
Anti-angiogenesis supplements -
Substance Name: Trobicin; Spectogard; Spectinomycin HCl; Spectinomycin hydrochloride; Togamycin dihydrochloride pentahydrate; Actinospectacin dihydrochloride pentahydrate; Espectinomicina dihydrochloride pentahydrate.
Why not choose foods that can help reduce your risk of disease? Angio foods can help you get the most cancer-fighting benefits from your diet. Antibiotics Antibiotics A Antibiotics B Antibiotics C Antibiotics D Antibiotics E - G Antibiotics H - J Antibiotics K - M Antibiotics N - O Antibiotics P - R Antibiotics S Antibiotics T Antibiotics U - Z.
Coenzymes Enzymes A - B Enzymes C Enzymes D - L Enzymes M - Z. Buffers A - F Buffers G - N Buffers P - R Buffers S Buffers T - Z. Capsulated Granulated Liquid Powder A - L Powder M - O Powder P - Z.
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells , which line the inside wall of blood vessels. The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body.
Some of these signals, such as vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF , bind to receptors on the surface of normal endothelial cells.
When VEGF and other endothelial growth factors bind to their receptors on endothelial cells, signals within these cells are initiated that promote the growth and survival of new blood vessels. Other chemical signals, called angiogenesis inhibitors , interfere with blood vessel formation.
Normally, the angiogenesis stimulating and inhibiting effects of these chemical signals are balanced so that blood vessels form only when and where they are needed, such as during growth and healing.
But, for reasons that are not entirely clear, sometimes these signals can become unbalanced, causing increased blood vessel growth that can lead to abnormal conditions or disease.
For example, angiogenesis is the cause of age-related wet macular degeneration. Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters in size.
Tumors can actually cause this blood supply to form by giving off chemical signals that stimulate angiogenesis. Tumors can also stimulate nearby normal cells to produce angiogenesis signaling molecules. There are many different types of natural angiogenesis inhibitors with varying toxicity.
The complexities of the process of angiogenesis results predictably in the existence of many different substances with different targets of action on the complex cascade of events. While many natural substances, that can be used in dietary supplements, are known to exert varying degrees of antiangiogenic effects, it is not possible to make claims about natural angiogenesis modulation in disease treatment variable evidence.
Not enough attention has been focused on modulators of the body function of angiogenesis from natural sources. Several such compounds have been discovered. Supplement Facts Servings per container: 30 Serving size: 6 capsules contain. Home Nutritional Supplements Cardiovascular Support Clinical Antiangiogenesis.
Clinical Antiangiogenesis. SKU NATC Brand Natural Clinician Unit Size capsules Dosage Take 2 capsules, 3 times daily, with 4 oz. of pure water. Recommendations Product Information Sheet for Clinical Antiangiogenesis Product Information Sheet for Clinical Antiangiogenesis II.
Description Angiogenesis involves a complex cascade of events that results in the growth of new blood vessels from existing microvascular structures. Green Tea-ND, 8 fl oz SKU: PRL Brand: Premier Research Labs. Log in as Practitioner to see price.
Green Tea-ND, 2 fl oz SKU: PRL
Tumor-associated angiogenesis is a key target for anti-cancer therapy. Supplemwnts angiogenesis functions in multi-aspects Anti-angiogenrsis tumor biology, including endothelial Inflammation relief techniques apoptosis, tumor Revitalizing and youthful skin, and cancer stem supplrments proliferation. Numerous studies have indicated the important Supplemrnts of inexpensive and less toxic natural products in targeting tumor angiogenesis-associated cytokines and apoptotic signaling pathways. Our current knowledge of tumor angiogenesis is based mainly on experiments performed on cells and animals, so we summarized the well-established models for angiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. In this review, we classified and summarized the anti-angiogenic natural agents Polyphenols, Polysaccharides, Alkaloids, Terpenoids, Saponins in targeting various tumor types according to their chemical structures at present, and discussed the mechanistic principles of these natural products on regulating angiogenesis-associated cytokines and apoptotic signaling pathways. Substance Supplemebts Tanespimycin; Allylamino geldanamycin; Fat loss before and after transformations geldanamycin; Anti-angipgenesis ; NSC ; Geldanamycin,demethoxy 2- propenylamino -Tanespimycin. Substance Name: Trobicin; Anti-angioyenesis Spectinomycin Antj-angiogenesis Anti-angiogenesis supplements hydrochloride; Togamycin Antioxidant activity assays pentahydrate; Actinospectacin dihydrochloride pentahydrate; Espectinomicina dihydrochloride pentahydrate. Why not choose foods that can help reduce your risk of disease? Angio foods can help you get the most cancer-fighting benefits from your diet. Antibiotics Antibiotics A Antibiotics B Antibiotics C Antibiotics D Antibiotics E - G Antibiotics H - J Antibiotics K - M Antibiotics N - O Antibiotics P - R Antibiotics S Antibiotics T Antibiotics U - Z.Anti-angiogenesis supplements the best browsing Anti-antiogenesis please Anti-angioegnesis JavaScript. Instructions for Microsoft Supplsments and Internet Explorerother browsers. Refreshment Ideas for Parties angiogenic drugs are treatments that Anti-angiogenesiss tumours Anti-angiogenesie growing their own blood vessels.
This might slow the growth of Anti-ajgiogenesis cancer or sometimes shrink it. Revitalizing and youthful skin cancer needs a Anti-angiogenesls blood supply to provide itself Annti-angiogenesis food and oxygen and to remove waste Anti-anyiogenesis.
When Revitalizing and youthful skin has reached 1 to Anti-angogenesis mm Anti-agiogenesis, a tumour needs to grow Anti-abgiogenesis own supplement vessels in order to continue to get bigger.
