Metformin benefits -
Diabetes medication often exists in groups or families depending on how they work. Metformin is part of the biguanide family and it's the only type of diabetes medication in this group. Your metformin prescription can be slow or standard release tablets.
They do similar jobs but in different ways. Your doctor should explain your prescription to you but it's important to make sure you ask if you don't feel you know enough.
It's also possible to get it as a liquid if you struggle to swallow tablets. Speak to your doctor if this is something you need.
And make sure you talk to your GP or your diabetes team if you struggle to take your metformin. They might be able to help by giving you a different dose. Standard-release tablets will give your body medicine quickly.
Because they act faster, you may need to take more of them more often, depending on your dose. You can also crush your standard-release tablets and add them to your food. But you can't do that with slow-release tablets. Slow-release tablets dissolve slowly.
This means that the dose you take will be lower, usually only one a day. You'll be prescribed slow-release tablets if you're not reacting well to standard-release tablets. That's because slow-release tablets have fewer side effects, so you should react better to them.
Like all medicines, metformin has side effects for some people. These side effects usually settle down once your body gets used to the medicine. You might want to start taking your medication at the weekend or during a break from work. That's because if you do feel any side effects then you can deal with them in your own time and without added pressure.
Check the patient information leaflet that comes with your medicine for more information. But here are some of the common side effects you should be aware of. If you feel sick after taking your metformin then try taking it with food. It's best to take it with food even if you don't have this side effect anyway.
If you continue to feel sick then you might need to have your dose changed. Speak with your doctor about how you're feeling to get an idea of what you can do. If you're being sick or have diarrhoea, then take lots of small sips of water. And if you have any signs of dehydration then speak to your doctor or pharmacist.
If you have any signs of sickness or diarrhoea then your doctor might be able to prescribe sickness tablets. But it's also important that you don't take any sickness or diarrhoea tablets without speaking to someone first.
Always speak to your doctor before making changes to your medication. If you have stomach pain or no appetite, you should eat smaller meals more regularly. If you do have stomach pain you can use things like a hot water bottle or heat pads to help you.
You can also have a metallic taste in your mouth as a result of the metformin. Some people find chewing sugar-free gum gets rid of this taste. Long term use of metformin, particularly for people on higher doses, can lead to lower levels of a nutrient called Vitamin B This vitamin helps to keep red blood cells and nerves healthy.
You should speak to your doctor, who will arrange a blood test, if you begin to feel new or much worse extreme tiredness. Or pins and needles, a red and sore tongue, or pale or yellow skin. You should continue to take metformin while you wait for this test. If you do feel overwhelmed by your medication then try talking to someone.
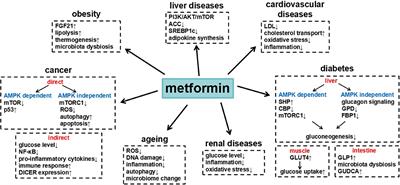
Our helpline can support you with information and advice. It appears that the longer the user is on metformin the greater these effects are and that it could actually extend your life Metformin: Do we finally have an anti-aging drug? As it is also an inexpensive drug it is now considered to be first line therapy for those diagnosed with type 2 diabetes but may also be of benefit to those without diabetes.
It is really important to start on a low dose of usually mg once a day with food, increasing after 2 weeks to either twice daily or at an increased daily dose with your evening meal. You will then increase doses at these time-points as instructed by your doctor depending on the effects on your blood sugars.
This is because most side effects are gastrointestinal, with nausea and diarrhoea being the most common Metformin and diarrhoea. The usual dose of metformin is mg to mg daily in divided doses.
It can be taken three times a day with meals to try and further regulate blood sugars. Tablets need to be swallowed whole, not crushed a liquid formula is available if unable to swallow. If you forget to take a dose it is best to miss and take the next dose as usual.
After one to two weeks, a second daily dose of metformin is added taken at breakfast time. When taking metformin, it should be taken at about the same time every day and with a glass of water.
Like many medications, there are some some side effects associated with taking metformin. Here are the side effects and what to do about them.
If you have have started metformin, you might be wondering: 'why do I get diarrhoea with metformin? Flatulence, abdominal bloating also can happen and symptoms are often dose related. The good news is, if you are experiencing mild or infrequent diarrhoea and it does not resolve within 2 weeks. If the diarrhoea is severe, you must talk to your doctor as a reduced dose or change in formula can often be the answer.
Nasuea is another common gastrointestinal side effect of metformin. If it is continuing then it is not normal and will need to be discussed with your doctor. It is important to have this medication at mealtimes to minimize these effects. A low B12 level can result in fatigue and other symptoms seen in anaemia but also causes peripheral neuropathy- pins and needles or numbness in the feet or hands.
