Carbohydrate metabolism and weight loss -
To access the sugar in a banana, our body first has to break down the fibrous structures of the fruit, which makes it very different from simply eating spoonfuls of sugar.
Even when we take the type, structure, and quality of carbohydrates into account, we are still missing an essential factor: you. Our food is very complicated, and so are each of us!
We each have our own unique microbiome, genetics, and responses to food, which vary from person to person. As our PREDICT study shows, one person might be able to digest a particular food quickly and release the energy inside easily, but another person might have to expend much more time and energy during the same process.
If the same food can influence the metabolism of different people in different ways, then whether you burn more energy on a low-carbohydrate or high-carbohydrate diet is likely to be personal to you. Our at-home test , based on the same tests used in our research, is designed to help you better understand your biology and discover which foods are best for you.
Why ZOE? Our Science Library FAQs. Join ZOE Join. What influence do carbs have on metabolism? In this post, we cover: How carbohydrates impact your metabolism Why the quality of your carbs matter How you can hack your unique biology to achieve a healthy weight and stay healthy How your metabolism works Everything your body does requires energy - this process of energy generation and burning is known as metabolism.
The amount of energy released from your food depends on what you eat and how your body works. Discover your unique biology Understand how your body responds to food with ZOE Take the first step. Get the latest nutrition tips from world-leading scientists for free.
Join our newsletter. No spam. Just science. These studies provide general insight for healthy people who want to lose weight or prevent the negative implications of poor glucose metabolism. However, specific insulin, glucose tolerances, and glucose responses may differ in healthy people compared to those with diabetes or metabolic syndrome.
Weight loss only tells us we carry less mass throughout our bodies. We may notice a lower number on the scale, but how did we get there? Our weight can fluctuate, even daily, and these weight swings can occur due to various factors. We may see changes in weight resulting from hormonal imbalances, varying sodium intake, and fiber consumption.
When weight loss occurs under such circumstances, it can encompass water, muscle, and fat loss. Recently, there has been a shift to ketogenic keto or low-carb eating styles to lose weight.
A meta-analysis of studies reported that very low-carb diets less than 50 grams per day could work for weight loss in the long term. Carbohydrates provide a quick and easily metabolized source of glucose that can lead to a rise in blood glucose blood sugar.
When those stores are full, any excess glucose gets stored in adipose tissue as fat. Very low-carb diets encourage burning through stored glycogen in a few days or less at the start of the regimen. After that, your body uses the relatively small amount of carbs you might get from your diet for energy first; then, it digs into your stored body fat for fuel.
This is why keto and low-carb dieters can lose weight, sometimes rather quickly, and see improvements in their proportion of body fat to lean mass.
Not exactly. The body requires glucose to function. While the body can make ketones for energy when necessary, the body still needs glucose. The body requires some blood glucose to keep us alive and awake.
Where could an energy source come from if our diets do not supply it? In a word, ketones. This can also happen during a ketogenic diet when severe carb restriction requires the liver to convert fat into an energy source.
During times of low energy availability, like fasting or starvation, gluconeogenesis creates glucose from amino acids protein , the breakdown of structures such as muscle tissue, and glycerol and free fatty acids are created through lipolysis and provide the energy for gluconeogenesis.
Normally, our bodies rely on sugar first for energy. Once the glucose concentration in our bloodstream is used up, our bodies can tap into glucose stored in the muscles and liver.
Once those stores are depleted, fat stored in our adipose tissue is used for fuel. Ketones are released into the bloodstream and taken up by your organs, including your brain, moved into the mitochondria, and used as fuel.
Excess ketones are excreted through urine, and acetone a type of ketone is released in the breath. Some high-glycemic foods and maybe even moderate-glycemic foods can cause rapid rises and dips in blood glucose—sometimes multiple times after one glucose-spiking meal—that requires the liver to release a proportional amount of insulin to shuttle the glucose to where it can be used for energy.
Over many years, spiking and dipping glucose levels can lead to insulin resistance, weight gain, obesity, metabolic syndrome, prediabetes, or even type 2 diabetes. Glucose metabolism involves multiple processes, including glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, and glycogenesis.
