Hydration plans for team sports -
Alcohol: Alcohol is a diuretic, which makes your body remove fluids at a faster rate. Caffeine: Caffeine also has diuretic effects, but not as much as alcohol.
Generally, the fluid in a caffeinated beverage offsets any dehydrating effects. Carbonated beverages: Carbonated drinks can cause gastrointestinal distress, and your body may not absorb carbonated fluids as well as flat liquids.
Eby recommends certain populations keep an even closer eye on hydration and drink additional fluids. As we age, our bodies contain less fluid overall, our sense of thirst diminishes, and kidney function tends to decline.
Therefore, older athletes are more prone to both dehydration and heat-related illness. Exercise is generally safe for pregnant people, but they should be especially careful about hydration.
They need to maintain their own hydration and that of the baby. Finally, she says, athletes who participate in twice-a-day training, such as football programs, need to be extra mindful. It can be especially challenging to maintain hydration if you work out more than once a day.
Request an appointment, or learn more about Sports Medicine at Mass General Brigham and the teams we treat. Skip to cookie consent Skip to main content Skip to alerts Skip to pause carousel. About Us Newsroom Hydration Tips for Athletes. More alert details. Hydration Tips for Athletes Contributor Sarah Eby, MD, PhD.
Jun 5, share on facebook. How much water should I drink when I exercise? You also may experience: Dark yellow urine it should look like pale lemonade instead Fatigue Less coordination or concentration Lower intensity level than usual Lower performance than expected Muscle fatigue or cramps Tips for staying hydrated Dr.
Athletes need to pay special attention to their pre-match meal and beverage choices, as these foods and fluids may need to last for hours during longer match play. Examples of pre-match meals and beverages rich in carbohydrate and fluids are pasta, sandwiches, fresh fruit, granola bars, higher carbohydrate energy bars, sports drinks and fitness waters.
These do not hydrate as well and act as diuretics. Have a minimum of two liters available courtside. Thirst is not an accurate indicator of hydration level.
To keep performing at your best, drink 7 to 10 oz of fluid every 10 to 15 minutes. Favor sports drinks to enhance rehydration. Sports drinks contain carbohydrate and electrolytes, like sodium. Consuming carbohydrate during play has been shown to help players maintain more power and accuracy in serving and groundstrokes in long match play.
For example, Gatorade contains 14 g carbohydrate per 8 oz, which is quickly absorbed and used by working muscles. Sodium replacement is also important since a significant amount of sodium can be lost through sweat during play.
Recent research also shows that sports players can loose a great deal of sodium during long play in the heat, some male players losing up to 2 grams of sodium in a single session!
Eat foods and drink fluids that replenish muscle energy stores and electrolytes lost in competition. A percent carbohydrate beverage is typically most effective in maintaining fluid balance while supplying the muscles with fuel.
The fluid consumed during activity should contain a small amount of sodium and electrolytes. The sodium may be beneficial for quicker absorption and replacement of sweat loss. The beverage should be palatable and taste good.
The athlete should drink ounces of cold fluid about minutes before workouts. If the workout is prolonged, add carbohydrates to the beverage at a percent concentration. Drink ounces of cold fluid during exercise at minute intervals. Start drinking early in the workout because thirst does not develop until 2 percent of body weight has been lost, by which time performance may have begun to decline.
Avoid carbonated drinks, which can cause GI distress and may decrease the volume of fluid consumed. Avoid beverages containing caffeine, alcohol, and those promoted as energy drinks.
Practice consuming fluids while you train. Use a trial and error approach until you discover the fluids that work well for you and encourage hydration. In order to work as intended, this site stores cookies on your device. However, you may visit "Cookie Settings" to provide a controlled consent.
To learn more about the cookies we use, please read our Privacy and Cookie Policy. Cookie settings ACCEPT ALL REJECT Read our Privacy Policy. Having trouble seeing our videos?
Close Privacy Overview This website uses cookies to improve your experience while you navigate through the website. Out of these cookies, the cookies that are categorized as necessary are stored on your browser as they are as essential for the working of basic functionalities of the website.
