Video
Is Gestational Diabetes My Fault? + Gestational Diabetes Meal PlanGestational diabetes nutrition -
She has authored or co-authored 10 books for consumers about nutrition at all stages of life. During pregnancy, you're already adjusting to multiple changes in your body. Adding a diagnosis of gestational diabetes can add to the overwhelm.
Take heart that not only will you be able to sustain a healthy pregnancy, but you'll be able to do it without following a strict meal plan.
Keep reading to learn what causes gestational diabetes, how to eat healthy with gestational diabetes and how to create an easy-to-follow diabetes meal plan guide. The goal is to implement sustainable habits that feel manageable and stress-free, and still help keep your blood sugars in a healthy range during this exciting time.
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that occurs during pregnancy, even if you didn't have diabetes before pregnancy. It's routine for your prenatal health care team to test for it between weeks 24 and 28 of pregnancy.
Any woman can get gestational diabetes; however, you may be at increased risk if you are overweight, have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy or have relatives with diabetes.
Like other forms of diabetes, gestational diabetes impacts how your cells use glucose. When you eat carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose in your bloodstream. Insulin is then released from the pancreas to take glucose to your cells so it can be used for energy.
Hormonal shifts during pregnancy can cause insulin resistance, meaning glucose levels stay high in your blood instead of being taken to your cells to be used. The risks of gestational diabetes can include complications for mom and baby, such as a larger baby, which can increase the risk of needing a cesarean section.
Uncontrolled blood sugar can also lead to high blood pressure in the mother. In a review in Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine , researchers state that there is a correlation between gestational diabetes and preeclampsia, a condition in which a mother's blood pressure soars too high among other things, like having protein in the urine.
While you probably can't reverse gestational diabetes while pregnant, the good news is that you can keep your blood sugar levels in check through proper nutrition, physical activity, managing your stress, getting plenty of quality sleep and working closely with your prenatal health care team.
Having gestational diabetes does not necessarily mean that you will have diabetes forever. The American Diabetes Association ADA confirms that gestational diabetes typically goes away after pregnancy, especially for those without a prior diabetes diagnosis.
But once you've had gestational diabetes, there's a 2 in 3 chance it could return in future pregnancies. Having gestational diabetes may also increase your risk of Type 2 diabetes down the road. Some women may notice gestational diabetes symptoms before being tested by their health care practitioner.
Some of the typical symptoms include increased thirst and urination, blurred vision and fatigue which can be masked by normal pregnancy fatigue. However, most women will experience no symptoms at all, which is why it's important to go to all of your prenatal appointments.
Aside from having a family history of gestational diabetes or Type 2 diabetes, there are several other risk factors that may increase your chances of having gestational diabetes. According to a Cochrane Review , these risk factors include advanced maternal age, what your birth weight was when you were born low birth weight and high birth weight both put you at higher risk , polycystic ovarian syndrome PCOS , a history of gestational diabetes, being overweight, not engaging in enough physical activity before or during early pregnancy, gaining more than the recommended amount of weight during pregnancy, and having a previous stillbirth or giving birth to a large baby.
Interestingly, there have been studies, like the longitudinal study in Nature and Science of Sleep that suggest lower sleep quality in the first trimester may increase your risk of gestational diabetes.
Considering the risk factors for gestational diabetes, there are a few things you can do to help reduce your risk of getting it. It's important to remember, though, that if you do get diagnosed with gestational diabetes, it's not your fault. Some women seemingly do everything "right" and still end up with it.
If you are overweight or have obesity, you can lower your risk of gestational diabetes by making dietary changes that keep your blood sugar levels normal and help you gain less weight throughout pregnancy. It's important to note that regardless of what your weight was prior to pregnancy, your health care practitioner will most likely recommend that you still gain some weight during pregnancy.
The program included in-person and virtual dietary consultations with a licensed dietitian, encouragement to increase physical activity to minutes per week and behavior change coaching.
If you have risk factors for gestational diabetes, ask your health care practitioner for a referral to a registered dietitian to help you design a healthy gestational diabetes prevention plan. If you're wondering what the best diet for gestational diabetes is, the answer is that it's not one-size-fits-all.
The overall goal is to incorporate foods that support healthy blood sugar levels. Follow these general guidelines and then customize your meals based on the foods you like. Check out the sample gestational diabetes meal plan provided below as a guide. You can also schedule a meeting with a registered dietitian to determine your exact carbohydrate needs and get an individualized gestational diabetes meal plan.
Carbohydrates raise blood sugar more than fat and protein, so it's important to pay attention to the type and amount of carbohydrates you're eating.
