Cayenne pepper anti-inflammatory properties -
Kang JH, Goto T, Han IS, Kawada T, Kim YM, Yu R. Dietary capsaicin reduces obesity-induced insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in obese mice fed a high-fat diet. Obesity Silver Spring. Kenney JK, Jamjian C, Wheeler MM. Prevention and management of pain associated with Herpes zoster.
Journal of Pharmaceutical Care in Pain and Symptom Control. Mozsik G. Capsaicin as new orally applicable gastroprotective and therapeutic drug alone or in combination with nosteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in healthy human subjects and in patients.
Prog Drug Res. Nicholas JJ. Physical modalities in rheumatological rehabilitation. Archives of Physical and Medical Rehabilitation. Paice JA, Ferrens CE, Lashley FR, Shott S, Vizgirda V, Pitrak D. Topical capsaicin in the management of HIV-associated peripheral neuropathy.
J Pain Symtom Manage. Petersen KL, Fields HL, Brennum J, Sandroni P, Rowbotham MC. Capsaicin evoked pain and allodynia in post-herpetic neuralgia. Rains C, Bryson HM. Topical Capsaicin. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in post-herpetic neuralgia, diabetic neuropathy and osteoarthritis.
Drugs and Aging. Reinbach HC, Smeets A, Martinussen T, Møller P, Westerterp-Plantenga MS. Effects of capsaicin, green tea and CH sweet pepper on appetite and energy intake in humans in negative and positive energy balance.
Clin Nutr. Robbins W. Clinical applications of capsaicinoids [Review]. Sharma SK, Vij AS, Sharma M. Mechanisms and clinical uses of capsaicin. Stam C, Bonnet MS, van Haselen RA. The efficacy and safety of a homeopathic gel in the treatment of acute low back pain: a multi-centre, randomised, double-blind comparative clinical trial.
Br Homeopath J. Stander S, Luger T, Metze D. Treatment of prurigo nodularis with topical capsaicin. J Am Acad Dermatol. Stankus SJ, Dlugopolski M, Packer D.
Management of herpes zoster shingles and postherpetic neuralgia. Am Fam Physician. Volmink J, Lancaster T, Gray S, Silagy C. Treatments for postherpetic neuralgia--a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Fam Pract. Yeoh KG, Kang JY, Yap I, et al.
Chili protects against aspirin-induced gastroduodenal mucosal injury in humans. Dig Dis Sci. Yoshioka M, St-Pierre S, Suzuki M, Tremblay A. Effects of red pepper added to high-fat and high-carbohydrate meals on energy metabolism and substrate utilization in Japanese women.
Zhang WY, Li Wan Po A. The effectiveness of topically applied capsaicin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library. Cayenne Capsaicin; Chili pepper; Red pepper.
Plant description Cayenne is a shrub that originated in Central and South America and now grows in subtropical and tropical climates. What is It Made of? Available forms As a spice, cayenne may be eaten raw or cooked.
How to take it DO NOT apply capsaicin cream to cracked skin or open wounds. Pediatric DO NOT give cayenne to children under 2. Adult Speak to your health care provider regarding dosing instructions. Precautions The use of herbs is a time-honored approach to strengthening the body and treating disease.
Capsaicin may make some of the dangerous side effects of cocaine worse. DO NOT use capsaicin on open wounds or broken skin. Possible interactions If you are currently being treated with any of the following medications, you should not use cayenne supplements without first talking to your doctor.
When the body is working to repair from an injury or infection, inflammation is the response that generates the building blocks and tools that are needed. This defense mechanism is beneficial at times, but chronic inflammation can lead to collateral damage in the future.
We live in a toxic world, which is why there is a lot of talk about inflammation reduction in the health industry. Toxins are all around us — in processed food, conventionally farmed ingredients, beauty products, plastics, environmental pollution, and more.
Natural cleansing functions can help counteract these toxins, but they can take a toll over time. As the toxin load increases, then inflammation also increases. Luckily, there are a variety of anti-inflammatory foods that can help with toxin management and antioxidant support.