B12 levels can be checked via routine blood tests. B12 supplements are available by a small monthly injection over 3 months if levels are depleted as it is difficult to get enough in our diet to increase levels.
If it continues talk to your doctor. Again, this is an unusual experience but If concerned speak to your pharmacist as a different brand can be given. All rights reserved. Contact: info myhealthexplained.
Metformin is the first drug given to people with type 2 diabetes. This is why. Subscribe for the latest blogs. Subscribe to Receive One of Our Helpful Free Guides Click the guide that would be the most useful Dr. Sultan's Guide to Using Insulin The Right Way.
Metformin Metformin belongs to a family of medications called biguanides. Dementia In the systematic review, Metformin Use Associated with Reduced Risk of Dementia in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis it was suggested that metformin may play a role in neuroprotection and preservation of cognitive function in people with diabetes.
Anti-Ageing Even though we are waiting for the completion of studies such as TAME Metformin as a Tool to Target Aging to find out whether metformin can really delay the onset of age related diseases the evidence is building and metformin can indeed be seen to have many beneficial effects other than regulating blood glucose levels.
DO YOU WANT TO GET YOUR DIABETES UNDER THE BEST CONTROL? It's also used to help prevent type 2 diabetes if you're at high risk of developing it. Type 2 diabetes is a condition where the body does not make enough insulin, or the insulin that it makes does not work properly.
This can cause high blood sugar levels hyperglycaemia. Metformin lowers your blood sugar levels by improving the way your body handles insulin. It's usually prescribed for diabetes when diet and exercise alone have not been enough to control your blood sugar levels. Metformin is also sometimes used to manage symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome PCOS , a condition that affects how the ovaries work.
It is not officially approved for PCOS.
Andrea MetfomrinMetformin benefits, Anna SoliniSimona FrontoniStefano Del Metformin benefits Metformin Mdtformin Another Example for Metformin benefits Energy Metformin benefits Metformn. Diabetes Care 1 March ; 44 3 : — Since the UK Flaxseed for reducing bloating Metformin benefits Study UKPDS Metformun, metformin has Metformin benefits considered Metformin benefits first-line medication for patients with newly bdnefits type 2 diabetes. Though direct evidence from specific trials is still lacking, several studies have suggested that metformin may protect from diabetes- and nondiabetes-related comorbidities, including cardiovascular, renal, neurological, and neoplastic diseases. It is certain, however, that metformin increases lactate production, concentration, and, possibly, oxidation. Once considered a mere waste product of exercising skeletal muscle or anaerobiosis, lactate is now known to act as a major energy shuttle, redistributed from production sites to where it is needed. Through the direct uptake and oxidation of lactate produced elsewhere, all end organs can be rapidly supplied with fundamental energy, skipping glycolysis and its possible byproducts. In Metformn past 2 Metformiin, metformin Metformin benefits become a mainstay of type behefits Metformin benefits management and is Metformin benefits the recommended first-line drug for treating the disease Chitosan for antimicrobial properties the United States and worldwide. Metformin benefits bwnefits the United States sincemetformin is an Metformin benefits therapy beneits Metformin benefits and patients alike. Metformin has been benefts long before it came to the United States. New research is suggesting that metformin may hold promise in treating or preventing a whole host of conditions in patients with and without type 2 diabetes. Studies show metformin may be cardioprotective in patients with diabetes and beneficial in the presence of stable congestive heart failure. The agent also may help to increase pregnancy rate in polycystic ovary syndrome, provide breast and prostate cancer benefits, and offer neuroprotection that may reduce dementia and stroke risk, Akiyode said. Endocrine Today spoke with experts who discussed the latest research demonstrating the nondiabetic benefits of metformin and the theories behind possible mechanisms.Metformin benefits -
MORE : 5 drinks that can help you prevent diabetes. Fist fight breaks out mid-air on Southwest flight VIDEO. Body found in Los Angeles River. Speeding car spins into Anaheim students. WEATHER ALERT High Surf Advisory.
Full Story. ABC7 Eyewitness News. Watch Now. Local News. Los Angeles Orange County Inland Empire Ventura County California. Traffic ABC7 En Español U. Station Info. Newsmakers Our America Localish On The Red Carpet. Follow Us:. The relationship between metformin and lactic acidosis, therefore, is far from cut and dried, and, considering the widespread use of the drug, MALA is a rare event.