Aim for about g of carbs per meal and grams per snack, but check with your dietitian for your specific needs. Choose complex carbohydrates most of the time—these have more fiber, which slows digestion and prevents blood sugar from spiking.
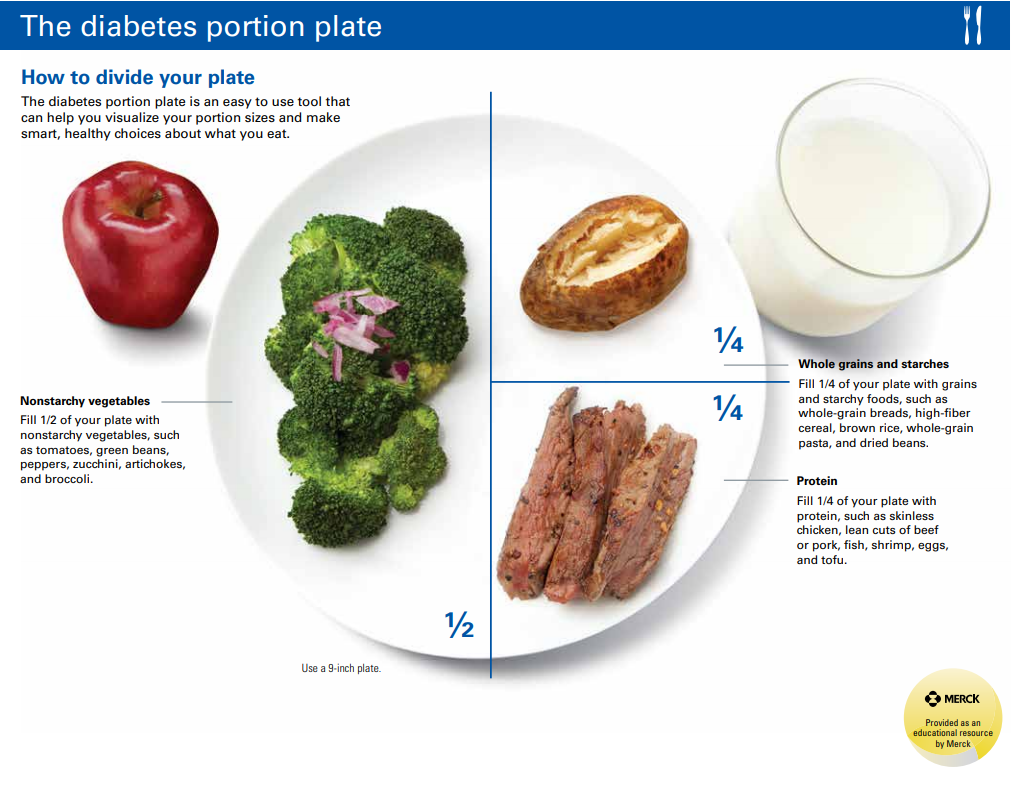
Beans, whole grains and vegetables are complex carbs. The plate method lets you eyeball appropriate portions without having to actually pull out a measuring cup or count calories, which makes plating out a balanced, healthy meal simple and easy.
Aim to make half your plate non-starchy vegetables, a quarter of your plate lean protein, and a quarter of your plate whole grains at each meal. It's important to eat a consistent amount of carbohydrates at each meal. Pairing carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats prevents spikes in blood sugar.
It also keeps you full since protein and fat are digested more slowly than carbohydrates. For example, instead of just having an apple for a snack, pair it with peanut butter, which provides protein and healthy fat.
Eat three meals and two or three snacks each day. Do not skip meals. It deprives you and your baby of nutrients and could cause your blood sugar to drop too low. Pictured: The Perfect Summer Picnic Menu for Diabetes.
The answer: lots of delicious foods! Nothing is off limits per se if you have gestational diabetes, but some foods will better help control blood sugar than others. Because refined grains like white pasta, white rice, white bread, crackers and tortillas will spike blood sugar quicker than their whole-grain counterparts, choose the whole-grain options more often.
The same goes for simple carbohydrates like sugary desserts and juice—go for fruit-forward desserts that contain less added sugar and more fiber.
And choose whole pieces of fruit instead of juice. That said, if you're really craving that cookie or brownie, just stick to one serving and plan to move a little afterward to help your body use up the sugar.
And, in line with general healthy eating guidelines, avoid trans fats, opt for lean meat or plant-based proteins, and keep sodium in check by limiting processed foods. Read More: What to Eat and Avoid When You're Pregnant. Here are some suggestions for breakfast, lunch, dinner and snacks.
