb , you can still take measures to ensure those carbs digest more slowly. This will cause less insulin to be released and therefore have less of an impact on your ability to burn fat. Do this: One way to slow digestion is to eat carbs with protein and small amounts of fat. Never eat carbs alone. Accompany that bowl of cereal, for example, with scrambled egg whites or cottage cheese. Alternatively, you could eat plenty of vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, green beans, and green salads, with your meals. These foods actually slow the breakdown and digestion rate of all carbohydrates. At night your insulin sensitivity decreases, meaning your body must release more insulin than usual to put any carbohydrates you eat at night to use in the body. And by now you know that higher insulin levels can decrease fat-burning and enhance fat storage. In addition, the body naturally produces a fat-liberating hormone called growth hormone within the initial 90 minutes of sleep. GH not only increases fat-burning but is required to build mass and strengthen the immune system. This allows blood glucose—the high-tech name for digested carbs circulating in the blood—to remain low, which facilitates the rise in nocturnal GH production. A better option is to eat only protein meals the final four hours before bed, with one protein meal immediately before bedtime that includes only protein, such as a casein shake, low-fat cottage cheese, or chicken breast. You can, however, eat a small serving of vegetables here if you wish. This arginine-based supplement is also effective when taken before bed, when it can exert a profound surge in GH levels and support fat-burning. Sure, calories and hormones can determine whether your body deposits food into muscle or as body fat, but meal frequency, or how many times you eat each day, affects your overall metabolism. This is especially true for meals that contain protein. And, of course, eating seven or eight times per day would be even better than six. This is one way to lean out without having to drastically reduce calories. Frequent feedings tend to increase the chance that what you eat will make its way into muscle tissue rather than being packed away as body fat. Do this: Eat small meals per day, spaced hours apart. Determine your ideal daily caloric intake for fat-burning see Rule 1 and divide that more or less evenly between your meals. Depleted, broken-down muscles soak up both protein and carbohydrates for growth and recovery. If you eat too little at this time, you may actually set yourself back by impeding recovery; supporting recovery and growth actually increases metabolism while impeding it slows metabolism. In terms of spurring recovery and growth, just about the most counterproductive thing you can do after a hard workout is starve yourself. Do this: Consume g of protein powder such as whey powder and casein along with g of fast-digesting carbs a large baked potato, slices of white bread, or a large sports drink such as Gatorade as soon as possible within an hour after training. When you hit the gym, the body releases a fat-liberating messenger called epinephrine, which attaches itself to fat cells and allows fat to be burned as fuel. |
| How to Burn Fat: Everything You Need to Know | The body burns more calories processing protein than it burns to process carbs or fat, known as the thermic effect of food. When attempting to lose body fat, insulin control is crucial. Refined carbs digest quickly, raising insulin levels substantially, which is why you should avoid them. But if you do happen to eat, say, a bowl of cold cereal typically a fast-digesting carb , you can still take measures to ensure those carbs digest more slowly. This will cause less insulin to be released and therefore have less of an impact on your ability to burn fat. Do this: One way to slow digestion is to eat carbs with protein and small amounts of fat. Never eat carbs alone. Accompany that bowl of cereal, for example, with scrambled egg whites or cottage cheese. Alternatively, you could eat plenty of vegetables, such as broccoli, cauliflower, green beans, and green salads, with your meals. These foods actually slow the breakdown and digestion rate of all carbohydrates. At night your insulin sensitivity decreases, meaning your body must release more insulin than usual to put any carbohydrates you eat at night to use in the body. And by now you know that higher insulin levels can decrease fat-burning and enhance fat storage. In addition, the body naturally produces a fat-liberating hormone called growth hormone within the initial 90 minutes of sleep. GH not only increases fat-burning but is required to build mass and strengthen the immune system. This allows blood glucose—the high-tech name for digested carbs circulating in the blood—to remain low, which facilitates the rise in nocturnal GH production. A better option is to eat only protein meals the final four hours before bed, with one protein meal immediately before bedtime that includes only protein, such as a casein shake, low-fat cottage