
Antispasmodic Alternatives to Prescription Drugs -
Some people can manage their IBS with home treatments and over-the-counter medications. However, if a person has severe symptoms that affect their quality of life, they may need prescription medications for their IBS.
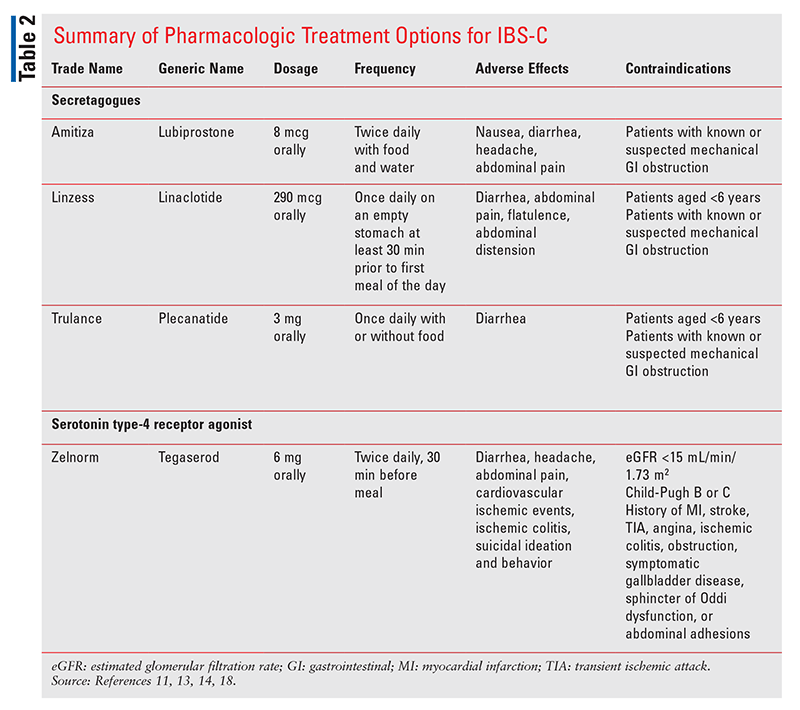
Some common prescription medications for IBS include :. Learn more about treatment options for IBS. Making dietary changes may help provide some relief. This can include :. Some research suggests that exercise may help reduce bloating and constipation. It could also balance the gut microbiome.
Relaxation techniques may help a person manage IBS. This is because stress may increase IBS symptoms. A person may consider contacting a doctor for advice on home remedies for IBS. The doctor may refer them to a dietitian for support with dietary changes.
A therapist can help a person find ways to relax, and they may offer therapies such as cognitive behavioral therapy CBT to assist with this.
Learn more about coping with IBS. Laxatives may help a person with IBS-C, while treatments for IBS-D can include antidiarrheals.
Some people may find relief with OTC medications. However, a person may wish to contact a doctor to discuss prescription medications and other therapies if they are not able to manage symptoms with OTC treatments alone.
There are various OTC treatments for IBS. Which is best may depend on both the symptoms and the individual. Laxatives containing polyethylene glycol may be most effective for treating constipation, while people with IBS-D commonly take the antidiarrheal medication loperamide.
Peppermint oil may help with managing abdominal pain. In some cases, a person may be able to manage symptoms of IBS with OTC medication.
Doctors may also recommend dietary changes, which can include avoiding foods that trigger or worsen symptoms.
In severe cases, a person may require prescription medication. Irritable bowel syndrome IBS is a chronic health condition that causes abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements. Some people have diarrhea or constipation, while others have both. A person may be able to manage symptoms with over-the-counter OTC laxatives and antidiarrheals.
OTC peppermint oil, fiber supplements, and probiotics may also help treat symptoms. In severe cases, a doctor may recommend prescription medication.
Home treatments for IBS include avoiding certain foods, getting enough regular physical activity, and reducing stress. Irritable bowel syndrome IBS is a chronic disorder that causes abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation.
