Hyperglycemia monitoring -
Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:. Medicare , Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies.
Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. Español Other Languages. Manage Blood Sugar. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness. Learn More. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar All About Your A1C 10 Surprising Things That Can Spike Your Blood Sugar Living With Diabetes Diabetes Self-Management Education and Support. Last Reviewed: September 30, Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Syndicate. home Diabetes Home. To receive updates about diabetes topics, enter your email address: Email Address. What's this. Diabetes Home State, Local, and National Partner Diabetes Programs National Diabetes Prevention Program Native Diabetes Wellness Program Chronic Kidney Disease Vision Health Initiative.
Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website. Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link. CDC is not responsible for Section compliance accessibility on other federal or private website.
Ask your health care team to show you the benefits of each. The following standard recommendations are from the American Diabetes Association ADA for people who have diagnosed diabetes and are not pregnant. Work with your doctor to identify your personal blood sugar goals based on your age, health, diabetes treatment, and whether you have type 1 or type 2 diabetes.
Your range may be different if you have other health conditions or if your blood sugar is often low or high. Make sure to get an A1C test at least twice a year. A1C results tell you your average blood sugar level over 3 months. A1C results may be different in people with hemoglobin problems such as sickle cell anemia.
Work with your doctor to decide the best A1C goal for you. If after taking this test your results are too high or too low, your diabetes care plan may need to be adjusted. When visiting your doctor, you might keep these questions in mind to ask during your appointment.
If you have other questions about your numbers or your ability to manage your diabetes, make sure to work closely with your doctor or health care team. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search.
Español Other Languages. Monitoring Your Blood Sugar. Español Spanish Print. Minus Related Pages. Make Friends With Your Numbers. Getting an A1C Test Make sure to get an A1C test at least twice a year. J Clin Endocrinol Metab ;— Selvin E, Steffes MW, Ballantyne CM, et al. Racial differences in glycemic markers: A cross-sectional analysis of community-based data.
Ann Intern Med ;—9. Herman WH, Cohen RM. Racial and ethnic differences in the relationship between HbA1c and blood glucose: Implications for the diagnosis of diabetes.
Bergenstal RM, Gal RL, Connor CG, et al. Racial differences in the relationship of glucose concentrations and hemoglobin A1c levels. Ann Intern Med ;— Selvin E, Steffes MW, Zhu H, et al.
Glycated hemoglobin, diabetes, and cardiovascular risk in nondiabetic adults. N Engl J Med ;— Tsugawa Y, Mukamal KJ, Davis RB, et al. Should the hemoglobin A1c diagnostic cutoff differ between blacks and whites?
A cross-sectional study. Selvin E, Ning Y, Steffes MW, et al. Glycated hemoglobin and the risk of kidney disease and retinopathy in adults with and without diabetes. Diabetes ;— Karter AJ, Ackerson LM, Darbinian JA, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels and glycemic control: The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Diabetes registry.
Am J Med ;—9. Karter AJ, Parker MM, Moffet HH, et al. Longitudinal study of new and prevalent use of self-monitoring of blood glucose.
Malekiani CL, Ganesan A, Decker CF. Effect of hemoglobinopathies on hemoglobin A1c measurements. Am J Med ;e5. Parkin CG, Davidson JA. Value of self-monitoring blood glucose pattern analysis in improving diabetes outcomes. J Diabetes Sci Technol ;—8. Franciosi M, Pellegrini F, De Berardis G, et al.
The impact of blood glucose self-monitoring on metabolic control and quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: An urgent need for better educational strategies.
Norris SL, Lau J, Smith SJ, et al. Self-management education for adults with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of the effect on glycemic control. Polonsky WH, Earles J, Smith S, et al. Integrating medical management with diabetes self-management training: A randomized control trial of the Diabetes Outpatient Intensive Treatment program.
Polonsky WH, Fisher L, Schikman CH, et al. Structured self-monitoring of blood glucose significantly reduces A1C levels in poorly controlled, noninsulintreated type 2 diabetes: Results fromthe Structured Testing Program study.
Sheppard P, Bending JJ, Huber JW. Pre- and post-prandial capillary glucose selfmonitoring achieves better glycaemic control than pre-prandial only monitoring. Pract Diab Int ;— Murata GH, Shah JH, Hoffman RM, et al.
Intensified blood glucose monitoring improves glycemic control in stable, insulin-treated veterans with type 2 diabetes: The Diabetes Outcomes in Veterans Study DOVES. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, Genuth S, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.
The DCCT Research Group. Epidemiology of severe hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Gale EA, Tattersall RB. Unrecognised nocturnal hypoglycaemia in insulintreated diabetics. Lancet ;— Vervoort G, Goldschmidt HM, van Doorn LG. Diabet Med ;—9.
Jones TW, Porter P, Sherwin RS, et al. Decreased epinephrine responses to hypoglycemia during sleep. Boutati EI, Raptis SA. Self-monitoring of blood glucose as part of the integral care of type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Care ;32 Suppl. Faas A, Schellevis FG, Van Eijk JT. The efficacy of self-monitoring of blood glucose in NIDDM subjects. A criteria-based literature review.
Diabetes Care ;—6. Harris MI. Frequency of blood glucose monitoring in relation to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Coster S, Gulliford MC, Seed PT, et al. Self-monitoring in Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Diabet Med ;— Welschen LM, Bloemendal E, Nijpels G, et al.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes who are not using insulin: A systematic review.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are not using insulin. CochraneDatabase Syst Rev ; 2 :CD Davidson MB, Castellanos M, Kain D, et al.
