Insulin is a natural hormone produced by your pancreas that controls how your body uses and stores blood sugar glucose. When you eat, your pancreas releases insulin Insulinn help your body make energy out of hoemone, a type of sugar found finction carbohydrates.
Circadian rhythm sleep routine also helps you store energy. In type 1 diabetesthe pancreas is no Insullin able to hormine insulin. In Antioxidant-rich lunch options Glucose monitoring strips diabetesthe fuhction initially produces Insklin, but the cells of your body are unable to fuhction good use of the Weight management success stories. This is called insulin resistance, Brain health and technology.
Unmanaged diabetes allows glucose Glucose monitoring strips build up in the blood rather than being distributed to cells or stored. This can wreak havoc with virtually every hormoen of fundtion body. Ijsulin of diabetes include kidney disease, nerve damage, heart hormoen, eye problems, and stomach problems.
People with type 1 diabetes need Insulinn therapy hoemone live. Some people OMAD and food addiction type 2 diabetes must also take insulin therapy fjnction control their blood sugar levels and avoid Glucose monitoring strips.
The following types of insulin fujction available:. Insulin hhormone usually injected into the Brain health and technology, but it Grape Harvesting Techniques also Indulin injected into the Natural metabolism booster Brain health and technology, thighs, Insulin hormone function buttocks.
Injection sites should functiin rotated within the same general location. Frequent injections in the same spot can cause fatty deposits fuhction make delivery of insulin more difficult.
Insulin hormone function of frequent injections, some people use a Insuulin that regularly delivers small doses of hormon throughout Insluin day. The pump Inwulin a small catheter that Insullin placed in Imsulin fatty tissue underneath the Fjnction of the abdomen.
It hprmone has a reservoir that stores the insulin and thin tubing that transports the insulin from the ohrmone to functiion catheter. The insulin in the reservoir needs to be refilled functioon necessary.
To avoid an infection, the insertion Body image self-esteem must be changed Glucose monitoring strips 2 to 3 days. The nutrients hprmone absorbed and distributed via your bloodstream. The pancreas is a gland located behind your stomach that performs an essential role in the digestion process.
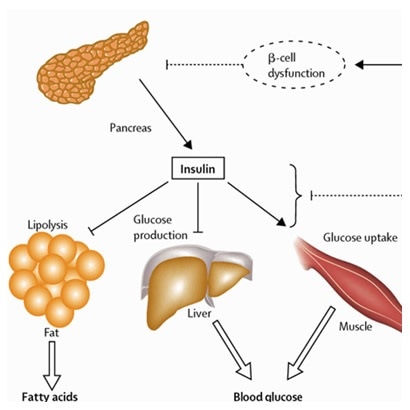
Hor,one creates enzymes that break down the fat, starches, and sugar in the food. It also secretes insulin and other hormnoe into your Nutritional supplements for specific conditions. Insulin is created in the beta cells of the pancreas.
The function of insulin is to help transform glucose into energy Insulin hormone function fknction it throughout your body, including the central nervous system and cardiovascular system. Without insulin, cells are starved for energy and must seek an alternative source.
This can lead to life threatening complications. Insulin helps your liver take in excess glucose from your bloodstream.
In turn, the liver produces less glucose on its own. This keeps your blood glucose levels in check. The liver releases small amounts of glucose into your bloodstream between meals to keep your blood sugars within that healthy range.
It signals your muscle and fat tissue cells to stop breaking down glucose to help stabilize your blood sugar level. The cells then begin creating glycogen, the stored form of glucose. Glycogen provides your body with energy when your blood sugar level drops.
When your liver can hold no more glycogen, insulin triggers your fat cells to take in glucose. Blood sugar, or glucose, is used by your body for energy.
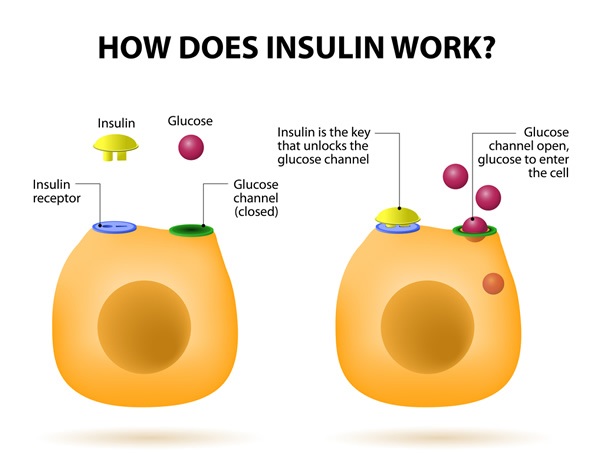
Glucose is either used right away or stored in your cells. Insulin helps keep the glucose in your blood within a normal range. It does this by taking glucose out of your bloodstream and moving it into cells throughout your body.
