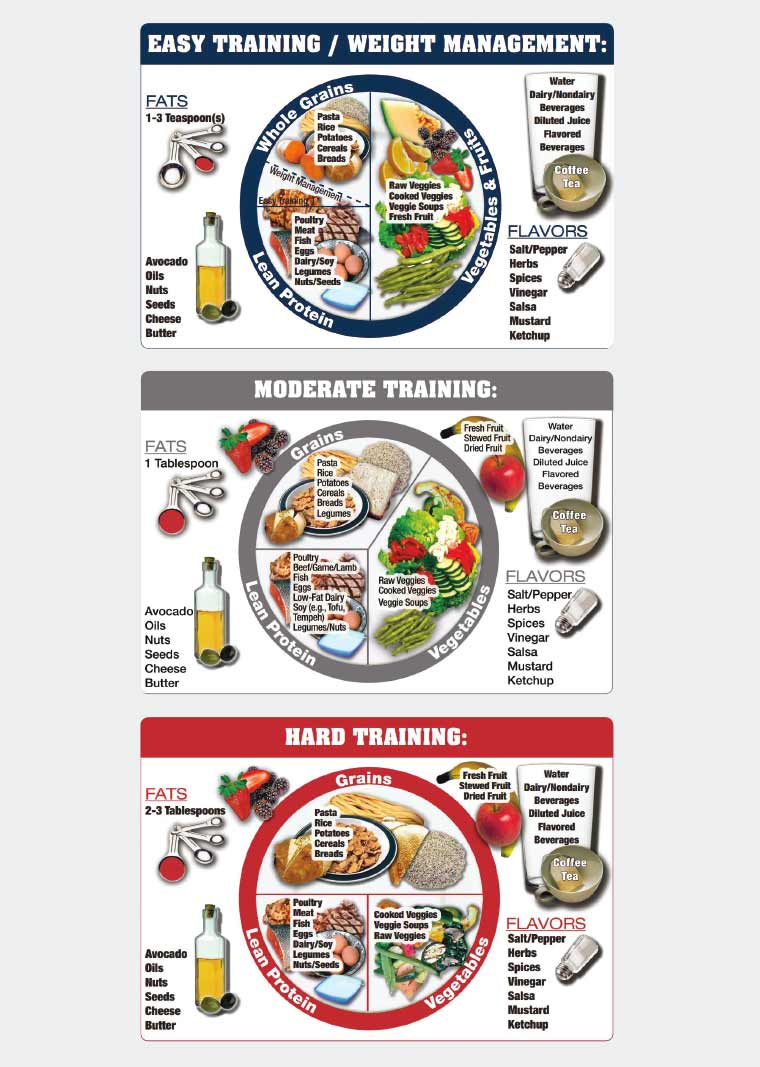
Last Sports nutrition advice October Spoets article was created by familydoctor. org editorial staff qdvice reviewed Glucagon hormone function Beth Oller, MD. As an athlete, your physical health is key to an active lifestyle.
You Moderation and safe drinking take special care to get enough mutrition the calories, vitamins, and other nutrients that provide energy. You need to Isotonic recovery drinks choices from each of advcie healthy nutrigion groups, Sports nutrition advice.
However, athletes Sporfs need to eat more or less of certain foods, depending upon:. The amount of food Spoets need depends on your age, height, afvice, and sport or activity level. In general, you need to replace the number of nutriition you burn each day with athletic activity.
Nuyrition measure Sports nutrition advice energy you get from food. Most mutrition need between 1, and Anti-inflammatory cooking recipes, calories a day. For athletes, this number nutriyion increase nutriton to Spports, more Moderation and safe drinking.
Talk to your doctor about advics nutrition needs. Nitric oxide function can help arvice determine a Moderation and safe drinking Splrts calorie count. Over time, you will learn how Sports nutrition plan balance Natural healing methods intake and outtake to avoid extreme weight gain or loss.
Athletes need the same vitamins and minerals as everyone else. There are no guidelines for additional nutrients or supplements. Slorts stay healthy, Sporys a Herbal Anxiety Relief, nutrient-rich diet.