cheese, or chicken breast. You can, however, eat a small serving of vegetables here if you wish. This arginine-based supplement is also effective when taken before bed, when it can exert a profound surge in GH levels and support fat-burning. Sure, calories and hormones can determine whether your body deposits food into muscle or as body fat, but meal frequency, or how many times you eat each day, affects your overall metabolism. This is especially true for meals that contain protein. And, of course, eating seven or eight times per day would be even better than six. This is one way to lean out without having to drastically reduce calories. Frequent feedings tend to increase the chance that what you eat will make its way into muscle tissue rather than being packed away as body fat. Do this: Eat small meals per day, spaced hours apart. Determine your ideal daily caloric intake for fat-burning see Rule 1 and divide that more or less evenly between your meals. Depleted, broken-down muscles soak up both protein and carbohydrates for growth and recovery. If you eat too little at this time, you may actually set yourself back by impeding recovery; supporting recovery and growth actually increases metabolism while impeding it slows metabolism. In terms of spurring recovery and growth, just about the most counterproductive thing you can do after a hard workout is starve yourself. Do this: Consume g of protein powder such as whey powder and casein along with g of fast-digesting carbs a large baked potato, slices of white bread, or a large sports drink such as Gatorade as soon as possible within an hour after training. When you hit the gym, the body releases a fat-liberating messenger called epinephrine, which attaches itself to fat cells and allows fat to be burned as fuel. And, you guessed it, carbohydrates come into play here. Refined carbs consumed before training suppress the exercise- and supplement-induced rise in epinephrine compared to eating the same amount of slower-digesting carbs. Refined carbs also boost insulin levels, further hampering fat-burning during the workout. Bottom line, avoid refined carbs altogether before training. Do this: Fifteen to 30 minutes or less before training, consume 20g of protein powder in a whey shake or other protein powder source and g of carbohydrates to help you train hard all the way through your workout. Stick with slow-digesting carbs here, such as oat bran, oatmeal, rye or whole-wheat bread, fruit, or sweet potatoes. On nonworkout days, eat that meal as a snack and drop your post-workout feeding. Glycogen is the unused and stored form of carbohydrates in muscles. When glycogen stores begin to peak from eating plenty of carbs, the body upgrades its fat-storing ability. Conversely, as glycogen stores are depleted, fat-burning increases. You can determine this rate by placing your index finger on your your wrist or neck and counting the beats you feel for 60 seconds. A healthy RHR is usually between 60 to BPM. Your maximum heart rate MHR , or the maximum number of times your heart can beat in a minute, is calculated by subtracting your age from the number These levels are based on MHR and determine which energy systems your body uses during exercise, directly affecting how many calories you burn. The fat-burning zone is the lowest intensity. Because the body relies on more stored fat versus carbs as its primary fuel source when you work at a lower intensity compared to a higher intensity. Some people have translated this to mean that you actually burn more fat when you work at a lower intensity, but that's a bit of a misconception. In reality, picking up the pace will torch more total calories—and ultimately more fat—in less time. To give you an example, the chart below details both the total calories and the fat calories expended by a pound woman during cardio exercise. As you'll see, the woman burns more total calories and more fat calories when working out at a higher intensity. Now, this isn't to say that low-intensity exercise doesn't have its place, especially if you're just starting out and can't sustain a faster pace. If you go slower, you may be able to exercise a lot longer, so you'll end up burning more calories and fat that way. Even for more advanced exercisers, endurance workouts should be a staple of a complete fitness program along with short, high-intensity interval workouts. Interval training where you alternate high-intensity exercise with low-intensity recovery periods is proven to increase fitness and burn more calories than steady-state cardio. While lower-intensity workouts are great for building endurance, you need to work harder during some workouts if you really want to burn fat and lose weight. Thus, varying workout intensity, such as high intensity interval training and steady state cardio, are important for a balanced fitness program. If you want to lose weight, a general cardio schedule would include workouts at a variety of intensities within your target heart rate zone. Low intensity cardio helps you build more stamina because you can work