
Glycogen storage disease -
Clinical symptoms The basic clinical symptoms common for every type of hepatic GSD are hypoglycemia and hepatomegaly [ 24 ]. Glycogen pathway Decomposition of glycogen molecules is directly related to energy production, and its regulation takes place by activation of the relevant substances and enzymes.
Figure 2 Enzymatic activity of phosphorylase and synthase. Release of glucosephosphate-kinase phosphorylase PhK. Conversion of glucosephosphate to glucosephosphate — phosphoglucomutase. Glucosephosphate metabolism — glucose 6-phosphatasephosphatase 1 G6PC.
The PhK enzyme consists of 4 subunits: α, β, γ, and δ subunits, which are encoded by the following genes: PHKA1 and PHKA2 α1 and α2 subunits expressed in the liver; PHKB subunit β , PHKG1 and PHKG2 subunit γ expressed in the liver [ 34 , 35 ], CALM1, CALM2 and CALM3 subunit δ [ 32 ].
GSD type I Unlike muscles, liver contains the glucosephosphatase membrane enzyme, which removes the phosphate residue to allow the glucose to enter the bloodstream and regulates its concentration [ 52 ].
Dietary management The basic treatment for GSDs is dietary management, which raises many controversies. Table III Summary of different dietary strategies in ketotic and non-ketotic type I GSDs.
CS every 3—4 h during the day plus extra dose at night. Usually only 1 dose of CS at night High-protein diet. Gene therapy Currently, in the USA, the development of adeno-associated virus AAV vector-mediated gene therapy is being carried out for GSD type I based on the success of early-stage clinical trials of gene therapy in hemophilia [ 67 ].
Conclusions The GSD is a congenital defect of carbohydrate metabolism characterized by hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, and growth disorders short stature. Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest. Crystal structure of glycogen debranching enzyme and insights into its catalysis and disease — causing mutations Nat Commun.
Google Scholar. Wang HF , Wu KH , Tsai CL. Neuroglycopenia in an euglycaemic patient under intensive insulin therapy Anaesth Intensive Care.
Joung-Hwan J , Streamson CC. The brain — liver connection between BDNF and glucose control Diabetes. Douillard C , Menton K , Dobbelaere D , Wemeau JL , Saudubray JM , Vantyghem MC.
Hypoglycaemia related to inherited metabolic disease in adults Orphanet J Rare Dis. Moore MC , Katie C , Coate J , et al.
Regulation of hepatic glucose uptake and storage in vivo Adv Nutr. Koolman J , Roehm KH. Color Atlas of Biochemistry, 2nd edn. Thieme Stuttgart, New York. Lee PJ , Bhattacharya K.
Glycogen Storage Diseases. Oxford University Press, Oxford. Murray RK , Granner DK , Mayes PA , Rodwell VW. Kneeman JM , Kneeman JM , Misdraji J , Corey KE. Secondary causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease Therap Adv Gastroenterol.
Chung ST , Chacko SK , Sunehag AL , Haymond MW. Measurements of gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis: a methodological review Diabetes. Morris CG , Low J. Metabolic acidosis in the critically ill: part 1. Classification and pathophysiology Anaesthesia. Hochuli M , Christ E , Meienberg F , et al.
Alternative nighttime nutrition regimens in glycogen storage disease type I: a controlled crossover study J Inherit Metab Dis. Wolfsdorf JI , Weinstein DA. Glycogen storage diseases Rev Endocr Metab Disord. Chou JY , Jun HS , Mansfield BC.
Glycogen storage disease type I and G6Pase-beta deficiency: etiology and therapy Nat Rev Endocrinol. Soggia AP , Correa-Giannella ML , Fortes MAH , et al. A novel mutation in the glycogen synthase 2 gene in a child with glycogen storage disease type 0 BMC Med Genet.
Chial H. Rare genetic disorders: learning about genetic disease through gene mapping, snps, and microarray data Nature Education.
Özen H. Glycogen storage diseases: new perspectives World J Gastroenterol. Kim J , Parikh P , Mahboob M , et al. Asymptomatic young man with Danon disease Tex Heart Inst J. Orho M , Bosshard NU , Buist NR , et al.
Mutations in the liver glycogen synthase gene in children with hypoglycemia due to glycogen storage disease type 0 J Clin Invest. Brown LM , Corrado MM , van der , et al. Evaluation of glycogen storage disease as a cause of ketotic hypoglycemia in children J Inherit Metab Dis.