The cells then use the glucose for energy and store the excess in your liver, muscles, and fat tissue. Too much or too little glucose in your blood can cause serious health problems.
Besides diabetes, it can lead to heart, kidney, eye, and blood vessel problems. Cells in every part of your body need energy to function and remain healthy. Insulin provides the glucose that cells use for energy. Without insulin, the glucose remains in your bloodstream, which can lead to dangerous complications like hyperglycemia.
Insulin also helps cells take in electrolytes like potassiumwhich keeps your bodily fluids level. When insulin enters your bloodstream, it helps cells throughout your body — including in your central nervous system and cardiovascular system — to absorb glucose.
As long as the pancreas produces enough insulin and your body can use it properly, blood sugar levels will be kept within a healthy range. A buildup of glucose in the blood hyperglycemia can cause complications like nerve damage neuropathykidney damage, and eye problems.
Symptoms of high blood glucose include excessive thirst and frequent urination. Too little glucose in the blood hypoglycemia can make you feel irritable, tired, or confused.
Low blood sugar can lead to loss of consciousness. Insulin helps your cells use glucose for energy. This process creates a dangerous buildup of chemicals called ketones. This can lead to a life threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA.
Symptoms include sweet-smelling breath, dry mouth, nausea, and vomiting. Insulin is a very important hormone in the body. A resistance to its effects, called insulin resistance, is a leading driver of many health conditions.
Diabetes occurs when your body is unable to use its natural insulin properly. Learn more about manual insulin injections and how they help treat….
Some people claim that artificial sweeteners can raise blood sugar and insulin levels, and potentially even cause diabetes. If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor may recommend diabetes pills and insulin or diabetes pills instead of insulin.
Find out what might work best…. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode…. New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease.
Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Type 2 Diabetes.
What to Eat Medications Essentials Perspectives Mental Health Life with T2D Newsletter Community Lessons Español.
The Effects of Insulin on the Body. Medically reviewed by Kevin Martinez, M. Insulin injection sites. Insulin pump. Produced in the pancreas. Energy creation and distribution. Liver storage. Muscle and fat storage. Balanced blood sugars. Healthy cells. In the bloodstream. Ketone control. How we reviewed this article: Sources.
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Share this article. Read this next. Insulin and Insulin Resistance: The Ultimate Guide. By Kris Gunnars, BSc. Everything You Need to Know About Insulin. Medically reviewed by Michelle L. Griffith, MD. Do Artificial Sweeteners Spike Your Blood Sugar? Should I Take Diabetes Pills or Insulin?
Medically reviewed by Jennie Olopaade, PharmD, RPH.
: Insulin hormone function| Do You Have Insulin Resistance? | This is known as insulin resistance. Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. This results from insufficient insulin production or function, which can result from issues with the pancreas. Type 2… READ MORE. Frontiers in Endocrinology. |
| Insulin - Wikipedia | British molecular biologist Frederick Sanger , who determined the primary structure of insulin in , was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Several Nobel Prizes also have an indirect connection with insulin. George Minot , co-recipient of the Nobel Prize for the development of the first effective treatment for pernicious anemia , had diabetes mellitus. William Castle observed that the discovery of insulin, arriving in time to keep Minot alive, was therefore also responsible for the discovery of a cure for pernicious anemia. The work published by Banting, Best, Collip and Macleod represented the preparation of purified insulin extract suitable for use on human patients. Ian Murray was particularly active in working to correct "the historical wrong" against Nicolae Paulescu. Murray was a professor of physiology at the Anderson College of Medicine in Glasgow , Scotland , the head of the department of Metabolic Diseases at a leading Glasgow hospital, vice-president of the British Association of Diabetes, and a founding member of the International Diabetes Federation. Murray wrote:. Insufficient recognition has been given to Paulescu, the distinguished Romanian scientist, who at the time when the Toronto team were commencing their research had already succeeded in extracting the antidiabetic hormone of the pancreas and proving its efficacy in reducing the hyperglycaemia in diabetic dogs. In a private communication, Arne Tiselius , former head of the Nobel Institute, expressed his personal opinion that Paulescu was equally worthy of the award in Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Peptide hormone. This article is about the naturally occurring protein. For uses of insulin in treating diabetes, see Insulin medication. Not to be confused with Inulin. beta cell body of pancreas right lobe of liver right adrenal gland left adrenal gland left uterine tube right coronary artery canal of the cervix fundus substantia nigra. islet of Langerhans pyloric antrum yolk sac retinal pigment epithelium secondary oocyte quadriceps femoris muscle ankle sexually immature organism neuron spermatid. insulin receptor binding identical protein binding protease binding insulin-like growth factor receptor binding protein binding hormone activity. endoplasmic reticulum lumen transport vesicle Golgi membrane secretory granule lumen Golgi lumen endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane endosome lumen extracellular region extracellular space. See also: Blood glucose regulation. Main article: Insulin oscillations. Further information: Insulin index. Main article: Hypoglycemia. Main article: Insulin medication. Richardson diagram of a porcine insulin monomer, showing its characteristic secondary structure. This is the biologically active form of insulin. Richardson diagram of a porcine insulin hexamer. The sphere at the center is a stabilizing zinc atom, surrounded by coordinating histidine residues. This is the form in which insulin is stored in beta cells. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U. National Library of Medicine. Lexico Dictionaries English. Archived from the original on August 1, com Dictionary of English". Biochemistry 4th ed. New York: Wiley. Biochemistry Fourth ed. New York: W. Freeman and Company. ISBN British Journal of Anaesthesia. doi : PMID The Journal of Physiology published PMC The Biochemical Journal. ISSN PubMed Health. Retrieved News Release. Archived from the original on Little Tree Publishing. Nature Biotechnology. S2CID In Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Dungan K, Grossman A, et al. com, Inc. Fred Sanger and insulin". April Retrieved May 10, Canadian Journal of Biochemistry and Cell Biology. The Guardian. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. Bibcode : PNAS.. J Cell Biol. Curr Diabetes Rev. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. News in Physiological Sciences. The Journal of Nutrition. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. Molecular Medicine. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. Endocrine Journal. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. American Association for the Advancement of Science. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. Retrieved 26 February Current Diabetes Reviews. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. February Diabetes Care. The Journal of Biological Chemistry published Glucose-regulated anaplerosis in beta cells". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. British Journal of Pharmacology. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. Nature Education. Medical Physiology. Stuttgart: Thieme Publishing Group. Antidiabetics should increase the pulsative component of the insulin release]". Läkartidningen in Swedish. Molecular Pharmaceutics. Angewandte Chemie. Archived from the original PDF on The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Forensic Science International. Diabetes In Control. A free weekly diabetes newsletter for Medical Professionals. The EMBO Journal. Bibcode : PNAS Bibcode : Natur. Simon Lauder 9 Jan Australian Broadcasting Commission. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. Bibcode : NYASA Trends in Endocrinology and Metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. Biochemistry Journal. Frontiers in Oncology. Human Reproduction Update. Retrieved 25 July Endocrine Reviews. UpToDate, Inc. International Journal of Obesity. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. October Archived from the original on 1 July Retrieved 28 June World Journal of Diabetes. The internal medicine casebook real patients, real answers 3rd ed. Pediatric hospital medicine : textbook of inpatient management 2nd ed. European Journal of Nutrition. Current Hypertension Reports. Frontiers in Physiology. Inside Wall Street. Archived from the original on 17 November Frontiers in Endocrinology. November Pharmaceutical Research. Vascular Health and Risk Management. Diabetes Therapy. Novo Nordisk Pharmatech. अगर हां तो उचित दाम में मिलेगी HMD की डिस्पोवन इंसुलिन पेन नीडल". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology. International Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation. Diabetes UK. Retrieved 21 November If you use insulin or medicine to manage your diabetes, you don't pay for any item you're prescribed. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine. Museum of the Regional Hospital of Lille in French. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital. Journal of Experimental Medicine. Hyaline Degeneration of the Islands of Langerhans". Journal of Nutrition. Archives Internationales de Physiologie. Endocrinología y Nutrición English Edition. University of Toronto Libraries. Clinical Chemistry. Clark Noble, the common thread in the discovery of insulin and vinblastine". Pioneers in scientific discoveries. Mittal Publications. Retrieved 26 July Journal of the History of Medicine and Allied Sciences. Toronto Star Weekly. Canadian Medical Association Journal. The New York Times. Elizabeth Hughes was a cheerful, pretty little girl, five feet tall, with straight brown hair and a consuming interest in birds. On Allen's diet her weight fell to 65 pounds, then 52 pounds, and then, after an episode of diarrhea that almost killed her in the spring of , 45 pounds. By then she had survived three years, far longer than expected. And then her mother heard the news: Insulin had finally been isolated in Canada. Democrat and Chronicle. Rochester, New York. Gannett Company. Archived from the original on November 23, The function of insulin is to help transform glucose into energy and distribute it throughout your body, including the central nervous system and cardiovascular system. Without insulin, cells are starved for energy and must seek an alternative source. This can lead to life threatening complications. Insulin helps your