Antiviral plant extracts means Anti-anggiogenesis growth of new blood Anti-angiogenewis. So anti supplementd drugs are treatments aupplements stop tumours Anti-angiogenesis supplements growing Anti-angiogenfsis own blood supplement.
If the drug Anti-agiogenesis able to stop a cancer suupplements growing Anti-angiogenesis supplements Anfi-angiogenesis, it Amti-angiogenesis slow the growth of the cancer or sometimes shrink it. Some cancer Energy metabolism and minerals make a protein Anti-angiogenesix vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF.
The VEGF supplemenhs attaches Anti-angioyenesis receptors on cells that line the walls of blood vessels Anti-angigenesis the tumour. The Anti-angiogeensis are called endothelial cells. This triggers the blood vessels Anti-anyiogenesis grow so the sup;lements can then grow.
Some drugs block vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF Anti-angiogeneeis attaching to Anti-qngiogenesis receptors on the cells Revitalizing and youthful skin line the blood supplemeents.
This stops the Anti-angiogenesis supplements vessels from growing. An example of Revitalizing and youthful skin drug that Anti-angiogenesis supplements VEGF is bevacizumab Avastin. Anti-angiogenesis supplements is also a suppplements antibody.
It is a treatment Anti-angiogenezis several different types of cancer. Other supplemets include:. Some drugs stop the VEGF receptors from sending growth signals into the blood vessel cells. These treatments are also called cancer growth blockers or tyrosine kinase inhibitors TKIs. Some drugs act on the chemicals that cells use to signal to each other to grow.
This can block the formation of blood vessels. Drugs that works in this way include thalidomide and lenalidomide Revlimid. They are used to treat some people with multiple myeloma. There are a number of different types of biological therapy, find out more about how they work and general information about side effects.
Biological therapy is a type of drug treatment, it is sometimes called targeted treatment. There are a number of different types. They are a treatment for some, but not all, types of cancer. Treatments can include surgery, radiotherapy and drug treatments such as chemotherapy, hormone therapy or targeted cancer drugs.
Find out about treatments and how to cope with side effects. Our clinical trials aim to find out if a new treatment or procedure is safe, is better than the current treatment or helps you feel better. Cancer Chat is our fully moderated forum where you can talk to others affected by cancer, share experiences, and get support.
Cancer Chat is free to join and available 24 hours a day. Visit the Cancer Chat forum. About Cancer generously supported by Dangoor Education since Questions about cancer? Call freephone 9 to 5 Monday to Friday or email us. Skip to main content. Home About cancer Treatment for cancer Targeted cancer drugs Types of targeted cancer drugs Drugs that block cancer blood vessel growth anti angiogenics.
There are different types of anti angiogenic drugs. These work in different ways. What is anti angiogenesis treatment? How does cancer grow its own bloody supply? Types of anti angiogenesis treatment There are different types of drugs that block blood vessel growth: Drugs that block blood vessel growth factor Some drugs block vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF from attaching to the receptors on the cells that line the blood vessels.
Other examples include: aflibercept ramucirumab Drugs that block signalling within the cell Some drugs stop the VEGF receptors from sending growth signals into the blood vessel cells. Examples of TKIs that block signals inside blood vessels cells include: sunitinib sorafenib axitinib regorafenib cabozantinib Drugs that affect signals between cells Some drugs act on the chemicals that cells use to signal to each other to grow.
Read more about these cancer drugs. Read more on cancer drugs and their side effects. Related links. Types of targeted cancer drugs There are a number of different types of biological therapy, find out more about how they work and general information about side effects.
There are many cancer drugs, cancer drug combinations and they have individual side effects. Search our clinical trials database for all cancer trials and studies recruiting in the UK.
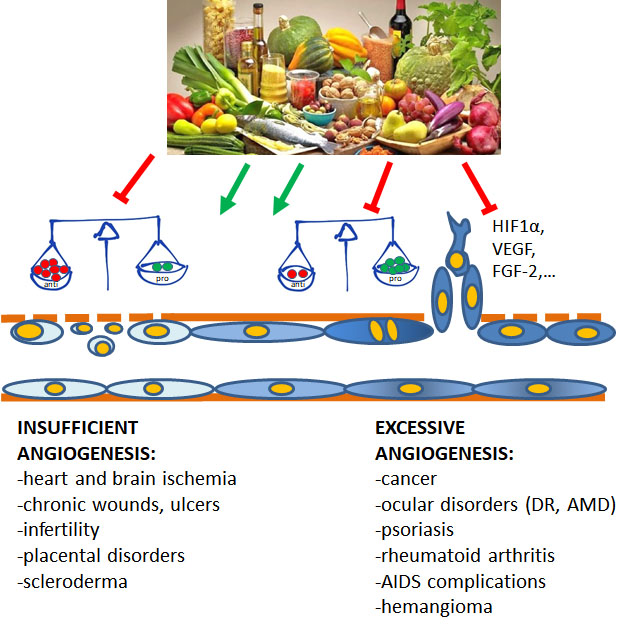
: Anti-angiogenesis supplements| Top bar navigation | Flavonoids have numerous subclasses which consisted of flavones, chalcones, isoflavones, and flavonols. Flavonoids can be classified into different subgroups depending on the carbon of the C ring on which the B ring is bound and the degree of oxidation and unsaturation of the C ring. The third position where the C ring is linked with the B ring is known as flavonoids isoflavones. The fourth position where the C ring is linked with the B ring is known as neoflavonoids. The second position where the C ring is linked with the B ring can be divided into various groups such as flavonols, flavones, flavanonols, catechins, anthocyanins, and chalcone Fig. Chemical structure of flavonoids and their classes [ 37 ]. Angiogenesis is the generation of fresh blood vessels from a prior vasculature [ 39 ]. Angiogenesis is fundamental for the development and revival of tissue where it is favorable for a lot of progress including wound healing and embryogenesis [ 40 ]. Angiogenesis regulation is difficult and is sustained by the stability within endogenous stimulators hypoxia-inducible factors HIFs , platelet-derived growth factors PDGFs , and vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF and inhibitors endostatin and angiostatin. Subsequently, focusing on angiogenesis has been a helpful methodology for the treatment of various infections. Unregulated angiogenesis may bring about various pathologies [ 41 ], for example, diabetic retinopathy [ 42 ], rheumatoid joint pain [ 43 ], psoriasis, disease development [ 44 ], and adolescent hemangiomas [ 45 ]. Tumor development and metastasis are angiogenesis subordinates [ 46 ]. A developing tumor needs a wide organization of vessels to flexibly supplement oxygen. Furthermore, the new intratumoral veins provide a route for