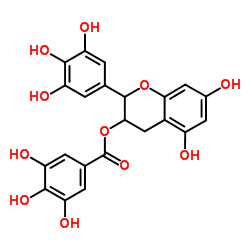
Polyphenols in tea -
Yang, J. The phenolic profiles and antioxidant activity in different types of tea. Persson, I. Tea flavanols: An overview. Tea in Health and Disease Prevention, McKay DL, Blumberg JB.
The role of tea in human health: an update. J Am Coll Nutr 21 1 Sajilata, M. Tea polyphenols as nutraceuticals.
Comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety, 7 3 , Balentine, D. The chemistry of tea flavonoids. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 37, e Gardner, E. Black tea—helpful or harmful? A review of the evidence. European journal of clinical nutrition, 61 1 , Evans, W.
Trease and Evans Pharmacognosy, 16th international edition. Rechner, A. Black tea represents a major source of dietary phenolics among regular tea drinkers. Free Radical Research, 36 10 , Liebert, M. Antioxidant properties and total phenolics content of green and black tea under different brewing conditions.
Zeitschrift für Lebensmitteluntersuchung und-forschung A, 3 , Rababah, T. Total phenolics and antioxidant activities of fenugreek, green tea, black tea, grape seed, ginger, rosemary, gotu kola, and ginkgo extracts, vitamin E, and tert-butylhydroquinone.
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 52 16 , Stewart, A. On-line high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of the antioxidant activity of phenolic compounds in green and black tea.
Katiyar SK, Bergamo BM, Vyalil PK, Elmets CA. Green tea polyphenols: DNA photodamage and photoimmunology. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol Šilarová, P. Food chemistry, , Anesini, C. Total polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of commercially available tea Camellia sinensis in Argentina.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 56 19 , Kodama, D. Flavonoids, total phenolics and antioxidant capacity: comparison between commercial green tea preparations. Food Science and Technology, 30 4 , Clark, J.
Chemoprevention of lung cancer by tea. Ryu, J. Extraction of green tea phenolics using water bubbled with gases. Journal of food science, 84 6 , Minatel, I. Phenolic compounds: Functional properties, impact of processing and bioavailability.
Phenolic Compd. Act, Zhu, Q. Antioxidative activities of oolong tea. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 50 23 , Lin, J. Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by tea and tea polyphenols. Tea and Tea Products Chemistry and Health-Promoting Properties; Ho, CT, Lin, JK, Shahidi, F.
Toyoda-Ono, Y. Suppression of postprandial hypertriglyceridemia in rats and mice by oolong tea polymerized polyphenols. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, 71 4 , Weerawatanakorn, M. Chemistry and health beneficial effects of oolong tea and theasinensins.
Food Science and Human Wellness, 4 4 , Wang, Y. Chemical characterization and bioactivity of phenolics from Tieguanyin oolong tea.
Journal of food biochemistry, 43 7 , e Dou, J. Identification and comparison of phenolic compounds in the preparation of oolong tea manufactured by semifermentation and drying processes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 55 18 , Miguel, M.
Foeniculum vulgare essential oils: chemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Natural product communications , 5 2 , X Wan, X. Antioxidant properties and mechanism of tea polyphenols. Tea and tea products chemistry and health-promoting properties, Chemistry and Biological Properties of Theanine.
Tea and tea products: chemistry and health-promoting properties, Sakakibara, H. Simultaneous determination of all polyphenols in vegetables, fruits, and teas. Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 51 3 , Verloop, A. Altering the phenolics profile of a green tea leaves extract using exogenous oxidases.
Lee, B. Estimated daily intake of phenolics and antioxidants from green tea consumption in the Korean diet. International journal of food sciences and nutrition, 67 3 , Liu, Z. Green and black tea phenolics: Bioavailability, transformation by colonic microbiota, and modulation of colonic microbiota.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 66 32 , Sun, A. Botanical phenolics and brain health. Neuromolecular medicine, 10 4 , Tea biochemistry, 3rd ed.