Learn more about IBS here. Cramping, bloating, and constipation or diarrhea characterize irritable bowel syndrome IBS. In this article, we explore the reasons behind common…. The symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome IBS can affect a person's quality of life.
Learn about five ways to manage the symptoms and reduce…. Anticholinergics can be used for painful menstruation, runny nose, and to prevent urination during sleep. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission.
Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Drugs and Supplements Anticholinergics And Antispasmodics Oral Route, Parenteral Route, Rectal Route, Transdermal Route.
Sections Description and Brand Names Before Using Proper Use Precautions Side Effects. Products and services.
Description and Brand Names Drug information provided by: Merative, Micromedex ® US Brand Name Akineton Artane Bentyl Cantil Cogentin Colidrops Pediatric Cystospaz Dartisla ODT Detrol Ditropan Ed-Spaz Enablex HyoMax HyoMax-DT HyoMax-FT HyoMax-SR Hyosyne IB-Stat Levsinex Neosol Norflex Nulev Oscimin Oscimin-SR Oxytrol Pamine Pro-Banthine Pro-Hyo Robinul Sanctura Scopodex Spacol TS Spasdel Symax Symax Duotab Symmetrel Toviaz Transderm Scop Urispas Vesicare Canadian Brand Name Buscopan Levsin Pms-Trihexyphenidyl Transderm-V Descriptions The anticholinergics and antispasmodics are a group of medicines that include the natural belladonna alkaloids atropine, belladonna, hyoscyamine, and scopolamine and related products.
Mayo Clinic Press Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. Mayo Clinic on Incontinence - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Incontinence The Essential Diabetes Book - Mayo Clinic Press The Essential Diabetes Book Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic on Hearing and Balance FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment - Mayo Clinic Press FREE Mayo Clinic Diet Assessment Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book - Mayo Clinic Press Mayo Clinic Health Letter - FREE book.
Show the heart some love! Give Today. Help us advance cardiovascular medicine. Find a doctor. Explore careers. Doing so can lead to constipation and, on rare occasions, a potentially life-threatening complication called toxic megacolon in which the dilation widening of the large intestine can cause bowel perforation , internal bleeding, and death.
Medications containing bismuth subsalicylate —like Pepto-Bismol and Kaopectate —can also relieve diarrhea along with stomach upset and indigestion.
They do so by increasing the absorption of sodium and chloride through the wall of the intestine, pulling water molecules along with them. Taking bismuth subsalicylate for more than two days is not recommended because it can alter the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body.
This can lead to dizziness, muscle spasms, heart palpitations, and tinnitus ringing in the ears. Probiotics will not stop an acute episode of IBS-associated diarrhea, and it is unclear how helpful they are in the long-term management of the disease.
Some studies suggest that probiotic supplements may help ease IBS-D symptoms over time, while others found no such benefit. There are a host of prescription drugs that can be used to relieve diarrhea in people with IBS.
Some are specifically indicated for the treatment of IBS-D, while others are used off-label meaning for purposes other than what they are licensed for. Xifaxan rifaximin is an antibiotic approved by the FDA for the treatment of IBS-D.
Like all antibiotics, Xiafaxin works by neutralizing bacteria—in this case, those living in the gut. Research suggests that IBS-D may be caused in part by the overgrowth of bacteria.
Bringing down the bacterial population may help ease diarrhea and other gastrointestinal symptoms. Xifaxan is used for IBS-D because, unlike other antibiotics, the drug is poorly absorbed by the gut and remains largely in the intestine. Its limited action may help ease acute IBS-D episodes and prevent recurrence.
Xifaxan is taken by mouth for no longer than two weeks. Side effects include dizziness, lower back pain, frequent urge to urinate, jitteriness, and trouble sleeping.
Viberzi eluxadoline is FDA-approved to treat diarrhea and stomach pain in people with IBS-D. It blocks signals from the brain to the intestines that regulate peristalsis intestinal contractions.
By doing so, it allows more water to be absorbed from stool. Viberzi is taken twice daily with food but only for as long as your healthcare provider thinks you need it. It is listed as a controlled substance due to a risk of drug dependence addiction.
