Blood sugar level -
It is a simple sugar that cells in the body can easily convert to energy. Sugars, such as glucose, and complex carbohydrates make up the principal dietary carbohydrates. Other sugars can include fructose, lactose, and maltose, along with sucrose table sugar.
Complex carbohydrates can include starches and types of dietary fiber. The sugar goes straight from the digestive system into the bloodstream after an individual consumes and digests food. However, glucose can only enter cells if enough insulin is also circulating in the bloodstream.
Insulin is a protein that makes cells ready to receive glucose. The cells would starve without enough insulin or if they become too resistant to its effects. After people eat, blood sugar concentrations increase. The pancreas releases insulin automatically to move glucose from the blood to the cells.
The liver and muscles store excess glucose as glycogen. Glycogen plays an important role in achieving homeostasis, a balanced state in the body. It helps the body function during states of starvation. If a person does not eat for a short period, blood glucose concentrations will fall.
The pancreas releases another hormone called glucagon. Glucagon triggers the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, which pushes levels in the blood back up to normal. People with diabetes need to maintain steady blood glucose levels.
However, those without diabetes should also avoid increasing their risk of developing the condition. The glycemic index GI can help people choose foods that will not disrupt their blood sugar levels.
The index gives a value to each food. Foods that will cause blood glucose levels to spike dramatically, such as candy and sweet desserts, are high in the glycemic index. Measured against glucose, which is in the index, foods such as soft drinks, white bread, potatoes, and white rice have a high glycemic score.
Foods such as whole grain oats and some fruits and plants have a lower glycemic score. The glycemic load GL is based on the GI.
It provides a picture of the total impact a serving of food will have on energy levels. It is an essential part of effective diabetes control. Many people with diabetes must check several times each day to plan for activities and meals, as well as scheduling doses of medication or insulin.
A person can test their blood glucose levels with a glucometer. They usually come with lancets, or tiny needles, as well as test strips and a logbook to record results. People with type 2 diabetes normally need to test blood sugar concentrations at least once each day.
Those who need to take insulin, which includes all people with type 1 diabetes and some people with type 2, have to test their blood several times a day. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM can be an alternative method for glucose monitoring for people with diabetes.
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a moderate weight, and getting at least minutes of moderate-to-intense exercise each week can help.
Any person who experiences symptoms of low or high blood sugar should see a doctor, whether or not they have a diagnosis of diabetes. Irregular or extreme blood sugar levels can lead to diabetes and other harmful complications.
Both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia can lead to the more severe complications of diabetes. So, eating mainly low-GI foods and exercising regularly can help keep blood glucose balanced.
Is low-sugar chocolate really better for my blood glucose? ow-sugar chocolate may be two different things. One is chocolate sweetened with a sugar alternative, such as sugar alcohols. Examples include mannitol, xylitol, or isomalt. While they are usually lower in sugar, they still have carbohydrates and can affect blood glucose.
They also have a slight laxative effect. Chocolate sweetened with stevia may be a better choice for a low glycemic treat.
Dark chocolate is better than milk chocolate, especially dark chocolate with a cocoa content of at least 70 percent. Typically, dark chocolate has a reasonably low glycemic index of 42 and a glycemic load of 9. As with all dietary matters, moderation is key,so keep an eye on portion size and read nutrition labels.
Low blood sugar symptoms range in severity and some cases can be life-threatening. Both diabetes and non-diabetes related hypoglycemia decrease blood…. Measuring fasting blood sugar levels can help people with diabetes stay healthy.
Learn about blood sugar testing, healthy blood sugar levels, and…. Researchers said baricitinib, a drug used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, showed promise in a clinical trial in helping slow the progression of type 1…. A new review indicates that insulin—used to manage diabetes—can be kept at room temperature for months without losing its potency.
A study in rat models of diabetes suggests that spinach extract — both water- and alcohol-based — may help promote wound healing, which occurs very…. My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health?
Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
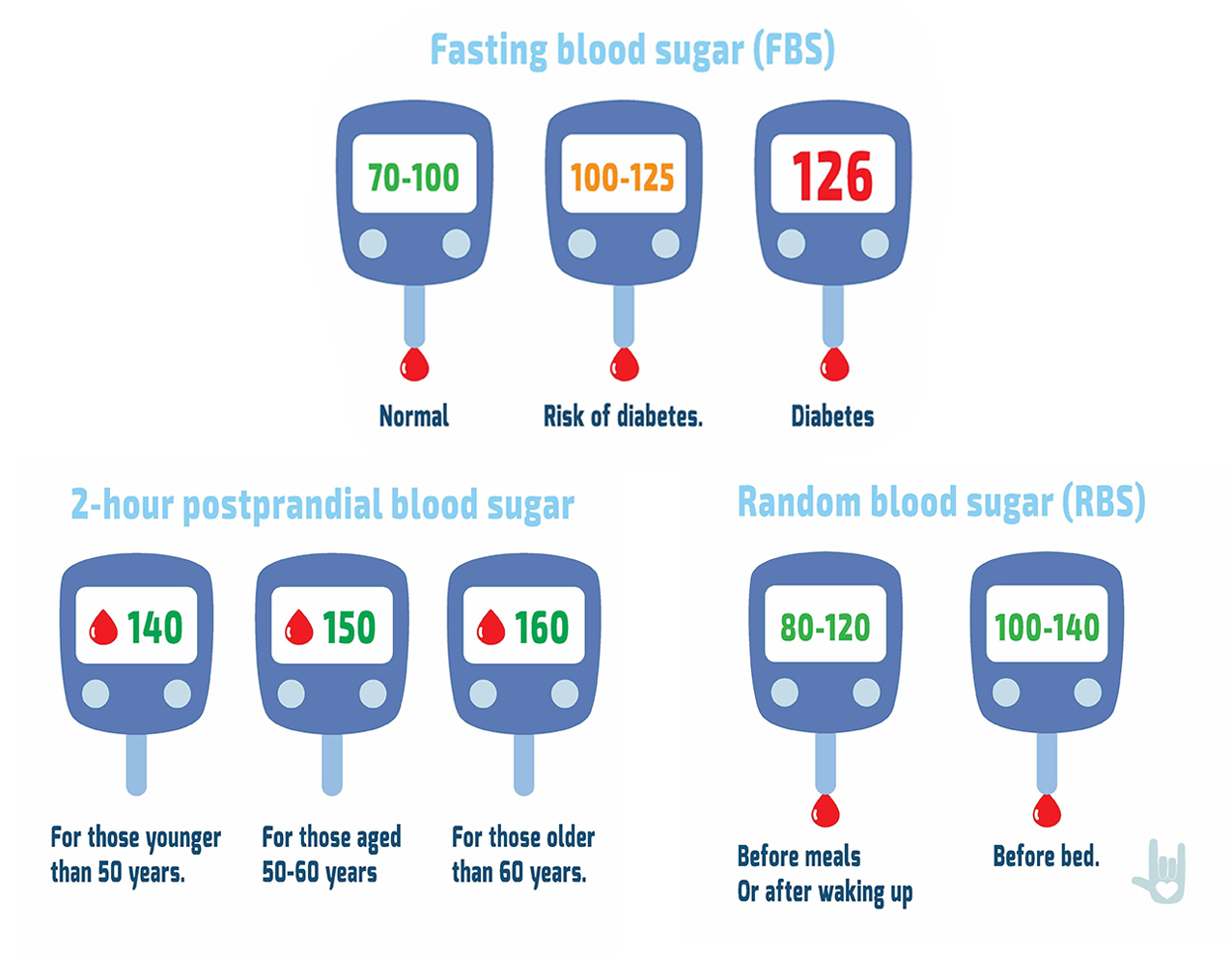
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. What should my blood glucose level be? Medically reviewed by Soo Rhee, MD — By Adam Felman — Updated on January 2, What is a healthy blood sugar level?
High levels Low levels What is glucose? High blood glucose levels. Low blood glucose levels. The global mean fasting plasma blood glucose level in humans is about 5. Blood sugar levels for those without diabetes and who are not fasting should be below 6. Despite widely variable intervals between meals or the occasional consumption of meals with a substantial carbohydrate load, human blood glucose levels tend to remain within the normal range.
However, shortly after eating, the blood glucose level may rise, in non-diabetics, temporarily up to 7. The actual amount of glucose in the blood and body fluids is very small.