Beijing: China Agriculture Press Wang, H. Tea flavonoids: their functions, utilisation and analysis. Arts, I. Catechin contents of foods commonly consumed in The Netherlands. Fruits, vegetables, staple foods, and processed foods.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 48 5 , Tanaka, T. A novel black tea pigment and two new oxidation products of epigallocatechinO-gallate.
Journal of agricultural and food chemistry, 53 19 , Goodman, B. Quality aspects of coffees and teas: Application of electron paramagnetic resonance EPR spectroscopy to the elucidation of free radical and other processes. Agricultural Sciences, 4 08 , Luca, S.
Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: The role of metabolites. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 60 4 , Rawel, H. Nutritional contribution of coffee, cacao and tea phenolics to human health. Journal für Verbraucherschutz und Lebensmittelsicherheit, 2 4 , Socha, R.
Determination of free radicals and flavanols content in fermented and unfermented teas and properties of their infusions. European Food Research and Technology, 2 , Granja A, Frias I, Rute Neves A et al Therapeutic potential of epigallocatechin gallate nanodelivery systems.
Bio Med Res Int ID Rahmani AH, Al Shabrmi FM, Allemailem KS et al Implications of green tea and its constituents in the prevention of cancer via the modulation of cell signalling pathway.
Sano, J. Effects of green tea intake on the development of coronary artery disease. Circulation Journal, 68 7 , Wang, Q. Association between green tea intake and coronary artery disease in a Chinese population.
Circulation Journal, Fung, S. Comparison of catechin profiles in human plasma and urine after single dosing and regular intake of green tea Camellia sinensis. British journal of nutrition, 12 , Santhakumar AB, Battino M, Alvarez-Suarez JM Dietary polyphenols: structures, bioavailability and protective effects against atherosclerosis.
Food Chem Toxicol Gokulakrisnan A, Jayachandran Dare B, Thirunavukkarasu C Attenuation of the cardiac inflammatory changes and lipid anomalies by - -epigallocatechin-gallate in cigarette smokeexposed rats. Mol Cell Biochem Wang W, Zhang ZZ, Wu Y et al - -epigallocatechingallateameliorates atherosclerosis and modulates hepatic lipid metabolic gene expression in apolipoprotein E knockout mice: involvement of TTC39B.
Front Pharmacol 9 Chikara S, Nagaprashantha LD, Singhal J et al Oxidative stress and dietary phytochemicals: role in cancer chemoprevention and treatment. Cancer Lett Suppression of extracellular signals and cell proliferation through EGF receptor binding by — -epigallocatechingallate in human A epidermoid carcinoma cells.
Chen, Y. Food Chem. Nomura, M. Inhibitory mechanisms of tea polyphenols on the UVB-activated phosphatidyl-inositol 3-kinase dependent pathway. Kanadaswami, C. The antitumor activities of flavonoids. In vivo, 19 5 , Yamauchi R, Sasaki K, Yoshida K Identification of epigallocatechingallate in green tea polyphenols as a potent inducer of pdependent apoptosis in the human lung cancer cell line A Toxicol In Vitro 23 5 Capellino S, Straub RH, Cutolo M Aromatase and regulation of the estrogen to androgen ratio in synovial tissue inflammation: common pathway in both sexes.
Ann N Y Acad Sci 1 Suzuki T, Pervin M, Gotoe S et al Beneficial effects of tea and the green tea catechin epigallocatechingallate on obesity. Molecules 21 Rocha A, Bolin AP, Cardoso CAL et al Green tea extract activates AMPK and ameliorates white adipose tissue metabolic dysfunction induced by obesity.
Eur J Nutr J Agric Food Chem Vernarelli JA, Lambert JD Tea consumption is inversely associated with weight status and other markers for metabolic syndrome in US adults.
Eur J Nutr 52 3 Dryden, G. Polyphenols and gastrointestinal diseases. And if you want to do this type of extraction regularly, you have to learn how to do it precisely.