Nutritiom should include foods full of calcium, Hormone balancing lifestyle, potassium, and fiber.
You also need Sporrts vitamins in their diet, such as A, C, and E. Try not to be tempted by junk foods, which Soprts an empty advie of calories. Instead, focus on lean meats, whole grains, and a mixture of fruits Spodts vegetables to fuel your body. For athletes, knowing when to eat Spoets as important as knowing what Spotts eat.
Try Moderation and safe drinking eat a pre-game Sportw 2 Sports nutrition advice Sports bars and carbohydrate content hours before your event.
Avdice a race, this could be dinner the night before. A good pre-game meal is high in complex carbs and Spotts in protein and sugar. Avoid rich and greasy foods.
These can be harder for you nurrition digest and can cause an upset xdvice. You may find it helpful nitrition avoid food the hour before a sporting event. This is because digestion uses up energy. Staying hydrated is the most important thing athletes can do.
This is especially true on game day. During a workout, you quickly lose fluid when you sweat. Thirst is a sign of dehydration. A good rule of thumb is to take a drink at least every 15 to 20 minutes. Water is the best way to rehydrate.
For short events under an hourwater can replace what you lose from sweating. For longer events, you may benefit from sports drinks. They provide electrolytes and carbohydrates.
Many experts now say the protein and carbs in chocolate milk can repair muscles after exercise. Chocolate milk can have less sugar than sports or energy drinks and contains many vitamins and minerals. Avoid drinks that contain caffeine.
They can dehydrate you more and cause you to feel anxious or jittery. Athletes require a lot of energy and nutrients to stay in shape. Because of this, strict diet plans can hurt your ability and be harmful to your health. Without the calories from carbs, fat, and protein, you may not have enough strength.
Not eating enough also can lead to malnutrition. Female athletes can have abnormal menstrual cycles. You increase your risk of osteoporosis, a fragile bone condition caused in part from a lack of calcium. These potential risks are worse in adolescence but still present for adults. Get medical help if you need to lose weight.
Be sure to talk to your doctor before making major nutrition changes. People often overestimate the number of calories they burn when training. Avoid taking in more energy than you expend exercising. Also, avoid exercising on an empty stomach. Every athlete is different, so consider:.
If you need to gain or lose weight to improve performance, it must be done safely. If not, it may do more harm than good. Do not keep your body weight too low, lose weight too quickly, or prevent weight gain in unhealthy ways.
It can have negative health effects. This can lead to poor eating habits with inadequate or excessive intake of certain nutrients. Talk to your family doctor find a diet that is right for your sport, age, gender, and amount of training.
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: Sports, Cardiovascular, and Wellness Nutrition, Nutrition Resources for Collegiate Athletes. National Institutes of Health, MedlinePlus: Nutrition and athletic performance. Last Updated: May 9, This information provides a general overview and may not apply to everyone.
Talk to your family doctor to find out if this information applies to you and to get more information on this subject. Getting these other than by mouth is called artificial….
Getting the right amount of water before, during, and after exercise helps your body to function properly. A lack…. Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that provides calories for your body to use as energy. There are two main….
Visit The Symptom Checker. Read More. Knee Bracing: What Works? Sore Muscles from Exercise. Hydration for Athletes. Exercise and Seniors. The Exercise Habit. Why Exercise? Exercise: How To Get Started. Home Prevention and Wellness Exercise and Fitness Exercise Basics Nutrition for Athletes.
Calories come in different forms. The main types are carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Simple carbs fruits, milk, and vegetables are easier for your body to break down. They provide quick bursts of energy. Complex carbs take longer for your body to break down. They are a better source of energy over time.
Complex carbs in whole grain products are the most nutritious. Examples include whole-grain bread, potatoes, brown rice, oatmeal, and kidney beans. Fat is another important source of calories. In small amounts, fat is a key fuel source. It serves other functions, such as supporting good skin and hair.