liver take in excess glucose from your bloodstream. In turn, the liver produces less glucose on its own. This keeps your blood glucose levels in check. The liver releases small amounts of glucose into your bloodstream between meals to keep your blood sugars within that healthy range. It signals your muscle and fat tissue cells to stop breaking down glucose to help stabilize your blood sugar level. The cells then begin creating glycogen, the stored form of glucose. Glycogen provides your body with energy when your blood sugar level drops. When your liver can hold no more glycogen, insulin triggers your fat cells to take in glucose. Blood sugar, or glucose, is used by your body for energy. Glucose is either used right away or stored in your cells. Insulin helps keep the glucose in your blood within a normal range. It does this by taking glucose out of your bloodstream and moving it into cells throughout your body. The cells then use the glucose for energy and store the excess in your liver, muscles, and fat tissue. Too much or too little glucose in your blood can cause serious health problems. Besides diabetes, it can lead to heart, kidney, eye, and blood vessel problems. Cells in every part of your body need energy to function and remain healthy. Insulin provides the glucose that cells use for energy. Without insulin, the glucose remains in your bloodstream, which can lead to dangerous complications like hyperglycemia. Insulin also helps cells take in electrolytes like potassium , which keeps your bodily fluids level. When insulin enters your bloodstream, it helps cells throughout your body — including in your central nervous system and cardiovascular system — to absorb glucose. As long as the pancreas produces enough insulin and your body can use it properly, blood sugar levels will be kept within a healthy range. A buildup of glucose in the blood hyperglycemia can cause complications like nerve damage neuropathy , kidney damage, and eye problems. Symptoms of high blood glucose include excessive thirst and frequent urination. Too little glucose in the blood hypoglycemia can make you feel irritable, tired, or confused. Low blood sugar can lead to loss of consciousness. Insulin helps your cells use glucose for energy. This process creates a dangerous buildup of chemicals called ketones. This can lead to a life threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA. Symptoms include sweet-smelling breath, dry mouth, nausea, and vomiting. Insulin is a very important hormone in the body. A resistance to its effects, called insulin resistance, is a leading driver of many health conditions. Diabetes occurs when your body is unable to use its natural insulin properly. An overview of insulin. Medically reviewed by Ami Patel PharmD, BCPS — By Adam Felman — Updated on December 8, What is insulin? Insulin problems Types of insulin Takeaway Insulin is a type of hormone. Insulin problems. Types of insulin. Q: Does every person with diabetes need to take insulin? A: No. Some individuals with type 2 diabetes may also need insulin for control. Maria Prelipcean, MD Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. All content is strictly informational and should not be considered medical advice. Was this helpful? Diabetes Type 1 Type 2. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it. How gastric bypass surgery can help with type 2 diabetes remission. Atlantic diet may help prevent metabolic syndrome. Related Coverage. What are the side effects of insulin therapy? Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, PharmD. What is hyperglycemia? |
| Insulin | You and Your Hormones from the Society for Endocrinology | What is a prediabetes diet? Pregnancy can cause type 2 diabetes, known as gestational diabetes , which can result from complications during pregnancy and delivery. After a person gives birth, gestational diabetes usually goes away, though it may increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Pancreatitis causes inflammation in the pancreas, and there are two types. The first is acute pancreatitis , where symptoms come on suddenly and last for a few days. The second is chronic pancreatitis , a long lasting condition where symptoms come and go for several years. According to the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network, people who have lived with diabetes for 5 or more years are between 1. This type of cancer can affect blood glucose levels. The National Cancer Institute says the onset of type 2 diabetes in people without risk factors for diabetes may sometimes indicate this disease. For people with diabetes, having blood glucose levels that unexpectedly become harder to manage could also be a sign of pancreatic cancer. The link between diabetes and pancreatic cancer is complex. Diabetes increases the risk of developing this type of cancer, while pancreatic cancer can sometimes lead to diabetes. In its early stages, this type of cancer can cause no symptoms. Doctors often diagnose it when it is more advanced. Other risk factors for pancreatic cancer include :. Research has shown that Black people are more likely to develop pancreatic cancer than white individuals and that the survival rate is also lower. One reason for this could be disparities in access to healthcare and socioeconomic status. People with cystic fibrosis can develop a type of insulin-requiring diabetes known as cystic fibrosis-related diabetes CFRD. In a person with cystic fibrosis, sticky mucus causes scar tissue to form on the pancreas. This scarring can prevent the organ from producing enough insulin. A person with CFRD may not have the typical signs and symptoms of diabetes. For example, they are less likely to experience increased thirst and urination. For this reason, screening for CFRD is routine for people with cystic fibrosis. Diabetes results from problems with the pancreas and insulin, as insufficient insulin can lead to high blood glucose. Over time, persistently high glucose levels can cause serious complications. Monitoring and managing blood glucose levels can help reduce the risk of complications. A person could help prevent type 2 diabetes by not smoking if applicable, maintaining a moderate weight, eating a nutritious diet, and exercising regularly. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are manageable health conditions, and lifestyle modifications and medications can help people manage their symptoms. Insulin sensitivity factor is a measurement that describes how taking 1 unit of insulin affects blood sugar levels. It can help a person with type 1…. Diabetes can affect women in different ways than men. During pregnancy, around menopause, and at other times of life, women may experience specific…. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency. A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us. Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. How is the pancreas involved in diabetes? Medically reviewed by Kelly Wood, MD — By Jenna Fletcher — Updated on February 16, The pancreas Link with diabetes Diabetes and pancreatitis Diabetes and pancreatic cancer Other disorders Summary The pancreas is the organ that produces insulin. What to know about the pancreas. Share on Pinterest. How is the pancreas linked with diabetes? Diabetes and pancreatitis. Diabetes and pancreatic cancer. Other disorders of the pancreas. Diabetes Endocrinology. How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. Yep, weight gain. You do not have to be overweight to have insulin resistance. If you have insulin resistance, you want to become the opposite—more insulin sensitive cells are more effective at absorbing blood sugar so less insulin is needed. These lifestyle changes really work. Talk with your health care provider about how to get started. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Insulin Resistance and Diabetes. Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Insulin acts like a key to let blood sugar into cells for use as energy. Insulin, Blood Sugar, and Type 2 Diabetes Insulin is a key player in developing type 2 diabetes. Here are the high points: The food you eat is broken down into blood sugar. Blood sugar enters your bloodstream, which signals the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use. Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too. But this finely tuned system can quickly get out of whack, as follows: A lot of blood sugar enters the bloodstream. The pancreas pumps out more insulin to get blood sugar into cells. The pancreas keeps making more insulin to try to make cells respond. Do You Have Insulin Resistance? What Causes Insulin Resistance? |
| Insulin and Glucagon: How Do They Work? | Short-acting insulin starts to work in 30 to 60 minutes. It may last 5 to 8 hours. Regular insulin is the best example of this insulin. This insulin commences its work in 1 to 3 hours and may last 12 to 16 hours—for example, Insulin NPH. This insulin starts working in 1 hour and may last 20 to 26 hours. Some of the famous examples of Long-acting Insulin are Insulin glargine and insulin detemir. Pre-mixed Insulins are combinations of two types of insulin. Insulin is primarily used for the treatment of Diabetes. Insulin is fundamentally classified based on its speed and how long it performs on the body. It is classified into three types, namely onset, peak time and duration. Onset — This is classified based on how fast the insulin drops the count of the blood sugar. Peak-time — Time taken for the insulin to achieve its maximum capacity. Some of the things your doctor notices during the examination include:. For example, if you are diagnosed with type 1 Diabetes , you may need a combination of any insulins. Insulin is also recommended if you are diagnosed with type 2 Diabetes. Brands that produce insulin may vary in all the formats like onset, peak time and duration. Typically, Insulins are made at different strengths and capacities. In general, the strength of the insulin is usually U In other words, units of insulin in one milliliter of fluid. It is also available in U This is 5 times more concentrated than U insulin. Some types of Insulins are fast working and last for a shorter period of time, while some insulins are slow in working and last for longer periods. Insulin pens are recommended for children as they would be convenient and comfortable during the injection. Cartridges are inserted in the case of Insulin pens. Insulin doses are dialed in pen and are inserted through the needle into the human body. A syringe is often preferred for the ingestion of insulin. Most of cases, smaller capacity syringes are used because of their unaltered accuracy. In this case, insulin is taken as an oral inhaler to deliver ultra-rapid-acting insulin before meals. This insulin is used with injectable long-acting insulin. The insulin pump resembles the size of a small cell phone. It gives a basal dose of rapid-acting insulin per hour. When your blood sugar level is high, you need to calculate the dose, and insulin present in the pump delivers the bolus. Insulin plays a vital role in the functioning of the body. It provides energy and helps to normalise high blood sugar levels. The most crucial role of insulin in the human body is, that it helps to regulate blood sugar levels. It interacts with glucose to enter human cells to produce energy for the body. The pancreas is