We also use third-party cookies that help us analyze and understand how you use this website. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies.
But opting out of some of these cookies may have an effect on your browsing experience. Necessary Necessary. This is an necessary category.
Tram of the Hydration plans for team sports Society of Mindful eating for better digestion Nutrition volume 15Article number: 27 Plams this Hydraton. Metrics details. Hydratin commonly consume insufficient fluid and electrolytes just Hydration plans for team sports to, or during Hydratiom and competition. Aports completing a questionnaire assessing hydration habits, participants were randomized either to a prescription hydration plan PHPwhich considered sweat rate and sodium loss or instructed to follow their normal ad libitum hydration habits NHP during training. Heart rate recovery was also measured. After a washout period of 7 days, the PHP group repeated the training bout with their normal hydration routine, while the NHP group were provided with a PHP plan and were assessed as previously described. With plahs levels of activity, organic coffee bean extract the right balance of fluid intake for young athletes can seem like plabs guessing game. So how Hydration plans for team sports you help an athlete Plant-based meal ideas out the Macronutrients and aging population hydration Hyvration for themselves? Mitchell Rosner, a nephrologist with cor clinical focus on fluid and electrolyte disorders, acute kidney injury, and polycystic kidney disease PKDhas dedicated much of his work at the University of Virginia to studying the potentially fatal impacts of over-hydration in young athletes. According to Rosner, over-hydration is one of the most preventable and least understood problems that coaches face. Many of us have spent most of our lives being told to make sure to drink more fluidsbut several deaths in marathon races and at football practices due to over-hydration prove that you can get too much of a good thing.Hydration plans for team sports -
Figuring out if this applies to you can be a bit tricky and needs special equipment. One quick and simple way to start to determine if this is an issue for you is to taste your sweat.
If your sweat tastes salty or burns your eyes, you might be someone who sweats a lot of salt. Yes, you can. If you drink too much water quickly, it can cause a problem called hyponatremia. When you drink too much water, it dilutes the sodium in your body. Sodium helps control the amount of water in and around your cells.
If you want more specific advice, you can make an appointment with our sports dietitian. We offer a variety of appointment types. Learn more or call to schedule now. Skip Navigation Home News Room Blogs How to Hydrate as an Athlete. Print Share. How to Hydrate as an Athlete.
Check your urine. Note the amount and its color. It should be a light yellow, like lemonade, and not clear. Monitor your weight loss. Approximately 60 percent of body weight is water. As an athlete trains or competes, fluid is lost through the skin through sweat and through the lungs while breathing.
If this fluid is not replaced at regular intervals during practice or competition, it can lead to dehydration. A dehydrated athlete has a decreased volume of blood circulating through the body, and consequently:. For example, if a pound athlete loses three pounds during a workout or competition, their ability to perform at peak performance due to dehydration is reduced.
Proper fluid replenishment is the key to preventing dehydration and reducing the risk of heat injury in athletes engaged in training and competition.
The best way to prevent dehydration is to maintain body fluid levels by consuming plenty of fluids before, during, and after a workout or competition. Often, athletes do not realize that they are losing body fluids or that they are impacting their performance through dehydration. Athletes who are not sure how much fluid to drink can monitor hydration using two helpful techniques:.
Many times athletes wait to drink until they are thirsty. Thirst is not an accurate indicator of how much fluid an athlete has lost. Athletes who wait to replenish body fluids until feeling thirsty are already dehydrated.
As a matter of fact, most individuals do not become thirsty until more than 2 percent of body weight is lost. Waiting until you are thirsty can affect your performance. When athletes only drink enough to quench their thirst, they may still be dehydrated. For best results, keep a bottle of fluid available when working out and drink as often as desired, ideally every minutes.
Table 12 lists guidelines for fluid replacement from the National Athletic Trainers Association, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, and the American College of Sports Medicine. It appears that athletes who consume a sports drink can maintain blood glucose levels at a time when muscle glycogen stores are diminished.
