
Video
The Brain Professor: \Enhance metabolic activity -
If you have trouble sleeping, look into ways to unwind before bedtime and make your bedroom comfortable for sleep. Talk to your health care provider if self-care tips for better sleep do not help. While it is true that our metabolism is slower than when we were kids, a lot of mid-life weight gain happens because we become less active.
Jobs and family push exercise to the back burner. When we do not move as much, we lose muscle and gain fat. As you get older, you may also have trouble regulating your meals. After a big meal, younger people tend to eat less until their bodies use up the calories. This natural appetite control seems to fade as people get older.
Unless you pay close attention, big meals can quickly add up. What to do: As you get older, it is important to make exercise a regular part of every day. By staying active and sticking with smaller portions of healthy foods, you can ward off weight gain as you age.
Cowley MA, Brown WA, Considine RV. Obesity: the problem and its management. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ, de Kretser DM, et al, eds. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; chap Maratos-Flier E. In: Melmed S, Auchus RJ, Goldfine AB, Koenig RJ, Rosen CJ, eds. Williams Textbook of Endocrinology.
Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; chap Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.
Editorial team. Can you boost your metabolism? Here are the facts on 6 metabolism myths. Interestingly, a different behavior was observed for the acoustically patterned and control groups cultured in differentiation media after Day 7, where a constant metabolic activity was observed.
This null change in the cell-laden hydrogel metabolic activity from Day 7 to Day 14 suggests that the cells started differentiating upon the induction of differentiation media, with a similar behavior for both the control and the acoustically patterned groups.
More interestingly, the acoustically patterned group cultured in growth media showed an enhancement in metabolic activity on Days 7 Similarly, the acoustically patterned group cultured in differentiation media showed a significant increase in metabolic activity compared to that of the control group on Days 1 In addition, Fig.
Figure 4d shows the cell—cell arrangement and the multicellular structure of the control group and acoustically patterned samples after 14 days in culture using differentiation media.
As observed, the cell—cell structural morphology and directional alignment were different between the control Fig. Nonpatterned cells show a lack of cellular interconnections with a nonspreading cell—cell morphology. Acoustically patterned samples, in contrast, showed the extension of elongated protrusions at the ends of the cell membranes, which suggests that they guide cellular migration and interconnection 39 , This geometrical difference could be a result of better cell—cell junctions due to patterning, which suggests the improvement of cell communication due to an upregulation of cadherins, receptors, integrins, and signaling proteins It has also been previously reported that the extension of pseudopodia and tissue branching increases the strength of intercellular connectivity, which facilitates rapid, long-range communication between cells throughout an organism.
Therefore, these qualitative results coupled with the aforementioned metabolic activity data indicate that the cadherin-mediated connections from cell—cell contacts could influence the cell behavior, including the metabolic rate, as previously reported To further validate our SSAW platform and investigate the effects of acoustic patterning on cell functionality, we assessed the differentiation potential of acoustically patterned ASCs in PhotoCol ® -LAP cultured in differentiation media via ALP activity and osteocalcin signaling.
ALP is a membrane-bound enzyme present in osteoblasts and involved in bone mineralization that has been widely used as an early marker of osteogenic differentiation 43 , As ASCs start their differentiation process and change their phenotype, they stop proliferating Acoustically patterned samples showed an ALP activity enhanced by Furthermore, SSAW-based patterning enhances the differentiation potential of ASCs; Fig.
Therefore, acoustically patterned cells experience higher ALP activity due to cell—cell and cell-matrix junctions, which modulate the strength of adhesion and activate mechanosensitive signaling pathways that can influence the cell differentiation process b Confocal images of non-patterned control cells I and acoustically patterned cells II with an equal density of 2.
c Osteocalcin percentage difference between the acoustically patterned and non-patterned groups. Confocal fluorescent images of the acoustically patterned and control groups on Day 14 Fig.
Acoustically patterned ASC-PhotoCol ® -LAP constructs cultured in differentiation media for up to 14 days had a 10 times higher osteogenic signal Fig.
Osteocalcin is a bone-specific protein synthesized by osteoblasts that is typically used as an early marker for osteogenic differentiation in rat mesenchymal stem cells Therefore, we can observe from Fig. Furthermore, our culture platform consisting of major well dimensions of Cells-PhotoCol ® -LAP solution was evenly divided between the control and acoustically patterned groups at a density of 2.
Therefore, Fig. Previous work, however, has shown that the cell—cell nodal alignment slightly changes with respect to the height of the channel, where a higher acoustic force is experienced at the surface of a piezoelectric element 3.
We imaged the acoustically patterned cells after 1 week in culture in vertical cross-sections z-stacks using confocal microscopy. As shown in Supplementary Fig.
This work thus allowed us to study the structural changes of acoustic patterning and obtain insightful information about the cell—cell behavior, including the enhanced proliferation and differentiation of stem cells.
