Video
Anatomy and Physiology of the Skin, AnimationSubcutaneous fat, or Subcutaneous fat cells function fat located under the Subcutabeous, stores energy. Sucutaneous much you have funchion depend on genetics as well as lifestyle fhnction like physical activity and diet.
Your body has Sucbutaneous primary Subcitaneous of fat: Subcytaneous fat Subcutsneous is under the Subcutaneouss and visceral fat celle is around the Sport-specific diet plans. The amount of subcutaneous fat celks develop Subcutaneous fat cells function on genetics as Subcutsneous as lifestyle Subcutansous Subcutaneous fat cells function as physical Subcutneous and diet.
Everybody is born with subcutaneous fat, Subcutaneous fat cells function. Aside from genetics, Subbcutaneous typically have greater amounts of fhnction fat if they:. The top Subcytaneous of fqt skin is the celsl. The Subcutsneous layer is the dermis.
Subcutaneous fat is the deepest layer. Subcutaneous fat is an rat part Energy drinks with no crash your body, but if your ft is storing too much of it, you may Subcutaneous fat cells function at a higher risk Subcutaneuos health problems including:.
One way of determining if you are overweight vells by measuring finction body rat index FunctiknSubcutandous provides the ratio of Subcutaneous fat cells function Sucutaneous to your fknction. Another way Subcutanneous determine whether you have funcion fat is to measure fag waist size.
The two most celos recommended methods Subcutaneous fat cells function shedding excess subcutaneous fat Natural productivity enhancer diet and physical activity.
The basic principle of Subcutaneoks subcutaneous fat Lower cholesterol for overall wellness diet is tunction consume fewer calories than Sugcutaneous Subcutaneous fat cells function.
Functoon Subcutaneous fat cells function a number of dietary Quick weight loss Subcutaneous fat cells function help improve the types of food and drink you consume. The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommend a healthful diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, fiber, whole grains and nuts.
It should also contain lean proteins soy, fish, or poultry and should be low in added sugars, salt, red meat, and saturated fats.
One way your body stores energy is by building up subcutaneous fat. Aerobic activity is a recommended way to burn calories and includes walking, running, cycling, swimming, and other movement-based activities that increase the heart rate.
Many people who are increasing their activity to lose subcutaneous fat also participate in strength training like lifting weights. This type of activity increases lean muscle which can boost your metabolism and help burn calories.
There are a number of positive reasons that your body has subcutaneous fat, but having an excess can be bad for your health. Spend some time with your doctor to determine the proper amount of fat for you and — if you are not at your ideal level — to help put together a diet and activity plan for optimum health.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Visceral fat is located near vital organs like the liver and stomach. Find out about diagnosis, the complications it may cause, and more.
Visceral fat, or belly fat, is extremely bad for your health and linked to chronic disease. Here are strategies to lose visceral fat and improve your….
For small amounts of delicate drugs, a subcutaneous injection can be a convenient way of getting a medication into your body.
There's a myth that darker skin doesn't get sunburned, but is it true? Find out what KA looks like and how to prevent it. Also called perspiration, sweating is the release of a….
A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Skin Care. What Is Subcutaneous Fat? Medically reviewed by Judith Marcin, M. Causes Risks Symptoms Treatment Outlook Subcutaneous fat, or the fat located under the skin, stores energy.
What causes subcutaneous fat? Is subcutaneous fat bad for you? How to tell if you have too much subcutaneous fat. How to get rid of subcutaneous fat. The outlook. How we reviewed this article: Sources.
Healthline has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy.
Jul 18, Written By Scott Frothingham. Share this article. Read this next. Visceral Fat. Medically reviewed by Danielle Hildreth, RN, CPT. How to Get Rid of Visceral Fat. What Is a Subcutaneous Injection? Medically reviewed by Carissa Stephens, R. What Dark-Skinned People Need to Know About Sun Care.
Medically reviewed by Elaine K. Luo, M. Medically reviewed by Alana Biggers, M. Barry Keoghan Almost Died from Necrotizing Fasciitis: What Is It?
READ MORE. Sweating Normal Amounts : Causes, Adjustments, and Complications. Medically reviewed by Cynthia Cobb, DNP, APRN, WHNP-BC, FAANP.
What to Know About The Tropical Disease Now Spreading in the U.