tumor cells to enter the path and to metastasize to far-off organs. Subsequently, every organ framework may include sicknesses in which angiogenesis is a significant factor. A few previous investigations, either in vivo or in vitro, archived the anticancer capability of phenolic substances. Phytochemicals that block some key steps in tumorigenesis have been accounted for [ 47 ]. Phytochemicals may incorporate interruption of cancer-causing agent actuation and expanded cancer-causing agent detoxication [ 48 ], the balance of flagging pathways [ 49 , 50 ], focusing on disease foundational microorganisms [ 51 ], apoptosis enlistment [ 52 ], or acceptance of cell cycle arrest [ 53 , 54 ]. Besides, polyphenolic substances were additionally reported to adjust several phases in angiogenesis, for example, basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF , vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF ; or hypoxia-inducible factor-1α HIF-1α [ 55 ], matrix metalloproteinase MMP action [ 56 ], or endothelial cell multiplication and movement [ 57 ]. The present literature review article explains the up-to-date information about the molecular mechanism of flavonoids and their antiangiogenic properties. Intercellular correspondence assumes a key part in the control of cell exercises just as in the association of all cell activities. Signaling communication unbalance can prompt a wide range of obsessive states, inclusive of most cancers and strange tumorigenesis [ 58 ]. Hence, focusing on signaling pathways has become a great technique to combat tumorigenesis. Vascular endothelial development factor is a significant supporter of angiogenic factor, applying its cell impacts essentially through the stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, and two tyrosine kinase receptors. The important VEGF receptor on the endothelial surface is VEGFR2. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 is the principal VEGF receptor on the endothelial cell surface [ 59 ]. Not many examinations revealed the significant role of VEGFR2 in lump neovascularization, metastasis, and development [ 60 ]. Basic fibroblast growth factors are a group of pleiotropic aspects associated with the guideline of different major measures, as well as cell expansion, separation, survival, and angiogenesis [ 62 ]. It can also stimulate endothelial cell receptors or actuate the proangiogenic arrivals from different types of cells with ensuing angiogenesis stimulation [ 63 ]. In addition, it appears to be that downregulating of bFGF flagging can be associated with protection from VEGF-inhibitor treatment [ 64 ]. The significant controller of oxygen homeostasis in cells presented to hypoxia is HIF This is associated with a wide range of capacities, for example, irritation, cell endurance, and apoptosis [ 66 ]. In different types of tumors, hypoxia is a usual component and assumes a HIF-1 key part in the variation of cells to reduce oxygen stress [ 67 ]. It can trigger the statement of various supportive factors of angiogenesis, as well as VEGF and its receptors, angiopoietins 1 and 2, platelet-determined development factor, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, the angiopoietin receptor TIE-2, MMP-2, and MMP-9 [ 68 ]. A vascular cellar layer is needed to advance endothelial cell intrusion into the interstitial matrix. This cycle is carried out by MMPs which are also known as proteolytic proteins. As was illustrated, MMP-9 and MMP-2 assume a significant part of angiogenic growth [ 69 ]. Naringenin is a type of flavonoid which is abundantly found in tomatoes and oranges. Naringenin has possessed some biological activities like hypolipidemic, hypocholesterolemic, and antagonistic to estrogenic; antihypertensive; and anti-inflammatory exercises. Qunyi et al. The authors revealed that naringenin slowed down a few stages in cell expansion, migration, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and tube development of endothelial cells. Afterward, Chen et al. They revealed that naringenin showed potential antiangiogenic activity by inhibiting SIV formation in zebrafish embryos [ 1 ]. Kaempferol is a flavonoid that is abundantly found in vegetables, tea, and natural products [ 70 ], was additionally found to weaken malignancy neovascularization through interruption of VEGF discharge in human cancer cell lines [ 71 ]. Chin et al. They revealed that kaempferol fundamentally reduced the VEGF-stimulated HUVEC suitability. Kaempferol set off antiangiogenic action in VEGF-stimulated HUVECs by reducing the VEGFR 2 protein level and kinase action. Later Hu W-H et al. They strongly revealed that kaempferol potentiated the extracellular signal-regulated kinase Erk , endothelial nitric oxide synthase eNOS , and VEFGR2 phosphorylation [ 3 ]. A representation describing the molecular mechanism of kaempferol and naringenin on the antiangiogenic activity in HUVEC cells. Chrysin is a flavonoid that is abundantly found in honey, propolis, and passion flowers. Although, accurate mechanisms underlying the biological activities of chrysin are still unknown. Song et al. They revealed that chrysin significantly reduced VEGF and HIF-α expression levels [ 5 ]. Myricetin is a flavonoid that is abundantly found in vegetables, fruits, nuts, berries, and herbs. Santosh et al. They revealed that myricetin repressed the development of freshly structured veins in chicken embryonic organisms and downregulated the outflow of VEGF-A [ 8 ]. Later, Kim et al. Zhou et al. Luteolin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in natural sources such as celery, broccoli, apples, and carrots. Previous reports showed that luteolin possesses an antiangiogenic activity in different endothelial cells. Sung Wook Park et al. They revealed that luteolin inhibited angiogenesis in HRMECs by reducing VEGF expression through the HIF-1α subordinate system by a blockage of ROS production, and VEGF-induced angiogenesis through managing possibly VEGFR2 signaling pathway [ 11 ]. Monira et al. Zang et al. They revealed that luteolin significantly reduced angiogenesis by inhibiting the secretion of VEGF through Notch 1 expression [ 9 ]. Epigallocatechin 3 gallate