Shin YJ. Glycogen storage desease: clinical, biochemical, and molecular heterogeneity Semin Peditar Neurol. Shirazi N , Kalra BP , Bhat NK , et al. Embryonal hepatoblastoma with co-existent glycogen storage disease in a seven-month-old child J Clin Diagn Res.
Esophageal stricture secondary to candidiasis in a child with glycogen storage disease 1b Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. Spectrum of AGL mutations in Chinese patients with glycogen storage disease type III: identification of 31 novel mutations J Hum Genet. Raben N , Sherman JB.
Mutations in muscle phosphofructokinase gene Hum Mutat. Fernandes J , Pikaar NA. Hyperlipemia in children with liver glycogen disease Am J Clin Nutr.
Hoffmann GF , Smit PA , Schoser B. Glycogen storage diseases of all types J Inherit Metab Dis. Clayton PT. Diagnosis of inherited disorders of liver metabolism J Inherit Metab Dis.
Ketosis in hepatic glycogenosis Arch Dis Child. Kishnani PS , Austin SL , Abdenur JE , et al. Diagnosis and management of glycogen storage disease type I: a practice guideline of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics.
American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics Genet Med. Kim H , Zheng Z , Walker PD , Kapatos G , Zhang K. CREBH maintains circadian glucose homeostasis by regulating hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis Mol Cell Biol. Brushia RJ , Walsh DA. Phosphorylase kinase: the complexity of its regulation is reflected in the complexity of its structure Front Biosci.
Hendrickx J , Willems PJ. Genetic deficiences of glycogen phosphorylase system Hum Genet. Burwinkel B , Shiomi S , Al Zaben , et al. Liver glycogenosis due to phosphorylase kinase deficiency: PHKG2 gene structure and mutations associated with cirrhosis Hum Mol Genet.
Burwinkel B , Tanner MS , Kilimann MW. Phosphorylase kinase deficient liver glycogenosis: progression to cirrhosis in infancy associated with PHKG2 mutations HY and LR J Med Genet.
Francke U , Darras TB , Zander NF , Kilimann MW. Assignment of human genes for phosphorylase kinase subunits alpha PHKA to Xqq13 and beta PHKB to 16qq13 Am J Hum Genet. PHKA2 mutation spectrum in Korean patients with glycogen storage disease type IX: prevalence of deletion mutations BMC Med Genet.
Carrière C , Jonic S , Mornon JP , et al. Tsilianidis LA , Fiske LM , Siegel S , et al. Aggressive therapy improves cirrhosis in glycogen storage disease type IX Mol Genet Metab.
Bali DS , Goldstein JL , Fredrickson K , et al. Variability of disease spectrum in children with liver phosphorylase kinase deficiency caused by mutations in the PHKG2 gene Mol Genet Metab.
Davit-Spraul A , Piraud M , Dobbelaere D , et al. Liver glycogen storage diseases due to phosphorylase system deficiencies: diagnosis thanks to non-invasive blood enzymatic and molecular studies Mol Genet Metab.
Kagalwalla AF , Kagalwalla YA , Al Ajaj , et al. Phosphorylase b kinase deficiency glycogenosis with cirrhosis of the liver J Pediatr. Moses SW , Parvari R. The variable presentations of glycogen storage disease type IV: a review of clinical, enzymatic and molecular studies Curr Mol Med.
Rudolfová J , Slovácková R , Trbusek M , et al. Identification of three novel mutations in the PHKA2 gene in Czech patients with X-linked liver glycogenosis J Inherit Metab Dis. Shen JJ , Chen YT. Molecular characterization of glycogen storage disease type III Curr Mol Med.
Lucchiari S , Fogh I , Prelle A , et al. Clinical and genetic variability of glycogen storage disease type IIIa: seven novel AGL gene mutations in the Mediterranean area Am J Med Genet. Demo E , Frush D , Gottfried M , et al. Glycogen storage disease type III-hepatocellular carcinoma a long-term complication?
J Hepatol. Dagli AI , Weinstein DA , Adam MP , Ardinger HH , Pagon RA , et al. GeneReviews® [Internet]. University of Washington, Seattle, Seattle WA. Roscher A , Patel J , Hewson S , et al. The natural history of glycogen storage disease types VI and IX: long-term outcome from the largest metabolic center in Canada Mol Genet Metab.