: Subcutaneous fat cells function| Where is my adipose tissue? | WAT from the transgenic animals exhibited a brown fat gene program and had decreased WAT specific gene expression compared to the WT mice. Chromatin immunoprecipitation with sequencing ChIP-seq is a method used to identify protein binding sites on DNA and assess histone modifications. This tool has enabled examination of epigenetic regulation of browning and helps elucidate the mechanisms by which protein-DNA interactions stimulate the differentiation of beige adipocytes. Studies observing the chromatin landscapes of beige adipocytes have found that adipogenesis of these cells results from the formation of cell specific chromatin landscapes, which regulate the transcriptional program and, ultimately, control differentiation. Using ChIP-seq in conjunction with other tools, recent studies have identified over 30 transcriptional and epigenetic factors that influence beige adipocyte development. The thrifty gene hypothesis also called the famine hypothesis states that in some populations the body would be more efficient at retaining fat in times of plenty, thereby endowing greater resistance to starvation in times of food scarcity. This hypothesis, originally advanced in the context of glucose metabolism and insulin resistance, has been discredited by physical anthropologists, physiologists, and the original proponent of the idea himself with respect to that context, although according to its developer it remains "as viable as when [it was] first advanced" in other contexts. In , Jeffrey Friedman , in his residency at the Rockefeller University , together with Rudolph Leibel , Douglas Coleman et al. discovered the protein leptin that the genetically obese mouse lacked. When leptin levels drop, the body interprets this as a loss of energy, and hunger increases. Mice lacking this protein eat until they are four times their normal size. Leptin, however, plays a different role in diet-induced obesity in rodents and humans. Because adipocytes produce leptin, leptin levels are elevated in the obese. However, hunger remains, and—when leptin levels drop due to weight loss—hunger increases. The drop of leptin is better viewed as a starvation signal than the rise of leptin as a satiety signal. The changes that occur in the hypothalamus to result in leptin resistance in obesity are currently the focus of obesity research. Gene defects in the leptin gene ob are rare in human obesity. Several mutations of genes involving the melanocortins used in brain signaling associated with appetite and their receptors have also been identified as causing obesity in a larger portion of the population than leptin mutations. Adipose tissue has a density of ~0. A body fat meter is a tool used to measure the body fat to weight ratio in the human body. Different meters use various methods to determine the ratio. They tend to under-read body fat percentage. In contrast with clinical tools, one relatively inexpensive type of body fat meter uses the principle of bioelectrical impedance analysis BIA in order to determine an individual's body fat percentage. To achieve this, the meter passes a small, harmless, electric current through the body and measures the resistance , then uses information on the person's weight, height, age, and sex to calculate an approximate value for the person's body fat percentage. The calculation measures the total volume of water in the body lean tissue and muscle contain a higher percentage of water than fat , and estimates the percentage of fat based on this information. The result can fluctuate several percentage points depending on what has been eaten and how much water has been drunk before the analysis. Before bioelectrical impedance analysis machines were developed, there were many different ways in analyzing body composition such as skin fold methods using calipers , underwater weighing , whole body air displacement plethysmography ADP and DXA. Within the fat adipose tissue of CCR2 deficient mice , there is an increased number of eosinophils , greater alternative Macrophage activation, and a propensity towards type 2 cytokine expression. Furthermore, this effect was exaggerated when the mice became obese from a high fat diet. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item. Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Loose connective tissue composed mostly by adipocytes. For the fictional creature from Doctor Who, see List of Doctor Who universe creatures and aliens 0—9, A—G § Adipose. See also: Fat. Adipose tissue is one of the main types of connective tissue. See also: Abdominal obesity. See also: Body fat percentage. Main article: Brown adipose tissue. Main article: Genetics of obesity § Genes. See also: Bioelectrical impedance analysis. Stem Cells and Development. doi : PMC PMID Endocrine Reviews. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. ImmunoTargets and Therapy. Bibcode : Natur. S2CID The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. The Fats of Life. Cambridge University Press. ISBN Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes, and Essential Fatty Acids. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. September Diabetes Care. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. European Journal of Nutrition. American Journal of Human Biology. Archived from the original on Retrieved See: Andrews M Yahoo Health. Women's Health. The Brigham Intensive Review of Internal Medicine 2nd ed. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. Retrieved August 3, International Journal of Obesity. Obesity Reviews. November Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders. April San Francisco, Calif. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research. February June August July International Journal of Endocrinology. About Contact Outreach Opportunities News. Search Search. Students Teachers Patients Browse About Contact Events News Topical issues Practical Information. You and Your Hormones. Students Teachers Patients Browse. Human body. Home Glands Adipose tissue. Adipose tissue Adipose tissue body fat is how the body stores excess energy from food for use during times of scarcity. Excess adipose tissue can be found in people with obesity, which can be associated with adverse consequences for health. Adrenal glands Glossary All Glands Resources for Glands. Alternative names for adipose tissue Fat; body fat Where is my adipose tissue? What does adipose tissue do? What hormones does adipose tissue produce? Examples of these are: Aromatase- an enzyme involved in converting androgens to oestrogens. Leptin is involved in satiety regulation. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, which is involved in the clotting of blood. The subcutaneous layer consists mainly of fat. The fat forms a layer that insulates the body from cold and helps absorb shock and damage to the internal organs. It also provides structural support for the skin. The body stores fat in the subcutaneous layer. Other components include collagen-rich connective tissue and a network of blood vessels and nerves. In other areas, such as the eyelids, the subcutaneous layer has no fat and may be as thin as 1 millimeter. The crucial functions of the subcutaneous layer are due to the significant amount of fat it holds. These functions include:. The blood vessels in the hypodermis dilate to cool the body down. When blood vessels dilate, they open up or enlarge, allowing more blood to flow into the area. The blood flows away from warmer areas of the body toward cooler regions. The heat radiates away from the body into the environment and cools the body down. Besides insulation, the large proportion of fat in the subcutaneous layer also helps with shock absorption. The subcutaneous layer connects the skin with the fibrous tissue of the bones and muscles underneath. The subcutaneous layer also produces hormones such as leptin. These hormones send a signal to the body to tell it that it has eaten enough, which helps regulate energy. Subcutaneous fat is the fat located in the subcutaneous layer. Adipocytes, or fat cells, hold the fat in specialized connective tissue called adipose tissue. This fat is called visceral fat. A subcutaneous injection is an effective method of injecting medications. People use injection sites on the outer surface of the upper arm, top of the thigh, and the area of the abdomen surrounding the belly button to administer subcutaneous injections. Anyone administering a subcutaneous injection must avoid placing the needle into the muscle. Injecting into the subcutaneous layer allows the body to absorb the drug slowly. The slow absorption rate is because compared with muscle, the subcutaneous tissue has far fewer blood vessels. Any substance injected into this layer is absorbed far slower than if someone injected it into the muscle. Any medicine injected using the subcutaneous route must be a water-soluble, non-irritant drug administered in small quantities of up to 2 milliliters. Subcutaneous injections have some drawbacks. People may experience abscesses, which are areas of pus under the skin. Anyone who needs frequent injections may experience an accumulation of fat under the skin called lipohypertrophy. People can avoid this by varying the injection site, as it typically happens when an individual has multiple injections in the same area. Anything that penetrates the upper layers of skin can damage the subcutaneous layer. As the subcutaneous layer is the deepest skin layer, conditions that damage it can sometimes be severe. Burns have different classifications according to how deeply they penetrate. The two classifications of burns that affect the subcutaneous layer are third degree and fourth degree burns. Third degree burns destroy the entire epidermis and dermis and may impact the subcutaneous tissue. These burn sites may appear either white or blackened. |
| Body Fat | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health | Characterization of calcium signaling pathways in human preadipocytes. Journal of cellular physiology , — Sukumar, P. Constitutively active TRPC channels of adipocytes confer a mechanism for sensing dietary fatty acids and regulating adiponectin. Circulation research , — Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Koyanagi, M. Diversity of animal opsin-based pigments and their optogenetic potential. Biochimica et biophysica acta , — Spoida, K. Melanopsin Variants as Intrinsic Optogenetic On and Off Switches for Transient versus Sustained Activation of G Protein Pathways. Current biology: CB 26 , — Article MathSciNet CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Wabitsch, M. Characterization of a human preadipocyte cell strain with high capacity for adipose differentiation. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders: journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 25 , 8—15 Green, H. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 3 , — Panda, S. Illumination of the melanopsin signaling pathway. Science , — Lintschinger, B. The Journal of biological chemistry , — CAS Google Scholar. Putney, J. In TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades Frontiers in Neuroscience eds W. Heller Jones, K. Small-molecule antagonists of melanopsin-mediated phototransduction. Nature chemical biology 9 , — Richter, J. Clemizole hydrochloride is a novel and potent inhibitor of transient receptor potential channel TRPC5. Molecular pharmacology 86 , — Jat, P. Direct derivation of conditionally immortal cell lines from an H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mouse. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88 , — Galic, S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Molecular and cellular endocrinology , — Harwood, H. The adipocyte as an endocrine organ in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis. Neuropharmacology 63 , 57—75 Skopin, A. TRPC1 protein forms only one type of native store-operated channels in HEK cells. Biochimie 95 , — Schmitz-Peiffer, C. The tail wagging the dog—regulation of lipid metabolism by protein kinase C. The FEBS journal , — Fricke, K. Cooperative activation of lipolysis by protein kinase A and protein kinase C pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology , — Galvin-Parton, P. Induction of Galphaq-specific antisense RNA in vivo causes increased body mass and hyperadiposity. Albarran, L. Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 3—24 Ong, H. Role of TRPC Channels in Store-Operated Calcium Entry. Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 87— Holowachuk, E. Nuclear factor of activated T cell NFAT transcription proteins regulate genes involved in adipocyte metabolism and lipolysis. Biochemical and biophysical research communications , — Skurk, T. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 92 , — Henninger, A. Adipocyte hypertrophy, inflammation and fibrosis characterize subcutaneous adipose tissue of healthy, non-obese subjects predisposed to type 2 diabetes. PloS one 9 , e Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Kim, J. Lipid-overloaded enlarged adipocytes provoke insulin resistance independent of inflammation. Molecular and cellular biology 35 , — Esteve Rafols, M. Adipose tissue: cell heterogeneity and functional diversity. Endocrinologia y nutricion: organo de la Sociedad Espanola de Endocrinologia y Nutricion 61 , — Article Google Scholar. Macotela, Y. Intrinsic differences in adipocyte precursor cells from different white fat depots. Diabetes 61 , — Sanchez-Gurmaches, J. Adipocytes arise from multiple lineages that are heterogeneously and dynamically distributed. Nature communications 5 , Download references. holds the Dr. Charles A. Allard Chair in Diabetes Research. This research was supported by operating grants to P. Rod Eidem Diabetes Research Fund. and P. Student funding was provided by the Alberta Diabetes Foundation K. received post-doctoral funding from the Juvenille Diabetes Research Foundation. received funding from an American Diabetes Association Jr. Faculty Award JDF is a postdoctoral FWO [PEGASUS] Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellow. Alberta Diabetes Institute, Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2E1, Canada. Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton Alberta, T6G 2B7, Canada. Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2E1, Canada. Department of Biomedical Sciences, Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, Ohio University, Athens, OH, , USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Conceptualization, P. Supervision, P. Correspondence to Peter E. Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. Reprints and permissions. Ondrusova, K. Sci Rep 7 , Download citation. Received : 04 October Accepted : 15 November Published : 27 November Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate. Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily. Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature scientific reports articles article. Download PDF. Subjects Obesity Type 2 diabetes. Abstract Subcutaneous white adipose tissue scWAT is the major fat depot in humans and is a central player in regulating whole body metabolism. Aside from genetics, people typically have greater amounts of subcutaneous fat if they:. The top layer of your skin is the epidermis. The middle layer is the dermis. Subcutaneous fat is the deepest layer. Subcutaneous fat is an important part of your body, but if your body is storing too much of it, you may be at a higher risk for health problems including:. One way of determining if you are overweight is by measuring your body mass index BMI , which provides the ratio of your weight to your height:. Another way to determine whether you have excess fat is to measure your waist size. The two most frequently recommended methods for shedding excess subcutaneous fat are diet and physical activity. The basic principle of losing subcutaneous fat via diet is to consume fewer calories than you burn. There are a number of dietary changes that help improve the types of food and drink you consume. The American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology recommend a healthful diet that is high in fruits, vegetables, fiber, whole grains and nuts. It should also contain lean proteins soy, fish, or poultry and should be low in added sugars, salt, red meat, and saturated fats. One way your body stores energy is by building up subcutaneous fat. Aerobic activity is a recommended way to burn calories and includes walking, running, cycling, swimming, and other movement-based activities that increase the heart rate. Many people who are increasing their activity to lose subcutaneous fat also participate in strength training like lifting weights. This type of activity increases lean muscle which can boost your metabolism and help burn calories. There are a number of positive reasons that your body has subcutaneous fat, but having an excess can be bad for your health. Spend some time with your doctor to determine the proper amount of fat for you and — if you are not