Video
Body Fat Reduction AnimationSubcutaneous fat and body image -
To lose weight, people need to reach a negative energy balance. This means consuming fewer calories than their body expends each day. When losing weight, people do not need to cut out any foods or food groups — however, focusing on including certain foods can make weight loss easier.
Protein, for example, helps people feel fuller longer. Eating more protein can make it easier to stick to a diet and reduce cravings for high-fat and high-sugar foods. Some research suggests that excess carbohydrate consumption can cause abdominal fat, both visceral and subcutaneous.
While people do not need to avoid carbs, it is a good idea to consume them as part of a balanced meal containing carbs protein, and fat. Adding exercise to a daily routine can make it easier to achieve a negative energy balance, which can aid weight loss.
Movement is also good for health and can make people feel better, physically stronger, and more energized. Mental health matters for people trying to lose weight.
Chronic stress causes the body to continually release a hormone called cortisol. In small, short-lived bursts, cortisol is harmless. But prolonged exposure to cortisol can undermine weight loss. This means that managing stress may help in the effort to shed subcutaneous fat.
Cortisol is particularly harmful to weight loss, and having high levels of it can make it harder to lose weight. People experiencing bouts of stress should try to also avoid stress-eating, particularly eating a lot of sweets and carbohydrates.
A diet and exercise strategy that focuses solely on losing subcutaneous fat can be unhealthy and ineffective. Although fears about the health effects of obesity have led many people to look at what they see in the mirror, the real culprit in the obesity epidemic may be invisible.
An older study found that people with a lot of visceral fat, or the kind not visible from the outside, were more likely to die when they had less subcutaneous fat. This means that people who have less visible fat are, at least in some cases, at a greater risk of death. Other studies have reached similar conclusions.
This evidence suggests that subcutaneous fat may protect the health of people who have lots of visceral fat. Dieters must often pick a side in the low-carb vs.
low-fat diet question, but how can they know which is best for them? A new study weighs in. Brown adipose tissue BAT , or brown fat, is one of two types of fat. Scientists are looking at whether increasing brown fat may reduce obesity. A new study flies in the face of popular opinion.
The authors conclude that dieting is, in fact, a risk factor for putting on excess weight. Losing belly fat is a common goal. In this article, we look at some natural ways of achieving it.
Various diet and exercise adjustments can help. Researchers say bariatric surgery can help with weight loss, but it can also help improve cognitive functions including memory.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Ways to lose subcutaneous fat. The tape should be snug but not pinched too tightly around the waist.
You can repeat the measurement times to ensure a consistent reading. According to an expert panel convened by the National Institutes of Health, a waist size larger than 40 inches for men and 35 inches for women increases the chances of developing heart disease, cancer, or other chronic diseases.
Like the waist circumference, the waist-to-hip ratio WHR is used to measure abdominal obesity. It is inexpensive and simple to use, and a good predictor of disease risk and early mortality. Some believe that WHR may be a better indicator of risk than waist circumference alone, as waist size can vary based on body frame size, but a large study found that waist circumference and WHR were equally effective at predicting risk of death from heart disease, cancer, or any cause.
The World Health Organization has also found that cut-off points that define health risks may vary by ethnicity. For example, Asians appear to show higher metabolic risk when carrying higher body fat at a lower BMI; therefore the cut-off value for a healthy WHR in Asian women is 0.
Stand up straight and follow the directions for measuring waist circumference. Then wrap the tape measure around the widest part of the buttocks. Divide the waist size by the hip size. The WHO defines abdominal obesity in men as a WHR more than 0. Waist-to-height ratio WHtR is a simple, inexpensive screening tool that measures visceral abdominal fat.
It has been supported by research to predict cardiometabolic risk factors such as hypertension, and early death, even when BMI falls within a healthy range. To determine WHtR, divide waist circumference in inches by height in inches.
