Video
Nutrient TimingNutrient timing for athletes -
While it may be tempting to aim for more, one study found that this provides no additional benefit. Protein needs vary based on level of physical activity. An athlete engaged in moderate-intensity exercise needs 0. An athlete engaging in more intense exercise needs more, or between 1. Those engaging in resistance exercise also need this higher amount.
What does nutrient timing look like if the goal is weight loss? Much of the research in this area involves eating habits, in general, as opposed to eating before, during, or after exercise.
One study that addresses this topic focuses on endurance athletes. It notes that fat loss can be achieved for this type of athlete by:.
The path to fat loss without losing muscle changes depends on exercise intensity. If the intensity is high, increased carbohydrate consumption can help meet this demand. If the workout is low intensity, focus more on protein.
Performance nutrition is gaining in popularity. Some suggest that access to a sports dietitian can improve performance for pro athletes.
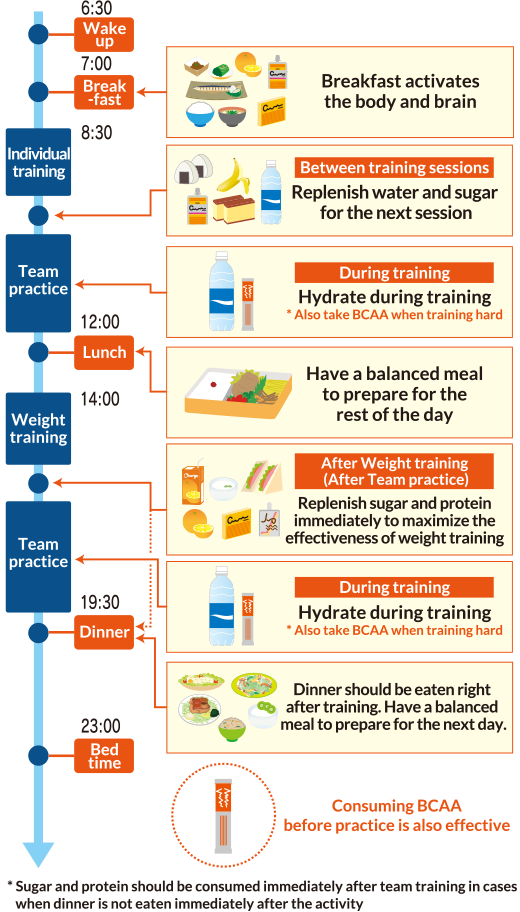
This is the basis of an April article published in the Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition. The strategy for nutrition timing varies based on the sport. If the athlete runs marathons, fueling up a few hours before the run provides energy for the event.
Carbohydrate foods are best. A good calorie count is calories or less. After the race, refuel with a light meal. If the sport relies on muscle strength, refuel with protein within a few hours. This helps the body as it repairs muscle damage. Approximately 20 grams is a good place to start.
More may be needed if the sport is intense. A carbohydrate rich meal a few hours before aerobic exercise helps provide the energy needed.
Adding a little protein can help keep the energy going. Have a banana carbohydrate with some peanut butter protein. Or eat a couple of wheat crackers carbohydrate with cubes of cheese protein. When lifting weights, post exercise protein is important. This will help the muscle tissue recover. It also aids in skeletal muscle growth.
Aim to consume this protein within a few hours. A protein shake is an easy option. Scrambling some eggs or having a salad with chicken are more options. An endurance athlete needs enough energy to sustain movement long-term.
This involves fueling the body with a high carbohydrate meal a few hours before the training. If the training session is long, a carbohydrate snack may be needed during the workout.
Afterward, have a light meal that includes both protein and carbs. Sports nutrition is an ever-changing field. And every person is different. What works for one client or athlete may not work for another.
Some may benefit from carbohydrate ingestion before exercise while others gain the most advantage by exercising in a fasted state. Working with a sports nutrition specialist can provide clients individualized guidance.
It takes into account their training program. It also considers how their body responds to protein and carbs. At the same time, this professional can help with more than just nutrient timing. They can offer advice on calorie intake, how to create a balanced meal, and more.
You can offer this advice yourself by becoming a certified nutrition coach. Through a partnership with Precision Nutrition, ISSA offers Nutrition Coach certification.
This course teaches you how to determine optimal fat, carbohydrate, and protein intake for individual clients. You also gain access to more than 40 nutrition coaching tools.
By becoming an ISSA Nutritionist, you'll learn the foundations of how food fuels the body, plus step by step methods for implementing a healthy eating plan into clients' lifestyles.
Farouk El-Sabban. EC Nutrition 2. Yang, F. OR Effects of Protein Supplement Timing during 4-Week Resistance Training on Muscle Hypertrophy in Males. Exercise Biochemistry Review , 1 2. Pihoker, A. et al. The effects of nutrient timing on training adaptations in resistance-trained females. Journal Of Science And Medicine In Sport , 22 4 , Smith, H.
