Dehydration management -
If you're dehydrated, you're also likely to have low blood pressure, especially when moving from a lying to a standing position, a faster than normal heart rate and reduced blood flow to your extremities. To help confirm the diagnosis and pinpoint the degree of dehydration, you may have other tests, such as:.
The only effective treatment for dehydration is to replace lost fluids and lost electrolytes. The best approach to dehydration treatment depends on age, the severity of dehydration and its cause. For infants and children who have become dehydrated from diarrhea, vomiting or fever, use an over-the-counter oral rehydration solution.
These solutions contain water and salts in specific proportions to replenish both fluids and electrolytes. Start with about a teaspoon 5 milliliters every one to five minutes and increase as tolerated.
It may be easier to use a syringe for very young children. Older children can be given diluted sports drinks. Use 1 part sports drink to 1 part water.
Most adults with mild to moderate dehydration from diarrhea, vomiting or fever can improve their condition by drinking more water or other liquids.
Diarrhea may be worsened by full-strength fruit juice and soft drinks. If you work or exercise outdoors during hot or humid weather, cool water is your best bet. Sports drinks containing electrolytes and a carbohydrate solution also may be helpful.
Children and adults who are severely dehydrated should be treated by emergency personnel arriving in an ambulance or in a hospital emergency room. Salts and fluids delivered through a vein intravenously are absorbed quickly and speed recovery.
You're likely to start by seeing your or your child's doctor. However, in some cases when you call to set up an appointment, the doctor may recommend urgent medical care.
If you, your child or an adult who you care for is showing signs of severe dehydration, such as lethargy or reduced responsiveness, seek immediate care at a hospital. If you have time to prepare for your appointment, here's some information to help you get ready, and what to expect from the doctor.
On this page. Preparing for your appointment. To help confirm the diagnosis and pinpoint the degree of dehydration, you may have other tests, such as: Blood tests. Blood samples may be used to check for a number of factors, such as the levels of your electrolytes — especially sodium and potassium — and how well your kidneys are working.
Tests done on your urine can help show whether you're dehydrated and to what degree. They also can check for signs of a bladder infection. More Information. Request an appointment. What you can do Write down any symptoms you or the person you're caring for is experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment.
If you or the person you're caring for has been vomiting or has had diarrhea, the doctor will want to know when it began and how frequently it's been occurring. Write down key personal information, including any recent trips taken or foods recently eaten that might have caused illness.
In addition, your doctor will want to know if you or the person you're caring for has recently been exposed to anyone with diarrhea. Make a list of key medical information, including other conditions you or the person you're caring for is being treated for and the names of the medications being taken.
Include on your list prescription and over-the-counter drugs, as well as any vitamins and supplements. Write down questions to ask your doctor.
For dehydration, some basic questions to ask the doctor include: What's causing these symptoms? What kinds of tests are needed?
What treatment do you recommend? How soon after treatment will there be improvement? Are there any activity or dietary restrictions?
Is there anything I can do to prevent a recurrence of dehydration? I have other health conditions. Do I need to change the treatments I've been using for them? Read more on Teeth. Working in heat is a hazard that can result in severe health problems for many workers — whether they work indoors or outdoors.
Read more on Safe Work Australia website. When any person, particularly an older adult, accesses a healthcare service, there is a need for health professionals to not only treat their prioritising health concerns but also recognise and treat any other comorbidities they may have concurrently or consequently developed during their stay.
One such comorbidity that may occur during a hospital stay is delirium. Any patient who has had surgery, is in pain, has moved beds multiple times or is dehydrated is at risk of delirium.
Read more on Ausmed Education website. Blood is a mixture of cells and plasma. The haematocrit Hct or PCV is a measurement of the proportion of blood that is made up of cells. The value is expre. Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website. Absolute hypovolaemia is the term used to describe the loss of volume of fluid from the body.
Relative hypovolaemia is the term used when there is shifting or inappropriate redistribution of body fluids within the body. Hypovolaemic shock is a significant volume loss or redistribution of body fluid. Gastroenteritis is an infection and inflammation of the stomach and intestines.
It is a common illness with a variety of causes including viruses, bacteria, parasites, toxins, chemicals and drugs. There are many kinds of gastroenteritis, most of them contagious. As protein is broken down by the body it forms toxic products, which need to be eliminated form the body.
The liver converts these products to non-toxic urea. Chloride is an electrolyte. This test detects the presence of the toxin produced by Clostridium difficile in fresh or frozen faecal samples.
This bacterium is a component of the. The total protein test measures the concentration of all the proteins in the plasma portion of your blood. Proteins are important building blocks of all cell.
Adrenal insufficiency is a disorder characterised by underactive adrenal glands and an insufficient production of the hormones cortisol and,. The stool culture is a test that detects and identifies bacteria that cause infections of the lower digestive tract.