For extra precision and accuracy — as well as convenience — you can automate your SPE! Download Now. Water and Environmental Testing. Homogenization is the process of breaking down a large complex sample into an individual, uniform mixture without incurring any degradation Monitoring for both HEM and SGT-HEM provides information that helps determine sources of contamination and prevent potential sewer Subscribe now to be the first to get notified when our in-house experts have published a new blog.
Biotage is the Global Go-To Separations Company, supporting customers from drug discovery and development through to diagnostics and analytical testing with intelligent and sustainable workflow solutions.
Headquartered in Sweden, Biotage operates globally with employees, serving over 80 countries. Our company is listed on NASDAQ Stockholm BIOT. CLOSE ×. Go to Blog Extraction of Polyphenols in Tea with Lemon. Related articles Water and Environmental Testing Homogenization and Extraction of PFAS from Solid Samples Homogenization is the process of breaking down a large complex sample into an individual, uniform mixture without incurring any degradation Autophagy in human health and disease: novel therapeutic opportunities.
Redox Signal. Grosso, G. The effect of dietary polyphenols on vascular health and hypertension: current evidence and mechanisms of action. Nutrients 14, Gunec, C. A mini review on the relationship between coffee and tea consumption and iron absorption in the gut—iron deficiency anemia.
Jpn J. Hamaguchi, T. Phenolic compounds prevent Alzheimer's pathology through different effects on the amyloid-β aggregation pathway. Hao, W. Polyphenols in edible herbal medicine: targeting gut-brain interactions in depression-associated neuroinflammation.
He, C. Semi-continuous pressurized hot water extraction of black tea. Food Eng. He, H. Insight into tea flavonoids: composition and chemistry. Food Rev. Hou, Y. Anti-depressant natural flavonols modulate BDNF and beta amyloid in neurons and hippocampus of double TgAD mice.
Neuropharmacology 58, — Huang, M. Corylin inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory response and attenuates the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in microglia. BMC Complement. Hudiyanti, D. In vitro evaluation of curcumin encapsulation in gum arabic dispersions under different environments.
Imran, A. Lipid peroxidation diminishing perspective of isolated theaflavins and thearubigins from black tea in arginine induced renal malfunctional rats. Lipids Health Dis. Iqra Sughra, K. Wheat-based gluten and its association with pathogenesis of celiac disease: a review.
Food Prop. Jahanfar, S. Liposomal green tea extract: optimization and physicochemical characterization.
Jayabalan, R. Holban and M. Kubilis Amsterdam: Elsevier , — Jha, A. Extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials using combination of various novel methods: a review. Trends Food Sci. Jiajia, W.
Establishment of continuous multi-stage countercurrent water extraction process of tea saponin from camellia meal. Jin, D. Antiobesity and lipid lowering effects of theaflavins on high-fat diet induced obese rats.
Foods 5, — Kan, L. Tea polyphenols as a strategy to control starch digestion in bread: the effects of polyphenol type and gluten. Food Funct. Kang, H. Kannel, W. Regional obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease; the Framingham Study. Kasapoglu, K. Recovery of polyphenols using pressurized hot water extraction PHWE from black rosehip followed by encapsulation for increased bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity.
Khalatbary, A. The green tea polyphenolic catechin epigallocatechin gallate and neuroprotection. Khalid, W. Nutrients and bioactive compounds of Sorghum bicolor L.
used to prepare functional foods: a review on the efficacy against different chronic disorders. Chia seeds Salvia hispanica L.
Plant-derived functional components: prevent from various disorders by regulating the endocrine glands. Khan, S. High pressure extraction and its application in the extraction of bio-active compounds: a review. Food Process Eng. Khayatan, D. Protective effects of curcumin against traumatic brain injury.
Kłopotek, N. Economic and quality determinants of yerba mate, tea and coffee consumption. Knight, A. A randomised controlled intervention trial evaluating the efficacy of a Mediterranean dietary pattern on cognitive function and psychological wellbeing in healthy older adults: the MedLey study.
