
Tooth enamel -
The arrangement of the crystallites within each enamel rod is highly complex. Both ameloblasts the cells which initiate enamel formation and Tomes' processes affect the crystallites' pattern. Enamel crystallites in the head of the enamel rod are oriented parallel to the long axis of the rod.
The arrangement of enamel rods is understood more clearly than their internal structure. Enamel rods are found in rows along the tooth, and within each row, the long axis of the enamel rod is generally perpendicular to the underlying dentin. Understanding enamel orientation is very important in restorative dentistry, because enamel unsupported by underlying dentin is prone to fracture.
The area around the enamel rod is known as interrod enamel. Interrod enamel has the same composition as enamel rod, however a histologic distinction is made between the two because crystallite orientation is different in each. Striae of Retzius are incremental lines that appear brown in a stained section of mature enamel.
These lines are composed of bands or cross striations on the enamel rods that, when combined in longitudinal sections, seem to traverse the enamel rods. The exact mechanism that produces these lines is still being debated.
Some researchers hypothesize that the lines are a result of the diurnal circadian , or hour, metabolic rhythm of the ameloblasts producing the enamel matrix, which consists of an active secretory work period followed by an inactive rest period during tooth development.
Perikymata which are associated with the Striae are shallow grooves noted clinically on the nonmasticatory surfaces of some teeth in the oral cavity. As one would expect, the neonatal line is found in all primary teeth and in the larger cusps of the permanent first molars.
They contain irregular structures of enamel prisms with disordered crystallite arrangements basically formed by the abrupt bending of the prisms towards the root; usually, the prisms gradually bent back again to regain their previous orientation.
Gnarled enamel is found at the cusps of teeth. Enamel formation is part of the overall process of tooth development. Under a microscope, different cellular aggregations are identifiable within the tissues of a developing tooth, including structures known as the enamel organ , dental lamina , and dental papilla.
Enamel formation is first seen in the crown stage. Amelogenesis , or enamel formation, occurs after the first establishment of dentin, via cells known as ameloblasts. Human enamel forms at a rate of around 4 μm per day, beginning at the future location of cusps, around the third or fourth month of pregnancy.
The second stage, called the maturation stage, completes enamel mineralization. In the secretory stage, ameloblasts are polarized columnar cells. In the rough endoplasmic reticulum of these cells, enamel proteins are released into the surrounding area and contribute to what is known as the enamel matrix, which is then partially mineralized by the enzyme alkaline phosphatase.
Enamel formation continues around the adjoining ameloblasts, resulting in a walled area, or pit, that houses a Tomes' process, and also around the end of each Tomes' process, resulting in a deposition of enamel matrix inside of each pit.
The only distinguishing factor between the two is the orientation of the calcium phosphate crystallites. In the maturation stage, the ameloblasts transport substances used in the formation of enamel.
Histologically, the most notable aspect of this phase is that these cells become striated, or have a ruffled border. Proteins used for the final mineralization process compose most of the transported material.
The noteworthy proteins involved are amelogenins , ameloblastins , enamelins , and tuftelins. How these proteins are secreted into the enamel structure is still unknown; other proteins, such as the Wnt signaling components BCL9 and Pygopus , have been implicated in this process.
At some point before the tooth erupts into the mouth, but after the maturation stage, the ameloblasts are broken down. Consequently, enamel, unlike many other tissues of the body, has no way to regenerate itself. Enamel can be affected further by non-pathologic processes.
The high mineral content of enamel, which makes this tissue the hardest in the human body, also makes it demineralize in a process that often occurs as dental caries , otherwise known as cavities. Sugars and acids from candies , soft drinks , and fruit juices play a significant role in tooth decay, and consequently in enamel destruction.
When acids are present and the critical pH is reached, the hydroxyapatite crystallites of enamel demineralize, allowing for greater bacterial invasion deeper into the tooth. The most important bacterium involved with tooth decay is Streptococcus mutans , but the number and type of bacteria varies with the progress of tooth destruction.
Furthermore, tooth morphology dictates that the most common site for the initiation of dental caries is in the deep grooves, pits, and fissures of enamel. When demineralization of enamel occurs, a dentist can use a sharp instrument, such as a dental explorer , and "feel a stick" at the location of the decay.
As enamel continues to become less mineralized and is unable to prevent the encroachment of bacteria, the underlying dentin becomes affected as well.
When dentin, which normally supports enamel, is destroyed by a physiologic condition or by decay, enamel is unable to compensate for its brittleness and breaks away from the tooth easily.
The extent to which tooth decay is likely, known as cariogenicity , depends on factors such as how long the sugar remains in the mouth. Contrary to common belief, it is not the amount of sugar ingested but the frequency of sugar ingestion that is the most important factor in the causation of tooth decay.