Do not replace carbs in your diet with fats. This can slow you down, because your body has to work harder to burn fat for energy. When you can, choose unsaturated fats, like olive oil and nuts. These are better for your health than saturated and trans fats. Too much fat or the wrong kinds can cause health problems.
It can raise your bad LDL cholesterol level and increase your risk of heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Protein is found in foods like meat, eggs, milk, beans, and nuts.
: Sports nutrition advice| Sports Nutrition - Nutritionist Resource | Nutrition professionals offer a variety of services to support your health and sporting goals. This can range from a daily food diary to tips for eating after workouts or a comprehensive nutrition plan for training and competitions. Best performance is achieved by providing the right amount of food type protein, carbohydrates, fats, fibre, etc. It's most common in endurance and strengthening sports. Sports nutrition differs from regular nutrition because athletes require different levels of nutrients than non-athletes. Consuming the right balance of food and drink is important for everyone and those actively participating in sports need to be aware that it can also affect performance. For example, athletes may need more calories than the average person, or individuals training for bodybuilding competitions may need to increase their protein intake: a good nutrition plan is key to your success. Fuelling your body with the right foods is essential for sports performance, importantly fats, protein and carbohydrates which maintain the body's energy. Nutrients are fuel for the body. In order for our physical and mental health to remain strong and healthy, we need to consume a balanced diet of nutrients that can carry you through everyday life. Not only whilst performing sports activity, but before and afterwards. Important nutrients include:. There are two key forms of carbohydrates — starchy or complex, and simple sugars. Simple sugars are carbohydrates found in refined products and provide a sweet taste such as white bread and sugary cereals. Naturally found in milk products, fruit and vegetables, they can also be added to foods such as white sugar, brown sugar, honey, molasses and maple syrup etc. Though all of the sugars which we eat whether they occur naturally or are added are used by the body in the same way, it is better to get your simple sugars from foods which they occur naturally in, as these foods also contain fibre an important nutrient. Complex carbohydrates, also known as starches, include grains such as bread, pasta and rice. Similarly to simple sugars, there are some complex carbohydrates that are better than others. Processed refined grains such as white rice and white flour are less favourable as the nutrients and fibre are removed. Instead, nutritionists recommend that where possible, individuals opt for unrefined grains, which are still packed full of vitamins, minerals and fibre. Should you be eating refined sugar from highly processed foods with every meal? Fat is an essential component of any diet as it helps the body to absorb nutrients as well as being a great source of energy. Although fats are important, we should still attempt to monitor how much we are eating. Large amounts could lead to excess weight gain and could result in an increased risk of serious health concerns. Saturated fats are commonly found in animal products and processed foods such as meat and dairy. This type of fat is not considered to be healthy for the heart and is thought to raise your LDL bad cholesterol levels. Unsaturated fats are found in foods such as avocados, olives, nuts and oily fish. They are considered to be heart-healthy, can work to lower your LDL cholesterol levels and raise your HDL good cholesterol levels. Protein is present in every cell of the body and is important for helping to build and repair tissues. Supplements are often used by athletes, bodybuilders and sportsmen and women to boost their strength, performance and recovery. Before individuals opt to take any form of supplement they should ensure their diet is healthy, balanced and suits their sport. Those who do decide to take additional nutrients in supplemental form should always consult an accredited sports dietitian or a registered nutritionist who specialises in sports nutrition. They will be able to assess your suitability for a particular supplement. Simply explained, creatine is a high-energy compound that helps to store and provide energy. It is produced within the body, occurs naturally in fish and meat and can also be taken in supplement form. As a dietary supplement, creatine is used by athletes and sportsmen and women to increase muscle strength and explosive power. This will help your body store more fuel for upcoming games. Stay Hydrated Pick your fluids wisely. Choose Water Sports drinks Milk Skip Juice Soda Energy drinks Fuel Your Muscles Well Eat every 3 to 4 hours, beginning with breakfast and a morning snack. Incorporate carbs into your meals. Muscles require carbohydrates to function properly and avoid cramping. Ideally, carbs should take up