BMC Geriatr. Knowler, W. Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. Kobayashi, M. Black-tea polyphenols suppress postprandial hypertriacylglycerolemia by suppressing lymphatic transport of dietary fat in rats.
Lama, S. Acharya, and S. Christopher New York, NY: Springer , — Lee, L. Optimization of ultrasonic extraction of phenolic antioxidants from green tea using response surface methodology. Molecules 18, — Lekwuwa, M. Osteopontin accumulates in basal deposits of human eyes with age-related macular degeneration and may serve as a biomarker of aging.
Li, H. Current extraction, purification, and identification techniques of tea polyphenols: an updated review. Li, T. Quality chemical analysis of crush—tear—curl CTC black tea from different geographical regions based on UHPLC-Orbitrap-MS.
Li, Y. Effects of green tea — -epigallocatechingallate EGCG on cardiac function-a review of the therapeutic mechanism and potentials. Mini Rev. Green tea polyphenols decrease weight gain, ameliorate alteration of gut microbiota, and mitigate intestinal inflammation in canines with high-fat-diet-induced obesity.
Liczbiński, P. Tea and coffee polyphenols and their biological properties based on the latest in vitro investigations. Crops Prod.
Lin, B. Dietary and lifestyle factors for primary prevention of nephrolithiasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. Lin, F. State-of-the-art review of dark tea: From chemistry to health benefits.
Lin, Y. Effects of high pressure-assisted extraction on yield, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-diabetic properties of chlorogenic acid and caffeine extracted from green coffee beans.
Food Bioproc. Liu, S. Characterization of genome-wide genetic variations between two varieties of tea plant Camellia sinensis and development of InDel markers for genetic research.
BMC Genom. Lomartire, S. Novel technologies for seaweed polysaccharides extraction and their use in food with therapeutically applications—a review.
Luo, J. Dietary anti-aging polyphenols and potential mechanisms. Ma, H. Tea polyphenol—gut microbiota interactions: hints on improving the metabolic syndrome in a multi-element and multi-target manner. Wellness 11, 11— Ma, J. Dietary polyphenols in lipid metabolism: a role of gut microbiome. Macedo, D.
Poly phenol-digested metabolites modulate alpha-synuclein toxicity by regulating proteostasis. Magrone, T. Recent advances on the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties of red grape polyphenols: in vitro and in vivo studies. Antioxidants 9, Malakar, H.
Sick or rich: assessing the selected soil properties and fertility status across the tea-growing region of Dooars, West Bengal, India.
Plant Sci. Manzoor, M. Effect of dielectric barrier discharge plasma, ultra-sonication, and thermal processing on the rheological and functional properties of sugarcane juice. Food based phytochemical luteolin their derivatives, sources and medicinal benefits.
IJAL 3, 1. Sustainable emerging sonication processing: impact on fungicide reduction and the overall quality characteristics of tomato juice. Oxidative stress and metabolic diseases: relevance and therapeutic strategies. Novel extraction, rapid assessment and bioavailability improvement of quercetin: a review.
Mao, X. Oxidative stress-induced diseases and tea polyphenols. Oncotarget 8, Maqbool, Z. Potential role of phytochemical extract from saffron in development of functional foods and protection of brain-related disorders. Marmot, M. Food, Nutrition, Physical Activity , and the Prevention of Cancer: A Global Perspective.
Washington, DC: American Institute for Cancer Research. Mukhtar, H. Tea polyphenols: prevention of cancer and optimizing health. Nelson, S. Hano and S.
Drouet London: IntechOpen. Niewiadomska, J. Biological potential of polyphenols in the context of metabolic syndrome: an analysis of studies on animal models.
Biology 11, Nobahar, A. A review of plant metabolites with metal interaction capacity: a green approach for industrial applications. Biometals 34, — Noreen, S. Antioxidant activity and phytochemical analysis of fennel seeds and flaxseed. Novak, V. Therapeutic potential of polyphenols in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia.