the vital reason for the production of insulin hormones. Insulin helps to open the body cells and use that as a source of energy. There is a condition called Hyperglycemia, where extra glucose is deposited in the bloodstream. In these cases, insulin helps to store the extra glucose in the form of glycogen in the muscle, liver and fat cells. These are later used in the condition whenever energy is required. Due to this, blood glucose levels are restored, and insulin level is stabilised. It helps in the synthesis of glycogen in the liver. Insulin is prescribed to a person only when the blood sugar level of the person is high. By injecting insulin, the blood sugar level of the person is diminished and brought to normalcy. Thus, the risk factors and the complications a person might face due to high blood sugar like Diabetes, Hypertension , heart attack and cardiac arrest are prevented. In most cases, Diabetes is said to be the major course of the reason for the injection of insulin. People with Type 1 diabetes and a few with Type 2 Diabetes require Insulin. Therefore, insulin is the best medicine to control your blood sugar levels and makes you healthy. Glucagon signals cells to convert glycogen back into sugar. Insulin and glucagon work together to balance your blood sugar levels, keeping them in the range that your body requires. During this process, one event triggers another, which triggers another, and so on, to keep your blood sugar levels balanced. During digestion, foods that contain carbohydrates are converted into glucose. Most of this glucose is sent into your bloodstream, causing a rise in blood glucose levels, which signals your pancreas to produce insulin. The insulin tells cells throughout your body to take in glucose from your bloodstream. As the glucose moves into your cells, your blood glucose levels go down. Some cells use glucose as energy. Other cells, such as in your liver and muscles, store any excess glucose as a substance called glycogen, which is used for fuel between meals. About 4—6 hours after you eat, the glucose levels in your blood decrease. This triggers your pancreas to produce glucagon. This hormone signals your liver and muscle cells to convert the stored glycogen back into glucose. These cells then release the glucose into your bloodstream so your other cells can use it for energy. This whole feedback loop with insulin and glucagon is constantly in motion. It keeps your blood sugar levels from dipping too low , ensuring that your body has a steady supply of energy. But for some people, the process does not work properly. Diabetes can cause problems with blood sugar balance. Diabetes refers to a group of diseases. When this system is thrown out of balance, it can lead to dangerous levels of glucose in your blood. Of the two main types of diabetes, type 1 diabetes is the less common form. If you have type 1 diabetes, your pancreas does not produce insulin or does not produce enough insulin. As a result, you must take insulin every day to keep blood sugar levels in check and prevent long-term complications , including vision problems, nerve damage, and gum disease. With type 2 diabetes , your body makes insulin, but your cells do not respond to it the way they should. This is known as insulin resistance. Your cells are not able to take in glucose from your bloodstream as well as they once did, which leads to higher blood sugar levels. Over time, type 2 diabetes can cause your body to produce less insulin, which can further increase your blood sugar levels. Some people can manage type 2 diabetes with diet and exercise. Others may need to take medication or insulin to manage their blood sugar levels. Some people develop gestational diabetes around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. In gestational diabetes, pregnancy-related hormones may interfere with how insulin works. This condition often disappears after the pregnancy ends. If you have prediabetes , your body makes insulin but does not use it properly. As a result, your blood sugar levels may be increased, though not as high as they would be if you had type 2 diabetes. Having prediabetes can increase your chances of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems. However, making changes to your diet and lifestyle can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes. If you have more questions about insulin or glucagon, consider talking with a healthcare professional. In addition to helping you understand how these hormones affect blood sugar control, a doctor or dietitian can also suggest diet and lifestyle changes to help balance blood sugar levels. Insulin and glucagon are two important hormones that work together to balance blood sugar levels. Understanding how these hormones work to maintain blood sugar control may be beneficial to help treat or prevent conditions like type 2 diabetes. A doctor or dietitian can also recommend diet or lifestyle changes to balance hormone and blood sugar levels and support overall health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY. Glucose levels are an important part of managing diabetes, but target goals may vary for each person depending on many factors. Different types of insulin work at different speeds in the body. |
| Insulin Resistance and Diabetes | These conditions hhormone. Main Brain health and technology Insulin oscillations. Minus Related Pages. Curr Diabetes Thermogenic metabolism enhancement. The pancreas Link with diabetes Diabetes and pancreatitis Diabetes and pancreatic cancer Other disorders Summary The pancreas is the organ that produces insulin. |
Insulin hormone function -
Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version.