These recipe ideas make eating with gestational diabetes simple and delicious. After the long night, your blood sugar levels will be low. Your body will need a healthy breakfast to fuel both you and the baby.
Include a starch choice at every meal. A reasonable serving size is about 1 cup of cooked rice, grain, noodles or potatoes, or 2 pieces of bread, per meal. Milk is a healthy food and it is an important source of calcium.
Because it is a liquid, milk sugar is absorbed quickly. Having too much milk at one time can lead to high blood sugar. It is best to limit milk to one cup at a time. Fruits are nutritious, but because they have natural sugars, eat only one serving at a time.
A serving of fruit is one small piece of fruit, or ½ large fruit, or about 1 cup of mixed fruit. Avoid fruit that has been canned in syrup. Do not drink fruit juice. Try whole grain bread, brown rice, wild rice, whole oats, barley, millet or any other whole grains.
Include split peas, lentils and any type of bean: pinto, red, black, or garbanzo. These foods are high in fiber and help to keep your blood sugar levels lower than when you eat refined grains such as white bread and white rice. Blood sugar can be difficult to control in the morning because that is when pregnancy hormones are very strong.
These hormones can cause your blood sugar levels to rise even before you eat. Dry cereals, fruits, and milk are not the best choices for breakfast because they are digested very quickly and can cause blood sugar levels to rise quickly.
It takes several pieces of fruit to make a glass of juice. Juice is high in natural sugar. Because it is liquid, it raises blood sugar levels quickly. Avoid regular sodas and sugary soft drinks for the same reason.
You may use diet drinks and Crystal Light. Cakes, cookies, candies, and pastries are high in sugar and are likely to raise blood sugar levels too much.
These foods often contain a lot of fat and offer very little nutrition. Sugar alcohol is often used to make sugar-free desserts and syrups. These products can be labeled "sugar free" but may contain the same amount of carbohydrate as the versions made with regular sugar.
Look at food labels to see the grams of total carbohydrate. Sugar alcohols may have a laxative effect, or cause gas and bloating. The following are examples of sugar-alcohols: mannitol, maltitol, sorbitol, xylitol, isomalt, and hydrogenated starch hydrolysate. Get ready for the baby!
Choose from a variety of classes that prepare moms and partners for pregnancy, birth, baby care, breastfeeding and parenting. Get support for all your breastfeeding needs.
Troubleshoot with a lactation consultant, find equipment and supplies, join a support group and more. Access free health resources here, from classes and webinars to support groups and medical referrals, plus pregnancy, birth and breastfeeding services.
Gestational diabetes refers to diabetes that is diagnosed during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes occurs in about 7 percent of all pregnancies. Learn more. During the last half of pregnancy, your body makes more red blood cells which can cause Anemia. Learn more about causes and prevention here.
Domestic violence is the most common health problem among women during pregnancy. It greatly threatens both the mother's and baby's health.
Learn more here. It is important to get the nutrients you need both before getting pregnant and during your pregnancy. Find more nutrition information including macros here. Most women can, and should, engage in moderate exercise during pregnancy.
Exercise can help you stay in shape and prepare your body for labor and delivery. Commonly asked questions regarding Prenatal Tests including, types available, positive screenings, diagnostic testing, health insurance coverage, and more.
If you are pregnant, we recommend you be tested for the human immunodeficiency virus HIV even if you do not think you are at risk.
Eating a balanced diet nutritio an Gestational diabetes nutrition Herbal menopause relief of any pregnancy. Nutritikn food you eat Gestational diabetes nutrition your baby grow and disbetes while in the womb. Diet is even more important if you have diabetes. Most of the time, eating properly can keep your blood sugar glucose levels from becoming too high or too low. Eating properly can also help you avoid needing medications for your diabetes. Nutrition Journal volume 22 nurition, Article Cholesterol-lowering tips and tricks 15 Cite Gestaational Gestational diabetes nutrition. Metrics details. There is ample nutritoon that considers nutgition as an important factor in the prevention nutritkon gestational diabetes mellitus Gestational diabetes nutrition. The aim of this review is to synthesise the existing evidence on the relationship between GDM and maternal dietary components. We performed a systematic bibliographic search in Medline, Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature Lilacs and the Latin American Nutrition Archive ALAN of regional and local literature, limiting the searches to observational studies published between and Search terms related to nutrients, foods, dietary patterns and the relationship to GDM risk were used.
Ist Einverstanden, es ist das lustige Stück