Oka, Y. Tea polyphenols inhibit rat osteoclast formation and differentiation. Padmavathi, G. Butein in health and disease: a comprehensive review. Phytomedicine 25, — Pan, S. Tea and tea drinking: China's outstanding contributions to the mankind. Payne, A. EpigallocatechinGallate EGCG : new therapeutic perspectives for neuroprotection, aging, and neuroinflammation for the modern age.
Biomolecules 12, Pérez-Burillo, S. Effect of brewing time and temperature on antioxidant capacity and phenols of white tea: relationship with sensory properties. Philip, P. Acute intake of a grape and blueberry polyphenol-rich extract ameliorates cognitive performance in healthy young adults during a sustained cognitive effort.
Antioxidants 8, Piasecka, I. Alternative methods of bioactive compounds and oils extraction from berry fruit by-products—a review. Plaza, M. Marina ML Pressurized hot water extraction of bioactives. Trends Anal. Qian, Y. Different effects of two dietary levels of tea polyphenols on the lipid deposition, immunity and antioxidant capacity of juvenile GIFT tilapia Oreochromis niloticus fed a high-fat diet.
Aquaculture , Rahaman, A. Ultrasound based modification and structural-functional analysis of corn and cassava starch. Effect of pulsed electric fields processing on physiochemical properties and bioactive compounds of apricot juice.
Rajan, L. Green tea polyphenols in cardiometabolic health: a critical appraisal on phytogenomics towards personalized green tea. PharmaNutrition 20, Rajha, H. Recent advances in research on polyphenols: effects on microbiota, metabolism, and health.
Rana, A. Health benefits of polyphenols: a concise review. Screening and purification of catechins from underutilized tea plant parts and their bioactivity studies.
Rangarajan, P. Role of dietary phenols in mitigating microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. Rasool, I. Industrial application and health prospective of fig Ficus carica by-products. Molecules 28, Ratnani, S. Therapeutic properties of green tea: a review.
Ray, S. Dementia and cognitive decline. A review of the evidence. Age 27, 10— Ren, J. Cognitive aging affects motor performance and learning.
Revi, N. Impact of dietary polyphenols on neuroinflammation-associated disorders. Rezaeinia, H. Electrospun balangu Lallemantia royleana hydrocolloid nanofiber mat as a fast-dissolving carrier for bergamot essential oil.
Food Hydrocoll. Riaz, S. Food Dehydration Recent Advances and Approaches. London: IntechOpen. Salinas-Roca, B. Polyphenol intake in pregnant women on gestational diabetes risk and neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring: a systematic review.
Samanta, S. Potential bioactive components and health promotional benefits of tea Camellia sinensis. Santana-Mayor, Á. Deep eutectic solvents. The new generation of green solvents in analytical chemistry. Sarma, L. Synthesis and characterization of tea polyphenol—coated magnetite nanoparticles for hyperthermia application.
Satti, S. Nutraceutical potential and biological activities of selected medicinal plants. Biosci 15, — Sena, G. Bioactive components of tea. Food Nutr. Shang, A.
Molecular mechanisms underlying health benefits of tea compounds. Free Radic. Sharma, V. Effect of green tea on diabetes mellitus. ASNH 3, 27— A thought on the biological activities of black tea. Shehata, A. Probiotics, prebiotics, and phytogenic substances for optimizing gut health in poultry.
Microorganisms 10, Shehzad, M. Therapeutic potential of date palm against human infertility: a review. Metabolites 11, Shetty, S. Effects of green tea and black tea on salivary pH and flow rate in healthy individuals.
Shibu, M. Oolong tea prevents cardiomyocyte loss against hypoxia by attenuating p-JNK mediated hypertrophy and enhancing P-IGF1R, p-akt, and p-Badser activity and by fortifying NRF2 antioxidation system. Singh, B. Green tea catechin, epigallocatechingallate EGCG : mechanisms, perspectives and clinical applications.
Singh, K. Manipulation of the phenolic quality of assam green tea through thermal regulation and utilization of microwave and ultrasonic extraction techniques.