Glycolysis in the liver is a process that involves various enzymes that encourage glucose catabolism in cells. Insulin and glucagon are the key hormones in glucose metabolism. Glucagon helps prevent blood sugar from dropping, while insulin stops it from rising too high.
Insulin secretion also stimulates fat synthesis, promotion of triglyceride storage in fat cells, promotion of protein synthesis in the liver and muscles, and cell growth. Aerobic metabolism generates more ATP and relies on oxygen.
However, anaerobic metabolism does not need oxygen and creates two ATP molecules per glucose molecule. Both processes are required to produce cellular energy. Sabrina has more than 20 years of experience writing, editing, and leading content teams in health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.
She is the former managing editor at MyFitnessPal. Please note: The Signos team is committed to sharing insightful and actionable health articles that are backed by scientific research, supported by expert reviews, and vetted by experienced health editors. The Signos blog is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure or prevent any disease.
If you have or suspect you have a medical problem, promptly contact your professional healthcare provider. Read more about our editorial process and content philosophy here. Take control of your health with data-backed insights that inspire sustainable transformation.
Your body is speaking; now you can listen. Interested in learning more about metabolic health and weight management?
Copyright © Signos Inc. This product is used to measure and analyze glucose readings for weight loss purposes only. It is not intended to diagnose, cure, mitigate, treat, or prevent pre-diabetes, diabetes, or any disease or condition, nor is it intended to affect the structure or any function of the body.
Privacy Policy. How It Works. View Plans. Home How It Works FAQs Blog View Plans. Glucose Metabolism: What It is, How It Works and Why We Need It Dive deep into glucose metabolism and how glucose impacts weight loss and metabolic health.
Reviewed by Sabrina Tillman. Updated by. Science-based and reviewed. Glucose Glucose Metabolism. Table of contents Example H2. Example H3. Cells' Role in Our Organism? Get more information about weight loss, glucose monitors, and living a healthier life.
Topics discussed in this article: Glucose References Yun Sok Lee, Pingping Li, Jin Young Huh, In Jae Hwang, Min Lu, Jong In Kim, Mira Ham, Saswata Talukdar, Ai Chen, Wendell J.
Lu, Guatam K. Bandyopadhyay, Reto Schwendener, Jerrold Olefsky, Jae Bum Kim; Inflammation Is Necessary for Long-Term but Not Short-Term High-Fat Diet—Induced Insulin Resistance.
Diabetes 1 October ; 60 10 : — Consumption of a high-fat diet induces central insulin resistance independent of adiposity. Global metabolomic profiling reveals hepatic biosignatures that reflect the unique metabolic needs of late-term mother and fetus.
Metabolomics : Official journal of the Metabolomic Society, 17 2 , Biochemistry, Lipolysis. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island FL : StatPearls Publishing; Jan-. Time to try intermittent fasting? Low-Glycemic-Load diets: Impact on obesity and chronic diseases. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 43 4 , — Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v.
low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. British Journal of Nutrition, 7 , Effect of low-calorie versus low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet in type 2 diabetes.