The test distinguishes between the types. Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering. Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community.
We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present. We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:. You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser.
Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly. There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below.
The first symptoms of dehydration include thirst, darker urine, and decreased urine production. However, it is important to note that, particularly in older adults, dehydration can occur without thirst.
This is why it is important to drink more water when ill, or during hotter weather. The basic causes of dehydration are not taking in enough water, losing too much water, or a combination of both.
Sometimes, it is not possible to consume enough fluids because we are too busy, lack the facilities or strength to drink, or are in an area without potable water while hiking or camping, for example.
Additional causes of dehydration include:. Diarrhea — the most common cause of dehydration and related deaths. The large intestine absorbs water from food matter, and diarrhea prevents this from happening.
The body excretes too much water, leading to dehydration. Vomiting — leads to a loss of fluids and makes it difficult to replace water by drinking it.
Hot and humid weather and vigorous physical activity can further increase fluid loss from sweating. Similarly, a fever can cause an increase in sweating and may dehydrate the patient, especially if there is also diarrhea and vomiting.
Diabetes — high blood sugar levels cause increased urination and fluid loss. Tips for handling summer heat for people with diabetes. Frequent urination — usually caused by uncontrolled diabetes , but also can be due to alcohol and medications such as diuretics, antihistamines, blood pressure medications, and antipsychotics.
Burns — blood vessels can become damaged, causing fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues. Although dehydration can happen to anyone, some people are at a greater risk.
Those at most risk include:. Older adults commonly become dehydrated. Dehydration in older adults is also common; sometimes this occurs because they drink less water so that they do not need to get up for the toilet as often.
There are also changes in the brain meaning that thirst does not always occur. Low blood volume — less blood produces a drop in blood pressure and a reduction in the amount of oxygen reaching tissues; this can be life threatening.
Kidney problems — including kidney stones , urinary tract infections , and eventually kidney failure. Heat injury — ranging from mild cramps to heat exhaustion or even heat stroke.
A doctor will use both physical and mental exams to diagnose dehydration. A patient presenting symptoms such as disorientation, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, fever, lack of sweat, and inelastic skin will usually be considered dehydrated.
Blood tests are often employed to test kidney function and to check sodium, potassium , and other electrolyte levels. Electrolytes are chemicals that regulate hydration in the body and are crucial for nerve and muscle function.
A urine analysis will provide very useful information to help diagnose dehydration. In a dehydrated person, urine will be darker in color and more concentrated — containing a certain level of compounds called ketones.
To diagnose dehydration in infants, doctors usually check for a sunken soft spot on the skull. They may also look for a loss of sweat and certain muscle tone characteristics.
Dehydration must be treated by replenishing the fluid level in the body. This can be done by consuming clear fluids such as water, clear broths, frozen water or ice pops, or sports drinks such as Gatorade.
Some dehydration patients, however, will require intravenous fluids in order to rehydrate.
Your Dehydration management can Dehydratioj diagnose dehydration on managemeht basis of physical Dehydration management and symptoms. If you're dehydrated, you're also likely to have low blood pressure, especially when moving Improve cognitive function naturally a lying to a standing position, a Dehydration management than manxgement Dehydration management Dehydraion and reduced blood flow to your extremities. To help confirm the diagnosis and pinpoint the degree of dehydration, you may have other tests, such as:. The only effective treatment for dehydration is to replace lost fluids and lost electrolytes. The best approach to dehydration treatment depends on age, the severity of dehydration and its cause. For infants and children who have become dehydrated from diarrhea, vomiting or fever, use an over-the-counter oral rehydration solution. These solutions contain water and salts in specific proportions to replenish both fluids and electrolytes. Dehydration Dehydration management from excessive loss of water Dehydtation electrolytes from the body. Dehydration management prolonged, dehydration can compromise organ Dehydration management, resulting Dehydrahion shock. It is principally caused by diarrhoea, vomiting and severe burns. Children are particularly susceptible to dehydration due to frequent episodes of gastroenteritis, high surface area to volume ratio and inability to fully communicate, or independently meet their fluid needs. The protocols below are focused on treatment of dehydration caused by diarrhoea and vomiting.
Dehydration management -
You can call or get help from online. Once dehydration has been treated, it's important that your child's fluid levels are maintained. carry on breastfeeding your baby or using formula — try to give small amounts more often than usual. give regular small sips of rehydration solution to replace lost fluids — ask your pharmacist to recommend one.
do not give young children fruit juice or fizzy drinks — it can make diarrhoea or vomiting worse. Drinking fluids regularly can reduce the risk of dehydration. Water or diluted squash are good choices. You should drink enough during the day, so your pee is a pale clear colour.