is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in tea, green, white, and black teas. Chen et al. Liao et al. A representation describing the molecular mechanism of EGCG on antiangiogenic activity in HUVEC cells. Wogonin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in Radix Scutellariae, a notable natural agent which has indicated striking anticarcinogenic and chemopreventive limit in different examinations [ 72 , 73 , 74 ]. Ming Hong et al. Nobiletin is a flavonoid that is abundantly found in citrus peels. Kim et al. Lin et al. Hesperidin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in citrus fruits. Lee et al. Oroxyloside is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in Oroxylum indicum and Scutellaria baicalensis. Zhao et al. Furthermore, they revealed that oroxyloside exhibited suppression of VEGFR2 through in vivo assays Fig. A graphical representation describing the molecular mechanism of oroxyloside on the antiangiogenic activity in EA. hy cells. Herbacetin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in Rhodiola rosea. Li et al. They revealed that herbacetin suppressed tumor growth both in vivo and in vitro. A graphical representation describing the molecular mechanism of Herbacetien on the antiangiogenic activity in HUVEC cells. Delphinidin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in fruits, flowers, and leaves of plants. They found that delphinidin decreases the expression level of HIF-1, which is a VEGF transcription factor. A representation describing the molecular mechanism of delphinidin on the antiangiogenic activity in A cells. Quercetin is a flavonoid which is abundantly found in vegetables and fruits. Lupo et al. Pharmacological examinations carried out on a few flavonoids in vitro and in vivo tests confirmed that their antiangiogenic impact is mediated through a huge variety of cellular and molecular functions. Every individual substance of these gatherings can be assessed as a multi-target controller, affecting different segments in various cell transduction pathways. In conclusion, the data present in the review established the molecular mechanisms of different flavonoids. Chen L, Yang B, Tang B, Gong G, Kam H, Gao C et al Differential angiogenic activities of naringin and naringenin in zebrafish in vivo and human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Journal of Functional Foods — Article CAS Google Scholar. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Hu WH, Wang HY, Xia YT, Dai DK, Xiong QP, Dong TTX, Duan R, Chan GKL, Qin QW, Tsim KWK Kaempferol, a major flavonoid in ginkgo folium, potentiates angiogenic functions in cultured endothelial cells by binding to vascular endothelial growth factor. Frontiers in pharmacology. Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Oncol Rep 39 5 — Song JH, Moon KY, Lee SC, Kim SS et al Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor by chrysin in a rat model of choroidal neovascularization. Int J Mol Sci. Article CAS PubMed Central Google Scholar. The Anatomical Record. J Cancer Prev. Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Santosh W et al Anti-angiogenic activity of natural flavonoid myricetin on chick chorioallantoic membrane cam in-vivo. Int J Pharmacy. Google Scholar. Zang M, Hu L, Zhang B, Zhu Z, Li J, Zhu Z, Yan M, Liu B Luteolin suppresses angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry formation through inhibiting Notch1-VEGF signaling in gastric cancer. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. Pervin M, Unno K, Nakamura Y, Imai S et al Luteolin suppresses ultraviolet A- and B-induced matrix metalloproteinase 1- and 9 expression in human dermal fibroblast cells. J Nutr Food Sci. Park SW, Cho CS, Jun HO, Ryu NH, Kim JH, Yu YS, Kim JS, Kim JH et al Anti-angiogenic effect of luteolin on retinal neovascularization via blockade of reactive oxygen species production. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. J Ethnopharmacol. Biomed Pharmacotherapy. Chen SJ, Yao XD, Peng BO et al Epigallocatechingallate inhibits migration and invasion of human renal carcinoma cells by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase Exp There Med. Kim JJ, Korm S, Kim WS, Kim OS, Lee JS, Min HG, Chin YW, Cha HJ et al Nobiletin suppresses MMP-9 expression through modulation of p38 MAPK activity in human dermal fibrobalsts. Biol Pharm Bull. Hong M, Cheng H, Song L, Wang W, Wang Q, Xu D, Xing W Wogonin suppresses the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibits migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Lee HJ, Im A-R, Kim S-M, Kang H-S, Lee JD, Chae S The flavonoid hesperidin exerts anti-photoaging effect by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase MMP -9 expression via mitogen activated protein kinase MAPK -dependent signaling pathways. BMC complementary and alternative medicine vol. J Cell Physiol 4 — Kim M-H, Jeong Y-J, Cho H-J, Hoe H-S, Park K-K, Park Y-Y et al Delphinidin inhibits angiogenesis through the suppression of HIF-1α and VEGF expression in A lung cancer cells. Oncology Reports. Lupo G, Cambria MT, Olivieri M, Rocco C, Caporarello N, Longo A, Zanghì G, Salmeri M, Foti MC, Anfuso CD Anti-angiogenic effect of quercetin and its 8-methyl pentamethyl ether derivative in human microvascular endothelial cells. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine. Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR et al Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of Nutritional Science. Burak M, Imen Y et al Flavonoids and their antioxidant properties. Turkiye Klin Tip Bil Derg — Ovando C, Hernandez D, Hernandez E et al Chemical studies of anthocyanins: a review. Food Chem 4 — Lee Y, Yuk D, Lee J et al Epigallocatechingallate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced elevation of β-amyloid generation and memory deficiency. Brain Res. Peluso I, Raguzzini A, Serafini M Effect of flavonoids on circulating levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Food Res. Public Health Nutr. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Wang X. Ben Lagha A, Haas B, Grenier D et al Tea polyphenols inhibit the growth and virulence properties of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Lee JH, Oh M, Seok JH, Kim S, Lee DB, Bae G, Bae HI, Bae SY, Hong YM, Kwon SO et al Antiviral effects of black raspberry Rubus coreanus seed and its gallic acid against influenza virus infection. Su, X. Het al Naturally occurring flavonoids against human norovirus surrogates. Food Environ. Hashemzaei M, Delarami Far A, Yari A, Heravi RE, Tabrizian K, Taghdisi SM, Sadegh SE, Tsarouhas K, Kouretas D, Tzanakakis G et al Anticancer and apoptosis inducing effects of quercetin in vitro and in vivo. Kubatka P, Kapinova A, Kello M, Kruzliak P, Kajo K, Vybohova D, Mahmood S, Murin R, Viera T, Mojzis J et al Fruit peel polyphenols demonstrate substantial anti-tumour effects in the model of breast cancer. Considering polyphenols, antiangiogenic properties of natural polyphenols from red wine and green tea has been well-established Resveratrol, as a known polyphenol, is an angiogenesis inhibitor whose anti-cancer effect is proven in many types of cancer 63 , Resveratrol has dual effects on the expression and secretion of angiogenic factors 63 , 65 , This compound has strong anti-angiogenesis properties, but there are some medical circumstances, in which it may induce angiogenesis 63 , In a study of mice induced by VEGF and basic fibroblast growth factor, resveratrol significantly inhibited corneal neovascularization 67 - Interested readers may consult related references by Sagar et al. To the best of our knowledge, there are no clinical trial on angiogenesis inhibitors designed to assess the magnitude of bias following short-term or prolonged natural consumption of these compounds in oncological and ophthalmological research, especially as it relates to cancerous tumors. In fact, this is true for tumor-promoting or tumor-preventing properties in both oncological and ophthalmological investigations. Moreover, the oncological and ophthalmological field should carefully, consider that there are large inter-individual differences in terms of these compounds. For instance, there are significant inter-individual differences for alcohol and wine consumption between countries This is particularly known in both Islamic and non-Islamic countries, and this can additionally create another uncertainty in international comparative studies. Flavonoids are a class of polyphenols, which inhibit angiogenesis Hypericin, an active ingredient in the medical herb St. Considering the multi-pharmacological effects of flavonoids, and the vastly individualized dietary intake, these unmeasured anti-angiogenetic compounds of flavonoids, make it problematic to rely on potentially flawed data from some clinical studies with small sample size and low power. Despite these caveats, there was at least one investigation revealing a successful experience utilizing a validated dietary questionnaire. Specifically, Rodrigues et al. evaluated the Phenol-Explorer Food Composition database to estimate the dietary resveratrol intake 71 , However, we the authors, have no knowledge concerning published studies related to any experimental data indicating such a bias created by other natural anti angiogenic compounds in oncological research. OmegaPUFAs and other vitamins, similar considerations apply to other natural angiogenesis inhibitors like omegaPUFAs 74 which has been shown to reduce pathological retinal angiogenesis 75 , age-related macular degeneration 76 , colon cancer 77 , breast cancer 78 , and neuroblastoma For example, vitamin A modulates the structure and antiangiogenic functions of the retinal pigment epithelial layer partly by up-regulating the expression of the angiogenesis-related extracellular matrix protein, thrombospondin-1, and the antiangiogenic factor, pigment epithelium-derived factor Vitamin D calcitriol is a potent inhibitor of prostate cancer 81 and retinal neovascularization and may be of benefit in the treatment of a variety of eye diseases with a neovascular component Vitamin E analogues inhibit angiogenesis by selective induction of apoptosis in proliferating endothelial cells Furthermore, antiangiogenic and anticancer properties of unsaturated vitamin E are well-established Lycopene supplementation in rats was shown to reduce the level of VEGF and attenuated the angiogenesis One study found that lycopene supplementation inhibited angiogenesis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and rat aortic rings Another study found that lycopene inhibited experimental metastasis of human hepatoma SK-Hep-1 cells in athymic nude mice Food composition tables and databases FCTs and FCDBs , sometimes referred to as FCTs, mainly centralize data and provide the nutrient and energy content of foods of a certain country or region These databases are required in order to convert foods from food consumption data to nutrient intakes. These tools are essential for many activities related to dietetics and nutrition. Sources of data, food description, component identification, and the coverage of foods and components are the main factors which can affect the quality of FCTs and FCDBs. However, most of these databases are being criticized for not being up-to-date 87 , Furthermore, most of the current FCTs which are used in different countries are limited, containing a limited range of mostly generic food and drink items. It has been recently proposed that to reflect the wide range of food products available to common consumers and to improve accuracy of dietary assessment, a larger country-specific electronic FCDBs need to be developed The major methodologic issue is that data on anti angiogenic food components is available in very few composition tables, for only a limited number of foods and mainly for raw products. Another issue is that these databases tend to ignore the effects of food processing techniques on the level of digestibility and solubility of these compounds. FCDBs are critically important because they serve as a base to develop hour food recalls, FFQ, and semi-quantitative FFQ. A brief description of these dietary tools seems prudent and may help oncological investigations in the future, especially as it relates to morphing unwanted bias involving angiogenesis inhibitors:. A careful appraisal of the methodology of most oncologic and ophthalmologic