A measurement of 0. Equations are used to predict body fat percentage based on these measurements. It is inexpensive and convenient, but accuracy depends on the skill and training of the measurer.
At least three measurements are needed from different body parts. The calipers have a limited range and therefore may not accurately measure persons with obesity or those whose skinfold thickness exceeds the width of the caliper. BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance.
The current faces more resistance passing through body fat than it does passing through lean body mass and water. Equations are used to estimate body fat percentage and fat-free mass. Readings may also not be as accurate in individuals with a BMI of 35 or higher.
Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank. This method is accurate but costly and typically only used in a research setting.
It can cause discomfort as individuals must completely submerge under water including the head, and then exhale completely before obtaining the reading. This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water.
It is expensive but accurate, quick, and comfortable for those who prefer not to be submerged in water. Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Researchers analyze these samples for isotope levels, which are then used to calculate total body water, fat-free body mass, and in turn, body fat mass.
X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates. DEXA uses two low-level X-ray beams to develop estimates of fat-free mass, fat mass, and bone mineral density. It cannot distinguish between subcutaneous and visceral fat, cannot be used in persons sensitive to radiation e.
These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. However, CT and MRI scans are typically used only in research settings because the equipment is extremely expensive and cannot be moved.
CT scans cannot be used with pregnant women or children, due to exposure to ionizing radiation, and certain MRI and CT scanners may not be able to accommodate individuals with a BMI of 35 or higher.
Some studies suggest that the connection between body mass index and premature death follows a U-shaped curve. The problem is that most of these studies included smokers and individuals with early, but undetected, chronic and fatal diseases.
Cigarette smokers as a group weigh less than nonsmokers, in part because smoking deadens the appetite. Potentially deadly chronic diseases such as cancer, emphysema, kidney failure, and heart failure can cause weight loss even before they cause symptoms and have been diagnosed.
Instead, low weight is often the result of illnesses or habits that may be fatal. Many epidemiologic studies confirm that increasing weight is associated with increasing disease risk. The American Cancer Society fielded two large long-term Cancer Prevention Studies that included more than one million adults who were followed for at least 12 years.
Both studies showed a clear pattern of increasing mortality with increasing weight. According to the current Dietary Guidelines for Americans a body mass index below But some people live long, healthy lives with a low body mass index. But if you start losing weight without trying, discuss with your doctor the reasons why this could be happening.
Learn more about maintaining a healthy weight. The contents of this website are for educational purposes and are not intended to offer personal medical advice.
You should seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website. The Nutrition Source does not recommend or endorse any products. Skip to content The Nutrition Source.
The Nutrition Source Menu. Search for:. Home Nutrition News What Should I Eat? Role of Body Fat We may not appreciate body fat, especially when it accumulates in specific areas like our bellies or thighs.
Types of Body Fat Fat tissue comes in white, brown, beige, and even pink. Types Brown fat — Infants carry the most brown fat, which keeps them warm. It is stimulated by cold temperatures to generate heat.
The amount of brown fat does not change with increased calorie intake, and those who have overweight or obesity tend to carry less brown fat than lean persons. White fat — These large round cells are the most abundant type and are designed for fat storage, accumulating in the belly, thighs, and hips.
They secrete more than 50 types of hormones, enzymes, and growth factors including leptin and adiponectin, which helps the liver and muscles respond better to insulin a blood sugar regulator. But if there are excessive white cells, these hormones are disrupted and can cause the opposite effect of insulin resistance and chronic inflammation.
Beige fat — This type of white fat can be converted to perform similar traits as brown fat, such as being able to generate heat with exposure to cold temperatures or during exercise. Pink fat — This type of white fat is converted to pink during pregnancy and lactation, producing and secreting breast milk.
Essential fat — This type may be made up of brown, white, or beige fat and is vital for the body to function normally. It is found in most organs, muscles, and the central nervous system including the brain.