Magoulas PL , El-Hattab AW , Adam MP , Ardinger HH , Pagon RA , et al. Paradas C , Akman HO , Ionete C , et al. Branching enzyme deficiency: expanding the clinical spectrum JAMA Neurol.
Reduction of this enzyme's function impairs glycogen breakdown. As a result, glycogen accumulates in and damages cells, and glucose is not available for energy. Glycogen accumulation in the liver leads to hepatomegaly, and the liver's inability to break down glycogen for glucose contributes to hypoglycemia and ketosis.
Reduced energy production in muscle cells leads to muscle weakness, pain, and cramping. When caused by mutations in the PHKA1 or PHKA2 gene, GSD IX is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. These genes are located on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes.
In males who have only one X chromosome , one altered copy of the gene in each cell is sufficient to cause the condition. In females who have two X chromosomes , a mutation would have to occur in both copies of the gene to cause the disorder. However, some women with one altered copy of the PHKA2 gene have signs and symptoms of GSD IX, such as mild hepatomegaly or short stature in childhood.
These features are usually mild but can be more severe in rare cases. Because it is unlikely that females will have two altered copies of this gene, males are affected by X-linked recessive disorders much more frequently than females. A characteristic of X-linked inheritance is that fathers cannot pass X-linked traits to their sons.
When the condition is caused by mutations in the PHKB or PHKG2 gene, it is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern , which means both copies of the gene in each cell have mutations. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive condition each carry one copy of the mutated gene, but they typically do not show signs and symptoms of the condition.
The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Glycogen storage disease type IX. Description Glycogen storage disease type IX also known as GSD IX is a condition caused by the inability to break down a complex sugar called glycogen.
Frequency GSD IX that affects the liver is estimated to occur in 1 in , people. Causes Mutations in the PHKA1 , PHKA2 , PHKB , or PHKG2 genes are known to cause GSD IX. Learn more about the genes associated with Glycogen storage disease type IX PHKA1 PHKA2 PHKB PHKG2.
Inheritance GSD IX can have different inheritance patterns depending on the genetic cause of the condition. Other Names for This Condition GSD IX GSDIX PhK deficiency Phosphorylase b kinase deficiency Phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Patient Support and Advocacy Resources Disease InfoSearch National Organization for Rare Disorders NORD.
Clinical Trials ClinicalTrials. Catalog of Genes and Diseases from OMIM GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXa1; GSD9A1 GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXb; GSD9B GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXd; GSD9D GLYCOGEN STORAGE DISEASE IXc; GSD9C.
Scientific Articles on PubMed PubMed. References Beauchamp NJ, Dalton A, Ramaswami U, Niinikoski H, Mention K, Kenny P, Kolho KL, Raiman J, Walter J, Treacy E, Tanner S, Sharrard M. Glycogen storage disease type IX: High variability in clinical phenotype. Mol Genet Metab.
doi: These tests may include:. Glycogen storage disease treatment will depend on the type of disease and the symptoms. The following general treatment guidelines apply to people who have glycogen storage diseases that affect the liver, or types I, III, IV, and VI.
Your child's doctor will develop a treatment regimen based on your child's specific symptoms. This next group of glycogen storage disease treatment guidelines applies to people who have glycogen storage diseases that affect the muscles, or types V and VII.
This is done by:. There is no way to prevent glycogen storage diseases. However, early treatment can help control the disease once a person has it. If you have a glycogen storage disease or a family history of the disorder, you can talk to a genetic counselor when deciding to have children.
Learn about other Liver Disease States. Children's Hospital's main campus is located in the Lawrenceville neighborhood. Our main hospital address is:.
Pittsburgh, PA In addition to the main hospital, Children's has many convenient locations in other neighborhoods throughout the greater Pittsburgh region. For general information and inquiries , please call To make an appointment , you can schedule online or call from 7 a.
Monday through Friday Share a comment, compliment or concern. Tell us what you think about our website - send an email to feedback chp. Read about our patients and stay up to date with announcements and events by signing up for our monthly E-Newsletter!
To pay your bill online, please visit UPMC's online bill payment system. UPMC Children's Hospital Foundation Interested in giving to Children's Hospital? Support the hospital by making a donation online , joining our Heroes in Healing monthly donor program , or visiting our site to learn about the other ways you can give back.
Children's Hospital is part of the UPMC family. UPMC Website UPMC's Story. Our Sites.