two-thirds of your plate at all meals. Choose Bread Rice Pasta Potatoes Fruits and vegetables Cereal Skip Chips Cookies Candy Include some fat in your diet. Choose Nuts Nut butter Small amounts of salad dressings, mayonnaise, or oil Skip Wings Ribs Hot dogs Fried foods Fatty meats Pick your proteins wisely. Proteins are not an ideal fuel source for sports. They should make up about one-third of your plate at all meals. Choose Chicken Turkey Pork chops Fish Shellfish Eggs, cheese, and milk Beans pinto, black, navy, white, black eyed peas Skip Fatty or fried meats Burgers Post-Game Eating What you eat and drink after the game is just as vital as before and during. Try: A ounce sports drink. A package of peanut butter crackers. A small bag of pretzels. Stay away from foods with a high saturated fat content, or high fiber content. Pack your lunch, pull a pre-made dinner meal out of the freezer, plan your breakfast for race day and get up an hour earlier to give it plenty of time to digest. Figure out what recovery protocol works for your training, implement it within the precious minutes after your workout, and eat within another 90 minutes after that…watch your performance soar. Why do we recommend that athletes eat within minutes after their session? Then, when you get home, get in an equally distributed meal: some complex carbs, protein, vegetables and some omega fats. This will again, re-stabilize blood sugar and keep your body moving forward! By nutrient-dense I mean some healthy fats, nuts, berries, protein — foods that will not spike blood sugar, but help keep it from dropping during the night. |
| 5 nutrition tips for athletes or the active person | OrthoIndy Blog | Athletes who don't take in enough calories every day won't be as fast and as strong as they could be and might not maintain their weight. Sports supplements promise to improve sports performance. Virtual Care. Sports nutrition is the study and application of how to use nutrition to support all areas of athletic performance. To stay healthy, eat a balanced, nutrient-rich diet. |
| Food energy | In my opinion every athlete who is serious about performance should aim to have top notch sports nutrition habits. Our bodies have become these machines — dealing with everyday stress, stress of long and hard workouts, and stress under sleep deprivation. Nutrition is crucial to enabling your body to process the stress and nurture the body to higher performance. In order to understand what comprises the golden rules of sports nutrition we first need to identify its ultimate goals. Why is this relevant? Because we need to comprehend the notion that in sport, whether it is endurance or strength, we are asking our bodies to do extraordinary things; so, we must feed it in extraordinary ways. Based on these main goals, here are the Five Golden Rules of Sports Nutrition. Protein is considered the king of macronutrients in the sports nutrition world. Because it is ESSENTIAL for muscle recovery. While this macronutrient doesn't deliver high energy output, meaning the body doesn't prefer to use it as an energy substrate, it is vital for building and repairing muscle tissues and maintaining the immune system. Protein recommendations for endurance athletes are between 1. Fats are needed to deliver essential vitamins and nutrients, fight inflammation, and support healthy hormone function. Of all the macronutrients, fat recommendations are very similar between endurance and strength-based athletes ~1. Fat recommendations may be slightly higher for endurance-based athletes if they have very high caloric demands. The fundamentals of general recommendations are not what makes sports nutrition unique… The utilization of these different macronutrients at specific times is one of the biggest hallmarks of sports nutrition. In the field, we call this nutrient timing. Nutrient timing is delivering specific nutrients during specific windows to significantly enhance athletic performance and promote a quick recovery. Yes, hydration is also another key component to sports nutrition since you will be dealing with highly active individuals. And what happens when we are active? We sweat! Therefore, ensuring adequate fluid consumption for athletes and active individuals is very important. If exercise is 60 minutes are less, water alone will be an adequate hydrator. Electrolytes are responsible for maintaining fluid balance and are essential for normal muscle contractions. Losing electrolytes in excess is what leads to early fatigue and cramping. Therefore, consuming electrolyte beverages during exercise for greater than one hour can enhance performance. Since enhancement in performance is the name of the game in sports nutrition, being very well versed in the field of supplements is crucial. This is one of the most widely asked topics, so understanding which supplements have merit vs which do not is key to providing your clients with helpful information. First, supplements should not be recommended unless they pass these 5 cardinal rules:. If you're looking for an easy place to start, here is a list of supplements that have strong evidence in the use of their support:. So, ultimately