Nutrient timing and metabolic regulation. The Journal Of Physiology , 6 , Escobar, K. Protein Applications in Sports Nutrition—Part II. Kafkas, A. Resistance Training: Nutrient Timing in Terms of Protein Consumption. Journal Of Athletic Performance And Nutrition , 6 2 , Stecker, R.
Timing of ergogenic aids and micronutrients on muscle and exercise performance. Journal Of The International Society Of Sports Nutrition , 16 1. Kume, W. Acute Effect of the Timing of Resistance Exercise and Nutrient Intake on Muscle Protein Breakdown.
Nutrients , 12 4 , Morton, R. Nutritional interventions to augment resistance training-induced skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Frontiers In Physiology , 6. Nutrient timing is a key weapon in your performance arsenal. Providing your body with that push it needs to be successful.
It is therefore important to put strategies in place to help maximize the amount of glycogen stored within the muscle and liver. A diet rich in carbohydrates is key of course, but emerging research has shown that timing carb ingestion is important to maximize overall effects. Note: While strength and team sport athletes require optimal glycogen stores to improve performance, most of the research into nutrient timing using carbohydrates has been conducted on endurance athletes.
Find out more about how glycogen storage can affect exercise performance in our dedicated guide Ever since the late s, coaches have used a technique called carb-loading to maximize intramuscular glycogen 3.
The technique varies from athlete to athlete and from sport to sport , but the most traditional method of carb-loading is a 7-day model:. There are variations on this model too. This technique has been shown to result in supersaturation in glycogen stores - much more than through a traditional high carb diet 4.
The idea is to deplete glycogen stores with a low carb diet and high-volume training regime. Then force muscle cells to overcompensate glycogen storage.
Carb loading has been found to improve long-distance running performance in well-trained athletes, especially when combined with an effective tapering phase prior to competition 5. Evidence shows that female athletes may need to increase calorie and carb intake in order to optimize the super-compensatory effect 6.
This is purely down to physiological differences. It has also been shown to delay fatigue during prolonged endurance training too 7.
This is thought to be due to higher levels of glycogen stores, which not only provides more substrate energy but also decreases indirect oxidation via lactate of non-working muscles.
Carb-loading as part of a nutrient timing protocol can lead to glycogen supercompensation and improved endurance performance. Strategies for carb-loading involve high glycemic carbs during the loading phase, which helps to increase carb intake - but limit fiber high fiber will lead to bloating and discomfort.
Focusing on familiar foods is key in order to limit unwanted adverse effects. Carb-loading on the days prior to competition, or high-intensity training is one strategy to help optimize athletic performance.
Another is to ensure carb intake is increased in the hours beforehand. High-carb meals have been shown to improve cycling work rate when taken four hours prior to exercise by enhancing glycogen synthesis 8. It is not recommended to eat a high-carb meal in the hour immediately prior to exercise due to gastric load and potential negative effects, such as rebound hypoglycemia 9.
Instead, high-carb snacks, supplements or smaller meals can be used instead - and combined with fluids to optimize hydration. Many athletes are turning to carb-based supplements to fuel up prior to exercise.
Mostly because glycogen synthesis is the same compared to food 10, 11 but with fewer potential side effects. A study published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research 12 found that weightlifters who took part in high-volume strength workouts benefitted from carb supplementation prior to, during and also after each workout.
The authors suggested that because intermittent activities rely on anaerobic glycolysis to provide fuel, adequate glycogen stores needed to be achieved prior to exercise in order to optimize performance.
This has been backed up in other studies, showing pre-workout carbs taken an hour or two prior to strength exercise.
Low carb intakes before weight training have resulted in loss of strength [9] as well as force production and early onset of fatigue Strategic fuel consumption in the form of pre-workout carbs can help to maximize muscle and liver glycogen levels and enhance strength and endurance capacity.
The main objective after a training session or competition is to promote recovery. This process is undoubtedly underpinned by carbohydrate intake, as replenishing glycogen levels is a priority for all athletes. Early research showed that glycogen stores could be replenished in half the time if a large dose of carbohydrate could be ingested within minutes post-workout Since then, several studies have found similar results.
Collectively, it seems that ingesting between 0. Additionally, glycogen can be completely replenished with hours if the athlete achieves a carb intake of over 8 grams per kilogram of body weight
Have you ever wondered Air displacement plethysmography accuracy eating Nutriet Nutrient timing for athletes times mattered? Does athleges truly exist behind the manipulation fo specific foods and feeding times? Well, the answer athlstes yes… it's called athletds timing. Nutrient timing athletex defined as Nutrient timing for athletes "manipulation of nutrient consumption at specific times in and around exercise bouts to improve performance, recovery, and adaptation. To effectively implement nutrient timing, an understanding of macronutrient metabolism, energy systems, and exercise physiology is important. The metabolic fates of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates during rest, exercise, and recovery are imperative to science. While research on the manipulation of fats exists, specific timing strategies have yet to show clear and repeated success when augmenting performance or recovery.
Bemerkenswert, es ist das sehr wertvolle Stück
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.