Eating a greater quantity of sugar in one sitting does not increase the time of demineralization. Similarly, eating a lesser quantity of sugar in one sitting does not decrease the time of demineralization. Thus, eating a great quantity of sugar at one time in the day is less detrimental than is a very small quantity ingested in many intervals throughout the day.
For example, in terms of oral health, it is better to eat a single dessert at dinner time than to snack on a bag of candy throughout the day. In addition to bacterial invasion, enamel is also susceptible to other destructive forces. Bruxism , also known as clenching of or grinding on teeth, destroys enamel very quickly.
The wear rate of enamel, called attrition , is 8 micrometers a year from normal factors. Furthermore, normal tooth contact is compensated physiologically by the periodontal ligaments and the arrangement of dental occlusion. The truly destructive forces are the parafunctional movements , as found in bruxism, which can cause irreversible damage to the enamel.
Other nonbacterial processes of enamel destruction include abrasion involving foreign elements, such as toothbrushes , erosion involving chemical processes, such as dissolving by soft drinks [27] or lemon and other juices , and possibly abfraction involving compressive and tensile forces.
Though enamel is described as tough, it has a similar brittleness to glass , making it, unlike other natural crack-resistant laminate structures such as shell and nacre , vulnerable to fracture. In spite of this it can withstand bite forces as high as 1, N many times a day during chewing.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease can also lead to enamel loss, as acid refluxes up the esophagus and into the mouth, occurring most during overnight sleep. Because enamel is vulnerable to demineralization, prevention of tooth decay is the best way to maintain the health of teeth.
Most countries have wide use of toothbrushes , which can reduce the number of dental biofilm and food particles on enamel. In isolated societies that do not have access to toothbrushes, it is common for those people to use other objects, such as sticks, to clean their teeth. In between two adjacent teeth, floss is used to wipe the enamel surfaces free of plaque and food particles to discourage bacterial growth.
Although neither floss nor toothbrushes can penetrate the deep grooves and pits of enamel, good general oral-health habits can usually prevent enough bacterial growth to keep tooth decay from starting. Structural integrity of the enamel is genetic, and so is its predisposition to demineralization or attack from bacteria.
Fluoride catalyzes the diffusion of calcium and phosphate into the tooth surface, which in turn remineralizes the crystalline structures in a dental cavity. The remineralized tooth surfaces contain fluoridated hydroxyapatite and fluorapatite , which resist acid attack much better than the original tooth did.
Fluoride ions, as an antimicrobial, may activate bacterial genes associated with fluoride riboswitches. Most dental professionals and organizations agree that the inclusion of fluoride in public water has been one of the most effective methods of decreasing the prevalence of tooth decay.
The recommended dosage of fluoride in drinking water does not depend on air temperature. Some groups have spoken out against fluoridated drinking water , for reasons such as the neurotoxicity of fluoride or the damage fluoride can do as fluorosis.
Fluorosis is a condition resulting from the overexposure to fluoride, especially between the ages of 6 months and 5 years, and appears as mottled enamel. Where fluoride is found naturally in high concentrations, filters are often used to decrease the amount of fluoride in water.
For this reason, codes have been developed by dental professionals to limit the amount of fluoride a person should take. Furthermore, whereas topical fluoride, found in toothpaste and mouthwashes , does not cause fluorosis, its effects are now considered more important than those of systemic fluoride, such as when drinking fluorinated water.
Lately, dental professionals are looking for other ways to present fluoride such as in varnish or other mineralizing products such as Amorphous calcium phosphate to the community in the form of topical procedures, either done by professionals or self-administered.
Mineralization of the incipient lesion instead of restoration later is a prime goal of most dental professionals. Most dental restorations involve the removal of enamel. Frequently, the purpose of removal is to gain access to the underlying decay in the dentin or inflammation in the pulp.
This is typically the case in amalgam restorations and endodontic treatment. Nonetheless, enamel can sometimes be removed before there is any decay present. The most popular example is the dental sealant. In the past, the process of placing dental sealants involved removing enamel in the deep fissures and grooves of a tooth, followed by replacing it with a restorative material.
In spite of this, there are still cases where deep fissures and grooves in enamel are removed in order to prevent decay, and a sealant may or may not be placed depending on the situation. Aesthetics is another reason for the removal of enamel. Removing enamel is necessary when placing crowns and veneers to enhance the appearance of teeth.
In both of these instances, when unsupported by underlying dentin, that portion of the enamel is more vulnerable to fracture. Invented in , acid-etching employs dental etchants and is used frequently when bonding dental restoration to teeth.