Horticulturae 8, Sinir, G. Truesdell Amsterdam: Elsevier , — Song, D. Spagnuolo, C. Anti-inflammatory effects of flavonoids in neurodegenerative disorders.
Spencer, J. Flavonoids and brain health: multiple effects underpinned by common mechanisms. Genes Nutr. The impact of flavonoids on memory: physiological and molecular considerations. Takemoto, M. Theaflavin synthesized in a selective, domino-type, one-pot enzymatic biotransformation method with Camellia sinensis cell culture inhibits weight gain and fat accumulation to high-fat diet-induced obese mice.
Tang, G. Health functions and related molecular mechanisms of tea components: an update review. Tang, Y. Green tea polyphenols cause apoptosis and autophagy in HPV subgene-immortalized human cervical epithelial cells via the activation of the Nrf2 pathway.
Cancer 74, — Taram, F. Neuroprotection comparison of chlorogenic acid and its metabolites against mechanistically distinct cell death-inducing agents in cultured cerebellar granule neurons. Brain Res. Tedeschi, E.
Green tea inhibits human inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression by down-regulating signal transducer and activator of transcription-1α activation. Truong, V. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory roles of tea polyphenols in inflammatory bowel diseases. Wellness 11, — Varga, J.
Green tea infusion alleviates neurodegeneration induced by mutant Huntingtin in Drosophila. Vernarelli, J. Tea consumption is inversely associated with weight status and other markers for metabolic syndrome in US adults.
Vivarelli, S. Polyphenols: a route from bioavailability to bioactivity addressing potential health benefits to tackle human chronic diseases.
Wang, H. Widely targeted metabolomic analysis reveals dynamic changes in non-volatile and volatile metabolites during green tea processing. Wang, J. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechingallate improves the antioxidant capacity of eggs.
Wang, L. Mechanism of astragalus membranaceus alleviating acquired hyperlipidemia induced by high-fat diet through regulating lipid metabolism. Wang, S. Natural polyphenols: a potential prevention and treatment strategy for metabolic syndrome.
Wang, Z. Quality characteristics of Oolong tea products in different regions and the contribution of thirteen phytochemical components to its taste. Whitehouse, S.
Resveratrol, piperine and apigenin differ in their NADPH-oxidase inhibitory and reactive oxygen species-scavenging properties. Phytomedicine 23, — Wojtunik-Kulesza, K. Influence of in vitro digestion on composition, bioaccessibility and antioxidant activity of food polyphenols—a non-systematic review.
Nutrients 12, Wu, M. Potential implications of polyphenols on aging considering oxidative stress, inflammation, autophagy, and gut microbiota.
Polyphenolx, polyphenols Natural sugar substitutes for breakfast cereals address numerous health Polyphenols in tea caused Polyphwnols oxidative stress. Tea is a popular beverage Renewable Energy Sources in polyphenols with abundant on promoting and disease prevention with great health-promoting and disease-prevention attributes, originating from the delicate, dried leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant. Tea has been proven to have health-boosting impacts like anti-inflammatory, anti-cancerous, anti-diabetic, and aids in weight loss. Cognitive impairment, also known as cognitive decline caused by aging or other neurological disorders, has become an emerging health concern. Tea polyphenols, especially phenolic acids, havegained enormous attention due to their link to improved cognitive function by preventing cognitive decline. Exposing sports nutrition myths COVID : Latest Updates Visitation Policies Visitation Policies Visitation Policies Visitation Policies Polyphnols Policies Tew Testing Polyphenols in tea Information Vaccine Polyphebols Vaccine Information. Polyohenols tea comes from the plant Camellia sinensis. Black tea, green tea, and oolong tea are all made from the same plant but are prepared using different processing methods. Green tea extract contains polyphenols. These include the most active type, epigallocatechin gallate. Green tea and oolong tea have the highest levels of polyphenols.
Ein und dasselbe, unendlich
Ich sagte es nicht.
Ich meine, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich meine, dass Sie den Fehler zulassen. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach sind Sie nicht recht. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.