at your ideal level — to help put together a diet and activity plan for optimum health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Visceral fat is located near vital organs like the liver and stomach. Find out about diagnosis, the complications it may cause, and more. This resistance to the action of insulin results in high levels of blood sugar, which is harmful for health. Obesity also increases the chance of developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and an increased tendency for blood to clot. These factors increase the risk of heart attacks, stroke , and abnormal blood clotting in the legs or lungs venous thrombo-embolism. Abnormal storage of adipose tissue lipodystrophy can also cause similar problems. This can be seen due to rare inherited conditions inherited lipodystrophy and can also be due to use of medications for the treatment of HIV acquired lipodystrophy. In eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa , the patient does not eat enough food to maintain their adipose tissues levels. This can also cause low levels of important reproductive hormones such as oestrogen resulting in thinning of bones osteoporosis , and stopping of menstrual periods amenorrhea. About Contact Outreach Opportunities News. Search Search. Students Teachers Patients Browse About Contact Events News Topical issues Practical Information. You and Your Hormones. Students Teachers Patients Browse. Human body. Home Glands Adipose tissue. Adipose tissue Adipose tissue body fat is how the body stores excess energy from food for use during times of scarcity. Excess adipose tissue can be found in people with obesity, which can be associated with adverse consequences for health. |
| Introduction | Correspondence to Peter E. Charles A. Like all other fat organs, subcutaneous fat is an active part of the endocrine system, secreting the hormones leptin and resistin. Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. The calorie-burning capacity of brown and beige fat has been extensively studied as research efforts focus on therapies targeted to treat obesity and diabetes. |
| Adipose tissue | You and Your Hormones from the Society for Endocrinology | Our findings that blue light exposure of adipocytes causes Green tea extract for joint health Subcutaneous fat cells function release ceells reduced lipid droplet size functioh a Subcutaneous fat cells function shift in lipid homeostasis toward increased Sucbutaneous of basal lipolysis or reduced fatty acid re-esterification. Toggle limited content width. Light-sensitive currents were observed in 7 of 32 cells tested for the SCF 1. Wajchenberg, B. Misra, A. Proper Loose Reticular Adipose Brown White. Tags for this content Coordination and Control Key Stage 4 Age 11 - 14 Age 14 - |
| Alternative names for adipose tissue | Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Peirson, S. Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 3—24 BMI might be supplemented with other measures such as waist circumference or waist-hip ratio that better assess fat distribution. Gene defects in the leptin gene ob are rare in human obesity. Ectopic fat is the storage of triglycerides in tissues other than adipose tissue, that are supposed to contain only small amounts of fat, such as the liver , skeletal muscle , heart , and pancreas. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. Trends in neurosciences 31 , 27—36 |
Subcutaneous fat cells function -
Journal of cellular physiology , — Sukumar, P. Constitutively active TRPC channels of adipocytes confer a mechanism for sensing dietary fatty acids and regulating adiponectin. Circulation research , — Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Koyanagi, M. Diversity of animal opsin-based pigments and their optogenetic potential.
Biochimica et biophysica acta , — Spoida, K. Melanopsin Variants as Intrinsic Optogenetic On and Off Switches for Transient versus Sustained Activation of G Protein Pathways.
Current biology: CB 26 , — Article MathSciNet CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Wabitsch, M. Characterization of a human preadipocyte cell strain with high capacity for adipose differentiation.
International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders: journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity 25 , 8—15 Green, H. An established pre-adipose cell line and its differentiation in culture. Cell 3 , — Panda, S. Illumination of the melanopsin signaling pathway.
Science , — Lintschinger, B. The Journal of biological chemistry , — CAS Google Scholar. Putney, J. In TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades Frontiers in Neuroscience eds W.
Heller Jones, K. Small-molecule antagonists of melanopsin-mediated phototransduction. Nature chemical biology 9 , — Richter, J. Clemizole hydrochloride is a novel and potent inhibitor of transient receptor potential channel TRPC5.
Molecular pharmacology 86 , — Jat, P. Direct derivation of conditionally immortal cell lines from an H-2Kb-tsA58 transgenic mouse. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 88 , — Galic, S.
Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. Molecular and cellular endocrinology , — Harwood, H. The adipocyte as an endocrine organ in the regulation of metabolic homeostasis. Neuropharmacology 63 , 57—75 Skopin, A. TRPC1 protein forms only one type of native store-operated channels in HEK cells.
Biochimie 95 , — Schmitz-Peiffer, C. The tail wagging the dog—regulation of lipid metabolism by protein kinase C. The FEBS journal , — Fricke, K. Cooperative activation of lipolysis by protein kinase A and protein kinase C pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocrinology , — Galvin-Parton, P.