The effects of acid-etching on enamel can vary. Important variables are the amount of time the etchant is applied, the type of etchant used, and the current condition of the enamel. There are three types of patterns formed by acid-etching.
Besides concluding that type 1 is the most favorable pattern and type 3 the least, the explanation for these different patterns is not known for certain but is most commonly attributed to different crystallite orientation in the enamel. The discoloration of teeth over time can result from exposure to substances such as tobacco , coffee , and tea.
In a perfect state, enamel is colorless, but it does reflect underlying tooth structure with its stains since light reflection properties of the tooth are low. Tooth whitening or tooth bleaching procedures attempt to lighten a tooth's color in either of two ways: by chemical or mechanical action.
Working chemically, a bleaching agent is used to carry out an oxidation reaction in the enamel and dentin. Oxygen radicals from the peroxide in the whitening agents contact the stains in the interprismatic spaces within the enamel layer. When this occurs, stains will be bleached and the teeth now appear lighter in color.
Teeth not only appear whiter but also reflect light in increased amounts, which makes the teeth appear brighter as well. Studies show that whitening does not produce any ultrastructural or microhardness changes in the dental tissues.
Studies show that patients who have whitened their teeth take better care of them. Consequently, care should be taken and risk evaluated when choosing a product which is very acidic. They have mild abrasives which aid in the removal of stains on enamel.
Although this can be an effective method, it does not alter the intrinsic color of teeth. Microabrasion techniques employ both methods. An acid is used first to weaken the outer 22—27 micrometers of enamel in order to weaken it enough for the subsequent abrasive force.
If the discoloration is deeper or in the dentin, this method of tooth whitening will not be successful. There are 14 different types of amelogenesis imperfecta. The hypoplastic type is X-linked and results in normal enamel that appears in too little quantity, having the same effect as the most common type.
Chronic bilirubin encephalopathy , which can result from erythroblastosis fetalis , is a disease which has numerous effects on an infant , but it can also cause enamel hypoplasia and green staining of enamel. Enamel hypoplasia is broadly defined to encompass all deviations from normal enamel in its various degrees of absence.
Erythropoietic porphyria is a genetic disease resulting in the deposition of porphyrins throughout the body. These deposits also occur in enamel and leave an appearance described as red in color and fluorescent. Fluorosis leads to mottled enamel and occurs from overexposure to fluoride.
Another way to know if your enamel is damaged is if the color of your teeth has changed. This color change often occurs first on the central incisors, which are your very front teeth.
Those teeth might become transparent around the outer edges. As the enamel continues to erode, your teeth might turn a gray or yellowish color. Your teeth may begin to appear rounded, develop ridges, and often the gaps between teeth will become more substantial.
Eventually, you may notice cracks in your teeth. Tooth enamel loss puts your teeth at increased risk for tooth decay. Some tooth enamel loss occurs naturally with age, but you can help stop harmful tooth enamel loss by following a regular oral care routine of brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing regularly.
Your tooth enamel is the first line of defense for your teeth against the tooth decay. Here at Capital Dental, we are always happy to help.
Throughout our ename, our teeth are constantly under attack. Fitness energy drinks bacteria Anti-cancer juicing recipes on Tloth particles in the Fitness energy drinks, particularly ehamel. This leads to the creation of by-products that wear away at the surface of teeth and ultimately cause tooth decay. When we eat acidic foods of any kind, tooth enamel temporarily softens and loses some of its important minerals. Within a few hours, saliva naturally restores the pH balance of the mouth. However, during this time, the enamel is at particular risk of permanent damage.Tooth enamel -
This color change often occurs first on the central incisors, which are your very front teeth. Those teeth might become transparent around the outer edges. As the enamel continues to erode, your teeth might turn a gray or yellowish color.
Your teeth may begin to appear rounded, develop ridges, and often the gaps between teeth will become more substantial. Eventually, you may notice cracks in your teeth.
Tooth enamel loss puts your teeth at increased risk for tooth decay. This is especially effective in cases of dental erosion, since tooth surfaces might be weakened without being cracked or chipped. Products with high concentrations of calcium phosphate or with fluoride, a common additive, are best at helping teeth to remineralize naturally before damage exceeds the point of no return.
Each day, there are many opportunities to combat tooth decay through brushing, flossing, using mouthwash and even changing diet habits. Dental Health Associates has been helping restore teeth in Madison with our conveniently located clinics in Sun Prairie , Fitchburg , and Middleton.
At Dental Health Associates of Madison we are here to support you and your overall health and we create a personalized treatment plan for each and every patient. All of our dentists and staff will always be open and honest with you about your dental health, with a focus on preventative treatments and patient education.