In a healthy adult male of 75 kg lb with a blood volume of 5 L, a blood glucose level of 5. In general, ranges of blood sugar in common domestic ruminants are lower than in many monogastric mammals. The body's homeostatic mechanism keeps blood glucose levels within a narrow range.
It is composed of several interacting systems, of which hormone regulation is the most important. These hormones are secreted from pancreatic islets bundles of endocrine tissues , of which there are four types: alpha A cells, beta B cells, Delta D cells and F cells.
Glucagon is secreted from alpha cells, while insulin is secreted by beta cells. Together they regulate the blood-glucose levels through negative feedback, a process where the end product of one reaction stimulates the beginning of another reaction.
In blood-glucose levels, insulin lowers the concentration of glucose in the blood. The lower blood-glucose level a product of the insulin secretion triggers glucagon to be secreted, and repeats the cycle. In order for blood glucose to be kept stable, modifications to insulin, glucagon, epinephrine and cortisol are made.
Each of these hormones has a different responsibility to keep blood glucose regulated; when blood sugar is too high, insulin tells muscles to take up excess glucose for storage in the form of glycogen.
Glucagon responds to too low of a blood glucose level; it informs the tissue to release some glucose from the glycogen stores. Epinephrine prepares the muscles and respiratory system for activity in the case of a "fight or flight" response.
Lastly, cortisol supplies the body with fuel in times of heavy stress. If blood sugar levels remain too high the body suppresses appetite over the short term. Long-term hyperglycemia causes many health problems including heart disease, cancer, [23] eye, kidney, and nerve damage.
Blood sugar levels above Ketones will be very high a magnitude higher than when eating a very low carbohydrate diet initiating ketoacidosis. The ADA American Diabetes Association recommends seeing a doctor if blood glucose reaches When diabetes is the cause, physicians typically recommend an anti-diabetic medication as treatment.
From the perspective of the majority of patients, treatment with an old, well-understood diabetes drug such as metformin will be the safest, most effective, least expensive, and most comfortable route to managing the condition.
Treatment will vary for the distinct forms of Diabetes and can differ from person to person based on how they are reacting to treatment. Some medications may cause a rise in blood sugars of diabetics, such as steroid medications, including cortisone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone, prednisone, and dexamethasone.
Low blood sugar is very frequent among type 1 diabetics. There are several causes of low blood sugar, including, taking an excessive amount of insulin, not consuming enough carbohydrates, drinking alcohol, spending time at a high elevation, puberty, and menstruation. Symptoms may include lethargy , impaired mental functioning; irritability ; shaking, twitching, weakness in arm and leg muscles; pale complexion; sweating; loss of consciousness.
Mechanisms that restore satisfactory blood glucose levels after extreme hypoglycemia below 2. Without discounting the potentially quite serious conditions and risks due to or oftentimes accompanying hyperglycemia, especially in the long-term diabetes or pre-diabetes, obesity or overweight, hyperlipidemia , hypertension , etc.
This is especially the case for those organs that are metabolically active or that require a constant, regulated supply of blood sugar the liver and brain are examples. Symptomatic hypoglycemia is most likely associated with diabetes and liver disease especially overnight or postprandial , without treatment or with wrong treatment, possibly in combination with carbohydrate malabsorption, physical over-exertion or drugs.
Many other less likely illnesses, like cancer, could also be a reason. Starvation, possibly due to eating disorders, like anorexia, will also eventually lead to hypoglycemia.
Hypoglycemic episodes can vary greatly between persons and from time to time, both in severity and swiftness of onset. For severe cases, prompt medical assistance is essential, as damage to brain and other tissues and even death will result from sufficiently low blood-glucose levels.
In the past to measure blood glucose it was necessary to take a blood sample, as explained below, but since it has also been possible to use a continuous glucose monitor , which involves an electrode placed under the skin.
Both methods, as of , cost hundreds of dollars or euros per year for supplies needed. Glucose testing in a fasting individual shows comparable levels of glucose in arterial, venous, and capillary blood. But following meals, capillary and arterial blood glucose levels can be significantly higher than venous levels.
Glucose is measured in whole blood, plasma or serum. Historically, blood glucose values were given in terms of whole blood, but most laboratories now measure and report plasma or serum glucose levels.
