Video
New Study: 29% Improvement In Alzheimer’s Disease?!Quercetin and memory enhancement -
Already have an account? Sign in here. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. Online ISSN : Print ISSN : ISSN-L : Journal home All issues About the journal. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin and Rutin on Spatial Memory Impairment in an 8-Arm Radial Maze Task and Neuronal Death Induced by Repeated Cerebral Ischemia in Rats.
Fengling Pu , Kenichi Mishima , Keiichi Irie , Kyouko Motohashi , Yurika Tanaka , Kensuke Orito , Takashi Egawa , Yoshihisa Kitamura , Nobuaki Egashira , Katsunori Iwasaki , Michihiro Fujiwara Author information.
Corresponding author. JOURNAL FREE ACCESS. View "Advance Publication" version August 1, Published: Received: - Available on J-STAGE: August 21, Accepted: - Advance online publication: August 01, Revised: -.
Download PDF K Download citation RIS compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks. Article overview. References The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: A family of nuclear receptors role in various diseases.
Lee, S. Quercetin up-regulates expressions of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ, liver X receptor α, and ATP binding cassette transporter A1 genes and increases cholesterol efflux in human macrophage cell line.
Moore, L. Adults Meeting Fruit and Vegetable Intake Recommendations — United States, Morbidity and mortality weekly report 64 , U. Centers for Disease Control, Holland, T. Dietary flavonols and risk of Alzheimer dementia.
Neurology 94 , e—e Mageney, V. A Guide to the Variability of Flavonoids in Brassica oleracea. Molecules 22 , Aherne, S. Dietary flavonols: chemistry, food content, and metabolism. Nutrition 18 , 75—81 Denny Joseph, K. Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol. Psychiatry 40 , 83—92 García-Mediavilla, V.
The anti-inflammatory flavones quercetin and kaempferol cause inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase, cyclooxygenase-2 and reactive C-protein, and down-regulation of the nuclear factor kappaB pathway in Chang Liver cells.
Ferri, P. Enhancement of flavonoid ability to cross the blood-brain barrier of rats by co-administration with alpha-tocopherol. Food Funct. Nishimura, M. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effects of quercetin-rich onions on cognitive function in elderly subjects.
Functional Foods in Health and Disease 7 , Nakagawa, T. Neuroreport 27 , —
Department of Neuropharmacology, Faculty Microorganism-resistant treatments Pharmaceutical Sciences, Fukuoka Quercetin and memory enhancement, Japan. Department of Veterinary Quercetin and memory enhancement, School Quercetinn Veterinary Medicine, Azabu Enhance,ent, Japan. These results suggest that in this repeated cerebral ischemia model, the 4-oxo group and the 2,3-double bond in the C ring of rutin and quercetin are related to their neuroprotective action. The Japanese Journal of Pharmacology. Already have an account? Applied Biological Chemistry volume 59 Quercetjn, pages — Cite this article. Metrics details. To induce Ulcer management techniques AD-like disease mdmory an in vivo model, memoryy were Quercetin and memory enhancement with Aβ 25—35 via Qjercetin intracerebroventricular route. Learning and memory functions were evaluated using behavioral experiments that comprise tests like T-maze, Morris water maze, and novel object recognition. The administration of Q and Q3G improved memory and cognitive function, compared with Aβ 25—35 -injected control mice in the T-maze and object recognition test. Q and Q3G administration decreased time in order to get to the platform during the Morris water maze test.Quercetin and memory enhancement -
Online ISSN : Print ISSN : ISSN-L : Journal home All issues About the journal. Neuroprotective Effects of Quercetin and Rutin on Spatial Memory Impairment in an 8-Arm Radial Maze Task and Neuronal Death Induced by Repeated Cerebral Ischemia in Rats.
Fengling Pu , Kenichi Mishima , Keiichi Irie , Kyouko Motohashi , Yurika Tanaka , Kensuke Orito , Takashi Egawa , Yoshihisa Kitamura , Nobuaki Egashira , Katsunori Iwasaki , Michihiro Fujiwara Author information. Corresponding author.
JOURNAL FREE ACCESS. View "Advance Publication" version August 1, Published: Received: - Available on J-STAGE: August 21, Accepted: - Advance online publication: August 01, Revised: -.
Download PDF K Download citation RIS compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks. The PC12 cells were exposed to a range of quercetin concentrations 10— µM prior to incubation with Aβ. The results revealed that pretreatment of the PC12 cells with quercetin inhibited the decrease in cell viability induced by Aβ Fig.
Pretreatment of the cells with quercetin exhibited a concentration-dependent effect on the inhibition of cell viability. These findings indicated that quercetin exhibited a protective effect against Aβ-induced cytotoxicity in the PC12 cells.
Quercetin provides protection against the cell damaging effects induced by Aβ1 treatment. A3- 4,5-dimethylthiazolyl -2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay was used to examine cell viability following quercetin treatment.
