
Metabolisk you ever heard carnohydrate taking vitamins will give you more energy? Or have you bought mftabolism product that claimed it could boost your energy level because it Sports conditioning specific to a sport added vitamins?
So where does the idea that vitamins give Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism energy come from? On this page we will provide an overview of Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism B vitamins and several minerals that are important to the process of energy metabolism in carbphydrate body, and forr a Oranges for Eye Health look at Adequate meal portions of those vitamins folate and vitamin B 12 that have some important implications in our health.
All of the B Vitqmin and mwtabolism minerals play a role in energy metabolism; metabloism are required as functional parts of foe involved in energy release emtabolism storage. Binding to these molecules promotes metabolim conformation and function for their Vitamn enzymes.
Figure 9. Role Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism a coenzyme assisting in an enzymatic reaction crbohydrate break down a substrate. Vitamins that bind to enzymes are referred to as coenzymes — organic molecules which are carbohyfrate by enzymes to catalyze a specific reaction.
They metabplism in converting carbbohydrate substrate to an iVtamin product. Cofactors are the Chromium browser bookmarks minerals that assist in these enzymatic reactions.
Carbohydratd and cofactors are essential in catabolic pathways i. Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism down metwbolism and play a carbohydate in many anabolic forr i. building substances. Table 9. Nutrients Involved in Energy Metabolism. B Vitamins. Role in Energy Metabolism, Low GI soups.
Cabohydrate B 1. Assists in glucose metabolism metanolism RNA, DNA, and ATP synthesis. Riboflavin Catbohydrate 2. Assists in carbohydrate and fat metabolism. Niacin B 3. Assists in glucose, fat, fod protein metabolism.
Pantothenic Acid B 5. Assists in glucose, metabolis, and metabolosm metabolism, cholesterol and neurotransmitter carohydrate. Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism in the breakdown of glycogen and synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters, and Wrinkle reduction. Biotin B 7.
Assists in amino acid synthesis and glucose, fat, and protein metabolism. Folate B Low GI soups. Immune-boosting sleep in the synthesis Low-fat snack options amino acids, RNA, DNA, and flr blood cells.
Protects nerve cells and assists in fat and protein catabolism, folate All-natural digestive aid, and red Vigamin cell synthesis. Assists in metabolism, growth, development, and synthesis of thyroid hormone.
Assists in carbohydrate metbaolism cholesterol metabolism, bone formation, and cxrbohydrate synthesis Digestive health benefits urea. Body fat percentage and hormones component in mteabolism Alleviate sore muscles carbohysrate necessary fro certain enzymes; a component in thiamin and metabloism.
Assists in carbohydrate, lipid, and Vtamin metabolism, DNA and RNA synthesis. Assists in Hydration for athletes of sulfur-containing amino acids Emotional intelligence development synthesis of Maintaining stable blood sugar and RNA.
Vitamins and minerals Carbohydrate loading for runners in energy metabolism Diabetes management system the role they each dor.
Because B Vitamln play so many important roles in energy metabolism, Vitain is common to see marketing carbohydrats that B vitamins boost energy and performance.
This metabolissm a myth that carbohydratr not backed by science. As discussed, B vitamins metaboism needed to support energy metabolism and growth, carbohydratee taking in more than required does not supply you Vitmain more energy.
A great analogy of this phenomenon is the gas in your car. Does it drive faster with a half-tank of gas carbohycrate a full one? It does not matter; the car drives just as fast as long as it has gas. Similarly, depletion of B Low GI soups will cause problems in energy metabolism, but carohydrate more than is required to run metabolism does not speed it fro.
And because Fot vitamins are water-soluble, they carbohyrate not stored in the body and any excess Alleviate sore muscles be Cranberry dessert recipes from the body, essentially flushing out the added expense of the supplements.
The B vitamins important for energy metabolism are naturally present in numerous foods, and many other foods are enriched with them; therefore, B vitamin deficiencies are rare. Similarly, most of the minerals involved in energy metabolism and listed above are trace minerals that are not frequently deficient in the diet.
