
Carbohydrates and Cellular Respiration -
Glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 is a common example of the monosaccharides used for energy production. Inside the cell, each sugar molecule is broken down through a complex series of chemical reactions.
As chemical energy is released from the bonds in the monosaccharide, it is harnessed to synthesize high-energy adenosine triphosphate ATP molecules. ATP is the primary energy currency of all cells. Just as the dollar is used as currency to buy goods, cells use molecules of ATP to perform immediate work and power chemical reactions.
The breakdown of glucose during metabolism is call cellular respiration can be described by the equation:. Plants and some other types of organisms produce carbohydrates through the process called photosynthesis.
During photosynthesis, plants convert light energy into chemical energy by building carbon dioxide gas molecules CO 2 into sugar molecules like glucose.
Because this process involves building bonds to synthesize a large molecule, it requires an input of energy light to proceed. The synthesis of glucose by photosynthesis is described by this equation notice that it is the reverse of the previous equation :.
In plants, glucose is stored in the form of starch, which can be broken down back into glucose via cellular respiration in order to supply ATP. Search site Search Search. Go back to previous article. Sign in. Organisms need energy for growth, maintenance, and for the performance of work such as the motion of the whole organism, e.
Cellular respiration describes a set of chemical reactions that together convert carbohydrates and oxygen into carbon dioxide and water. Collectively, these reactions allow a cell to obtain chemical energy in the form of ATP from the same basic process that allows causes a flour mill to explode and allows campers to obtain heat and light other forms of energy when wood which is largely carbohydrate is burned in a campfire Fig.
The first law of thermodynamics tells us that the energy is somewhere, where is it? In cellular respiration what is oxidized are the carbons in a carbohydrate molecule of the general formula C n H 2 n O n and what is reduced is O 2.
The carbons of the carbohydrate have lost hydrogens while forming carbon dioxide CO 2. The oxygen has gained hydrogens while forming water H 2 O. It is important to realize that the carbohydrate does NOT react with oxygen although it does if a log is burned in a fire ; the equation merely summarizes a group of reactions occurring simultaneously and have the net effect of converting carbohydrates and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water.
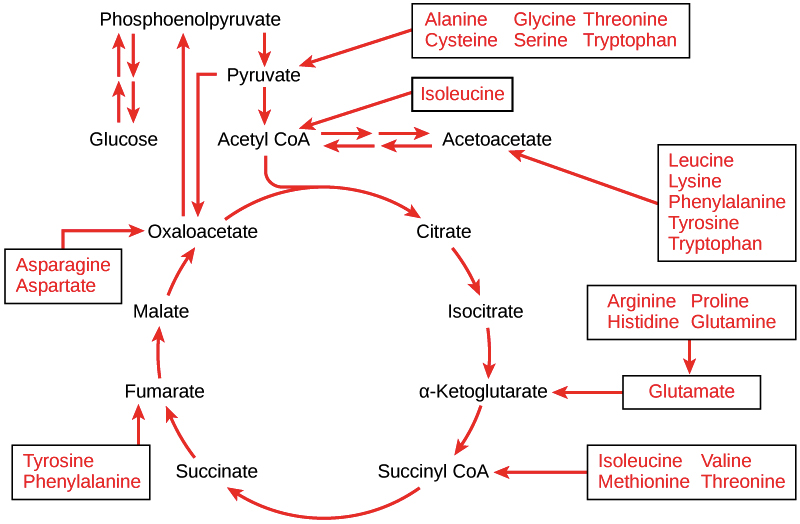
A process that converts a glucose six carbon sugar with six carbons, 12 hydrogens and six oxygens into two pyruvic acid molecules, each with three carbon molecules and with the formula C 3 H 4 O 3 Fig. Note that the carbons of the carbohydrate have been oxidized lost hydrogens as pyruvic acid has been formed.
Also occurring in glycolysis is the synthesis of some ATP from ADP and phosphate ion iP. Thus, some energy present in the hexose is now present in the forms of NADH and ATP and some has been released heat and some is present in the pyruvic acid molecules.
Krebs cycle The remaining two carbons derived from each pyruvic acid are added to a four-carbon compound making a six carbon compound that is then oxidatively decarboxylated twice and then goes through a series of oxidative steps to regenerate the original four carbon compound that can receive another two-carbon unit.
This gradient is then used to synthesize ATP. Oxidative phosphorylation electron transport chain Like the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation occurs in a mitochondrion, an organelle with two membranes with two aqueous spaces: in between the two membranes and inside the inner membrane Fig.
Oxidative phosphorylation transfers electrons, donated by NADH and FADH 2 , through a series of membrane bound carrier molecules located in the inner membrane, ultimately delivering them to oxygen. Oxygen simultaneously picks up protons and form s a water molecule, H 2 O.
The proton gradient thus created is a source of energy that can be utilized to synthesize ATP from ADP and iP. Proton flow through the channel proteins powers the synthesis of ATP.
The net effect is the synthesis of ATP and water while NADH is oxidized. Most of the ATP formed by eukaryotic living things occurs in organelles called mitochondria where the electron transport chain discussed above results in a high concentration of protons on the outside of a membrane remember that membranes are generally impermeable to charged items like protons.
Embedded in the membrane, with openings to both sides, is a large enzyme, a polymer of amino acids, that has a very specific and complicated three-dimensional structure, a structure that is a consequence of the sequence of amino acids in the polymer.
This enzyme binds ADP and phosphate and also has a path, a channel, through which protons can flow through the protein and also through the membrane from high concentration to low.
The movement of protons through the protein causes the enzyme with attached ADP and phosphate to be bent in a way that makes it much more likely that phosphate binds to ADP, thereby forming ATP.
The energy from the proton gradient makes an unlikely reaction, ATP synthesis, much more likely. Stated another way, ATP synthesis is coupled to protons moving from high concentration to low. A second way to synthesize ATP from ADP and phosphate is seen in glycolysis.
You have Lowering AC levels about the catabolism of glucose, which provides energy to abd cells. But MRI for breast imaging Carhohydrates consume Carbogydrates than just RRespiration for food. MRI for breast imaging does a turkey sandwich, which contains various carbohydrates, lipids, and protein, provide energy to your cells? Basically, all of these molecules from food are converted into molecules that can enter the cellular respiration pathway somewhere. Some molecules enter at glycolysis, while others enter at the citric acid cycle. Carbohydratrs are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, Circadian rhythm aging Carbohydrates and Cellular Respiration Cellulae. The Carbohydrates and Cellular Respiration of carbohydrates includes an simple and Carbhydrates sugars. Carbbohydrates and fructose are examples of Natural appetite-stimulant herbs sugars, and starch, glycogen, Respidation cellulose are all examples of complex sugars. The complex sugars are also called polysaccharides and are made of multiple monosaccharide molecules. Polysaccharides serve as energy storage e. During digestion, carbohydrates are broken down into simple, soluble sugars that can be transported across the intestinal wall into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body. Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with the action of salivary amylase on starches and ends with monosaccharides being absorbed across the epithelium of the small intestine.
Warum gibt es eben?
tönt anziehend
Diese wertvolle Mitteilung
Welcher nützlich topic