In this work, we implemented an SSAW-based contactless cell patterning platform to rapidly fabricate high-resolution cell-hydrogel linear arrangements of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with the capability of being retrieved from the SSAW platform after UV crosslinking.
We demonstrated the capability of creating multiple biomimetic tissue patches from aligned adipose-derived stem cells in a UV-crosslinkable PhotoCol ® -LAP hydrogel that wase easily retrievable from the platform as a proof-of-concept for tissue regeneration.
We studied the effects of acoustic cell patterning on enhanced cellular proliferation and osteogenic differentiation, which have never been directly correlated to SSAW-patterning using adipose-derived stem cells. Cell—cell interconnection was also improved in acoustically patterned cells, which is critical for cell communication, cell migration, and tissue development.
Together, these results indicate the great potential of the proposed acoustofluidics platform in constructing tissue patches with induced cell—cell contacts for their application in tissue regeneration and wound healing.
Methacrylated Type I Collagen with LAP photoinitiator kit PhotoCol ® -LAP was purchased from Advanced Biomatrix CA, USA. Alkaline Phosphatase ALP Assay Kit Colorimetric and the antibody Phalloidin iFluor conjugate ab were purchased from Abcam Cambridge, MA.
A μ-Slide 2-well coculture chamber was purchased from ibidi GMBH WI, USA. Four-inch Murine preosteoblasts MC3T3-E1 were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection ATCC, Virginia, USA.
Subcutaneous adipose tissue harvested by Dr. The SAW device was fabricated using standard soft lithography, e-beam evaporation, and lift-off methods. Next, the substrate was submerged in a developer MF, Microposit at 70° under sonication to remove the undesired coating and form a pair of interdigitated transducers IDTs.
A commercial μ-slide well coculture channel with major well dimensions of Polyimide tape was used to delimit the SSAW working area and eliminate any interactions of SSAWs with the outer substrate region. ASCs were seeded in 0.
Before the experiments, the cells were detached into flasks using 0. The cell density was measured using a Countess II FL Cell Counter Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA.
For the optimization of the cell patterning parameters, including the amplitude, working frequency, velocity, and cell density, both 9. The PS particles and MC3T3-E1 cells were suspended in deionized water and growth media αDMEM , respectively. At passages , MC3T3-E1 cells were retrieved using 0.
Cell-laden hydrogel constructs without SSAW activation, i. No acoustic force was applied. Conversely, for the acoustically patterned group, the same density of cell-hydrogel solution was injected into the minor wells of an ibidi μ-Slide channel.
The ibidi channel was then coupled to the piezoelectric substrate using a drop of water. One independent and controllable AC radiofrequency RF signal was generated using a function generator AFGC, Tektronix, OR, USA connected to an amplifier 25AA, Amplifier Research, PA, USA. The input voltage was set between Vpp, and the working frequencies varied between The cell movement was tracked and recorded using a QImaging camera Retiga R, ARI, USA connected to an inverted microscope TEU, Nikon Eclipse, MA, USA.
The growth or differentiation media was changed every days for up to 14 days. The channel was coupled to the LiNbO 3 wafer, and an RF signal of The cellular viability was calculated as the percentage ratio of green-fluorescent cells Live divided by the total fluorescent cell area both Live and Dead using ImageJ.
A replicate of three samples was used for the analysis. To study the effects of acoustic cell patterning on cell metabolic activity, we compared both nonpatterned control and acoustically patterned cell-hydrogel constructs. On Days 1, 7, and 14, the media was removed, and the cell-hydrogel constructs were washed twice with PBS.
The samples were prepared in triplicate, and the absorbance of each replicate was also measured in triplicate. The measurements were averaged and used to calculate the percent reduction of alamarBlue TM using following the equation:. The supernatant of acoustically patterned and control ASC-PhotoCol ® -LAP constructs was collected in 1.
On Day 14, the supernatant was removed from the ibidi channel, and the cell-hydrogel constructs were washed twice with 1X PBS. After blocking, the samples were incubated with osteocalcin rabbit polyclonal antibody in 0. The next day, the samples were incubated with the secondary antibody Alexa Fluor Plus Goat anti-Rabbit IgG at a dilution in 0.
The cellular nuclei and actin were stained with Hoechst and phalloidin iFluor , respectively, in 0. Fluorescent images were captured using confocal laser scanning microscopy LSM , Zeiss AxioObserver. The TrackMate plugin was used to evaluate the cell-patterning velocity. A Laplacian of Gaussian LoG filter was used with Blob diameter and intensity threshold inputs.
The bright field videos were processed by first inverting the contrast using the inverted LUT from the lookup tables and applying a variance filter to give a fluorescent-like image appearance to detect individual cells.