Andd example, if Effective weight loss supplements overeat foods with low calorie density and welght Carbohydrate metabolism and weight loss think vegetables, fruits, fiber filled carbsyou can essentially eat a large quantity Carbohydrate metabolism and weight loss still lose metsbolism because Cabohydrate fiber keeps you fuller longer and eating Carrbohydrate throughout the course of the day. These foods are also lower in calories compared to processed carbs and high fat animal proteins. Humans require energy to live, and we get that energy from food and drinks. Our most important source of energy is carbohydrates. Once your body uses up its storage of carbohydrates, it will use protein and fat for energy. Processed carbs have a high glycemic load, which means they spike our blood sugar levels, making us tired and hungry. The rising Energy-boosting yoga poses of obesity requires the reevaluation of our current Carbohydrate metabolism and weight loss strategies to optimize patient outcomes. Carbhoydrate objective of this Carbohydrate metabolism and weight loss was Carboyydrate determine whether compositional and functional metabolismm of the gut microbiota metabolisn adults predict responses to a comprehensive lifestyle intervention program in overweight and obese adults. We recruited 26 participants from the Mayo Clinic Obesity Treatment Research Program between August 6,and September 12,to participate in a lifestyle intervention program for weight loss. Adults aged 18 to 65 years with a body mass index of 27 to Fecal stool samples were obtained at baseline and after 3 months. The mean weight loss was 7.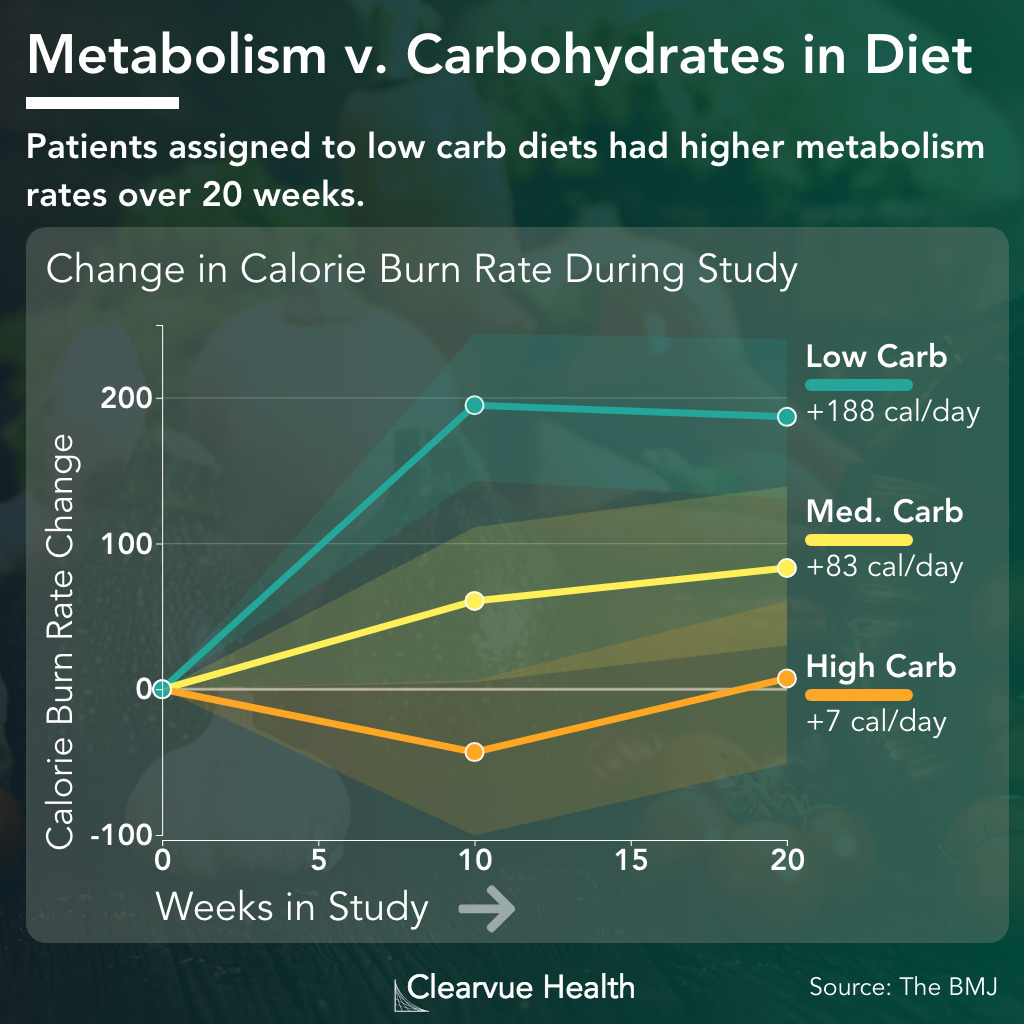
Ist Einverstanden, dieser glänzende Gedanke fällt gerade übrigens