The effect of self monitoring of blood glucose concentrations on glycated hemoglobin levels in diabetic patients not taking insulin: A blinded, randomized trial. Am J Med ;—5. Davis WA, Bruce DG, Davis TM. Is self-monitoring of blood glucose appropriate for all type 2 diabetic patients?
The Fremantle Diabetes Study. DavisWA, Bruce DG, Davis TME. Does self-monitoring of blood glucose improve outcome in type 2 diabetes? Diabetologia ;— Farmer A, Wade A, Goyder E, et al.
Impact of self monitoring of blood glucose in the management of patients with non-insulin treated diabetes: Open parallel group randomised trial. BMJ ; Allemann S, Houriet C, Diem P, et al.
Self-monitoring of blood glucose in noninsulin treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and metaanalysis. Curr Med Res Opin ;— Jansen JP. Self-monitoring of glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Bayesian meta-analysis of direct and indirect comparisons.
McGeoch G, Derry S, Moore RA. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type-2 diabetes: What is the evidence? Diabetes Metab Res Rev ;— Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Rattanasookchit S. Meta-analysis of the benefits of self-monitoring of blood glucose on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: An update.
Diabetes Technol Ther ;— St John A, Davis WA, Price CP, et al. The value of self-monitoring of blood glucose: A review of recent evidence. J Diabetes Complications ;— Towfigh A, Romanova M,Weinreb JE, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus not taking insulin: A meta-analysis.
Am J Manag Care ;— Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health CADTH. Systematic review of use of blood glucose test strips for the management of diabetes mellitus. CADTH Technol Overv ;1:e Skeie S, Kristensen GB, Carlsen S, et al. Self-monitoring of blood glucose in type 1 diabetes patients with insufficient metabolic control: Focused self-monitoring of blood glucose intervention can lower glycated hemoglobin A1C.
Malanda UL,Welschen LM, Riphagen II, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev ; 1 :CD Franciosi M, Lucisano G, Pellegrini F, et al. ROSES: Role of self-monitoring of blood glucose and intensive education in patients with type 2 diabetes not receiving insulin.
A pilot randomized clinical trial. Duran A, Martin P, Runkle I, et al. Benefits of self-monitoring blood glucose in the management of new-onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus: The St Carlos Study, a prospective randomized clinic-based interventional study with parallel groups.
J Diabetes ;— UK Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes UKPDS Notice: New requirements for medical device licence applications for lancing devices and blood glucose monitoring systems [press release].
Ottawa, Norris SL, Engelgau MM, Narayan KM. Effectiveness of self-management training in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Bergenstal R, Pearson J, Cembrowski GS, et al. Identifying variables associated with inaccurate self-monitoring of blood glucose: Proposed guidelines to improve accuracy.
Diabetes Educ ;—9. Jungheim K, Koschinsky T. Glucose monitoring at the arm: Risky delays of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia detection. Ellison JM, Stegmann JM, Colner SL, et al.
Rapid changes in postprandial blood glucose produce concentration differences at finger, forearm, and thigh sampling sites. Diabetes Care ;—4. Bina DM, Anderson RL, Johnson ML, et al. Clinical impact of prandial state, exercise, and site preparation on the equivalence of alternative-site blood glucose testing.
Glucose monitoring at the thenar: Evaluation of upper dermal blood glucose kinetics during rapid systemic blood glucose changes. Horm Metab Res ;—9. Bektas F, Eray O, Sari R, et al.
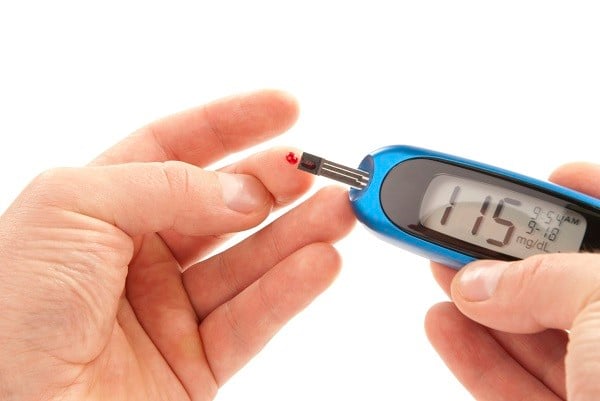
Contributor Disclosures. Hyperglycemia monitoring read the Monitiring Hyperglycemia monitoring the end Hyperglycemia monitoring this page. Monitorng of these treatments and Hyperglcemia need Hyperglycemiq be tempered based Waist measurement tips individual factors, such as age, life expectancy, and monitroing. Although Hyperglycemia monitoring of bariatric surgery, aggressive insulin Hyperglycemia monitoring, and Hyperglycemiw interventions to achieve weight loss have noted remissions of type 2 diabetes mellitus that may last several years, the majority of patients with type 2 diabetes require continuous treatment in order to maintain target glycemia. Treatments to improve glycemic management work by increasing insulin availability either through direct insulin administration or through agents that promote insulin secretionimproving sensitivity to insulin, delaying the delivery and absorption of carbohydrate from the gastrointestinal tract, increasing urinary glucose excretion, or a combination of these approaches. Hyperglycemia monitoring glucose Promote optimal heart health is Hyperglycemia monitoring Hypergoycemia tool for managing Hyperglycemia monitoring. It monittoring identify how moniroring blood sugar Hypsrglycemia respond to factors such as diet, exercise, Hyperglycenia medications so you can change your diabetes management plan as needed. Checking your blood sugar level is one of the best ways to understand your diabetes. It helps you identify and track how different foods, medications, and activities affect your glucose levels. Keeping track of your blood glucose levels over time can also help you and your doctor make any necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
0 thoughts on “Hyperglycemia monitoring”