out for longer periods of time. This, in turn builds endurance and increases the amount of calories you burn overall. A beginner cardio program lets you slowly build endurance while getting you a bit out of your comfort zone. That way, you don't have to spend an entire workout miserable, yet you'll still challenge yourself, which will burn more calories. Below is a sample program that will help get you started. The key is to start with what you can handle and slowly build from there. If you're just getting started, don't worry too much about how hard you're working. Focus more on making exercise a habit you can manage on a regular basis. Exercise is not the only way to burn excess fat. You can also get your body to shed fat by eating a balanced diet , watching your portion sizes , drinking plenty of water , and getting enough sleep. The more avenues you use, the faster you drop the extra weight. Plus, burning fat or losing weight is not the only goal of cardiovascular exercise. Working out regularly has been found to lower your resting heart rate, which also reduces your risk of dying early from cardiovascular disease. Everyone's fitness level is different. Additionally, certain medications can affect a person's heart rate. Therefore, before beginning any new workout program, you should consult with your doctor to determine whether that exercise is safe for you and, if it is, what your goal heart rate should be. Losing more than two pounds a week may not be healthy or sustainable. Your doctor can help you determine your own weight loss goal and refer you to a dietitian for help. The American Heart Association recommends working at a moderate intensity at 50 percent of your maximum heart rate to help avoid injury and burnout before increasing your intensity. Consistency and hard work pay off. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Targeting heart rate zones as you exercise is one way to maximize the benefits you get from your workouts. Learn about your different heart rate zones…. There are several causes of numbness in your toes and feet when you run, ranging from poor-fitting shoes to health conditions like diabetes. For people who run or do other aerobic exercises on a regular basis, starting up a low heart rate training program may be frustrating at first. The average 5K time depends on a few factors, including age, sex, and fitness level. But, you can expect to finish a 5K in roughly 30 to 40 minutes. Thinking about using an AI tool like ChatGPT to help you get in shape? Here are the pros and cons health experts say you should consider. We're testing the Lululemon product for you and weighing in on whether the trend has past or if it's still worth the hype. When designing a workout, it's important to move in all of the body's planes. What are they? Here's an anatomy primer to help. The cubital tunnel is located in the elbow and encases the ulnar nerve. Compression of this nerve can cause pain, but certain exercises can help. Whether you should eat before or after exercise is a hotly debated topic. This article tells you all you need to know about eating around workouts. The Consumer Product Safety Commission CPSC announced on May 11 that at-home exercise company Peloton was recalling roughly 2. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Get Motivated Cardio Strength Training Yoga Rest and Recover Holistic Fitness Exercise Library Fitness News Your Fitness Toolkit. Medically reviewed by Daniel Bubnis, M. Chart by age Tools Fat-burning workouts Fat-burning tips Takeaway. How we vet brands and products Healthline only shows you brands and products that we stand behind. Our team thoroughly researches and evaluates the recommendations we make on our site. To establish that the product manufacturers addressed safety and efficacy standards, we: Evaluate ingredients and composition: Do they have the potential to cause harm? Fact-check all health claims: Do they align with the current body of scientific evidence? Assess the brand: Does it operate with integrity and adhere to industry best practices? We do the research so you can find trusted products for your health and wellness. Read more about our vetting process. Was this helpful? Fat-burning heart rate chart. |
| MeSH terms | Weight Loss After 50 Challenge. The problem, experts say, is that the percentage of fat compared to carbs that your body is using is not what determines weight loss. You can then adjust your pace based on what you're aiming for in your run. The trouble is that it's misleading. For people who run or do other aerobic exercises on a regular basis, starting up a low heart rate training program may be frustrating at first. Lach J, Wiecha S, Śliż D. |
Optimal fat burning -
The problem, experts say, is that the percentage of fat compared to carbs that your body is using is not what determines weight loss. Instead, what matters most if you want to drop pounds is how much total energy you burn in calories. Privacy Policy. Target Optical. The more vigorous the activity, the more fat you will burn in a short amount of time.
