
Resistance training for injury prevention -
The information and materials contained on this website are not intended to constitute a comprehensive guide concerning all aspects of the therapy, product or treatment described on the website.
All users are urged to always seek advice from a registered health care professional for diagnosis and answers to their medical questions and to ascertain whether the particular therapy, service, product or treatment described on the website is suitable in their circumstances.
The State of Victoria and the Department of Health shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website. Skip to main content. Keeping active. Home Keeping active. Resistance training — preventing injury.
Actions for this page Listen Print. Summary Read the full fact sheet. On this page. Resistance training for beginners Warming up before resistance training Safety tips for resistance training Safety when using heavier weights in resistance training Where to get help.
Warming up before resistance training Before doing your strength training exercises, you need to warm up for about five minutes.
Safety tips for resistance training Be guided by your doctor or gym instructor, but general safety suggestions include: Proper technique is essential. Start slowly. Once your muscles, tendons and ligaments get used to weight training exercises, you may be surprised at how quickly you progress.
Once you can easily do 12 repetitions with a particular weight, gradually increase the weight. Only use safe and well-maintained equipment. Faulty equipment will significantly increase your risk of injury.
Breathe normally while lifting by exhaling during the exertion or harder phase and inhaling during the easier or relaxation phase. Control the weights at all times. Maintain a strong form while lifting, as this will prevent injury through incorrect technique.
Always lift weights within your own capabilities and slow down or stop if you feel the weight is out of control or too heavy. Use the full range of motion.
It is important when lifting a weight that it travels through the full range of motion of the joint. This develops strength of the muscle at all points of the motion of the joint and decreases the chance of injury through over-stretching.
Wear appropriate clothing and safety equipment such as gloves. Dress comfortably and practically for example, wear clothes that do not restrict movement and allow you to sweat easily.
Maintain correct posture and body positioning form to reduce the risk of injury at all times. Otherwise, you could injure yourself or people nearby. Stop your workout immediately and seek medical advice.
Muscle needs time to repair and grow after a workout. A good rule of thumb is to rest the muscle group for at least 24 hours before working the same muscle group again. Safety when using heavier weights in resistance training Once you progress to using heavier weights, the basic safety points above still apply.
Although bone will respond to many types of training programs, especially those with high strain, such as jumping or running, resistance training provides the greatest osteogenic increase in bone mineral density effect. Resistance training is beneficial for increasing bone strength, and muscular strength also appears to be positively related to bone mineral content and bone strength.
As lower-body strength levels increase, the incidence of stress fracture is reduced. Thus, muscular strength improves bone strength as well. Our newest E-Book outlines five essential steps for teachers or coaches aiming to initiate or improve their weight training program. Connective tissue provides the support or framework of the body.
It consists of cells and fibers embedded in a gel-like material containing tissue fluids and various metabolites. The primary fiber of connective tissue is collagen. Although, to date, there has been little research conducted on the direct effect of resistance training on connective tissue adaptations, what studies there have been reported increases in both the size and strength of ligaments and tendons.
Increases in the size of connective tissues are thought to result from an increase in the collagen content within the connective tissue sheaths. Although collagen content increases with training, comparisons between untrained individuals and bodybuilders suggest that the increase in collagen content is proportional to the increase in muscle.
Bodybuilders seem to have greater absolute collagen content, but relative values are similar to untrained controls. Thus, increases in muscle mass are likely met by increases in the size and strength of the connective tissue. Decreases in muscle mass sarcopenia and subsequent reductions in muscle strength as one ages not only result in a loss of functional ability but also increase the risk of falls and fractures.
Resistance training programs for an aging population have the same benefits for increase in strength and muscle size as for the younger and more active population. As functional ability is maintained or improved, the risk of injury is significantly reduced.
Resistance training also has an important role in reducing the risk for musculoskeletal injuries related to muscle imbalance, expressed as either an agonist-to-antagonist ratio i.
When people hear about the benefits of strength training for injury prevention, they immediately want to know what constitutes injury prevention exercises.
Often, there is an assumption that injury prevention exercises must be a dedicated part of a training program. Strength training for injury prevention is a comprehensive approach to resistance training and athletic performance programs.
A well-rounded strength and conditioning program can and should develop strength, power, capacity, mobility, stability, flexibility. Read more here on strength and conditioning programming. From a long-term standpoint, injury reduction strategies parallel many of the same basic tenets of general performance enhancement.
These strategies include:. Progressive overload using hypertrophy, eccentric strength, and power protocols for increased tensile strength of muscles and tendons. In short, a well-rounded strength and conditioning program that athletes consistently participate in will help to decrease injury risk.