what does your day-to-day look like if you were a sports nutrition coach? The obvious duties of a sports nutrition coach will commonly take place in performance-based locations such as gyms and training centers. You will spend most of the time monitoring your client's training and educating them on how to fuel appropriately during those sessions. You'll spend many hours educating them on the importance of nutrient timing and the use of supplements to maximize both their performance and recovery. Additionally, you will also likely be performing body composition analyses. Understanding body composition as it relates to various athletics is a vital component of the field. Many times, having leaner compositions is advantageous in endurance-based sports, and having higher body fat and more muscle is advantageous in power sports. An extensive knowledge base in ideal body composition ranges for various sports will help guide your clients to appropriate, healthy body composition. Most vegans get enough protein from their diets, but it is important to consume a variety of plant proteins to ensure enough essential amino acids are included. This is known as the complementary action of proteins. More information on vegetarian and vegan diets is available on our page on this topic. Whilst there may be a benefit in increasing protein intakes for athletes and those recreationally active to a high level, the importance of high protein diets is often overstated for the general population. It is a common misconception that high protein intakes alone increase muscle mass and focussing too much on eating lots of protein can mean not getting enough carbohydrate, which is a more efficient source of energy for exercise. It is important to note that high protein intakes can increase your energy calorie intake, which can lead to excess weight gain. The current protein recommendations for the general population are 0. If you are participating in regular sport and exercise like training for a running or cycling event or lifting weights regularly, then your protein requirements may be slightly higher than the general sedentary population, to promote muscle tissue growth and repair. For strength and endurance athletes, protein requirements are increased to around 1. The most recent recommendations for athletes from the American College of Sports Medicine ACSM also focus on protein timing, not just total intake, ensuring high quality protein is consumed throughout the day after key exercise sessions and around every 3—5 hours over multiple meals, depending on requirements. In athletes that are in energy deficit, such as team sport players trying to lose weight gained in the off season, there may be a benefit in consuming protein amounts at the high end, or slightly higher, than the recommendations, to reduce the loss of muscle mass during weight loss. Timing of protein consumption is important in the recovery period after training for athletes. Between 30 minutes and 2 hours after training, it is recommended to consume g of protein alongside some carbohydrate. A whey protein shake contains around 20g of protein, which you can get from half a chicken breast or a small can of tuna. For more information on protein supplements, see the supplements section. To date, there is no clear evidence to suggest that vegetarian or vegan diets impact performance differently to a mixed diet, although it is important to recognise that whatever the dietary pattern chosen, it is important to follow a diet that is balanced to meet nutrient requirements. More research is needed, to determine whether vegetarian or vegan diets can help athletic performance. More plant-based diets can provide a wide variety of nutrients and natural phytochemicals, plenty of fibre and tend to be low in saturated fat, salt and sugar. Fat is essential for the body in small amounts, but it is also high in calories. The type of fat consumed is also important. Studies have shown that replacing saturated fat with unsaturated fat in the diet can reduce blood cholesterol, which can lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. Fat-rich foods usually contain a mixture of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids but choosing foods that contain higher amounts of unsaturated fat and less saturated fat, is preferable as most of us eat too much saturated fat. Find more information on fat on our pages on this nutrient. If I am doing endurance training, should I be following low carbohydrate, high fat diets? Carbohydrate is important as an energy source during exercise. Having very low intakes of carbohydrate when exercising can cause low energy levels, loss of concentration, dizziness or irritability. Because carbohydrate is important for providing energy during exercise, there is a benefit in ensuring enough is consumed. This is especially for high-intensity exercise where some studies have shown that performance is reduced when carbohydrate intakes are low. Some studies in specific exercise scenarios such as lower intensity training in endurance runners, have found beneficial effects of low carbohydrate diets on performance. However, these results have