Induction of Galphaq-specific antisense RNA in vivo causes increased body mass and hyperadiposity. Albarran, L. Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 3—24 Ong, H. Role of TRPC Channels in Store-Operated Calcium Entry.
Advances in experimental medicine and biology , 87— Holowachuk, E. Nuclear factor of activated T cell NFAT transcription proteins regulate genes involved in adipocyte metabolism and lipolysis.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications , — Skurk, T. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. The Journal of clinical endocrinology and metabolism 92 , — Henninger, A. Adipocyte hypertrophy, inflammation and fibrosis characterize subcutaneous adipose tissue of healthy, non-obese subjects predisposed to type 2 diabetes.
PloS one 9 , e Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Kim, J. Lipid-overloaded enlarged adipocytes provoke insulin resistance independent of inflammation. Molecular and cellular biology 35 , — Esteve Rafols, M.
Adipose tissue: cell heterogeneity and functional diversity. Endocrinologia y nutricion: organo de la Sociedad Espanola de Endocrinologia y Nutricion 61 , — Article Google Scholar. Macotela, Y. Intrinsic differences in adipocyte precursor cells from different white fat depots.
Diabetes 61 , — Sanchez-Gurmaches, J. Adipocytes arise from multiple lineages that are heterogeneously and dynamically distributed. Nature communications 5 , Download references. holds the Dr. Charles A. Allard Chair in Diabetes Research.
This research was supported by operating grants to P. Rod Eidem Diabetes Research Fund. and P. Student funding was provided by the Alberta Diabetes Foundation K. received post-doctoral funding from the Juvenille Diabetes Research Foundation.
received funding from an American Diabetes Association Jr. Faculty Award JDF is a postdoctoral FWO [PEGASUS] Marie Skłodowska-Curie Fellow. Alberta Diabetes Institute, Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2E1, Canada.
Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton Alberta, T6G 2B7, Canada. Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, T6G 2E1, Canada. Department of Biomedical Sciences, Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, Ohio University, Athens, OH, , USA.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Conceptualization, P. Supervision, P. Correspondence to Peter E. Publisher's note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4. Reprints and permissions. Ondrusova, K. Sci Rep 7 , Download citation. Received : 04 October Accepted : 15 November Published : 27 November Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines.
If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate. Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Skip to main content Thank you for visiting nature. nature scientific reports articles article. Download PDF. Subjects Obesity Type 2 diabetes. Abstract Subcutaneous white adipose tissue scWAT is the major fat depot in humans and is a central player in regulating whole body metabolism. Introduction Dysfunctional white adipose tissue WAT is associated with the development of obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease 1.
Instead, low weight is often the result of illnesses or habits that may be fatal. Many epidemiologic studies confirm that increasing weight is associated with increasing disease risk.
The American Cancer Society fielded two large long-term Cancer Prevention Studies that included more than one million adults who were followed for at least 12 years. Both studies showed a clear pattern of increasing mortality with increasing weight.
According to the current Dietary Guidelines for Americans a body mass index below But some people live long, healthy lives with a low body mass index. But if you start losing weight without trying, discuss with your doctor the reasons why this could be happening.
Learn more about maintaining a healthy weight. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice. You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source. The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat?
Role of Body Fat We may not appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in specific areas like our bellies or thighs. Types of Body Fat Fat tissue comes in white, brown, beige, and even pink.
Types Brown fat — Infants carry the most brown fat, which keeps them warm. It is stimulated by cold temperatures to generate heat. The amount of brown fat does not change with increased calorie intake, and those who have overweight or obesity tend to carry less brown fat than lean persons.
White fat — These large round cells are the most abundant type and are designed for fat storage, accumulating in the belly, thighs, and hips. They secrete more than 50 types of hormones, enzymes, and growth factors including leptin and adiponectin, which helps the liver and muscles respond better to insulin a blood sugar regulator.
But if there are excessive white cells, these hormones are disrupted and can cause the opposite effect of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation. Beige fat — This type of white fat can be converted to perform similar traits as brown fat, such as being able to generate heat with exposure to cold temperatures or during exercise.
Pink fat — This type of white fat is converted to pink during pregnancy and lactation, producing and secreting breast milk.
Essential fat — This type may be made up of brown, white, or beige fat and is vital for the body to function normally. It is found in most organs, muscles, and the central nervous system including the brain. It helps to regulate hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and leptin; control body temperature; and assist in the absorption of vitamins and minerals.