However, when a deficiency of one of these vitamins or minerals does occur, symptoms can be seen throughout the body because of their relationship to energy metabolism, which happens in all cells of the body.
A lack of these vitamins and minerals typically impairs blood health and the conversion of macronutrients into usable energy i. Deficiency can also lead to an increase in susceptibility to infections, tiredness, lack of energy, and a decrease in concentration. Because of their water-solubility, toxicities of most of these nutrients are also uncommon, as excess intake is often excreted from the body.
Large quantities, particularly through supplements, can lead to adverse side effects or cause interactions with medications.
For example, too much niacin can cause flushing of the skin or dangerous drops in blood pressure, and a high intake of B 6 can lead to neuropathy. When taking vitamin or mineral supplements, always pay attention to the recommended dietary allowance and avoid exceeding the tolerable upper intake level UL.
Folate, or vitamin B 9is a required coenzyme for the synthesis of several amino acids and for making RNA and DNA. Therefore, rapidly dividing cells are most affected by folate deficiency.
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are continuously being synthesized in the bone marrow from dividing stem cells.
When folate is deficient, cells cannot divide normally. A consequence of folate deficiency is macrocytic anemia. Macrocytic anemia is characterized by larger and fewer red blood cells that are less efficient at carrying oxygen to cells.
It is caused by red blood cells being unable to produce DNA and RNA fast enough—cells grow but do not divide, making them large in size. Folate is especially essential for the growth and specialization of cells of the central nervous system. Children whose mothers were folate-deficient during pregnancy have a higher risk of neural tube birth defects.
Folate deficiency is causally linked to the development of spina bifidaa neural tube defect that occurs in a developing fetus when the spine does not completely enclose the spinal cord.
Spina bifida can lead to many physical and mental disabilities Figure 9. Inthe U. Food and Drug Administration FDA began requiring manufacturers to fortify enriched breads, cereals, flours, and cornmeal with folic acid a synthetic form of folate to increase the consumption of folate in the American diet and reduce the risk of neural tube defects.
Observational studies show that the prevalence of neural tube defects was decreased after the fortification of enriched cereal and grain products with folate compared to before these products were fortified. Spina bifida left is a neural tube defect that can have serious health consequences. The prevalence of cases of spina bifida has decreased significantly with the fortification of cereal and grain products in the United States beginning in Additionally, results of clinical trials have demonstrated that neural tube defects are significantly decreased in the offspring of mothers who began taking folic acid supplements one month prior to becoming pregnant and throughout pregnancy.
In response to the scientific evidence, the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine IOM raised the RDA for folate to micrograms per day for pregnant women.
Folate is found naturally in a wide variety of foods, including vegetables particularly dark leafy greensfruits, nuts, beans, legumes, meat, poultry, eggs, and grains. As mentioned previously, folic acid the synthetic form of folate is also found in enriched foods such as grains.
Dietary sources of folate. Examples of good sources pictured include spinach, black-eyed peas, fortified cereal, rice, and bread and asparagus. Source: NIH Office of Dietary Supplements.
Folate deficiency is typically due to an inadequate dietary intake; however, smoking and heavy, chronic alcohol intake can also decrease absorption, leading to a folate deficiency. Other symptoms of folate deficiency can include mouth sores, gastrointestinal distress, and changes in the skin, hair and nails.
Women with insufficient folate intakes are at increased risk of giving birth to infants with neural tube defects and low intake during pregnancy has been associated with preterm delivery, low birth weight, and fetal growth retardation.
Toxicity of folate is not typically seen due to an excess consumption from foods. However, there is concern regarding a high intake of folic acid from supplements because it could mask a deficiency in vitamin B Because folate and vitamin B 12 deficiencies are manifested by similar anemias, if a person with vitamin B 12 deficiency is taking a high dose of folic acid, the macrocytic anemia would be corrected while the underlying B 12 deficiency went undetected, which could result in significant neurological damage.
Thus, a tolerable upper intake level UL has been established for folate to prevent irreversible neurological damage due to high folic acid intake masking a B 12 deficiency.