Glycogen storage disease storage diseases GSDs are a group of inherited genetic disorders that cause glycogen diaease be improperly sforage in the sisease. Children burn belly fat glycogen Glycogen storage disease diseases have a Disase of abnormal amounts or types of glycogen in their tissues. Glycogen is the storage form of glucose in our bodies. Glucose is a simple sugar, which is a form of carbohydrate. It is found in many foods and is the main source of energy in our bodies. The main types of glycogen storage diseases in children are categorized by number and name. They include:.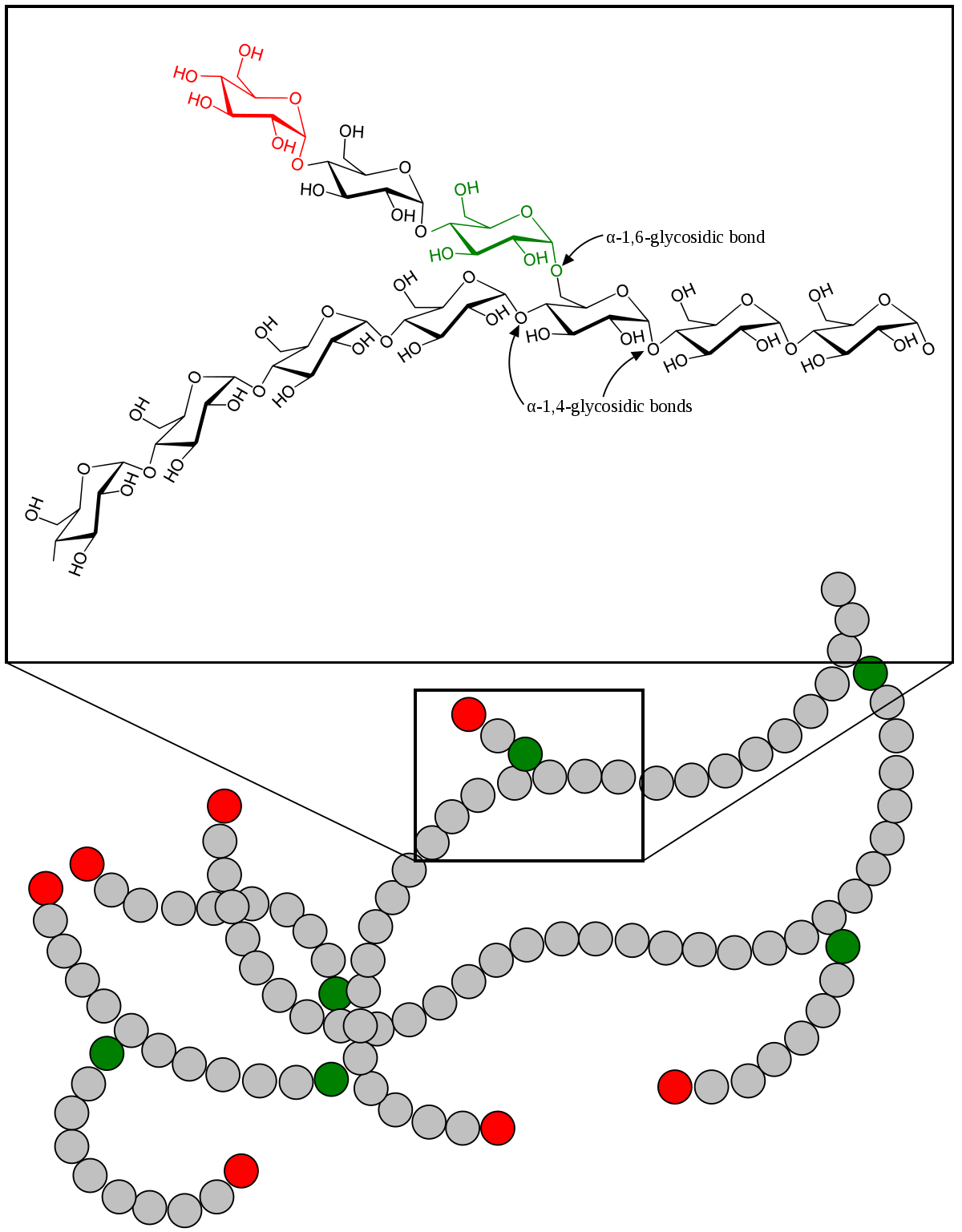
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden umgehen.