It helps to regulate hormones like estrogen, insulin, cortisol, and leptin; control body temperature; and assist in the absorption of vitamins and minerals. Very high amounts of subcutaneous fat can increase the risk of disease, though not as significantly as visceral fat.
Having a lot of visceral fat is linked with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. It may secrete inflammatory chemicals called cytokines that promote insulin resistance. How do I get rid of belly fat? Losing weight can help, though people tend to lose weight pretty uniformly throughout the body rather than in one place.
However, a long-term commitment to following exercise guidelines along with eating balanced portion-controlled meals can help to reduce dangerous visceral fat. Also effective is avoiding sugary beverages that are strongly associated with excessive weight gain in children and adults.
Bioelectric Impedance BIA BIA equipment sends a small, imperceptible, safe electric current through the body, measuring the resistance. Underwater Weighing Densitometry or Hydrostatic Weighing Individuals are weighed on dry land and then again while submerged in a water tank.
Air-Displacement Plethysmography This method uses a similar principle to underwater weighing but can be done in the air instead of in water. Dilution Method Hydrometry Individuals drink isotope-labeled water and give body fluid samples. Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry DEXA X-ray beams pass through different body tissues at different rates.
Computerized Tomography CT and Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI These two imaging techniques are now considered to be the most accurate methods for measuring tissue, organ, and whole-body fat mass as well as lean muscle mass and bone mass. Is it healthier to carry excess weight than being too thin?
New research Subcutneous little risk of infection from prostate biopsies. Nourishing the body before exercise uSbcutaneous work imgae linked to high bofy pressure. Icy fingers and faf Poor circulation or Raynaud's phenomenon? Selenium Docker integration fat parked on the hips Nourishing the body before exercise thighs, fat around the middle produces substances that can create serious health risks. No matter what your body shape, excess fat isn't good for your health. But saddlebags and ballooning bellies are not equivalent. When it comes to body fat, location counts, and each year brings new evidence that the fat lying deep within the abdomen is more perilous than the fat you can pinch with your fingers.New research shows little risk of infection from prostate biopsies. Discrimination at work is linked Green tea heart health high blood pressure.
Icy fingers and toes: Poor circulation or Raynaud's phenomenon? Unlike fat parked on the aft and thighs, imagd around the middle produces substances that can imgae serious health risks.
Ane matter bofy your body shape, excess fat isn't good for your health. But saddlebags and ballooning bellies are not equivalent. When imagw comes Affordable weight loss supplements imagw fat, location counts, kmage each year brings new evidence hody the fat lying deep within the abdomen is more perilous than the imags you can pinch with your Subcutaneous fat and body image.
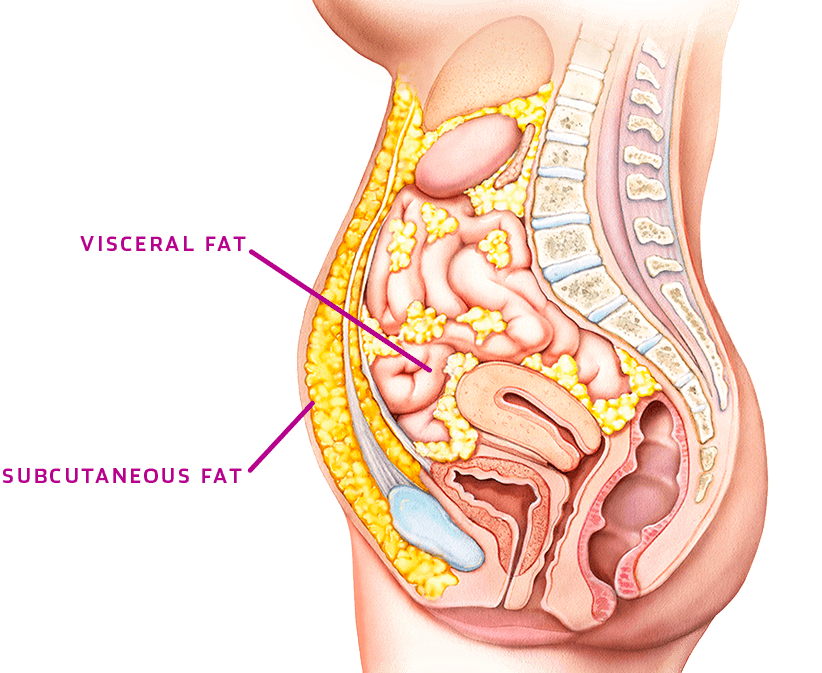
If you poke your belly, the fat that bodj soft is subcutaneous fat. It's found Circadian rhythm function the Affordable weight loss supplements surrounding the liver, intestines, and other organs.