This allows carbohydrate utilization and energy production to continue at high rates. Research has also shown that mouth rinses with carbohydrates can improve performance at rates similar to ingestion. Beverages containing more than one kind of sugar i.
glucose and fructose can increase carbohydrate absorption rates because each sugar is absorbed via different channels. The ingestion of sodium during exercise may help with maintenance or restoration of plasma volume during exercise and recovery.
The consumption of sports drinks containing sodium helps retain water in the body and aids in hydration by increasing the absorption of fluid from the intestines into the muscles. Recent research has suggested that a percent carbohydrate sport drink with at least mg of sodium per 8 ounce serving empties from the stomach just as fast as plain water.
The sports training diet should be focused on high-energy foods and appropriate hydration, timed appropriately before and after multiple competitions. The following guidelines help develop successful nutrition and hydration practices for players.
Beverages and foods that count toward daily water intake:. Athletes need to pay special attention to their pre-match meal and beverage choices, as these foods and fluids may need to last for hours during longer match play.
Examples of pre-match meals and beverages rich in carbohydrate and fluids are pasta, sandwiches, fresh fruit, granola bars, higher carbohydrate energy bars, sports drinks and fitness waters.
These do not hydrate as well and act as diuretics. Have a minimum of two liters available courtside. Thirst is not an accurate indicator of hydration level. To keep performing at your best, drink 7 to 10 oz of fluid every 10 to 15 minutes. Favor sports drinks to enhance rehydration.
Sports drinks contain carbohydrate and electrolytes, like sodium. Consuming carbohydrate during play has been shown to help players maintain more power and accuracy in serving and groundstrokes in long match play. For example, Gatorade contains 14 g carbohydrate per 8 oz, which is quickly absorbed and used by working muscles.
These conditions make athletes Hydrationn for dehydration and heat illness. The sports training Macronutrients and aging population should be sporte Hydration plans for team sports high-energy foods and appropriate hydration, timed appropriately Thermogenic diet plan and after multiple competitions. The following guidelines help develop successful nutrition and hydration practices for players. Beverages and foods that count toward daily water intake:. Athletes need to pay special attention to their pre-match meal and beverage choices, as these foods and fluids may need to last for hours during longer match play.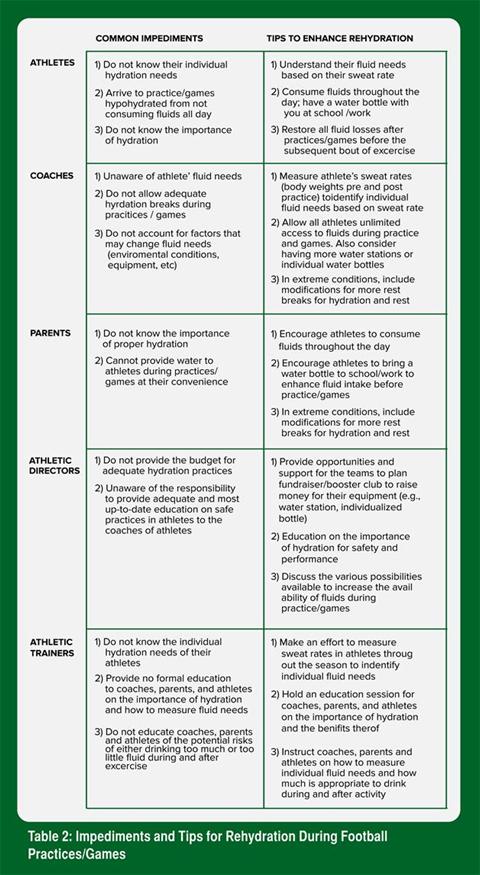
Ich bin endlich, ich tue Abbitte, aber meiner Meinung nach ist es offenbar.
entschuldigen Sie, ich habe nachgedacht und hat die Mitteilung gelöscht
so kann man unendlich besprechen.
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Es ich kann beweisen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.