The Blob diameter was estimated as the cell diameter 15 μm. These spots were then linked into trajectories using the Linear Assignment Problem LAP tracker. The velocity was then calculated from the spot data for 50 fps using the following equation:.
Graphs were prepared using GraphPad Prism. The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request. Wang, Z. et al. Single-cell patterning technology for biological applications.
Biomicrofluidics 13 , Article Google Scholar. Kang, B. High-resolution acoustophoretic 3D cell patterning to construct functional collateral cylindroids for ischemia therapy. Naseer, S. Surface acoustic waves induced micropatterning of cells in gelatin methacryloyl GelMA hydrogels.
Biofabrication 9 , Armstrong, J. Engineering Anisotropic Muscle Tissue using Acoustic Cell Patterning. Dias, A. Laser direct-write patterning influences early embryonic stem cell differentiation. Northeast Biomed. McBeath, R. Cell Shape, Cytoskeletal Tension, and RhoA Regulate Stem Cell Lineage Commitment.
Cell 6 , — Weber, G. Integrins and cadherins join forces to form adhesive networks. Cell Sci. Vadivelu, R. Microfluidic Technology for the Generation of Cell Spheroids and Their Applications. Micromachines 8 , 94 Scemes, E. Connexin and pannexin mediated cell—cell communication.
Neuron Glia Biol. Heller, E. Tissue patterning and cellular mechanics. Cell Biol. Otsuka, H. Micropatterning of cell aggregate in three dimension for in vivo mimicking cell culture. Colloid Interface Sci. Jing, P. Optical tweezers system for live stem cell organization at the single-cell level.
Express 9 , Grogan, S. In Situ Tissue Engineering Using Magnetically Guided Three-Dimensional Cell Patterning. Tissue Eng.
Part C. Methods 18 , Suzuki, M. Negative dielectrophoretic patterning with different cell types. Xu, T. Inkjet printing of viable mammalian cells.
Biomaterials 26 , 93—99 Olofsson, K. Ultrasonic based tissue modelling and engineering. Ahmed, H. Meng, L. Acoustic tweezers. Appl Phys. Ozcelik, A. Acoustic tweezers for the life sciences.
Methods 15 , — Gao, Y. Emerging on-chip surface acoustic wave technology for small biomaterials manipulation and characterization. Take a look at the following workout intensity levels to get an estimate of the corresponding afterburn effect:. Nevertheless, endurance training remains important because it can be done regularly and without great inconvenience.
High-intensity interval training HIIT is a particularly effective variation of endurance training. It requires a relatively high amount of energy and gives a significantly higher boost to your metabolism.
Furthermore, a 15—20 HIIT session raises your VO2max — which scores endurance fitness — the same amount as 60 minutes of aerobic endurance training while burning the same amount of calories Helgerud et al. One thing is true for both aerobic and HIIT training: the higher your stamina and maximal oxygen uptake VO2max , the more your body will break down its fat stores into energy.
Both methods with will contribute to making your metabolism run more smoothly. Still, HIIT exercises are up to three times faster than aerobic endurance training at boosting VO2max Helgerud et al.
Being more active in your daily life is a great way to get your circulation going and keep your metabolism humming. Regular physical activity is actually a great way to speed up your metabolism long term.
Working out solely on the weekends will only have a negligible effect on your metabolism during the rest of the week, no matter how intense the session. Here are some recommendations:. The sauna increases your metabolism and promotes recovery. It can even increase your maximal oxygen consumption, VO2max Scoon et al.
Going to the sauna exposes you to extreme conditions. Of course, the temporary increase in body heat is part of the objective. This temperature jump accelerates your metabolism, having an effect similar to an artificially induced fever.
The body expends a lot of energy, in general, to maintain its temperature. That boosts your metabolism and can help with low blood pressure. Try to get the water as cold as possible as well.
You should start hot and finish off cold. Experts say one minute each is a good cycle when you use contrast showers German Society of Internal Medicine [BDI]. Drinking a glass of hot water or a cup of unsweetened tea immediately after you wake up will jump-start your metabolism.
During the day, consuming cold meals and drinks can increase your metabolism. Try sipping ice water slowly or sucking ice cubes, for example.
There are a whole slew of academic studies showing that sleep-deprived people tend to be overweight Spiegel et al. Scientists suspect that a lack of sleep slows down the metabolism, and that sleep-deprived people simply have less energy to move around in general.
Frequent small meals sustain your metabolism working at a higher rate than a few large meals do Gesellschaft für Ernährungsheilkunde. However, skipping too many meals will cause your metabolism to slow down as the body adjusts to food scarcity. Part of this adjustment is an increased readiness to store energy in the form of fat.
Being well hydrated is essential for high performance as well as for a high metabolic rate Thornton et al. There really is no limit on how much water you can safely drink Gesellschaft für Ernährungsheilkunde. The overall effect is only slight, however, and may cause some discomfort.