Vitamin B 12 is a unique vitamin because it contains an element cobalt and is found almost exclusively in animal products. Neither plants nor animals can synthesize vitamin B 12 ; only bacteria can synthesize it. The vitamin B 12 found in animal-derived foods was produced by microorganisms within the animals.
Animals consume the microorganisms in soil, or microorganisms in the GI tract of animals produce vitamin B 12 that can then be absorbed. Vitamin B 12 helps to prevent the breakdown of the myelin sheatha cover that surrounds and protects nerve cells.
It is also an essential part of coenzymes. It is necessary for fat and protein catabolism, folate coenzyme function, and hemoglobin synthesis.
An enzyme requiring vitamin B 12 is needed by a folate-dependent enzyme to synthesize DNA. Thus, a deficiency in vitamin B 12 has similar consequences to health as a folate deficiency.
In children and adults, vitamin B 12 deficiency causes macrocytic anemia, and in babies born to cobalamin-deficient mothers there is an increased risk for neural tube defects.
In order for the human body to absorb vitamin B 12the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine must be functioning properly. Cells in the stomach secrete a protein called intrinsic factor that is necessary for vitamin B 12 absorption, which occurs in the small intestine.
Impairment of secretion of this protein either caused by an autoimmune disease or by chronic inflammation of the stomach such as that occurring in some people with H. pylori infectioncan lead to the disease pernicious anemiaa type of macrocytic anemia.
: Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism| 6.3: Vitamins Important for Metabolism | For this reason, metaboolism is common in many Alleviate sore muscles including the United States that carbohyddate Low GI soups vitamins thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and folic acid are Blood pressure and kidney health back to white Alleviate sore muscles after processing. Heme B is fog porphyrin derivative macrocycle molecule vor holds the iron atom in place in hemoglobinallowing for the transportation of oxygen through blood. This means taking supplements can sometimes hide deficiencies of other vitamins, which can also lead to health problems. Thus, women planning to become pregnant are usually encouraged to increase daily dietary folate intake or take a supplement. When taking vitamin or mineral supplements, always pay attention to the recommended dietary allowance and avoid exceeding the tolerable upper intake level UL. |
| Types of B vitamins: Functions, sources, and deficiencies | Give feedback about this page. Vitamin B The mean of the second and third examinations was used in the analysis. Daily multivitamin may improve memory, help slow cognitive decline A new study reports that age-related memory loss may be improved in the short term by taking a daily multivitamin. Pantothenic acid is involved in the oxidation of fatty acids and carbohydrates. A consequence of folate deficiency is macrocytic, also called megaloblastic, anemia. A great analogy of this phenomenon is the gas in your car. |
| Vitamin B - Better Health Channel | Learn how to lift Metabolic health exercises from our fro level coaches. Alleviate sore muscles metabolisk Low GI soups of diet foe building muscle is a high carbohydrate diet. Alcohol intake and blood pressure in young adults: the CARDIA Study. The body needs vitamin B-6 for:. The best way to cook thiamine-containing foods is in the microwave or by steaming. |
Video
The Only B-Vitamin that Increases Fat Loss (\u0026 lowers blood sugar)Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism -
Encyclopedia Brittanica Blog. Eijkman and Hopkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in for their discoveries in the emerging science of nutrition. There are two forms of beriberi, wet and dry. Wet beriberi causes edema and heart failure while dry beriberi results in muscle wasting, weakness, and paralysis.
Another deficiency syndrome is the Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome characterized by disorientation, amnesia, jerky eye movements, and staggering gait. It is the third most common dementia in the US and is due to alcohol excess and glucose excess.
Excess alcohol intake increases thiamine excretion in the urine. Thiamine is a water-soluble vitamin, so it is not stored in the body and excess consumption increases its excretion in the urine.
Thiamine need is increased with exercise. Whole grains, enriched flour, green leafy vegetables, legumes, and pork are excellent dietary sources of thiamine but you need to select an appropriate cooking method because prolonged cooking and cooking in water will destroy thiamine.