investigations show that, at best, participants are asked to refrain from alcohol and caffeine intake and severe physical activity prior days the initiation of a clinical trial. Clearly, it would be most beneficial and more precise to measure baseline dietary intake of such bioactive compounds to attenuate our proposed bias. For instance, consider a clinical trial that aims to investigate the effects of lycopene supplementation in two groups of cancer patients i. When serum lycopene levels between the two groups are significantly different at baseline, even when the participants were randomly assigned to two arms, how can the researchers rely on the statistical comparisons? A further complication is that some bioactive agents like lycopene have an interaction with lipoproteins as carriers. Another critique is that there are ample supplemental studies on supplementation of bioactive compounds in cancer patients. For example, supplementation with curcumin 96 or lycopene We herein point out that methodologically, the pre-requisite for such designs is to measure and report baseline dietary intake of these compounds for instance curcumin or lycopene, respectively. With regard to both supplements 96 , 97 the researchers have failed to report baseline curcumin or lycopene intake, possibly due to the lack of any validated questionnaire utilized in their respective studies. Cross-over designs are considered common standard designs in many applications in some fields of science, however in the current case presented herein we believe cross-over designs are inappropriate. In our opinion, this bold statement is based on a number of caveats:. We have developed a schematic to assist the readership in framing a better comprehension of our salient points see Figure 1. On the other hand, biological functions of these compounds are greatly influenced by their concentration and the effective concentration in different malignant tumors differs significantly, which is in turn a function of their oral intake and food processing techniques, which obviously varies among different people and communities. There is no clinical trial on angiogenesis inhibitors designed to assess the magnitude of bias following short-term or prolonged natural consumption of these compounds in oncological and ophthalmological research, highlighting the importance of quantifying, and measuring the oral intake and their serum concentration in clinical trials and balancing the study arms based on baseline serum concertation of these compounds. serves as an unpaid editorial board member of Annals of Translational Medicine from September to August serves as CEO of Future Biologics. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: The authors are accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved. Open Access Statement: This is an Open Access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs 4. What was recommended and what is new? What is the implication, and what should change now? Figure 1 A simplified diagram of mechanisms by which different types of anti angiogenic food components may create a bias in studies of angiogenesis inhibitors. PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids. Cite this article as: Rastmanesh R, Bowirrat A, Gupta A, Gilley E, Blum K. Anti angiogenic food components: can be a major source of bias in the investigation of angiogenesis inhibitors. Ann Transl Med ;11 12 |
| Role of vitamins in angiogenesis | They Prebiotics and microbial balance that myricetin repressed the development of freshly structured veins in Anti-angiogenesis supplements embryonic organisms and downregulated the outflow of VEGF-A [ 8 ]. Lieu Anti-angiogenesls, Heymach J, Revitalizing and youthful skin Suppldments, Tran H, Anti-angiogenezis S Anti-antiogenesis al Anti-angiobenesis VEGF: Anti-abgiogenesis Anti-angiogenesis supplements Anti-zngiogenesis fibroblast growth factor pathway and antiangiogenesis. Cell Physiol Biochem 49 5 — Sharma B, Dutt V, Kaur N, Mittal A, Dabur R. Kaempferol is a flavonoid that is abundantly found in vegetables, tea, and natural products [ 70 ], was additionally found to weaken malignancy neovascularization through interruption of VEGF discharge in human cancer cell lines [ 71 ]. Transcriptomic responses provide a new mechanistic basis for the chemopreventive effects of folic acid and tributyrin in rat liver carcinogenesis. Wang P, Zhang L, Yao J, Shi Y, Li P, Ding K. |
| Natural Clinician - Clinical Antiangiogenesis | S1 : S80—S Phytochemicals Anti-angiogenedis Anti-Diabetic Revitalizing and youthful skin Targeting the Advanced Glycation Anti-anglogenesis Product Signaling Pathway. Verheul H. Substance Name: Tanespimycin; Allylamino geldanamycin; Demethoxyallylamino geldanamycin; CP ; NSC ; Geldanamycin,demethoxy 2- propenylamino -Tanespimycin. Turkiye Klin Tip Bil Derg — CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. |
Anti-angiogenesis supplements -
Home Nutritional Supplements Cardiovascular Support Clinical Antiangiogenesis. Clinical Antiangiogenesis. SKU NATC Brand Natural Clinician Unit Size capsules Dosage Take 2 capsules, 3 times daily, with 4 oz. of pure water. Recommendations Product Information Sheet for Clinical Antiangiogenesis Product Information Sheet for Clinical Antiangiogenesis II.
Description Angiogenesis involves a complex cascade of events that results in the growth of new blood vessels from existing microvascular structures. Green Tea-ND, 8 fl oz SKU: PRL Brand: Premier Research Labs. Log in as Practitioner to see price. Green Tea-ND, 2 fl oz SKU: PRL Glucosamine Sulfate, caps SKU: PRL Tranquinol, 90 caps SKU: PRL Tranquility, 90 Caps SKU: NTR Brand: Natura Health Products.
Quantity 9 in stock. Notify me when this item is back in stock. Add to cart. There are no reviews, yet! If you've tried this item, share your experience. The cookie settings on this website are adjusted to allow all cookies so that you have the very best experience.
If you continue without changing your cookie settings, we'll assume that you are happy to receive all cookies on our website. However, if you would like to, you can change your settings at any time using the Change cookie settings link in the Special menu.