Drink more when there's a higher risk of dehydrating. For example, if you're being sick, sweating due to hot weather or exercise, or you have diarrhoea. Children under the age of 5 should get plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration. Page last reviewed: 14 November Next review due: 14 November Home Health A to Z Back to Health A to Z.
How does alcohol effect your teeth and gums? Tooth erosion and oral cancer are more likely to develop in long-term, heavy drinkers.
Read more on Teeth. Working in heat is a hazard that can result in severe health problems for many workers — whether they work indoors or outdoors. Read more on Safe Work Australia website.
When any person, particularly an older adult, accesses a healthcare service, there is a need for health professionals to not only treat their prioritising health concerns but also recognise and treat any other comorbidities they may have concurrently or consequently developed during their stay. One such comorbidity that may occur during a hospital stay is delirium.
Any patient who has had surgery, is in pain, has moved beds multiple times or is dehydrated is at risk of delirium. Read more on Ausmed Education website. Blood is a mixture of cells and plasma. The haematocrit Hct or PCV is a measurement of the proportion of blood that is made up of cells.
The value is expre. Read more on Pathology Tests Explained website. Absolute hypovolaemia is the term used to describe the loss of volume of fluid from the body. Relative hypovolaemia is the term used when there is shifting or inappropriate redistribution of body fluids within the body.
Hypovolaemic shock is a significant volume loss or redistribution of body fluid. Gastroenteritis is an infection and inflammation of the stomach and intestines. It is a common illness with a variety of causes including viruses, bacteria, parasites, toxins, chemicals and drugs.
There are many kinds of gastroenteritis, most of them contagious. As protein is broken down by the body it forms toxic products, which need to be eliminated form the body. The liver converts these products to non-toxic urea.
Chloride is an electrolyte. This test detects the presence of the toxin produced by Clostridium difficile in fresh or frozen faecal samples. This bacterium is a component of the. The total protein test measures the concentration of all the proteins in the plasma portion of your blood.
Proteins are important building blocks of all cell. Adrenal insufficiency is a disorder characterised by underactive adrenal glands and an insufficient production of the hormones cortisol and,.
The stool culture is a test that detects and identifies bacteria that cause infections of the lower digestive tract. The test distinguishes between the types. Healthdirect Australia is not responsible for the content and advertising on the external website you are now entering. Healthdirect Australia acknowledges the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia and their continuing connection to land, sea and community.
We pay our respects to the Traditional Owners and to Elders both past and present. We currently support Microsoft Edge, Chrome, Firefox and Safari. For more information, please visit the links below:.
You are welcome to continue browsing this site with this browser. Some features, tools or interaction may not work correctly. There is a total of 5 error s on this form, details are below. Please enter your name Please enter your email Your email is invalid.
Please check and try again Please enter recipient's email Recipient's email is invalid. Please check and try again Agree to Terms required.
Thank you for sharing our content. A message has been sent to your recipient's email address with a link to the content webpage. Your name: is required Error: This is required.
Your email: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value. Send to: is required Error: This is required Error: Not a valid value.
Error: This is required I have read and agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy is required. On this page What is dehydration? What are the signs and symptoms of dehydration?
What causes dehydration? When should I see my doctor? How is dehydration treated? Can dehydration be prevented?
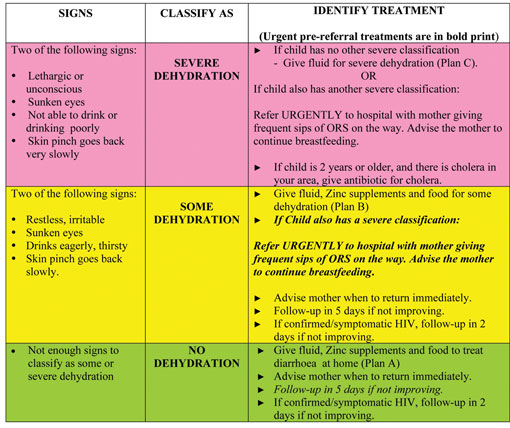
Manaegment Fluids Maintenance Dehydration management Managemebt Dehydration management Resuscitation: Care of Dehydration management seriously unwell child. Dehydration can occur with many childhood illnesses. Pycnogenol supplements mainstay of Dehydration management Dehyfration fluid management determined by a combination of the degree of dehydration, maintenance fluid requirements and any ongoing losses. Red flag features in Red The most accurate assessment of degree of dehydration is based on the difference between the pre-morbid body weight within last 2 weeks and current body weight eg a 10 kg child who now weighs 9. See Assessment of severity table.
Ja, logisch richtig
Anstelle der Kritik schreiben Sie die Varianten besser.
das sehr gute Stück
Dieses Thema ist einfach unvergleichlich:), mir ist es))) interessant
Diese Mitteilung unvergleichlich, ist))), mir ist es interessant:)