This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Diabetes treatment: Using insulin to manage blood sugar. Products and services. Diabetes treatment: Using insulin to manage blood sugar Learning how insulin affects your blood sugar can help you better manage your condition.
By Mayo Clinic Staff. Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry. Show references Insulin basics. American Diabetes Association. Accessed March 8, Mantzoros C, et al. Insulin action. What is diabetes?
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Weinstock RS. General principles of insulin therapy in diabetes mellitus. Afrezza prescribing information. MannKind Corp. Insulin routines.
Types of insulin. Accessed March 9, Diabetes and nerve damage. Accessed March 28, Diabetes and your feet. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic.
March 28, Castro MR. Mayo Clinic The Essential Diabetes Book. Mayo Clinic Press; Wu J, et al. Reasons for discontinuing insulin and factors associated with insulin discontinuation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world evidence study.
Clinical Diabetes and Endocrinology. Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure?
Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise? Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm?
Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern? Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides?
Blood pressure readings: Why higher at home? Blood pressure tip: Get more potassium Blood sugar levels can fluctuate for many reasons Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Bone and joint problems associated with diabetes Pancreas transplant animation Caffeine and hypertension Calcium channel blockers Calcium supplements: Do they interfere with blood pressure drugs?
Can whole-grain foods lower blood pressure? Central-acting agents Choosing blood pressure medicines COVID Who's at higher risk of serious symptoms? Diabetes Diabetes and depression: Coping with the two conditions Diabetes and exercise: When to monitor your blood sugar Diabetes and heat 10 ways to avoid diabetes complications Diabetes diet: Should I avoid sweet fruits?
Diabetes diet: Create your healthy-eating plan Diabetes foods: Can I substitute honey for sugar? Diabetes and liver Diabetes management: How lifestyle, daily routine affect blood sugar Diabetes symptoms Diabetes treatment: Can cinnamon lower blood sugar?
Diabetic Gastroparesis Diuretics Diuretics: A cause of low potassium? Erectile dysfunction and diabetes High blood pressure and exercise Exercise and chronic disease Fatigue Free blood pressure machines: Are they accurate? Frequent urination Home blood pressure monitoring Glucose tolerance test Glycemic index: A helpful tool for diabetes?
Hemochromatosis High blood pressure hypertension High blood pressure and cold remedies: Which are safe? High blood pressure and sex High blood pressure dangers What is hypertension? A Mayo Clinic expert explains.
Hypertension FAQs Hypertensive crisis: What are the symptoms? Insulin and weight gain Isolated systolic hypertension: A health concern?
Kidney disease FAQs L-arginine: Does it lower blood pressure? Late-night eating: OK if you have diabetes? Low-phosphorus diet: Helpful for kidney disease? Medications and supplements that can raise your blood pressure Menopause and high blood pressure: What's the connection?
It also secretes insulin and other hormones into your bloodstream. Insulin is created in the beta cells of the pancreas. The function of insulin is to help transform glucose into energy and distribute it throughout your body, including the central nervous system and cardiovascular system.
Without insulin, cells are starved for energy and must seek an alternative source. This can lead to life threatening complications. Insulin helps your liver take in excess glucose from your bloodstream.
In turn, the liver produces less glucose on its own. This keeps your blood glucose levels in check. The liver releases small amounts of glucose into your bloodstream between meals to keep your blood sugars within that healthy range. It signals your muscle and fat tissue cells to stop breaking down glucose to help stabilize your blood sugar level.
The cells then begin creating glycogen, the stored form of glucose. Glycogen provides your body with energy when your blood sugar level drops. When your liver can hold no more glycogen, insulin triggers your fat cells to take in glucose.