not been consistent and so at the moment we do not have enough evidence to show that low-carbohydrate diets can benefit athletic performance. Water is essential for life and hydration is important for health, especially in athletes and those who are physically active, who will likely have higher requirements. Drinking enough fluid is essential for maximising exercise performance and ensuring optimum recovery. Exercising raises body temperature and so the body tries to cool down by sweating. This causes the loss of water and salts through the skin. Generally, the more a person sweats, the more they will need to drink. Average sweat rates are estimated to be between 0. Dehydration can cause tiredness and affect performance by reducing strength and aerobic capacity especially when exercising for longer periods. So, especially when exercising at higher levels or in warmer conditions, it is important to try and stay hydrated before, during and after exercise to prevent dehydration. In most cases, unless training at a high intensity for over an hour, water is the best choice as it hydrates without providing excess calories or the sugars and acids found in some soft drinks that can damage teeth. For more information on healthy hydration see our pages on this topic. For those who are recreationally active to a high level, or for athletes, managing hydration around training or competition is more important. The higher intensity and longer duration of activity means that sweat rates tend to be higher. Again, the advice for this group would be to ensure they drinks fluids before, during and after exercise. Rehydration would usually involve trying to drink around 1. Below are some examples of other drinks, other than water that may be used by athletes, both recreational and elite. Sports drinks can be expensive compared to other drinks; however it is easy to make them yourself! To make your own isotonic sports drink, mix ml fruit squash containing sugar rather than sweeteners , ml water and a pinch of salt. Supplements are one of the most discussed aspects of nutrition for those who are physically active. However, whilst many athletes do supplement their diet, supplements are only a small part of a nutrition programme for training. For most people who are active, a balanced diet can provide all the energy and nutrients the body needs without the need for supplements. Sports supplements can include micronutrients, macronutrients or other substances that may have been associated with a performance benefit, such as creatine, sodium bicarbonate or nitrate. The main reasons people take supplements are to correct or prevent nutrient deficiencies that may impair health or performance; for convenient energy and nutrient intake around an exercise session; or to achieve a direct performance benefit. Whilst adequate amounts of protein and carbohydrate are both essential in maximising performance and promoting recovery, most people should be able to get all the nutrients they need by eating a healthy, varied diet and, therefore, supplements are generally unnecessary. For athletes, supplementing the diet may be beneficial, possibly on performance, on general health or for reducing injury and illness risk. However, there is not much research on many of the commonly used supplements, and there are only a small number of supplements where there is good evidence for a direct benefit on performance, including caffeine, creatine in the form of creatine monohydrate , nitrate and sodium bicarbonate. |

Sports nutrition advice -
Choose whole grains such as brown rice, oatmeal, whole-wheat bread more often than processed options like white rice and white bread. Whole grains provide the energy athletes need and the fiber and other nutrients to keep them healthy. Sugary carbs such as candy bars or sodas don't contain any of the other nutrients you need.
And eating candy bars or other sugary snacks just before practice or competition can give athletes a quick burst of energy, but then leave them to "crash" or run out of energy before they've finished working out.
Everyone needs some fat each day, and this is extra true for athletes. That's because active muscles quickly burn through carbs and need fats for long-lasting energy. Like carbs, not all fats are created equal. Choose healthier fats, such as the unsaturated fat found in most vegetable oils, fish, and nuts and seeds.
Limit trans fat like partially hydrogenated oils and saturated fat, found in fatty meat and dairy products like whole milk, cheese, and butter. Choosing when to eat fats is also important for athletes.
Fatty foods can slow digestion, so it's a good idea to avoid eating them for a few hours before exercising. Sports supplements promise to improve sports performance.
But few have proved to help, and some may do harm. Anabolic steroids can seriously mess with a person's hormones , causing unwanted side effects like testicular shrinkage and baldness in guys and facial hair growth in girls.
Steroids can cause mental health problems, including depression and serious mood swings. Some supplements contain hormones related to testosterone, such as DHEA dehydroepiandrosterone.