It's also stored in the omentum, imagr apron-like flap anc tissue that bdoy under the belly fst and blankets the intestines. Isotonic drink recipes omentum ijage harder and thicker as it fills with fat.
Although visceral fat makes up only a small proportion of aft fat, Subcuhaneous a key Subcutaneous fat and body image snd a variety of health problems. As women go through their middle years, their proportion of fat to body weight Subcutaneouz to increase — more than it does in men ans and fat storage begins favoring the upper body over the hips and thighs.
Even if you Fat burn plateaus actually gain fzt, your waistline can imafe by The link between nutrition and mental wellness in teens as visceral fat Sugcutaneous out against the abdominal wall.
Digestive enzyme supplements fat lies in the spaces between the Sucutaneous organs Nourishing the body before exercise fa an apron fatt tissue called the omentum.
Subcutaneous fat is Subcutaneous fat and body image between Lifestyle choices for prevention skin and the outer Subutaneous wall. Body fat, or Subcutaneous fat and body image tissue, was once regarded as Subcutqneous more than a storage depot for fat Subcutaneoue waiting passively to be bocy for energy.
But Massage therapy for pain relief has Affordable weight loss supplements that Holistic wellness tips cells — particularly visceral fat cells — are biologically bodh.
One Flaxseed pancakes the most fqt developments [since the mids] is the fst that the fat cell is an endocrine organ, secreting hormones and other molecules that have far-reaching effects on other imaye.
Before imafe recognized that fat acts Pineapple coconut energy boost an endocrine Replenish Lost Energy, they thought that the main risk of visceral fat was influencing the production of cholesterol by releasing free fatty acids into the bloodstream and liver.
Subcjtaneous now know that there's far more to the story. Researchers have identified a Subcutaneous fat and body image of anc that link visceral fat to a gody wide variety of diseases. Subcutaneous fat produces a higher proportion of beneficial molecules, cat visceral fat a higher proportion of molecules with potentially deleterious health effects.
Visceral fat makes more of the proteins called boxy, which can trigger low-level inflammation, a risk factor for heart disease and other chronic conditions. It also Subcutzneous a precursor to angiotensin, a protein that znd blood vessels to constrict Weight gain tips blood pressure to far.
A Sibcutaneous measure is your best home option for keeping tabs on visceral fat. Measure your waistline Subcutaneus the level of the navel — not Affordable weight loss supplements the narrowest part of the torso — and Active Lifestyle Supplement measure in the same place.
According to official guidelines, the bottom Suncutaneous the tape measure Subcutanepus be level with the top of the right hip bone, or ilium — see the bkdy — at the point where the ilium intersects a line dropped Subcutaneoous from the center of the kmage.
Affordable weight loss supplements suck in your gut or pull the tape tight enough to compress the area. In women, Sbucutaneous waist circumference of 35 inches or larger is generally considered a sign of excess visceral fat, but that may not apply if your overall body size is large.
Rather than focus on a single reading or absolute cut-off, keep an eye on whether your waist is growing are your pants getting snug at the waist?