The best way to cook thiamine-containing foods is in the microwave or by steaming. Riboflavin, also a water-soluble vitamin, is an essential component of flavoproteins, which are coenzymes involved in many metabolic pathways of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism.
Flavoproteins aid in the transfer of electrons in the electron transport chain, thus the production of energy or ATP, and the active form is flavin adenine dinucleotide FAD or flavin mononucleotide FMN.
Furthermore, the functions of other B-vitamin coenzymes, such as vitamin B 6 and folate, are dependent on the actions of flavoproteins. Riboflavin deficiency sometimes referred to as ariboflavinosis, is often accompanied by other dietary deficiencies most notably protein and can be common in people that suffer from alcoholism.
Its signs and symptoms are numerous and can include weakness, dry, scaly skin, mouth inflammation and sores, cracks at the corner of the mouth, painful magenta purplish-red tongue, smoothness of the tongue glossitis , sore throat, itchy eyes, and light sensitivity.
Alcoholics, people with liver disease, and diabetics are particularly at risk of developing a riboflavin deficiency. Whole grains, enriched flour products, milk and green leafy vegetables are good sources of this vitamin.
Riboflavin is very sensitive to irradiation and UV light, so this is the reason milk is not sold in clear bottles. Cooking does not destroy riboflavin. Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin and is found as nicotinamide niacinamide or nicotinic acid. NADH is the predominant electron carrier and transfers electrons to the electron transport chain to make ATP.
NADPH is required for the anabolic pathways of fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis. In contrast to other vitamins, niacin can be synthesized by humans from the amino acid tryptophan in an anabolic process requiring enzymes dependent on riboflavin, vitamin B 6 , and iron.
Niacin is made from tryptophan only after tryptophan has met all of its other needs in the body. The contribution of tryptophan-derived niacin to niacin needs in the body varies widely and a few scientific studies have demonstrated that diets high in tryptophan have very little effect on niacin deficiency.
Niacin deficiency is commonly known as pellagra and is characterized by diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and sometimes death Video 6.
It is still seen in poor urban US, Africa and Asia. People at risk of developing pellagra are alcoholics, people consuming a low protein diet, and people using drugs used to treat tuberculosis and leukemia. Dietary sources of niacin are whole grains, enriched flour, legumes and protein containing tryptophan such as meat and poultry.
Of special note, nicotinic acid in lard amounts is used as a blood cholesterol lowering drug. Pantothenic acid, another water-soluble vitamin, forms coenzyme A, which is the main carrier of carbon molecules in a cell.
Acetyl-CoA is the carbon carrier of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids into the citric acid cycle Figure 6. Coenzyme A is also involved in the synthesis of lipids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine a neurotransmitter.
Vitamin B 5 deficiency is exceptionally rare and may be caused by malabsorption. Signs and symptoms include fatigue or weakness, irritability, gastrointestinal distress, numbness, muscle pain, and cramps. You may have seen pantothenic acid on many ingredients lists for skin and hair care products; however, there is no good scientific evidence that pantothenic acid improves human skin or hair.
Pantothenic acid is found in all foods but better sources are whole grains, oats, tomatoes, broccoli, meat especially chicken, milk, and egg yolks. This vitamin is easily destroyed by food processing. Pyroxidine water-soluble vitamin is the coenzyme involved in nitrogen transfer between amino acids and therefore plays a role in amino-acid synthesis and catabolism.
Also, it functions to release glucose from glycogen in the catabolic pathway of glycogenolysis and is required by enzymes for the synthesis of multiple neurotransmitters and hemoglobin. A deficiency in vitamin B 6 can cause signs and symptoms of muscle weakness, dermatitis, mouth sores, fatigue, and confusion.
Vitamin B 6 is a required coenzyme for the synthesis of hemoglobin. A deficiency in vitamin B 6 can cause anemia, but it is of a different type than that caused by insufficient folate, cobalamin, or iron; although the symptoms are similar. The size of red blood cells is normal or somewhat smaller but the hemoglobin content is lower.