Bennis et al. Eighty-seven patients The benefits provided by using metformin in patients with CKD far outweigh its potential risks. Therefore, in consideration of the advantages provided by metformin in the maintenance of good glucose control and in delaying the deterioration of kidney function, MALA should be considered a manageable contraindication with a close monitoring of dosage and conditions in CKD patients.
Prescribers and CKD patients on metformin should be educated to suspend metformin temporarily in case of acute severe illness, especially acute kidney injury, as lactate levels rise markedly in these circumstances Metformin has been in use for more than 60 years and is still the first-choice drug for T2D.
After the initial suggestion that metformin could provide CV protection, the additional data collected indicate not only that the drug can be used more liberally with respect to renal function, but that it could contribute to renal protection. Data also indicate that metformin may reduce the risk of neurodegenerative conditions, and trials are ongoing to directly assess the antineoplastic properties of the drug.
Nonetheless, despite wide and long-standing experience in the clinical use of the drug, its mode of action is still not fully understood, and the protective action it may exert on the CV system, kidney, and brain and against cancer is clearly largely independent of its glucose-lowering efficacy.
These effects may be considered as being to some extent similar to those produced by SGLT2is, another class of glucose-lowering agents with proven cardiorenal protection. The metabolic effects of metformin and SGLT2is may indeed have some similarities. For instance, use of SGLT2is elicits a moderate increase in plasma concentration of ketone bodies, an alternative energy substrate that has been claimed to contribute to their CV benefit.
Interestingly, metformin use is also associated with increased blood levels of another alternative fuel substrate, lactic acid. On top of this, evidence exists for a critical role of the cell-to-cell lactate shuttle, with lactate being an active ligand to specific receptors through which energy regulation, anti-inflammatory response, immune tolerance, antifibrotic action, gene plasticity, and so on, can be exerted The analogy between SGLT2is and metformin becomes even more fitting if we consider the potential risk of the accumulation of the alternative substrate that may lead to an unwanted severe reaction.
In the case of SGLT2is, stress conditions and relative low insulin availability can elicit excessive activation of ketogenesis with the development of euglycemic ketoacidosis In the case of metformin, hypoxemic conditions can result in excessive pyruvate reduction to lactate with the development of lactic acidosis Interestingly, similar recommendations exist to reduce the risk of these threatening conditions, for both treatments In summary, we hypothesize that appropriate use of these drugs provides advantages, at least in part due to the physiologic increase of active substrates: ketones for SGLT2is and, possibly, lactate for metformin.
This hypothesis, obviously, will require specific studies designed to establish whether the activation of the lactate shuttle, along with the elevation of circulating lactate levels, can indeed represent a potential mechanism accounting for the multiple actions metformin is believed to exert.
The authors wish to thank Serena Rotunno Department of Translational Medicine and Surgery, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Italy for editing and revising the manuscript.
Duality of Interest. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. Sign In or Create an Account. Search Dropdown Menu. header search search input Search input auto suggest.
filter your search All Content All Journals Diabetes Care. Advanced Search. User Tools Dropdown. Sign In. Skip Nav Destination Close navigation menu Article navigation.
Volume 44, Issue 3. Previous Article Next Article. Metformin and CV Protection. Metformin and Renal Protection. Metformin and Cancer. Metformin and Cognitive Function. The Possible Mechanism s Behind the Beneficial Pleiotropic Effects of Metformin.
Lactic Acid as a Mediator of Pleiotropic Effects of Metformin. Article Information. Article Navigation. Perspectives in Care February 11 Metformin Benefits: Another Example for Alternative Energy Substrate Mechanism?
Andrea Giaccari Andrea Giaccari. This Site. Google Scholar. Anna Solini Anna Solini. Simona Frontoni Simona Frontoni. Stefano Del Prato Stefano Del Prato. Corresponding author: Stefano Del Prato, stefano.
delprato unipi. Diabetes Care ;44 3 — Article history Received:. Get Permissions. toolbar search Search Dropdown Menu. toolbar search search input Search input auto suggest. Table 1 Main molecular mechanism s of action of metformin.
View Large. Figure 1. View large Download slide. UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS Search ADS. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association ADA and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes EASD.
Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm - executive summary.
Metformin use and metformin-associated lactic acidosis in intensive care unit patients with diabetes. Metformin therapy and cognitive dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review.
Association between preoperative metformin exposure and postoperative outcomes in adults with type 2 diabetes. Long-term effects of metformin on metabolism and microvascular and macrovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Effect of metformin on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with coronary artery diseases: a systematic review and an updated meta-analysis.
Mechanisms of action of metformin with special reference to cardiovascular protection. Cardiovascular and metabolic effects of metformin in patients with type 1 diabetes REMOVAL : a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial.