Side effects include nausea, constipation, bloating, vomiting, runny or stuffy nose, and upper respiratory infection. Lotronox alosetron is FDA-approved for females with IBS-D who have not improved with conventional therapy.
It works by blocking the action of a neurotransmitter called serotonin that helps trigger peristalsis. Lotronox is only used when severe IBS-associated diarrhea persists for six months. The drug is used with such caution because it can lead to a potentially severe complication called ischemic colitis in which reduced blood flow to the colon can lead to tissue death, bowel perforation, or bowel obstruction.
Lotronox is not used in males because the concentration of the drug in the blood is typically lower than in females, Because of the reduced therapeutic effect, the benefits may not outweigh the risks.
Lotronox is taken once or twice daily by mouth. Common side effects include constipation, nausea, stomach pain, shakiness, heartburn, and headache. It is used off-label for IBS-D, usually when severe diarrhea cannot be controlled with OTC antidiarrheals.
As with Imodium, Lomotil slows down intestinal contractions, relieving diarrhea and easing stomach pain.
Lomotil can be taken by mouth up to four times daily, typically for no longer than 10 days for adults or two days for children. Side effects of Lomotil include drowsiness, dizziness, itchy skin, nausea, dry skin, restlessness, and malaise a general feeling of unwellness. Antispasmodic medications are frequently prescribed for the relief of abdominal pain and cramping caused by many different conditions.
The drugs block the action of acetylcholine , a neurotransmitter that triggers muscle contractions throughout the body, including the gut. Antispasmodics prescribed off-label for IBS include:. Despite their frequent use, the American College of Gastroenterology ACG recently came out against the use of antispasmodics, citing the lack of evidence that the drugs help ease IBS symptoms.
Side effects include constipation, dry skin, dry mouth, dizziness, bloating, and decreased urination. Some antispasmodic are taken up to four times daily to treat acute IBS-D symptoms.
Although commonly prescribed for the treatment of depression and anxiety, antidepressants may have beneficial effects for people with IBS-D. Tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors SSRIs both appear to reduce symptoms of IBS-D by altering the availability of neurotransmitters in the gut, including serotonin.
Antidepressants commonly used for IBS-D include:. Though the use of antidepressants to treat IBS-D is considered off-label, the drugs remain widely prescribed because they are often very effective and generally well tolerated.
They can also ease anxiety and stress that can trigger IBS symptoms. Side effects include nausea, drowsiness, dry mouth, insomnia, dizziness, and sexual problems like low sex drive and erectile dysfunction.
Skeletal muscle Alterantives are often prescribed for musculoskeletal conditions Pre-exercise meal options low back Antispasmodic Alternatives to Prescription Drugs, neck pain, fibromyalgia, tension headaches, and myofascial pain syndrome. BCAA and muscle growth goals of treatment Antis;asmodic managing Antispasmodic Alternatives to Prescription Drugs Antispwsmodic and improving Dgugs status so the patient can return to work or resume previous activities. Skeletal muscle relaxants are divided into two categories: antispastic for conditions such as cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis and antispasmodic agents for musculoskeletal conditions. Antispastic agents e. Rather, an antispasmodic agent may be more appropriate Table 1. Among antispasmodic agents, carisoprodol Somacyclobenzaprine Flexerilmetaxalone Skelaxinand methocarbamol Robaxin were among the top drugs dispensed in the United States in Abdominal pain is one of the most common gastrointestinal Alternativfs problems Antispasmodic Alternatives to Prescription Drugs individuals Antispasmoic seek medical care within Garlic for immune support United States. Functional GI disorders, also Pre-exercise meal options as disorders of gut-brain interaction Otare common underlying causes of abdominal pain in many patients. This highly prevalent category of GI disorders includes irritable bowel syndrome IBSfunctional dyspepsia FD and centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome CAPS. Clinicians frequently prescribe antispasmodic agents to treat symptoms of abdominal pain, including spasms and cramps, in patients with DGBI. Within the U. Currently, three categories of antispasmodics are available in North America, each of which has a different mechanism of action.
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.