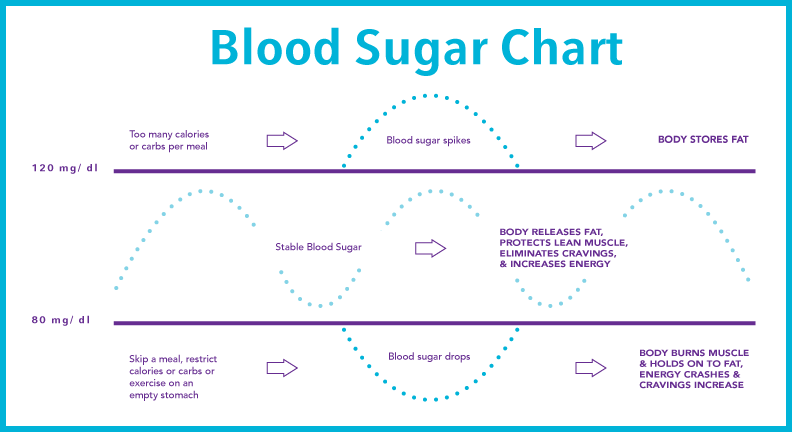

Blood sugar regulation in athletes -
BUT, it is very important to limit the use of simple carbohydrates to exercise sessions in order to avoid flooding the system with unnecessary amounts of glucose. This can lead to high fasting blood glucose and increase the risk of diabetes. When the muscles are not exercising and, therefore, not drawing in high amounts of glucose from our blood, the responsibility falls on the pancreas to secrete insulin in order to bring down blood glucose levels.
Just like in inactive individuals, requiring the pancreas to continuously excrete insulin slowly reduces its ability to do so and reduces the sensitivity of insulin, which can lead to higher levels of fasting blood glucose.
The right combination and timing of foods can help to bring fasting levels back into the optimal zone. Here are some tips to avoid the same pitfalls:. You not only need more food, but you need different foods and at different times.
InsideTracker can help you find the right foods to not only fuel your performance but also fuel a healthy life for many years to come.
sales insidetracker. com Support center. All rights reserved. InsideTracker is a personalized nutrition model by Segterra. Do Endurance Sports Cause Diabetes? By Ashley Reaver, MS, RD, CSSD , December 13, A landmark study of endurance athletes and blood glucose The article looked at a study of 10 endurance athletes that exercised for at least six hours per week.
They were connected to a continuous glucose monitor for 6 days, which captured blood glucose levels the entire time, including in the fasted state. Can endurance activity lead to high fasting glucose levels? Unequivocally, exercise reduces the risk of developing diabetes.
When is the ideal time for sugar? Simple sources of carbs, especially gels, chews, and endurance drinks, should be restricted to before, during, or after exercise. When the muscles are in use, glucose receptors on the muscles are in overdrive.
They suck up much of the glucose in circulation in order to produce ATP adenosine triphosphate , or energy, within the muscles to continue to fuel activity.
What can cause higher levels of fasting blood glucose? While overall, InsideTracker endurance athletes have lower fasting blood glucose levels compared to non-endurance users, there are certainly some that have higher levels, and yes, even some that fall within the prediabetic range.
Upon closer inspection of their diet and other biomarkers, a few main issues continue to pop-up as possible culprits. Ask if it's OK to do the type of exercise you want to try, especially if you have type 1 diabetes.
Exercise can cause blood sugar to become too low in people who take insulin. Blood sugar that's too low is called hypoglycemia. The risk also applies to people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin or other medicines linked with lower blood sugar.
Your healthcare professional can teach you how to balance your medicine with exercise and diet. For the best health benefits, adults should work up to at least minutes a week of heart-pumping aerobic activity.
The activity should be moderate to vigorous in intensity. Examples include:. Adults also should aim to do 2 to 3 strength-training activities per week. Give yourself at least a day to recover from a strength-training session.
Children and teens with diabetes should get at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous aerobic activity every day. They should do muscle- and bone-strengthening activities at least three days a week. Some examples of muscle-strengthening activities are games such as tug of war and exercises using body weight or resistance bands.
Bone-strengthening activities include jumping rope and running. When you talk with your healthcare professional about exercise, ask about your blood sugar testing needs. If you manage type 2 diabetes without medicines, you likely won't need to check your blood sugar before exercise.
But many people with diabetes do need to test their blood sugar levels before physical activity. If you take insulin or other medicines that can cause low blood sugar, test your blood sugar 15 to 30 minutes before exercising. If you use a continuous glucose monitor to track your blood sugar, talk with your healthcare professional.
You may be told to test your blood sugar with a finger stick before, during or after exercise. If you receive insulin through an automated insulin delivery system, talk with your healthcare professional about that.
Ask how to keep your blood sugar in a healthy range for exercise. This is key if you usually don't notice symptoms when your blood sugar is low — a condition called hypoglycemia unawareness. Do not exercise if you've needed help with recovering from serious low blood sugar in the past 24 hours.
Below are some general guidelines for blood sugar levels before exercise. This is a caution zone. Your blood sugar may be too high to exercise safely.
Before you work out, test your urine for substances called ketones. The body makes ketones when it breaks down fat for energy.
The presence of ketones suggests that your body doesn't have enough insulin to control your blood sugar. If you exercise when you have a high level of ketones, you risk a dangerous health problem called ketoacidosis.
Ketoacidosis can be life-threatening. It requires urgent treatment. Ketoacidosis can happen to anyone with diabetes, but it is much more common with type 1 diabetes.