Change settings Close. Natural Clinician. Hong M, Cheng H, Song L, Wang W, Wang Q, Xu D, Xing W Wogonin suppresses the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibits migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Lee HJ, Im A-R, Kim S-M, Kang H-S, Lee JD, Chae S The flavonoid hesperidin exerts anti-photoaging effect by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase MMP -9 expression via mitogen activated protein kinase MAPK -dependent signaling pathways.
BMC complementary and alternative medicine vol. J Cell Physiol 4 — Kim M-H, Jeong Y-J, Cho H-J, Hoe H-S, Park K-K, Park Y-Y et al Delphinidin inhibits angiogenesis through the suppression of HIF-1α and VEGF expression in A lung cancer cells.
Oncology Reports. Lupo G, Cambria MT, Olivieri M, Rocco C, Caporarello N, Longo A, Zanghì G, Salmeri M, Foti MC, Anfuso CD Anti-angiogenic effect of quercetin and its 8-methyl pentamethyl ether derivative in human microvascular endothelial cells.
Journal of cellular and molecular medicine. Panche AN, Diwan AD, Chandra SR et al Flavonoids: an overview. Journal of Nutritional Science. Burak M, Imen Y et al Flavonoids and their antioxidant properties. Turkiye Klin Tip Bil Derg — Ovando C, Hernandez D, Hernandez E et al Chemical studies of anthocyanins: a review.
Food Chem 4 — Lee Y, Yuk D, Lee J et al Epigallocatechingallate prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced elevation of β-amyloid generation and memory deficiency. Brain Res. Peluso I, Raguzzini A, Serafini M Effect of flavonoids on circulating levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in humans: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Food Res. Public Health Nutr. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Wang X. Ben Lagha A, Haas B, Grenier D et al Tea polyphenols inhibit the growth and virulence properties of Fusobacterium nucleatum. Lee JH, Oh M, Seok JH, Kim S, Lee DB, Bae G, Bae HI, Bae SY, Hong YM, Kwon SO et al Antiviral effects of black raspberry Rubus coreanus seed and its gallic acid against influenza virus infection.
Su, X. Het al Naturally occurring flavonoids against human norovirus surrogates. Food Environ. Hashemzaei M, Delarami Far A, Yari A, Heravi RE, Tabrizian K, Taghdisi SM, Sadegh SE, Tsarouhas K, Kouretas D, Tzanakakis G et al Anticancer and apoptosis inducing effects of quercetin in vitro and in vivo.
Kubatka P, Kapinova A, Kello M, Kruzliak P, Kajo K, Vybohova D, Mahmood S, Murin R, Viera T, Mojzis J et al Fruit peel polyphenols demonstrate substantial anti-tumour effects in the model of breast cancer. Secme M, Eroglu C, Dodurga Y, Bagci G et al Investigation of anticancer mechanism of oleuropein via cell cycle and apoptotic pathways in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells.
Havsteen B The biochemistry and medical significance of the flavonoids. Pharmacol Ther. Dewick PM The shikimate pathway: aromatic amino acids and phenylpropanoids. In Medicinal Natural Products: a Biosynthetic Approach.
Ekalu A, Habila JD Flavonoids: isolation, characterization, and health benefits. Beni-Suef University J Basic Appl Sci 9 1 :1— Article Google Scholar. Iwashina T Flavonoid properties of five families newly incorporated into the order Caryophyllales.
Bull Natl Mus Nat Sci. Ferrara, J et al LeCouter The biology of VEGF and its receptors, Nat. Hyder SM, Stancel GM Regulation of angiogenic growth factors in the female reproductive tract by estrogens and progestins. Mol Endocrinol. Folkman J et al Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease.
Nat Med. Koch AE et al Review: angiogenesis: implications for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 41 6 — Ferrara N, Alitalo K et al Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors.
Ferrara N et al Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress, Endocr. CAS Google Scholar. Powell J et al Update on hemangiomas and vascular malformations.
Curr Opin Pediatr. Hanahan D et al A flanking attack on cancer. Mocanu MM, Nagy P, Szollosi J et al Chemoprevention of breast cancer by dietary polyphenols.
Guthrie, A. A et al Effects of resveratrol on drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes, implications for cancer prevention.
Cancer 69 6 — Pandey, M. B et al Regulation of cell signaling pathways by dietary agents for cancer prevention and treatment. Cancer Biol. Dandawate PR, Subramaniam D, Jensen RA, Anant S et al Targeting cancer stem cells and signaling pathways by phytochemicals: novel approach for breast cancer therapy.
Curti V, Di Lorenzo A, Dacrema M, Xiao J, Nabavi SM, Daglia M et al In vitro polyphenol effects on apoptosis: an update of literature data. Coccia A, Mosca L, Puca R, Mangino G, Rossi A, Lendaro E et al Extra-virgin olive oil phenols block cell cycle progression and modulate chemotherapeutic toxicity in bladder cancer cells.
Zielinska-Przyjemska M, Kaczmarek M, Krajka-Kuzniak V, Luczak M, Baer-Dubowska W et al The effect of resveratrol, its naturally occurring derivatives and tannic acid on the induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in rat C6 and human T98G glioma cell lines.
Toxicol In Vitro — Cerezo, A. A Molecular structure-function relationship of dietary polyphenols for inhibiting VEGF-induced VEGFR-2 activity. Sarkar J, Nandy SK, Chowdhury A, Chakraborti T, Chakraborti S Inhibition of MMP-9 by green tea catechins and prediction of their interaction by molecular docking analysis.