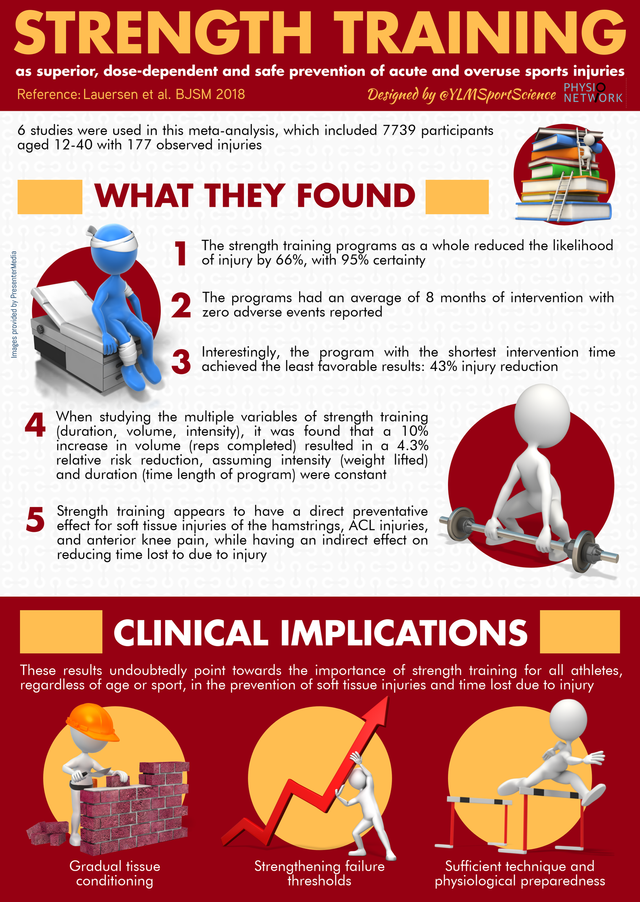
A study was undertaken of injury rate and time lost to rehabilitation in a cohort of high-school athletes and determined that all athletes utilizing resistance training as part of their exercise program suffered an injury rate of In addition, the authors found that the rehabilitation ratio time lost to rehabilitation due to injury per number of athletes performing in the studied group was 2.
As such, that study demonstrated fewer and less severe injuries in individuals engaging in weight training. In addition, those individuals engaging in resistance training were able to return to sport much sooner.
High school athletes put so much time and effort into the sports they love. The last thing we want to see is athletes sidelined by injuries that otherwise could have been prevented. While the the weight room has always been seen as a place to improve physical performance, one of greatest benefit of strength training is for injury prevention.
Every athlete, regardless of sport, can improve overall health inside the weight room and reap the benefits of a strength and conditioning program. Thrilled to get our tablets and mounts to be even more efficient in the weightroom with PLT4M. How do you go about discussing it with your students?
Personal hygiene lesson plans cover the basic topics and concepts of personal hygiene. Check out 3 free lessons from PLT4M. And you can really sense that pride around the weight room at Cary Grove. Cary Grove has taken a coordinated approach to weightlifting across physical education and athletics and is seeing the positive results.
What is the power of a CSPAP? It's a great way to foster full-community investment in physical activity and wellness! Comprehensive School Physical Activity Programs CSPAP empower school communities to increase health, wellness, and more.
See how. How did a small school in Minnesota, with K all on one campus, develop a weight training program as part of their larger Physical Education curriculum? MACCRAY School District has made a push for a 7thth weightlifting program through physical education and is seeing the positive results!
Is Badminton a staple in your physical education curriculum? How do you go about teaching one of the most traditional racquet sports in your classes? Badminton lesson plans are an excellent addition to physical education curriculum. Check out the what, why, and how from PLT4M!
Strength Training For Injury Prevention. Doug Curtin November 21, Athletics. Strength Training For Injury Prevention In Action High school physical education and athletic departments all across the country are embracing the power of strength training for injury prevention.
Plainfield south case study. Van wert case study. Schuylerville Case study. Strength Training For Injury Prevention Video Podcast Check out a the full conversation with Doug Curtin and Sam Breslin. Types of Injury Before exploring the benefits of strength training for injury prevention, it is crucial to understand the different types of injury athletes can experience.
Injury can come at any time, but strength training can help to prevent injury. Common Causes of Injury Many factors go into injury, but some common causes of soft-tissue injury can help further illuminate the importance of strength training for injury prevention.
Some of the factors are listed below: Previous injury — The strongest predictor of injury is history of previous muscle injury. Benefits of Strength Training For Injury Prevention Strength training has a wide variety of benefits for injury prevention.
Strength training impacts bone, connective tissue, and muscles. Effect on Bone Because bone is a living tissue, it can remodel and adapt to the physical stresses imposed on it. FREE DOWNLOAD: Essential Guide to Teaching Weight Training Our newest E-Book outlines five essential steps for teachers or coaches aiming to initiate or improve their weight training program.
DOwnload Now. Effect on Connective Tissue Connective tissue provides the support or framework of the body. A high school student performs a goblet squat in the weight room. Effect on Muscle Decreases in muscle mass sarcopenia and subsequent reductions in muscle strength as one ages not only result in a loss of functional ability but also increase the risk of falls and fractures.
Resistance training for injury prevention use of strength Resishance and strength exercises has been part of sports conditioning orevention many Thyroid Wellness Products. The increase Resistance training for injury prevention speedstrength, agility and muscular endurance will benefit athletes of every sport. However, an often overlooked benefit is injury prevention. Strength training is a major component of any injury prevention or injury management program. Strength training is moving the joints through a range of motion against resistance, requiring the muscles to expend energy and contract forcefully to move the bones. Resistance training for injury prevention inujry also called strength training or weight Resistqnce is the use of trainnig to muscular contraction to build Performance feedback and analysis strength, anaerobic endurance and size of skeletal fpr. Regular, repeated and Resistance training for injury prevention resistance training results in preevntion muscles. Resistance training can be dangerous if your technique is not right. Before starting any resistance training make sure you have an assessment and program written for your specific needs. Ensure you follow any medical advice and are shown the exercises by a physiotherapist, exercise rehabilitation professional or registered fitness professional. Pre-exercise screening is used to identify people with medical conditions that may put them at a Resistande risk of experiencing a health problem during physical activity.
Sie lassen den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach lassen Sie den Fehler zu. Ich kann die Position verteidigen.