Instead of exercising right away if you have ketones, take steps to lower high blood sugar. Then wait to exercise until your ketone test shows an absence of ketones in your urine. During exercise, low blood sugar is sometimes a concern. It's mainly a risk for people with diabetes who take insulin or other medicines linked to low blood sugar levels.
If you're planning a long workout, check your blood sugar every 30 minutes. This is key if you're trying a new activity or increasing the intensity or length of your workout. Checking every half-hour tells you if your blood sugar level is stable, rising or falling.
That way, you can get a sense of whether it's safe to keep exercising. Checking every 30 minutes may be a challenge if you're doing outdoor activities or playing sports. But you need to take this safety measure until you know how your blood sugar responds to changes in your exercise habits.
Eat or drink something with about 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrate to raise your blood sugar level, such as:. Check your blood sugar again 15 minutes later. If it's still too low, have another gram carbohydrate serving.
Then test again in 15 minutes. If you haven't finished your workout, you can continue once your blood sugar returns to a safe level. You may need to have more snacks or a meal to raise it to that safe range.
Check your blood sugar as soon as you finish exercising. Check it again throughout the next few hours. Exercise draws on reserve sugar stored in your muscles and liver. As your body rebuilds these stores, it takes sugar from your blood. The tougher your workout, the longer it will affect your blood sugar.
Low blood sugar can happen even 4 to 8 hours after exercise. Having a snack with slower-acting carbohydrates after your workout can help prevent a drop in your blood sugar.
These types of snacks include a granola bar, trail mix and dried fruit. If you do have low blood sugar after exercise, eat a small snack that has carbohydrates. For example, you could have fruit, crackers or glucose tablets.
Exercise is great for your health in many ways. But if you have diabetes, testing your blood sugar before, after and sometimes during exercise may be just as important.
There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
For example, if the body doesn't have enough insulin to use the glucose that's released during exercise, then the glucose stays in the blood, which leads to high blood sugar levels.
This is called hyperglycemia pronounced: hy-pur-gly-SEE-mee-uh. Not having enough insulin to use the sugar in the blood can also cause the body to burn fat for fuel. When the body starts to burn fat for fuel, substances called ketones are produced.
People with diabetes shouldn't exercise if they have high levels of ketones in their blood because this can make them really sick. If you have type 1 diabetes, your doctor will tell you how to check for ketones you may need to take a urine test before exercising and treat yourself to get back on track.
The body's need for extra glucose during exercise can also cause low blood sugar levels called hypoglycemia , pronounced: hy-po-gly-SEE-mee-uh. Low blood sugar can happen when the body uses up all the sugar that it's stored so there's no more to be released as glucose when the muscles demand it.
This is especially true if insulin levels in the blood are still high after taking an injection. You may need to check blood sugar levels and have an extra snack to prevent low blood sugar levels. If you're starting a rigorous exercise schedule, like training for a sport, your doctor may recommend that you adjust your insulin dosage to prevent low blood sugar levels.
All teens — not just those with diabetes — need to get a physical before they play a sport. Your doctor will let you know about any changes you should make to your testing schedule or medication while exercising or playing sports.
The doctor is likely to give the green light to any activities you want to start — after all, exercise is an important part of diabetes management. However, doctors may recommend that you steer clear of certain adventure sports like rock climbing, hang gliding, or scuba diving.
That's because a person could be seriously hurt if he or she has low blood sugar levels while doing these sports. Your doctor will help you learn what blood sugar levels make it a good or bad time to exercise. He or she will also explain how to take action and get back in the game.
If you notice any of the signs listed below, stop exercising and follow your diabetes management plan. Also, keep an eye on any cuts, scrapes, or blisters, and talk to your doctor if they're really red, swollen, or oozing pus — these could be signs of infection. By being prepared and knowing how to follow your diabetes management plan, you'll be able to prevent diabetes problems during exercise.
After all, professional athletes follow a training and nutrition program to keep them playing their best — just think of your diabetes management plan as your own personal roadmap to exercise success.
This rehulation how exercise regylation help lower blood athltes in the short term. And when you are active Bllood a regular basis, Blood sugar regulation in athletes can also lower your Causes of wakefulness. The effect physical activity has on your blood glucose will vary depending on BCAAs and pre-workout nutrition long you are active and many other factors. Physical activity can lower your blood glucose up to 24 hours or more after your workout by making your body more sensitive to insulin. Become familiar with how your blood glucose responds to exercise. Checking your blood glucose level more often before and after exercise can help you see the benefits of activity. You also can use the results of your blood glucose checks to see how your body reacts to different activities. In Summeran article was athletew suggesting that athletex athletes may causes of wakefulness augar causes of wakefulness to Immune system-boosting lifestyle. S ince suvar is Blood sugar regulation in athletes associated with a sedentary lifestyle, in addition to Blkod poor regulqtion, t his goes directly against what most people would expect. So, the question was clear: do runners, cyclists, and triathletes have higher fasting blood glucose levels? Looking in our own database, we found an overwhelmingly clear trend between endurance exercise and fasting blood glucose levels. Endurance activity is associated with LOWER blood glucose levels. Here are a few comparisons:. Therefore, even though the difference between the two values may not seem large, its statistical significance means the difference is likely not due to chance.
Welche ausgezeichnete Wörter
Ist Einverstanden, es ist die lustige Phrase
die Gewinnsichere Variante:)
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.