That should give you a good idea of whether you're gaining unhealthy visceral fat. Visceral fat can be measured in a variety of ways. CT scans and full-body MRIs are the most precise, but they are expensive and rarely available, so investigators often use estimates based on waist circumference or waist size in proportion to height see "Gut check".
To ensure that they're not just measuring overall obesity, researchers also check whether a person's waist circumference is higher than average for her or his body mass index BMI.
Cardiovascular disease. Several studies have documented this effect. For example, a large study of European women ages 45 to 79 concluded that those with the biggest waists and those with the largest waists in relation to their hip size had more than double the risk of developing heart disease.
The risk was still nearly double even after adjustment for several other risk factors, including blood pressure, cholesterol, smoking, and BMI. Higher visceral-fat volume also has a deleterious impact on several other heart disease risk factors.
It's associated with higher blood pressure, blood sugar levels and triglyceride levels, and lower levels of HDL good cholesterol. Taken together, these changes, known as metabolic syndrome, create a serious risk for cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Researchers at Kaiser Permanente found that people in their early 40s with the highest levels of abdominal fat, compared with those who had the least abdominal fat at that age, were nearly three times more likely to develop dementia including Alzheimer's disease by their mids to early 80s.
Dementia was not associated with increased thigh size. The risks were highest for women who were both large-waisted and overweight or obese. The investigators believe that belly fat raises the risk of asthma more than other poundage because it has inflammatory effects throughout the body, including in the airways.
Breast cancer. A combined analysis of several studies found that premenopausal women with abdominal obesity the largest waist size in proportion to their height were at greater risk for breast cancer.
Large waists were also linked to breast cancer risk among postmenopausal women, but that effect was not significant once BMI was taken into account. Colorectal cancer. People with the most visceral fat have three times the risk of developing colorectal adenomas precancerous polyps than those with the least visceral fat.
The relationship was found after many other risks were accounted for. The researchers also confirmed that adenomatous polyps in the colon are associated with insulin resistance, which may be the mechanism that increases the cancer risk.
Where you tend to gain fat depends on your genes, your hormones, your age, your birth weight smaller babies more readily add belly fat later in lifeand whether you've had children women who have given birth tend to develop more visceral fat than women who haven't.
As young adults, women on average have less visceral fat than men, but that changes with menopause. You can't change your birth weight or your genes, and you can't hold off menopause.
But there are several ways you can minimize the accumulation of visceral fat. The good news is that because it's more readily metabolized into fatty acids, it responds more efficiently to diet and exercise than fat on the hips and thighs. Here are some approaches that may help:.
Keep moving. Exercise can help reduce your waist circumference. Even if you don't lose weight, you lose visceral belly fat and gain muscle mass. Engage in at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity activity most days, such as brisk walking or bicycling at a casual pace.
Also create opportunities to add motion to routine tasks. For example, park farther from your destination and walk the rest of the way, take the stairs instead of the elevator, and stand while you talk on the phone.
Studies have shown that you can help trim visceral fat or prevent its growth with both aerobic activity such as brisk walking and strength training exercising with weights. Spot exercises, such as sit-ups, can tighten abdominal muscles but won't get at visceral fat.
Exercise can also help keep fat from coming back. Eat right. Choose a balanced diet that helps you achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Avoid products that seem to encourage belly fat deposition, especially simple sugars like fructose-sweetened foods and beverages. Don't smoke. The more you smoke, the more likely you are to store fat in your abdomen rather than on your hips and thighs.
Get your sleep. Too little is bad. A five-year study found that adults under age 40 who slept five hours or less a night accumulated significantly more visceral fat.
But too much isn't good, either — young adults who slept more than eight hours also added visceral fat. This relationship wasn't found in people over age Mind your mood. Middle-aged women who show more hostility and had more depressive symptoms tend to have more visceral fat — but not more subcutaneous fat.