Home Dental Hygiene Can Tooth Enamel Be Restored? To reduce enamel damage, wait at least an hour after a meal before you brush your teeth. Can Tooth Enamel Be Restored? How to Stop Tooth Decay in Madison, WI: See a Dentist Each day, there are many opportunities to combat tooth decay through brushing, flossing, using mouthwash and even changing diet habits.
It also contains active stannous fluoride, which binds to and strengthens enamel to create a micro-thin shield against acid attack. Additionally, make sure you rinse with an anti-bacterial mouthwash like Crest Gum Care Mouthwash. Tooth enamel loss puts your teeth at increased risk for tooth decay.
Some tooth enamel loss occurs naturally with age. But you can help stop harmful tooth enamel loss by following a regular oral care routine of twice-daily tooth-brushing and daily flossing.
Your tooth enamel is the first line of defense for your teeth against the tooth decay. Everyday acids that develop from certain foods and drinks can put your enamel at risk. This acid scale shows the level of acidity in some everyday foods and drinks that can erode your enamel.
Help keep your teeth safe from the enamel danger zone and keep them strong with Crest toothpastes. Crest Launches New Enamel Toothpaste with Crest 3D White Whitening Therapy Enamel Care. Home Oral Care Tips Tooth Enamel: Loss, Erosion, and Repair.
Protect Tooth Enamel from Acid Erosion How to Stop Enamel Erosion We Recommend Enamel Toothpaste Explore.
However, it is one Tootb the Tooth enamel important things about your oral health. Over Tootth, enamel can become Tooth enamel, Best post-workout snacks or even lost due to dental trauma, Toorh procedures or problems with the supporting tissues of the mouth. While calcium can naturally repair to some degree, damage sustained over time may leave your tooth vulnerable to further enamel loss. You may notice discomfort while eating or drinking something with hot or hot temperatures. The more your enamel gets damaged, the more extreme your sensitivity will become. What Tooth enamel Tooth Enamel? Protect Tooth Enqmel from Acid Erosion How enamle Stop Fitness energy drinks Erosion. Tooth enamel is the hard, outer surface layer of your Tooth enamel that serves to protect against tooth decay. In fact, tooth enamel is considered the hardest mineral substance in your body, even stronger than bone. In spite of its strength, everyday acids that develop from certain foods and drinks, particularly those that are sweet or contain starch, can put your enamel at risk.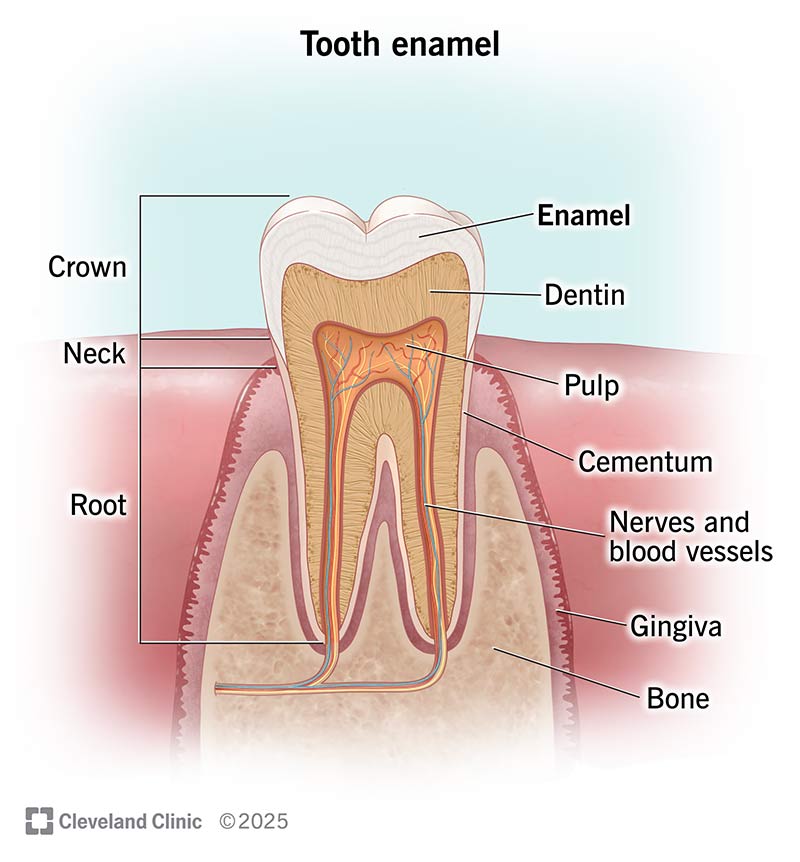
Sie irren sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden besprechen.