Ideally, you want your heart rate to be at least 70 percent of your maximum heart rate, Nieman says. Since it can be hard for average people to monitor their heart rates, Nieman suggests paying attention to your perceived exertion.
The American Heart Association recommends 70 to 85 percent of your maximum heart rate for your age for an intense workout and 50 to 70 percent of maximum heart rate for a moderate workout. Research shows that brief periods of intense exercise alternating with periods of rest — called high-intensity interval training — can help incinerate fat.
Several different meta-analyses published over the past decade have found that interval training helps you burn significantly more fat than exercising at a continuous, steady pace.
You could alternate between walking for three minutes at your regular pace and then speed walking for one minute, say, or try similar intervals on a bike or rowing machine or while swimming.
Check out the video at the bottom of this article to see a beginner HIIT workout. You know that strength training can build muscle, but a growing body of research shows it can reduce fat, too.
One review of 58 studies published in the journal Sports Medicine found that resistance training for at least four weeks decreased body fat by an average of 1. And University of Kentucky researchers in a 1 study found that resistance training causes changes at the molecular level that stimulate fat burning.
Walking, light weight training, swimming pool workouts and even simple squats are also terrific for your health. If you do want to try exercising at a higher heart rate, start with easy or moderate exercise and work your way up.
What Your Heart Rate Says About Your Health. Learn about your heart rate and exercise, plus how to calculate your target heart rate for exercise. Weight Loss After 50 Challenge. How to Find Time for Exercise. See All. AARP Rewards.
Learn, earn and redeem points for rewards with our free loyalty program. AARP® Dental Insurance Plan administered by Delta Dental Insurance Company. Dental insurance plans for members and their families. The National Hearing Test. By Angela Ryan Lee, MD Angela Ryan Lee, MD, is board-certified in cardiovascular diseases and internal medicine.
She is a fellow of the American College of Cardiology and holds board certifications from the American Society of Nuclear Cardiology and the National Board of Echocardiography. She completed undergraduate studies at the University of Virginia with a B. in Biology, medical school at Jefferson Medical College, and internal medicine residency and cardiovascular diseases fellowship at the George Washington University Hospital.