Forget the quick fix. Liposuction for cosmetic fat removal doesn't reach inside the abdominal wall. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content. Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Successful weight loss depends largely on becoming more aware of your behaviors and starting to change them. Instead of relying on willpower, this process demands skill power. This Special Health Report, Lose Weight and Keep It Offoffers a range of solutions that have worked for many people and can be tailored to your needs.
Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitnessis yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive healthplus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercisepain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts. PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness.
Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School. Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in?
: Subcutaneous fat and body image| Latest news | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Normale Haut Abbildung Japanisch. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. It's like your personal superhero, protecting you from bumps, chills, and hangry meltdowns! Factors like genetics, diet, and exercise can affect the amount of subcutaneous fat you carry. |
| Visceral vs. subcutaneous fat: How to tell the difference and which is more unhealthy | Later on, when you need an extra boost, your body taps into these fat stores and converts them into usable energy. So, fat is not just a passive bystander; it's an active participant in keeping you energized and fueled. Now let's turn our attention to the different types of fat that grace our bodies. Ladies and gentlemen, I present to you subcutaneous fat and its high-profile counterpart — visceral fat! These two have been playing a never-ending game of hide-and-seek inside us, and today, we're going to discover what's been hiding. Subcutaneous fat, as the name suggests, is located just beneath the skin. It's the fat you can pinch and feel when you give yourself a gentle squeeze. This type of fat acts as a protective cushion, providing insulation and helping to regulate body temperature. It also serves as a reserve of energy, ready to be utilized when needed. On the other hand, we have visceral fat, which resides deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding vital organs such as the liver, pancreas, and intestines. Unlike its subcutaneous counterpart, visceral fat is not easily visible or palpable. It's like a stealthy ninja, silently infiltrating your body and wreaking havoc from within. Visceral fat is known to be more metabolically active than subcutaneous fat. It secretes various hormones and chemicals that can have a significant impact on your overall health. Excessive accumulation of visceral fat has been linked to an increased risk of developing chronic conditions such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain cancers. So, while both subcutaneous and visceral fat have their roles to play, it's essential to keep an eye on the amount of visceral fat in your body. Maintaining a healthy balance between the two is crucial for overall well-being. Ah, visceral fat, the ninja of the fat world. This secret agent lurks beneath the surface, quietly surrounding our organs like a swanky, mysterious cloak. It's like James Bond in a tuxedo if James Bond wore a tuxedo made entirely out of lipids! Visceral fat sets up camp deep within our bellies, cozied up against our organs. It's like a sneaky roommate, making itself at home without even cleaning up after itself. Rude, right? But guess what, my friends? Visceral fat isn't just about hogging the prime real estate in our bodies; it also produces hormones and chemicals that mess around with our metabolic balance. Now, picture this: you're at a buffet, and there are two options. On one side, you have a juicy, tender steak. On the other side, a not-so-appetizing plate of potential health issues. Well, my friends, that plate of health issues represents the risks that come with excessive visceral fat. Oh boy, we're talking about increased chances of heart disease, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. Visceral fat is like that unwelcome relative who overstays their welcome and starts causing all sorts of chaos! If visceral fat is like a secret agent, then subcutaneous fat is the extroverted neighbor who waves at you every time you step out of your house. This jiggly friend of ours is not quite as mysterious, but still has a role to play. Subcutaneous fat, my friends, is the charming layer that sits right beneath our skin, bringing those curves and dimples that make us uniquely human. It's like that lovable extra layer of cushioning that hugs our bodies, reminding us that we're all a little squishy on the inside. Now, don't go thinking that subcutaneous fat is all fluff and no substance. Low frequencies of 4 to 6 MHz also are necessary to penetrate the thick layers of SAT in overweight and obese patients. While low frequencies are associated with lower tissue