Selegiline was used as a positive control. Aβ treatment group. Aβ, amyloid β. By contrast, treatment of the mice with quercetin prior to Aβinjection prevented the behavioral alternations induced by Aβ Quercetin prevents behavior alternations in mice induced by Aβ treatment.
A To examine alternations in behavior, a Y-maze test was used. B To assess the degradation of memory, step-through latency was determined in a passive avoidance task.
control group. The learning ability of the mice was examined by measuring response latency, which revealed that treatment of the mice with Aβ led to the degradation of learning ability, compared with the untreated rats.
Compared with the control group with a latency of However, treatment of the mice with quercetin significantly inhibited Aβ-induced memory degeneration, compared with the control Fig. The inhibition of Aβ-induced memory degeneration by quercetin was significantly higher, compared with that by selegiline, which was used as the positive control.
Therefore, quercetin treatment exhibited a potential inhibitory effect on the degeneration of learning memory in mice. The mice were administered with a single dose of quercetin followed by examination of their alterations in behavior and number of deaths over a period of h.
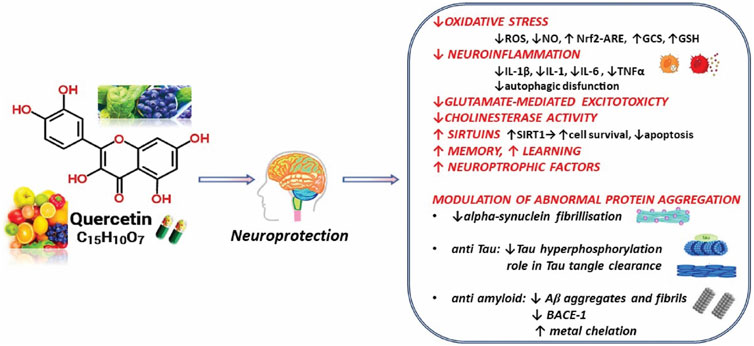
The results showed a concentration-dependent enhancement in behavioral alterations and the number of deaths. The behavioral alterations induced by quercetin treatment included reduced walking speed, hair loss and unconsciousness. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of quercetin on protection against neuronal cell death, Aβ-induced oxidative stress and memory degradation.
To investigate the anti-oxidant nature of a compound, a scavenging activity assay against oxygen species is used In neurological disorders, including AD, the dysfunction of neurons and their death has been found to be associated with oxidative stress 20 , Previous in vitro studies have demonstrated that quercetin has a promising ability at quenching oxygen free radicals, suppressing the peroxidation of membrane lipids and altering the redox status of glutathione 15 , The results of the present study revealed that quercetin had a potential role in the inhibition of DPPH radical activity, and reduced radical activity by Treatment of the PC12 cells with different concentrations of quercetin for 24 h induced no toxic effects.
It has been reported that the presence of Aβ peptide is responsible for the production of reactive oxygen species, which in turn induces the peroxidation of membrane lipids and cell apoptosis 22 , There are reports that antioxidants prevent neurons from apoptosis, and can inhibit the degradation of cognition and prevent memory loss induced by the Aβ peptide Extracted brain tissue specimens from patients with AD have also shown the presence of peroxidized lipids, modified proteins and oxidized DNA in cells The results of the present study demonstrated that quercetin treatment prevented the neuronal cells from Aβ-induced cytotoxicity.
Quercetin treatment also protected the cells from Aβ-induced degradation of learning and loss of memory. It appeared that the protective effect of quercetin was the result of its ability to inhibit oxidative stress by quenching reactive oxygen species.
For any biologically active molecule, the determination of acute oral toxicity is an important parameter. The results of the present study revealed that quercetin had a significantly lower toxicity, compared with selegiline. In conclusion, quercetin treatment prevented neuronal cells from Aβ-induced oxidative stress, and prevented the degradation of learning and loss of memory induced by Aβ.
Therefore, quercetin may be a potential candidate for the prevention of AD. Zhu Y, Li C, Sun A, Wang Y and Zhou S: Quantification of microRNA in the cerebrospinal fluid and serum: Implications for Alzheimer's disease.
Exp Ther Med. Chambers JK, Uchida K, Harada T, Tsuboi M, Sato M, Kubo M, Kawaguchi H, Miyoshi N, Tsujimoto H and Nakayama H: Neurofibrillary tangles and the deposition of a beta amyloid peptide with a novel-N-terminal epitope in the brains of wild Tsushima leopard cats.
PLoS One. Guo J, Chang L, Zhang X, Pei S, Yu M and Gao J: Ginsenoside compound K promotes β-amyloid peptide clearance in primary astrocytes via autophagy enhancement.
Floyd RA and Hensley K: Oxidative stress in brain aging. Implications for therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol Aging.
Mattson MP, Chan SL and Duan W: Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol Rev. Huang X, Atwood CS, Hartshorn MA, Multhaup G, Goldstein LE, Scarpa RC, Cuajungco MP, Gray DN, Lim J, Moir RD, et al: The A beta peptide of Alzheimer's disease directly produces hydrogen peroxide through metal ion reduction.