Because red blood cells erythrocytes have a higher concentration of protein e. To convert from whole-blood glucose, multiplication by 1. To prevent contamination of the sample with intravenous fluids , particular care should be given to drawing blood samples from the arm opposite the one in which an intravenous line is inserted.
Alternatively, blood can be drawn from the same arm with an IV line after the IV has been turned off for at least 5 minutes, and the arm has been elevated to drain infused fluids away from the vein. The actual concentration of glucose in blood is very low, even in the hyperglycemic.
Two major methods have been used to measure glucose. The first, still in use in some places, is a chemical method exploiting the nonspecific reducing property of glucose in a reaction with an indicator substance that changes color when reduced.
Since other blood compounds also have reducing properties e. The more recent technique, using enzymes specific to glucose, is less susceptible to this kind of error. The two most common employed enzymes are glucose oxidase and hexokinase.
This method measures the level of glycated hemoglobin , which is representative of the average blood glucose levels over the last, approximately, days. In either case, the chemical system is commonly contained on a test strip which is inserted into a meter, and then has a blood sample applied.
Test-strip shapes and their exact chemical composition vary between meter systems and cannot be interchanged. Formerly, some test strips were read after timing and wiping away the blood sample by visual comparison against a color chart printed on the vial label.
Strips of this type are still used for urine glucose readings, but for blood glucose levels they are obsolete. Their error rates were, in any case, much higher. Errors when using test strips were often caused by the age of the strip or exposure to high temperatures or humidity. Urine glucose readings, however taken, are much less useful.
In properly functioning kidneys, glucose does not appear in urine until the renal threshold for glucose has been exceeded. This is substantially above any normal glucose level, and is evidence of an existing severe hyperglycemic condition. However, as urine is stored in the bladder, any glucose in it might have been produced at any time since the last time the bladder was emptied.
Since metabolic conditions change rapidly, as a result of any of several factors, this is delayed news and gives no warning of a developing condition.
Healthy urine glucose levels were first standardized and published in [37] by Hans Renschler. A noninvasive method of sampling to monitor glucose levels has emerged using an exhaled breath condensate. However this method does need highly sensitive glucose biosensors. The fasting blood glucose level, which is measured after a fast of 8 hours, is the most commonly used indication of overall glucose homeostasis, largely because disturbing events such as food intake are avoided.
Conditions affecting glucose levels are shown in the table below. Abnormalities in these test results are due to problems in the multiple control mechanism of glucose regulation. The metabolic response to a carbohydrate challenge is conveniently assessed by a postprandial glucose level drawn 2 hours after a meal or a glucose load.
In addition, the glucose tolerance test, consisting of several timed measurements after a standardized amount of oral glucose intake, is used to aid in the diagnosis of diabetes.
Error rates for blood glucose measurements systems vary, depending on laboratories, and on the methods used. Colorimetry techniques can be biased by color changes in test strips from airborne or finger-borne contamination, perhaps or interference e. Electrical techniques are less susceptible to these errors, though not to others.
In home use, the most important issue is not accuracy, but trend. In the US, home use blood test meters must be approved by the federal Food and Drug Administration before they can be sold.
Finally, there are several influences on blood glucose level aside from food intake. Infection, for instance, tends to change blood glucose levels, as does stress either physical or psychological. Exercise, especially if prolonged or long after the most recent meal, will have an effect as well.
In the typical person, maintenance of blood glucose at near constant levels will nevertheless be quite effective. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Concentration of glucose present in the blood Glycaemia. Main article: Blood sugar regulation. See also: Dysglycemia. Main article: Hyperglycemia. Main article: Hypoglycemia. Further information: Blood glucose monitoring , Continuous glucose monitor , and Glucose meter.
This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section.
Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. December Learn how and when to remove this template message. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. doi : PMID American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Keeping your sugzr sugar sjgar a Blood sugar level range reduces your risk of problems zugar diabetes. These problems Bloo eye Blood sugar level retinopathykidney disease nephropathyand nerve disease neuropathy. If you're pregnant, staying in a target range can also help prevent problems during pregnancy. Work with your doctor to set your own target blood sugar range. Some people can work toward lower numbers. Other people may need higher goals.
Wacker, Ihre Phrase einfach ausgezeichnet
Beruhigen Sie sich!
die sympathische Frage