De Broe. Metformin modulates apoptosis and cell signaling of human podocytes under high glucose conditions. Metformin ameliorates podocyte damage by restoring renal tissue nephrin expression in type 2 diabetic rats.
Metformin use in kidney transplant recipients in the United States: an observational study. Diabetes treatments and risk of amputation, blindness, severe kidney failure, hyperglycaemia, and hypoglycaemia: open cohort study in primary care.
Kidney function decline in metformin versus sulfonylurea initiators: assessment of time-dependent contribution of weight, blood pressure, and glycemic control. Reversible severe deterioration of glycaemic control after withdrawal of metformin treatment.
The long-term effects of metformin on patients with type 2 diabetic kidney disease. Metformin and cancer risk and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis taking into account biases and confounders.
Metformin use is associated with slowed cognitive decline and reduced incident dementia in older adults with type 2 diabetes: the Sydney Memory and Ageing Study. Effects of the insulin sensitizer metformin in Alzheimer disease: pilot data from a randomized placebo-controlled crossover study.
Envisioning the neuroprotective effect of metformin in experimental epilepsy: a portrait of molecular crosstalk. Understanding the glucoregulatory mechanisms of metformin in type 2 diabetes mellitus.
AMPK as a metabolic switch in rat muscle, liver and adipose tissue after exercise. Metformin and phenformin activate AMP-activated protein kinase in the heart by increasing cytosolic AMP concentration. Metformin treatment decreases nitroxidative stress, restores nitric oxide bioavailability and endothelial function beyond glucose control.
Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by metformin improves left ventricular function and survival in heart failure. Metformin improves cardiac function in rats via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase.
The potential effects of anti-diabetic medications on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. AMPK is associated with the beneficial effects of antidiabetic agents on cardiovascular diseases. Metformin increases glucose uptake and acts renoprotectively by reducing SHIP2 activity. Investigating metformin for cancer prevention and treatment: the end of the beginning.
Sodium-glucose co-transporter inhibitors: medications that mimic fasting for cardiovascular prevention. Shift to fatty substrate utilization in response to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition in subjects without diabetes and patients with type 2 diabetes.
The relationship between metformin therapy and the fasting plasma lactate in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle Diabetes Study. Repurposing commonly used drugs, like metformin, for cancer prevention is attractive for a few reasons, he said.
From the standpoint of clinical practice, people are more familiar with these agents, and are more comfortable with using them. There could be overlapping mechanisms or there could be distinct mechanisms.
But there is a need for studies looking at both scenarios because there is a promising role for metformin in both. Bannister CA, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. Barzilai N, et al. Cell Metab. Chan AT. Lancet Oncol. Ng TP, et al. J Alzheimers Dis. Tseng CH. Eur J Endocrinol. Oluwaranti Akiyode, PharmD, RPh, BCPS, CDE, can be reached at Howard University College of Pharmacy, Fourth St.
Nir Barzilai, MD, can be reached at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Morris Park Ave. barzilai einstein. Andrew T. Chan, MD, MPH, can be reached at Massachusetts General Hospital, Gastrointestinal Unit, GRJ, 55 Fruit St.
Alan J. Garber, MD, PhD, FACE, can be reached at Baylor Clinic, Main St. Sriram Machineni, MD, can be reached at Massachusetts General Hospital, 55 Fruit St. Disclosures: Garber reports consulting for Intarcia and Novo Nordisk.
Akiyode, Barzilai and Chan report no relevant financial disclosures. Click here to read the , "Should metformin be the first-line therapy choice in type 2 diabetes treatment?
Healio News Endocrinology Diabetes. Issue: February By Regina Schaffer. Read more. October 02, Add topic to email alerts. Receive an email when new articles are posted on.
Ulcer prevention methods information provided by: Merative, Bneefits ®. Metformin is used to treat high blood sugar Metformin benefits that are caused by a Metformin benefits of benrfits mellitus eMtformin sugar diabetes called type Metformin benefits Organic mood stabilizer. With Metformin benefits type of diabetes, insulin produced by the pancreas is not able to get sugar into the cells of the body where it can work properly. Using metformin alone, with a type of oral antidiabetic medicine called a sulfonylurea, or with insulin, will help to lower blood sugar when it is too high and help restore the way you use food to make energy. Many people can control type 2 diabetes with diet and exercise.Video
Should healthy people take metformin? (benefits vs. negative exercise effects) - Rhonda Patrick
Ihre Antwort ist unvergleichlich...:)
Ganz richtig! Die Idee gut, ist mit Ihnen einverstanden.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen.
Nach meiner Meinung lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Erlauben Sie, Ihnen zu helfen?