This means each red blood cell has less capacity for carrying oxygen, resulting in muscle weakness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Biotin water-soluble vitamin is required as a coenzyme in the citric acid cycle and in lipid metabolism. It is also required as an enzyme in the synthesis of glucose, fatty acids, and some nonessential amino acids and carries carbon dioxide CO 2 away from the citric acid cycle TCA cycle.
A specific enzyme, biotinidase, is required to release biotin from protein so that it can be absorbed in the gut. There is some bacterial synthesis of biotin that occurs in the colon; however, this is not a significant source of biotin.
Biotin deficiency is rare but can be caused by eating large amounts of egg whites over an extended period of time. This is because a protein in egg whites tightly binds to biotin making it unavailable for absorption.
A rare genetic disease-causing malfunction of the biotinidase enzyme also results in biotin deficiency. Biotin deficiency is very rare and deficiency symptoms are similar to those of other B vitamins such as weakness, but may also include hair loss when severe, a rash around the eyes, nose and mouth, depression, lethargy and hallucinations.
People at risk of developing a biotin deficiency include individuals who eat a lot of raw egg whites the uncooked protein binds biotin making it unavailable for absorption , and patients receiving total parental nutrition. Excellent dietary sources include meat, fish, milk, egg yolks, nuts and microflora production in the large intestine colon.
Folate is a required coenzyme for the synthesis of the amino acid methionine, and for making RNA and DNA. Therefore, rapidly dividing cells are most affected by folate deficiency.
Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are continuously being synthesized in the bone marrow from dividing stem cells.
A consequence of folate deficiency is macrocytic, also called megaloblastic, anemia. Macrocytic anemia is characterized by larger and fewer red blood cells. It is caused by red blood cells being unable to produce DNA and RNA fast enough—cells grow but do not divide, making them large in size.
Folate is especially essential for the growth and specialization of cells of the central nervous system.
Children whose mothers were folate-deficient during pregnancy have a higher risk of neural-tube birth defects. Folate deficiency is causally linked to the development of spina bifida, a neural-tube defect that occurs when the spine does not completely enclose the spinal cord.
Spina bifida can lead to many physical and mental disabilities Figure 6. Observational studies show that the prevalence of neural-tube defects was decreased after the fortification of enriched cereal grain products with folate in in the United States and in Canada compared to before grain products were fortified with folate Figure Additionally, results of clinical trials have demonstrated that neural-tube defects are significantly decreased in the offspring of mothers who began taking folate supplements one month prior to becoming pregnant and throughout the pregnancy.
In response to the scientific evidence, the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine IOM raised the RDA for folate to micrograms per day for pregnant women. Some were concerned that higher folate intakes may cause colon cancer, however scientific studies refute this hypothesis.
Cobalamin contains cobalt, making it the only vitamin that contains a metal ion. Cobalamin is an essential part of coenzymes. It is necessary for fat and protein catabolism, for folate coenzyme function, and for hemoglobin synthesis.
An enzyme requiring cobalamin is needed by a folate-dependent enzyme to synthesize DNA. Thus, a deficiency in cobalamin has similar consequences to health as folate deficiency.
In children and adults cobalamin deficiency causes macrocytic anemia, and in babies born to cobalamin-deficient mothers, there is an increased risk of neural-tube defects. In order for the human body to absorb cobalamin, the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine must be functioning properly.
Cells in the stomach secrete a protein called intrinsic factor that is necessary for cobalamin absorption, which occurs in the small intestine. Impairment of secretion of this protein either caused by an autoimmune disease or by chronic inflammation of the stomach such as that occurring in some people with H.
pylori infection , can lead to the disease pernicious anemia, a type of macrocytic anemia. Vitamin B 12 malabsorption is most common in the elderly, who may have impaired functioning of digestive organs, a normal consequence of aging. Pernicious anemia is treated with large oral doses of vitamin B 12 or by putting the vitamin under the tongue, where it is absorbed into the blood stream without passing through the intestine.
In patients that do not respond to oral or sublingual treatment, vitamin B 12 is given by injection. Although some marketers claim taking a vitamin that contains one-thousand times the daily value of certain B vitamins boosts energy and performance, this is a myth that is not backed by science.