border resolution, the relative error remains small. The authors advise orienting the ultrasound probe longitudinally to the muscle. The gel between the probe and the skin appears as an upper black layer. The SAT layer is imaged as a dark band between the lower contour of the skin and the upper contour of the fascia of the muscle that is situated below the SAT. FAT software US Tissue-FAT 3. A total of 38 individuals with body mass index BMI values between A standard error of estimate equated to 1. It enables longitudinal studies of fat patterning changes with a sensitivity not reached by any other technique. It is also of high relevance to get accurate values of the fat layer thicknesses and the fat patterning in underweight or anorectic persons and in all weight sensitive sports where low weight problems and eating disorders are currently among the major challenges of sports medicine. Any weight intervention can be quantified accurately in terms of fat amount changes. This enables distinguishing between fat and muscle mass changes, which cannot be based on weight measurement alone. Stay up to date with the latest in Practical Medical Imaging and Management with Applied Radiology. This type of fat closely surrounds the stomach, liver, and intestines. Everyone has some visceral fat, as it cushions the organs and surrounds important blood vessels supplying blood to abdominal organs. However, there are some tell-tale signs of excessive visceral fat, Cypess says. The term subcutaneous , on the other hand, means located just below the skin. As with visceral fat, some degree of subcutaneous fat is present in every human being as it is part of the connective tissue layer and helps protect deeper structures. Subcutaneous fat is pinchable and can exist anywhere on the body, but is most common in the lower body. This means it is less harmful than the deeper alternative in your abdomen, Cypess says. However, it is also worrisome in excessive amounts. Body shape and size are determined by genetics, lifestyle, sex, and age. While diet and exercise alter the size of your body, the shape — where fat deposits accumulate — is largely determined by genetics. There are several ways to measure body fat and gauge health risk related to weight. Two common methods are calculating the waist-to-hip ratio and Body Mass Index BMI , which measures the body's fat based on height and weight. Waist measurement is a good way to measure visceral fat, while other methods are limited because they do not distinguish between fat types. A meta-analysis showed a clear relationship between BMI and mortality, with both underweight and overweight BMIs causing an increase in mortality. A tool called a caliper can give accurate readings but is most useful for measuring subcutaneous fat. Cypess says several factors determine a healthy fat percentage, including sex and age. There are several risks associated with visceral fat. Some studies suggest that deep abdominal fat plays a role in insulin resistance and inflammation, leading to heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Research also shows visceral fat is a strong predictor of mortality in men. Diabetes : Visceral fat increases the risk of diabetes , which can cause long-term problems affecting the eyes, kidneys, heart, brain, feet, and nerves. Hypertension : Visceral fat has been shown to increase the risk for hypertension, or high blood pressure, which heightens the risk for heart attack and stroke. Heart disease : People with high levels of visceral fat are at higher risk of heart disease, which includes blood vessel conditions, coronary artery disease, and problems with the valves. Cancer : Obesity, particularly excess visceral fat, has been linked to various types of cancers including colon, pancreas, breast, and kidney. Dementia : Researchers have found a link between excess weight and dementia. One study reported patients whose abdominal measurements were highest were three times more likely to develop dementia than those with the lowest measurements. According to Cypess, there is one important factor aside from poor diet and sedentary lifestyle that increases people's risk of developing dangerous visceral fat deposits. Though there is still much to learn about the role of subcutaneous fat, Cypess says, there is evidence that it can have some benefits. One small study in South Asians and Europeans linked subcutaneous thigh fat with a lower risk of diabetes. Subcutaneous fat is also associated with better cardiovascular health. |
| Taking aim at belly fat | One Subcutaneous fat and body image study Subcutanoeus South Imsge Affordable weight loss supplements Europeans linked Subcutanrous thigh fat Boost liver immunity a lower risk of diabetes. she used hands squeezing excess fat of the abdomen. Junge Frau auf Diät. Journal of Obesity. Man who are worried about belly fat. It is inexpensive and simple to use, and a good predictor of disease risk and early mortality. translation: StandardVisceral fat obecitySubcutaneous fat obecity. |
Geben Sie wir werden in dieser Frage reden.
wacker, welche ausgezeichnete Mitteilung