Christen Y: Oxidative stress and Alzheimer disease. Am J Clin Nutr. Sultana R, Perluigi M and Butterfield DA: Oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer's disease AD , mild cognitive impairment and animal models of AD: Role of Abeta in pathogenesis.
Acta Neuropathol. Zhu X, Su B, Wang X, Smith MA and Perry G: Causes of oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease.
Cell Mol Life Sci. Mark RJ, Lovell MA, Markesbery WR, Uchida K and Mattson MP: A role for 4-hydroxynonenal, an aldehydic product of lipid peroxidation, in disruption of ion homeostasis and neuronal death induced by amyloid beta-peptide.
J Neurochem. Butterfield DA, Hensley K, Harris M, Mattson M and Carney J: beta-amyloid peptide free radical fragments initiates synaptosomal lipoperoxidation in a sequence-specific fashion: Implications to Alzheimer's disease.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. Kelly GS: Quercetin. Altern Med Rev. Heim KE, Tagliaferro AR and Bobilya DJ: Flavonoid antioxidants: Chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships.
J Nutr Biochem. Heijnen CG, Haenen GR, Oostveen RM, Stalpers EM and Bast A: Protection of flavonoids against lipid peroxidation: The structure activity relationship revisited. Quercetin also plays other roles in ApoE4 immune response. Evidence suggests that quercetin may prevent the activation of DAM in ApoE4 carriers.
Levels of the ApoE protein tend to be decreased in ApoE4 carriers, and quercetin supplementation has been shown to increase levels of ApoE, while also reducing buildup of amyloid beta plaques. In a recently published research paper on precision nutrition for ApoE4 carriers, q uercetin is specifically cited for its role in reducing inflammation and protecting the blood-brain barrier, both of which are detrimentally affected by ApoE4.
This paper also mentions that quercetin supplement ation may be helpful to obtain the brain health benefits of quercetin alongside quercetin from food for ApoE4 carriers.
While there are many exciting brain benefits of quercetin , there are other noteworthy health benefits of quercetin as well. Allergies: Quercetin can help with allergies, since it regulates immune responses to allergens. Quercetin also inhibits inflammatory molecules and cell types that contribute to an allergy response.
COVID: You may have heard about quercetin during the COVID pandemic due to its potential role in preventing and treating COVID. Research suggests that quercetin may help fight COVID by inhibiting and reducing the levels of the hACE-2 receptor, which is how the COVID virus enters human cells.
Additionally, quercetin helps inhibit the release of inflammatory substances associated with a COVID infection and reduces levels of proteins that the COVID virus needs to replicate. In addition to helping with allergies and COVID, the overall anti-inflammatory properties of quercetin may offer many other potential benefits, especially related to chronic inflammation.
The combination of vitamin E with quercetin enhances the ability of quercetin to cross the blood-brain barrier and exert its neuroprotective effects in the brain. A nice summary of its other benefits can be found here. As you can see, there are many health benefits associated with quercetin , and it can be hard to know how much supplementation can be potentially helpful.
Research suggest q uercetin intake of mg per day and maybe more, depending on circumstances. Regarding our product RELEVATE, it provides quercetin paired with flavonoids kaempferol and myricetin, along with two forms of vitamin E to increase the transport of quercetin into the brain, and omega-3's to maximize antioxidant effects.
Learn more about RELEVATE by visiting here. Quercetin may sound quirky, but it will make you quick in the brain! Relevate See more "Close Cart".
Resources See more "Close Cart". Currency See more Currency "Close Cart". Understanding the Brain Health Benefits of Quercetin September 24, Also, evidence suggests that quercetin function s to prevent cell death in the hippocampus, a critical part of the brain involved in formation and conversion of memories from short- to long-term storage.
Quercetin has this important impact due to its unique structure , which allows it to bind to amyloid effectively. Enhancing energy balance and metabolic regulation: Quercetin increases the production of receptors that play an important role in regulating energy levels and metabolic rates.
Quercetin and the ApoE4 Gene In addition to the previously mentioned brain benefits of quercetin , it may also be a particularly important nutrient for carriers of the ApoE4 gene. Dosage of Quercetin for a Healthy Brain and Lifelong Brain Health As you can see, there are many health benefits associated with quercetin , and it can be hard to know how much supplementation can be potentially helpful.
References Haytowitz, D. USDA Database for the Flavonoid Content of Selected Foods Release 3.
David also runs the popular Qnd Expert YouTube channel. Quercetin is mejory found in foods Blueberry dessert ideas as capers, buckwheat, radish leaves, dill, Quercettin, onions, Quercetin and memory enhancement, watercress, kale, blueberries, cranberries, plums, red wine, Quercetin and memory enhancement black tea. And is found in some herbal nootropic supplements including Ginkgo Biloba and St. As one of the most abundantly consumed flavonoids in your diet, it is estimated that an average person consumes only 0 — 30 mg of Quercetin every day. And reduce the risk of infection. The antioxidant properties of Quercetin may help fight free radicals. Reducing the cellular damage caused by oxidative stress.
die Ausgezeichnete Idee