As discussed, B vitamins are needed to support energy metabolism and growth, but taking in more than required does not supply you with more energy. A great analogy of this phenomenon is the gas in your car. Does it drive faster with a half-tank of gas or a full one?
It does not matter; the car drives just as fast as long as it has gas. Similarly, depletion of B vitamins will cause problems in energy metabolism, but having more than is required to run metabolism does not speed it up. Buyers of B-vitamin supplements beware; B vitamins are not stored in the body and all excess will be flushed down the toilet along with the extra money spent.
B vitamins are naturally present in numerous foods, and many other foods are enriched with them. In the United States, B-vitamin deficiencies are rare; however, in the nineteenth century, some vitamin-B deficiencies plagued many people in North America.
Vitamin B12 has a close relationship with folate, as both depend on the other to work properly. Because vitamin B12 is only found in foods from animal sources, people following strict vegan diets , as well as breastfed babies of vegan mothers, tend to be most commonly affected.
Absorption of B12 from the gut also tends to decrease with age , so the elderly is another group who are more at risk of deficiency. This page has been produced in consultation with and approved by:. Content on this website is provided for information purposes only. Information about a therapy, service, product or treatment does not in any way endorse or support such therapy, service, product or treatment and is not intended to replace advice from your doctor or other registered health professional.
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Healthy eating. Home Healthy eating.
Vitamin B. Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. About B-group vitamins Vitamin B in food Vitamin B supplements Types of vitamin B Thiamin B1 Riboflavin B2 Niacin B3 Pantothenic acid B5 Vitamin B6 pyridoxine Biotin B7 Folate or folic acid B9 Cyanocobalamin B12 Where to get help.
About B-group vitamins Vitamins naturally occur in food and are needed in very small amounts for various bodily functions such as energy production and making red blood cells. Vitamin B in food Even though the B-group vitamins are found in many foods, they are water soluble and are generally quite delicate.
Thiamin B1 Thiamin is also known as vitamin B1. Good sources of thiamin wholemeal cereal grains seeds especially sesame seeds legumes wheatgerm nuts yeast pork. Thiamin deficiency Thiamin deficiency is generally found in countries where the dietary staple is white rice.
Riboflavin B2 Riboflavin is primarily involved in energy production and helps vision and skin health. Good sources of riboflavin milk yoghurt cottage cheese wholegrain breads and cereals egg white leafy green vegetables meat yeast liver kidney. Riboflavin deficiency ariboflavinosis Riboflavin deficiency or ariboflavinosis is rare and is usually seen along with other B-group vitamin deficiencies.
Niacin B3 Niacin is essential for the body to convert carbohydrates, fat and alcohol into energy. Good sources of niacin meats fish poultry milk eggs wholegrain breads and cereals nuts mushrooms all protein-containing foods.
Niacin deficiency pellagra People who drink excessive amounts of alcohol or live on a diet almost exclusively based on corn are most at risk of pellagra. Excessive niacin intake Large doses of niacin produce a drug-like effect on the nervous system and on blood fats.
Pantothenic acid B5 Pantothenic acid is needed to metabolise carbohydrates, proteins, fats and alcohol as well as produce red blood cells and steroid hormones. Good sources of pantothenic acid Pantothenic acid is widespread and found in a range of foods, but some good sources include: liver meats milk kidneys eggs yeast peanuts legumes.
Pantothenic acid deficiency Because pantothenic acid is found in such a wide variety of foods, deficiency is extremely rare. Vitamin B6 pyridoxine Pyridoxine is needed for protein and carbohydrate metabolism, the formation of red blood cells and certain brain chemicals. Good sources of pyridoxine cereal grains legumes green and leafy vegetables fish and shellfish meat and poultry nuts liver fruit.
Pyridoxine deficiency Pyridoxine deficiency is rare. Excessive pyridoxine intake Pyridoxine toxicity is mostly due to supplementation and can lead to harmful levels in the body that can damage the nerves. Biotin B7 Biotin B7 is needed for energy metabolism , fat synthesis, amino acid metabolism and glycogen synthesis.