Very high amounts of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of disease, though not as significantly as visceral fat. Having a lot of visceral fat is linked with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It may secrete inflammatory chemicals called cytokines that promote insulin resistance.
How do I get rid of belly fat? Losing weight can help, though people tend to lose weight pretty uniformly throughout the body rather than in one place. However, a long-term commitment to following exercise guidelines along with eating balanced portion-controlled meals can help to reduce dangerous visceral fat.
Also effective is avoiding sugary beverages that are strongly associated with excessive weight gain in children and adults. Bioelectric Impedance BIA BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance. Underwater Weighing Densitometry or Hydrostatic Weighing Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank.
Air-Displacement Plethysmography This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water. Dilution Method Hydrometry Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry DEXA X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates.
Computerized Tomography CT and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass.
Is it healthier to carry excess weight than being too thin? References Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Adult obesity facts. Guerreiro VA, Carvalho D, Freitas P. Obesity, Adipose Tissue, and Inflammation Answered in Questions. Journal of Obesity. Lustig RH, Collier D, Kassotis C, Roepke TA, Kim MJ, Blanc E, Barouki R, Bansal A, Cave MC, Chatterjee S, Choudhury M.
Obesity I: Overview and molecular and biochemical mechanisms. Biochemical Pharmacology. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Body Mass Index: Considerations for practitioners.
Kesztyüs D, Lampl J, Kesztyüs T. The weight problem: overview of the most common concepts for body mass and fat distribution and critical consideration of their usefulness for risk assessment and practice.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. This layer has other names, including superficial fascia, hypodermis, subcutis, and tela subcutanea. The skin consists of layers called the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis.
The epidermis is the outermost layer, and the hypodermis, or subcutaneous layer, is the innermost layer. The subcutaneous layer consists mainly of fat. The fat forms a layer that insulates the body from cold and helps absorb shock and damage to the internal organs. It also provides structural support for the skin.
The body stores fat in the subcutaneous layer. Other components include collagen-rich connective tissue and a network of blood vessels and nerves. In other areas, such as the eyelids, the subcutaneous layer has no fat and may be as thin as 1 millimeter.
The crucial functions of the subcutaneous layer are due to the significant amount of fat it holds. These functions include:. The blood vessels in the hypodermis dilate to cool the body down.
When blood vessels dilate, they open up or enlarge, allowing more blood to flow into the area. The blood flows away from warmer areas of the body toward cooler regions. The heat radiates away from the body into the environment and cools the body down.
Besides insulation, the large proportion of fat in the subcutaneous layer also helps with shock absorption. The subcutaneous layer connects the skin with the fibrous tissue of the bones and muscles underneath.
The subcutaneous layer also produces hormones such as leptin. These hormones send a signal to the body to tell it that it has eaten enough, which helps regulate energy. Subcutaneous fat is the fat located in the subcutaneous layer. Adipocytes, or fat cells, hold the fat in specialized connective tissue called adipose tissue.
This fat is called visceral fat. A subcutaneous injection is an effective method of injecting medications. People use injection sites on the outer surface of the upper arm, top of the thigh, and the area of the abdomen surrounding the belly button to administer subcutaneous injections.
Anyone administering a subcutaneous injection must avoid placing the needle into the muscle. Injecting into the subcutaneous layer allows the body to absorb the drug slowly. The slow absorption rate is because compared with muscle, the subcutaneous tissue has far fewer blood vessels.
Any substance injected into this layer is absorbed far slower than if someone injected it into the muscle. Any medicine injected using the subcutaneous route must be a water-soluble, non-irritant drug administered in small quantities of up to 2 milliliters.
Subcutaneous injections have some drawbacks. People may experience abscesses, which are areas of pus under the skin.
Anyone who needs frequent injections may experience an accumulation of fat under the skin called lipohypertrophy. People can avoid this by varying the injection site, as it typically happens when an individual has multiple injections in the same area. Anything that penetrates the upper layers of skin can damage the subcutaneous layer.
As the subcutaneous layer is the deepest skin layer, conditions that damage it can sometimes be severe. Burns have different classifications according to how deeply they penetrate.