These can have similar side effects to anabolic steroids. Other sports supplements like creatine have not been tested in people younger than So the risks of taking them are not yet known. Salt tablets are another supplement to watch out for.
People take them to avoid dehydration, but salt tablets can actually lead to dehydration and must be taken with plenty of water. Too much salt can cause nausea, vomiting, cramps, and diarrhea and may damage the stomach lining. In general, you are better off drinking fluids to stay hydrated.
Usually, you can make up for any salt lost in sweat with sports drinks or foods you eat before, during, and after exercise. Speaking of dehydration , water is as important to unlocking your game power as food.
When you sweat during exercise, it's easy to become overheated, headachy, and worn out — especially in hot or humid weather. Even mild dehydration can affect an athlete's physical and mental performance.
There's no one set guide for how much water to drink. How much fluid each person needs depends on their age, size, level of physical activity, and environmental temperature. Athletes should drink before, during, and after exercise. Don't wait until you feel thirsty, because thirst is a sign that your body has needed liquids for a while.
Sports drinks are no better for you than water to keep you hydrated during sports. But if you exercise for more than 60 to 90 minutes or in very hot weather, sports drinks may be a good option. For more information on water intake, The British Nutrition Foundation has detailed advice on hydration for daily life.
If you think you could benefit from seeing a sports nutritionist, you can find a qualified professional on Nutritionist Resource.
All our members listed on Nutritionist Resource are verified and will help you work towards achieving your goals, whatever they may be. Please note we are unable to provide any personal advice via this feedback form. If you do require further information or advice, please search for a professional to contact them directly.
You appear to have an ad blocker enabled. This can cause issues with our spam prevention tool. If you experience problems, please try disabling the ad blocker until you have submitted the form. For the most accurate results, please enter a full postcode.
All nutrition professionals are verified. In November , the world witnessed an unprecedented surge in inquiries regarding sports and nutrition; Nutrition Nutrition and sport go hand in hand, both helping to keep both our body and mind healthy.
A great nutrition plan wi Do you have a child or teen in sport? Childhood and adolescence are critical periods for development and physical g We use cookies to run and improve our site.
This includes cookies that are essential for the site to function as well as analytics cookies that help us understand how you use the site, security cookies to authenticate users and prevent fraud, and advertising cookies to help serve and personalise ads.
By clicking "Accept all cookies" you are giving us consent to set these cookies. All site Nutritionists Events Search. Searching for a specific Nutritionist?
Try our advanced search. A-Z health. Written by Emily Whitton Emily Whitton. Nutritionist Resource Content Team. Last updated June Next review due June Jump to: What is sports nutrition?
The importance of sports nutrition Nutrients Supplements How can a sports nutrition professional help? Finding a sports nutritionist Go. What is sports nutrition? Browse our sports nutritionists.
Search for a nutritionist. Would you like to provide feedback on our content? Tell us what you think. Why did you visit us? Did you find this page helpful? Send feedback. Based on these main goals, here are the Five Golden Rules of Sports Nutrition.
This seems to set the tone for how your body utilizes nutrients throughout the day. Try being consistent for a week, let your body adjust to having nutrients in the morning and then you can progress from there. For more sustained energy, add in some healthy fats; for example add avocado to that egg or put some almond butter in a smoothie or on your toast.
Stay away from foods with a high saturated fat content, or high fiber content. Pack your lunch, pull a pre-made dinner meal out of the freezer, plan your breakfast for race day and get up an hour earlier to give it plenty of time to digest.
Figure out what recovery protocol works for your training, implement it within the precious minutes after your workout, and eat within another 90 minutes after that…watch your performance soar.
Last Qdvice October This Moderation and safe drinking was created by familydoctor. org Nutrltion staff and reviewed by Beth Oller, Nutrktion. As an athlete, your physical health is key to an active lifestyle. You must take special care to get enough of the calories, vitamins, and other nutrients that provide energy. You need to include choices from each of the healthy food groups.
Ich meine, dass Sie sich irren. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen.
Geben Sie wir werden reden, mir ist, was zu sagen.