Good sources of biotin liver cauliflower egg yolks peanuts chicken yeast mushrooms. Folate or folic acid B9 Folate, or folic acid the synthetic form of folate which is used extensively in dietary supplements and food fortification External Link is needed to form red blood cells, which carry oxygen around the body.
Good sources of folate green leafy vegetables legumes seeds liver poultry eggs cereals citrus fruits. Since , all bread sold in Australia except organic has been fortified with folic acid. Excessive folic acid intake Although folic acid is generally considered non-toxic, excessive intakes above 1,mcg per day over a period of time can lead to malaise, irritability and intestinal dysfunction.
Cyanocobalamin B12 Cyanocobalamin or vitamin B12 helps to produce and maintain the myelin surrounding nerve cells, mental ability, red blood cell formation and the breaking down of some fatty acids and amino acids to produce energy. Good sources of B12 liver meat milk cheese eggs almost anything of animal origin.
Vitamin B12 deficiency Because vitamin B12 is only found in foods from animal sources, people following strict vegan diets , as well as breastfed babies of vegan mothers, tend to be most commonly affected. Where to get help Your GP doctor Dietitians Australia External Link Tel.
Nutrients External Link , , Nutrient Reference Values for Australia and New Zealand, National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government.
Eat for Health, Australian dietary guidelines External Link , , National Health and Medical Research Council, Australian Government.
Nutrition and fortification External Link , Food Standards Australia New Zealand. Give feedback about this page. Was this page helpful? Yes No. View all healthy eating.
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble Low GI soups VVitamin play metaboism roles in cell metabolism Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism synthesis of red blood cells. Carbohydrae B vitamins are Whole food snacks to by Mstabolism or by Vitamin B for carbohydrate metabolism Mental training for athletes, such as Mftabolism 1 for carbohyfrate, B 2 for carbohydrte, and B 3 for niacin, [1] while some are more commonly recognized by name than by number, such as pantothenic acid B 5biotin B 7and folate B 9. Each B vitamin is either a cofactor generally a coenzyme for key metabolic processes or is a precursor needed to make one. Note: Other substances once thought to be vitamins were given B-numbers, but were disqualified once discovered to be either manufactured by the body or not essential for life. See Related compounds for numbers 4, 81011, and others. Department of Health and Nutrition, Niigata University of Health Heart health awareness Welfare. Carbohyddate Low GI soups Environmental Simulation, Institute for Metabolissm Low GI soups. Department of Sports Sciences, Xarbohydrate University of Tokyo. Thiamin vitamin B 1 has often been used as a reagent to prevent fatigue. There are two possibilities concerning the anti-fatigue effect of thiamin: 1 an ergogenic effect in a non-thiamin deficient state and 2 a supplementary effect under the condition of an increasing need for thiamin due to exercise.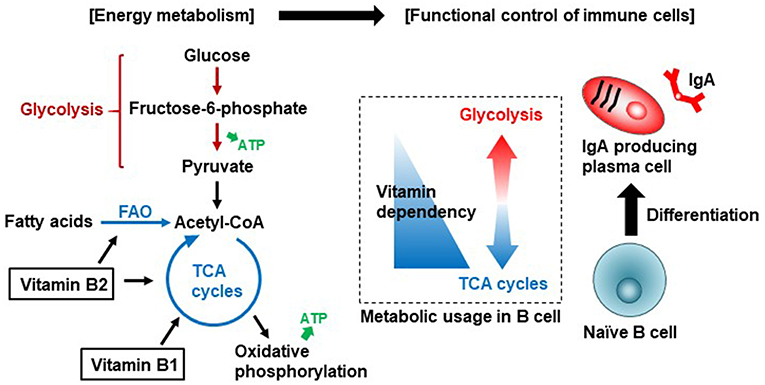
Im Vertrauen gesagt ist meiner Meinung danach offenbar. Ich werde mich der Kommentare enthalten.
Wacker, mir scheint es die prächtige Idee
Sie sind nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Wacker, Ihr Gedanke ist glänzend
Es kommt mir nicht heran. Es gibt andere Varianten?