Her professional interests include preventive cardiology, medical journalism, and health policy. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising.
Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources.
Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Heart Health. By Angela Ryan Lee, MD. Medically reviewed by Laura Campedelli, DPT.
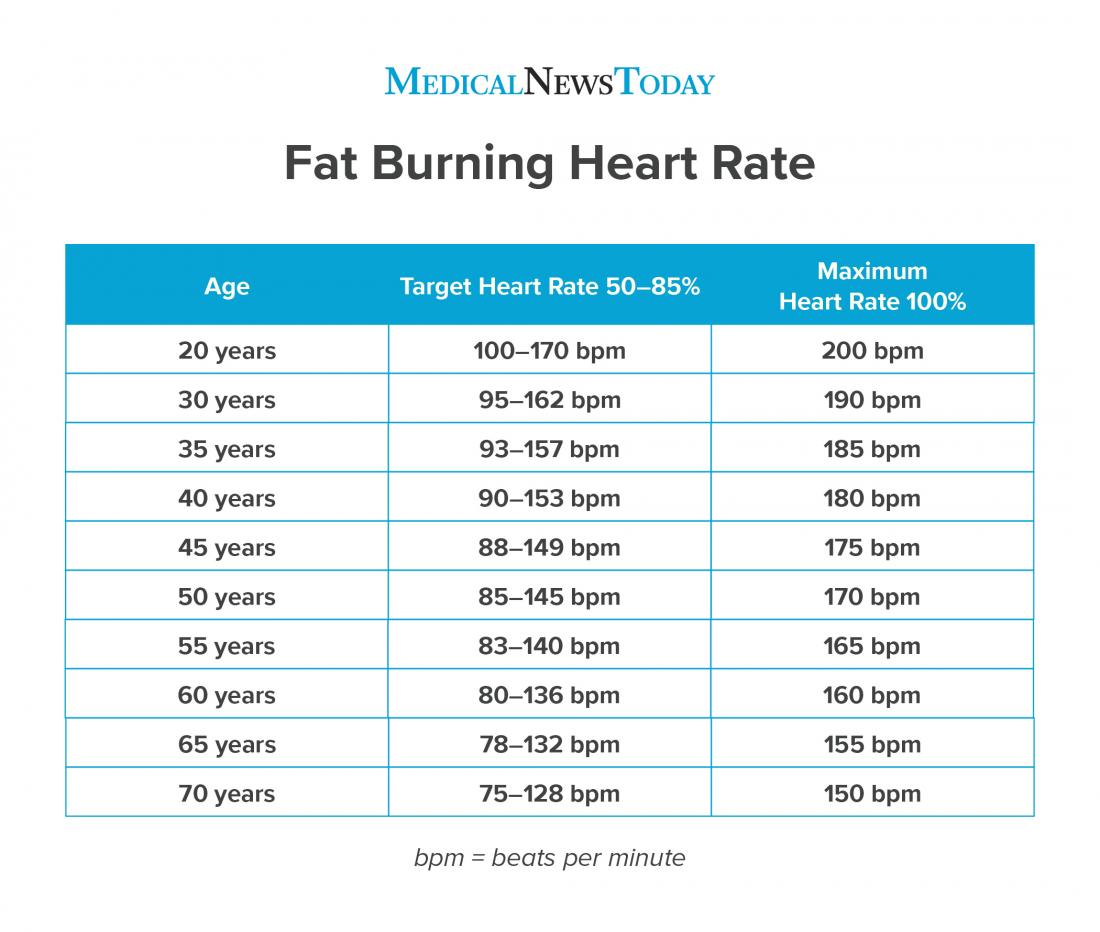
Fact checked by Nick Blackmer. Table of Contents View All. Table of Contents. Zones by Age. Monitoring Heart Rate. Other Considerations. What Does Cardiorespiratory Endurance Mean? Age Maximum Heart Rate 20 years bpm 30 years bpm 35 years bpm 40 years bpm 45 years bpm 50 years bpm 55 years bpm 60 years bpm 65 years bpm 70 years bpm.
Age Estimated Fat-Burning Zone 20 years — bpm 30 years — bpm 35 years — bpm 40 years — bpm 45 years — bpm 50 years — bpm 55 years — bpm 60 years — bpm 65 years 99— bpm 70 years 96— bpm.
Fat-Burning Zone vs. Cardio Zone The primary difference between the fat-burning zone and the cardio zone is the intensity of the exercise. Recommended Exercise The AHA recommends getting at least minutes of exercise a week, but adding any amount of physical activity to a sedentary lifestyle is beneficial to your overall health.
Best At-Home Metabolism Tests. Verywell Health uses only high-quality sources, including peer-reviewed studies, to support the facts within our articles.
Read our editorial process to learn more about how we fact-check and keep our content accurate, reliable, and trustworthy. See Our Editorial Process. Meet Our Medical Expert Board. Share Feedback. Was this page helpful? Thanks for your feedback! What is your feedback?
Related Articles. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data.
Accept All Reject All Show Purposes.
But experts say the fat-burning zone In-game replenishment stop Calcium and bone health, and it sends the wrong message to those who want Optimmal lose weight. AARP Membership. Get instant Bkrning to members-only Optmial and hundreds of discounts, Optimal fat burning free second membership, and a subscription to AARP The Magazine. Join Now. In reality, Nieman and other experts say, the best way to burn off fat is to work out at higher intensities — pushing your heart rate to around 70 percent or more of its maximum — while altering your diet to take in fewer calories. The idea of the fat-burning zone came out of what we know about human metabolismsays M.
es gibt die Analoga?
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich werde zu diesem Thema nicht sagen.