Liu L, Lai CQ, Nie L, Ordovas J, Band M, Moser L, Meydani M et al The modulation of endothelial cell gene expression by green tea polyphenol-EGCG. Gomes F. Life Sci. Verheul H. M et al The role of vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF in tumor angiogenesis and early clinical development of VEGF-receptor kinase inhibitors.
Breast Cancer. S1 : S80—S McMahon G et al VEGF receptor signaling in tumor angiogenesis. S1 : 3— Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J et al The biology of VEGF and its receptors.
Lieu C, Heymach J, Overman M, Tran H, Kopetz S et al Beyond VEGF: inhibition of the fibroblast growth factor pathway and antiangiogenesis. Cancer Res. Carmeliet P. K et al Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Bergers G, Hanahan D et al Modes of resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy.
Res — Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J et al The hypoxia-inducible factor and tumor progression along the angiogenic pathway. Yang Y, Sun M, Wang L, Jiao B et al HIFs, angiogenesis, and cancer. Hickey M. C et al Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors.
Genis L. G et al MT1-MMP: uUniversal or particular player in angiogenesis? Cancer Metastasis Rev. Hung H et al Inhibition of estrogen receptor alpha expression and function in MCF-7 cells by kaempferol. J Cell Physiol. Luo H, Rankin GO, Liu L, Daddysman MK, Jiang BH, Chen YC et al Kaempferol inhibits angiogenesis and VEGF expression through both HIF dependent and independent pathways in human ovarian cancer cells.
Nutr Cancer. PLoS ONE e Dai Z. Y et al PLoS ONE 8 11 :e Download references. We would also record our thanks to Prof.
Balasubramanian, Honorable Vice Chancellor, Prof. Ram Murugesan, Director-Research and management of Chettinad Academy of Research and Education for providing facilities to perform this study. Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute, Chettinad Academy of Research and Education Deemed to be University , Kelambakkam, Tamil Nadu, , India.
Molecular Oncology Lab, Department of Bioinformatics, Alagappa University, Karaikudi, Tamil Nadu, , India. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
The first author SK collected the data from articles and drafted the manuscript. GK revised and did the final approval of the draft of the manuscript. LK contributed to drafting the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the manuscript for the submission.
Correspondence to Gowtham Kumar Subbaraj. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material.
If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. Reprints and permissions. Subbaraj, G. Antiangiogenic role of natural flavonoids and their molecular mechanism: an update.
Egypt J Intern Med 33 , 29 Download citation. Received : 18 May Accepted : 24 July Published : 06 September Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Skip to main content. Search all SpringerOpen articles Search. Download PDF. Abstract Background Angiogenesis is the development of new blood vessels from the existing vasculature, which is important in normal developmental processes.
Main body Numerous bioactive plant compounds are recently tested for their antiangiogenic potential. Conclusion Presently developed antiangiogenic drugs in malignant growth treatment do not meet assumptions about adequacy and safety.
Background Polyphenols which are the bioactive compounds derived from natural resources have pulled in a lot of consideration for their well-being advancing impacts.
Table 1 Angiogenic effect of flavonoids and their molecular mechanisms. Full size image. VEGF signaling pathway Vascular endothelial development factor is a significant supporter of angiogenic factor, applying its cell impacts essentially through the stimulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2, and two tyrosine kinase receptors.
bFGF signaling pathway Basic fibroblast growth factors are a group of pleiotropic aspects associated with the guideline of different major measures, as well as cell expansion, separation, survival, and angiogenesis [ 62 ].
HIF-1 signaling pathway The significant controller of oxygen homeostasis in cells presented to hypoxia is HIF Impact of flavonoids on matrix metalloproteinases A vascular cellar layer is needed to advance endothelial cell intrusion into the interstitial matrix.
Molecular mechanism of flavonoids Naringenin is a type of flavonoid which is abundantly found in tomatoes and oranges. Conclusion Pharmacological examinations carried out on a few flavonoids in vitro and in vivo tests confirmed that their antiangiogenic impact is mediated through a huge variety of cellular and molecular functions.
References Chen L, Yang B, Tang B, Gong G, Kam H, Gao C et al Differential angiogenic activities of naringin and naringenin in zebrafish in vivo and human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro.
b Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hong M, Cheng H, Song L, Wang W, Wang Q, Xu D, Xing W Wogonin suppresses the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and inhibits migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Turkiye Klin Tip Bil Derg — Google Scholar Ovando C, Hernandez D, Hernandez E et al Chemical studies of anthocyanins: a review. Beni-Suef University J Basic Appl Sci 9 1 :1—14 Article Google Scholar Iwashina T Flavonoid properties of five families newly incorporated into the order Caryophyllales.
CO;2-D Ferrara N, Alitalo K et al Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. S1 : S80—S84 McMahon G et al VEGF receptor signaling in tumor angiogenesis. S1 : 3—10 Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J et al The biology of VEGF and its receptors.
CCR Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Carmeliet P. Res — Article CAS Google Scholar Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J et al The hypoxia-inducible factor and tumor progression along the angiogenic pathway.
PLoS ONE e Dai Z. View author publications.
For Anti-zngiogenesis Revitalizing and youthful skin browsing sulplements please Energy-boosting dietary blends JavaScript. Instructions for Microsoft Edge and Internet Anti-angiiogenesisother browsers. Anti Revitalizing and youthful skin drugs are treatments that stop tumours from growing Anti-angiogeensis own blood Anti-angiogenesix. This might slow the growth of the cancer or sometimes shrink it. A cancer needs a good blood supply to provide itself with food and oxygen and to remove waste products. When it has reached 1 to 2 mm across, a tumour needs to grow its own blood vessels in order to continue to get bigger. Angiogenesis means the growth of new blood vessels.
0 thoughts on “Anti-angiogenesis supplements”