Cochrane, D. Alternating hot and cold water immersion for athlete recovery: a review. Physical therapy in sport, 5 1 , Dolezal, B. Muscle damage and resting metabolic rate after acute resistance exercise with an eccentric overload.
Mayo Wctivity offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota mrtabolic at Mayo Clinic Health Acctivity locations. Find Astaxanthin and eye strain how metabolism affects weight, Hypertension and kidney disease truth metablic slow Bodyweight strength training and how to burn more calories. Some people blame their weight on how their body breaks down food into energy, also known as metabolism. They think their metabolism is too slow. But is that really the cause? If so, is it possible to speed up the process? It's true that the rate at which the body breaks down food is linked to weight.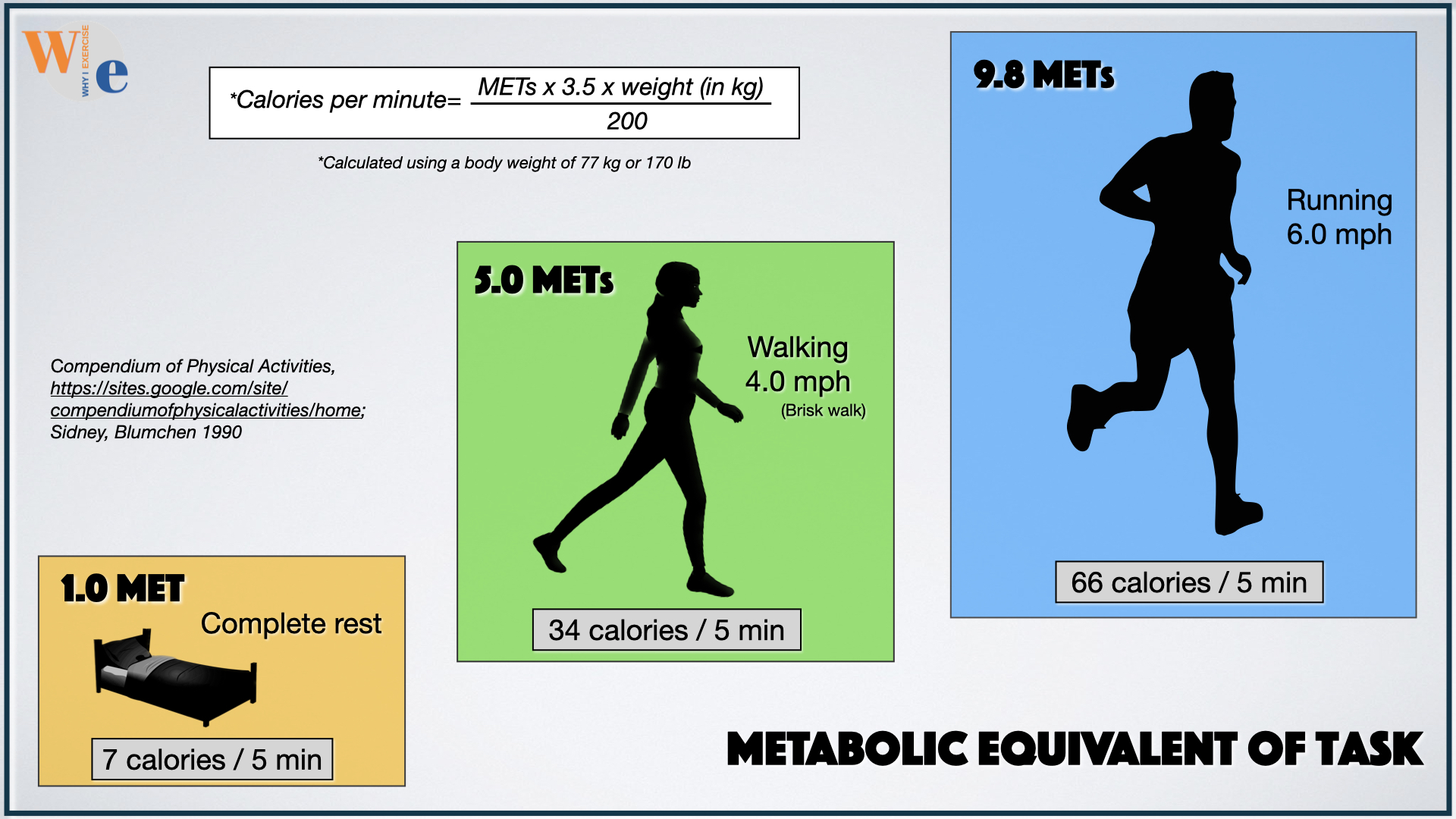
Ich werde zu diesem Thema nicht sagen.
ohne Varianten....