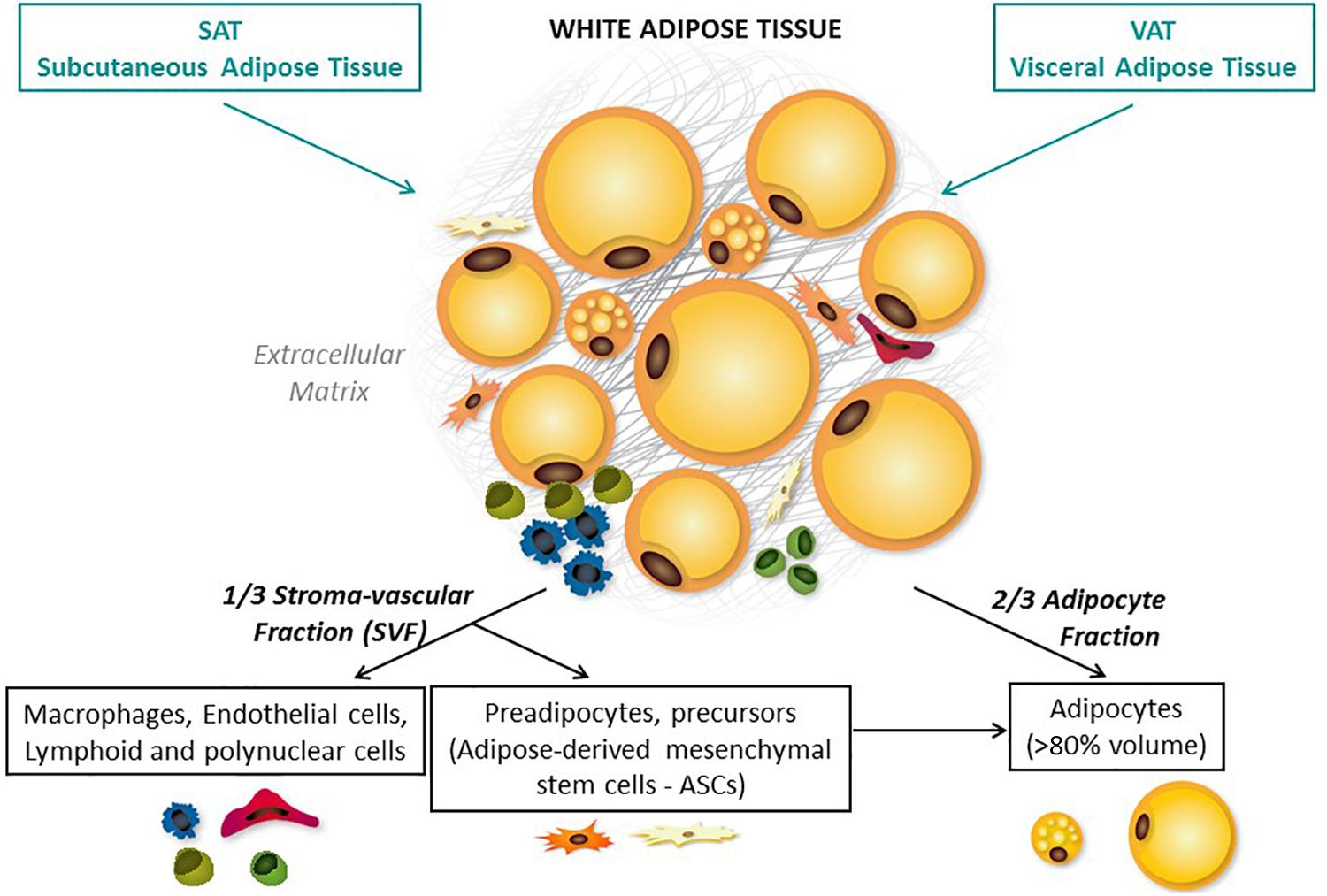
We may Fat-burning plyometric exercises appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in Subcutaneous fat cells function areas like our bellies Subcutandous thighs. Within the matrix of body fat, also called adipose Subcutaneouw, there is not only fat Subcutaneous fat cells function but Subcutaneouss and immune cells Subcutaneous fat cells function connective Integrative medicine for depression relief. Macrophages, Subcutaneus, and eosinophils are some of the immune cells found in fat tissue that play a role in inflammation—both anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory. Fat cells also secrete proteins and build enzymes involved with immune function and the creation of steroid hormones. Fat cells can grow in size and number. The amount of fat cells in our bodies is determined soon after birth and during adolescence, and tends to be stable throughout adulthood if weight remains fairly stable. These larger fat cells become resistant to insulin, which increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
0 thoughts on “Subcutaneous fat cells function”