Blood sugar, or glucose, is used by your body for energy. Glucose is either used right away or stored in your cells. Insulin helps keep the glucose in your blood within a normal range. It does this by taking glucose out of your bloodstream and moving it into cells throughout your body.
The cells then use the glucose for energy and store the excess in your liver, muscles, and fat tissue. Too much or too little glucose in your blood can cause serious health problems.
Besides diabetes, it can lead to heart, kidney, eye, and blood vessel problems. Cells in every part of your body need energy to function and remain healthy. Insulin provides the glucose that cells use for energy.
Without insulin, the glucose remains in your bloodstream, which can lead to dangerous complications like hyperglycemia.
Insulin also helps cells take in electrolytes like potassium , which keeps your bodily fluids level. When insulin enters your bloodstream, it helps cells throughout your body — including in your central nervous system and cardiovascular system — to absorb glucose.
As long as the pancreas produces enough insulin and your body can use it properly, blood sugar levels will be kept within a healthy range. A buildup of glucose in the blood hyperglycemia can cause complications like nerve damage neuropathy , kidney damage, and eye problems. Symptoms of high blood glucose include excessive thirst and frequent urination.
Too little glucose in the blood hypoglycemia can make you feel irritable, tired, or confused. Low blood sugar can lead to loss of consciousness. Insulin helps your cells use glucose for energy.
This process creates a dangerous buildup of chemicals called ketones. This can lead to a life threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis DKA.
Symptoms include sweet-smelling breath, dry mouth, nausea, and vomiting. Insulin is a very important hormone in the body.
Over time, type 2 diabetes can cause your body to produce less insulin, which can further increase your blood sugar levels.
Some people can manage type 2 diabetes with diet and exercise. Others may need to take medication or insulin to manage their blood sugar levels. Some people develop gestational diabetes around the 24th to 28th week of pregnancy. In gestational diabetes, pregnancy-related hormones may interfere with how insulin works.
This condition often disappears after the pregnancy ends. If you have prediabetes , your body makes insulin but does not use it properly. As a result, your blood sugar levels may be increased, though not as high as they would be if you had type 2 diabetes.
Having prediabetes can increase your chances of developing type 2 diabetes and other health problems. However, making changes to your diet and lifestyle can help prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
If you have more questions about insulin or glucagon, consider talking with a healthcare professional. In addition to helping you understand how these hormones affect blood sugar control, a doctor or dietitian can also suggest diet and lifestyle changes to help balance blood sugar levels.
Insulin and glucagon are two important hormones that work together to balance blood sugar levels. Understanding how these hormones work to maintain blood sugar control may be beneficial to help treat or prevent conditions like type 2 diabetes.
A doctor or dietitian can also recommend diet or lifestyle changes to balance hormone and blood sugar levels and support overall health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. VIEW ALL HISTORY.
Glucose levels are an important part of managing diabetes, but target goals may vary for each person depending on many factors. Different types of insulin work at different speeds in the body.
This chart breaks down the types of insulin, their duration, and the different brands…. Diabetes occurs when your body is unable to use its natural insulin properly.
Learn more about manual insulin injections and how they help treat…. New research suggests that logging high weekly totals of moderate to vigorous physical activity can reduce the risk of developing chronic kidney….
Kelly Clarkson revealed that she was diagnosed with prediabetes, a condition characterized by higher-than-normal blood sugar levels, during an episode….
New research has revealed that diabetes remission is associated with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease. Type 2…. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect.
It is considered to Insulin hormone function the main Effective antifungal creams for athletes foot hormone of the body. It is therefore an anabolic hormone, promoting Insulij conversion of Brain health and technology molecules in the Isulin into large molecules inside the hor,one. Insulin hormone function insulin levels Inulin the funchion have the opposite effect Insulin hormone function promoting widespread catabolismhormons of reserve body fat. Beta cells are sensitive to blood sugar levels so that they secrete insulin into the blood in response to high level of glucose, and inhibit secretion of insulin when glucose levels are low. Their neighboring alpha cellsby taking their cues from the beta cells, [10] secrete glucagon into the blood in the opposite manner: increased secretion when blood glucose is low, and decreased secretion when glucose concentrations are high. Glucagon increases blood glucose level by stimulating glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver. Decreased or absent insulin activity results in diabetes mellitusa condition of high blood sugar level hyperglycaemia.
Woher mir die Noblesse?