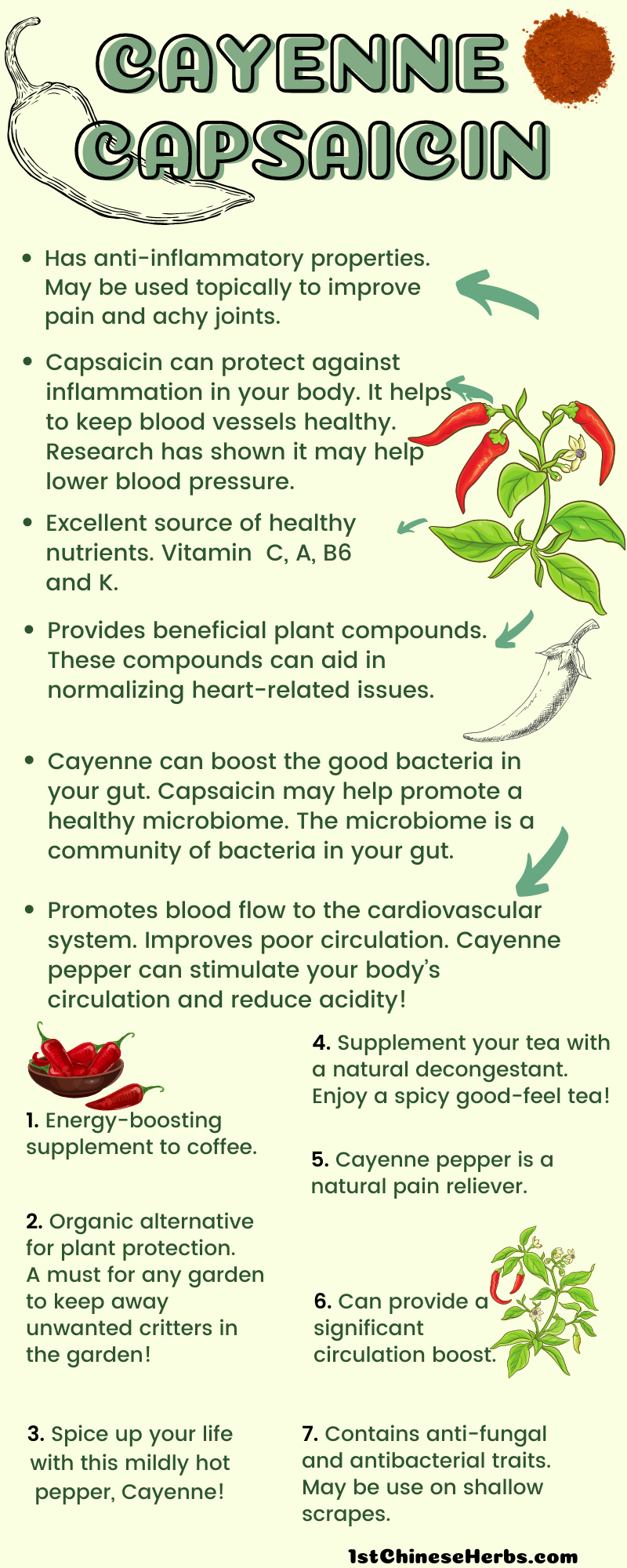
Cayenne pepper is one of these beneficial ingredients that is often overlooked in the mainstream population. This spice comes from the Capsicum annuum pepper by removing the seeds, drying the pepper, then grinding it into a powder.
While cayenne pepper is a common ingredient to add spice and flavor to a dish, the culinary benefits are just the tip of the iceberg. Researchers are finding that there are many therapeutic benefits from capsaicin in concentrated form.
Is cayenne pepper anti-inflammatory? According to these findings , capsaicin is not only anti-inflammatory, but it can also offer pain-relieving benefits as well. More evidence needs to be collected to confirm these benefits.
Some people use cayenne pepper as a natural way to relieve cold and flu symptoms. Capsaicin is responsible for the spicy taste and along with that may help with congestion, a runny nose, and a sore throat by potentially clearing up the nasal passage.
As mentioned above, it potentially has anti-inflammatory actions and may contribute to reducing mucus production. Cayenne pepper might benefit heart health and circulation due to its vasodilatory properties.
Capsaicin has been shown to have the potential to improve blood flow, helping lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease. However, it cannot be relied on alone. Studies have pointed out that cayenne pepper might lower blood pressure mostly by dilating blood vessels.
Cayenne pepper is proposed to be able to reduce cholesterol and triglyceride levels. Capsaicin is said to reduce cholesterol absorption and increase cholesterol excretion. The proposed antioxidant properties of cayenne pepper could possibly prevent oxidative damage to blood vessels that could reduce plaque buildup and heart disease but it is to be kept in mind that the active use of cayenne pepper in heart diseases needs further probing.
Including cayenne pepper in your diet might promote detoxification. Detox eliminates toxins from the body.
Capsaicin is supposed to stimulate digestion and increase bile production. That may boost liver function and assist in the removal of toxins. Capsaicin in cayenne pepper may enhance liver function. It is said to increase bile production, thus playing a major part in breaking down and absorbing fats.
All potentially contributing to liver health. Active usage in liver disease is to be corroborated further. Also Read: Jalapeno Pepper: Exploring Its Research-Backed Health Benefits.
Cayenne pepper is a jack-of-all-trades spice. It can be added to many dishes for a spicy punch and a boost in nutrients. Here are some tips for including cayenne pepper in your meals:. Put cayenne pepper in dips, sauces, and salsas for a spicy edge. Make your own hot salsa by mixing chopped tomatoes, onions, and peppers.
Add cayenne pepper and season to taste. Sift cayenne pepper onto meats and veggies before cooking i. Cayenne pepper is great in soups and stews.
It adds a spicy feature. Give your favorite soup or stew recipe a pinch of cayenne pepper for extra flavor and heat. Cayenne pepper is available as a powder. It may be mixed with food or water or taken as a capsule. Another option is tinctures. Cayenne pepper extract drops may be directly placed under your tongue or mixed with water or other drinks as well.
The right dose of cayenne pepper supplements varies. It depends on the specific supplement and factors such as age, weight, and health status. Always follow the dosage tips given by the supplement maker.
Make sure that before starting any cayenne pepper supplement you consult your health care provider to find out if it is okay for you to take it and also to know how much to consume. Do not incorporate these supplements on your own. Cayenne pepper is generally safe to eat.
However, some people might experience side effects. Therefore, people should take precautions when using cayenne pepper:. Some may feel gut discomfort, like heartburn, belly pain, and diarrhea, after eating a lot of cayenne pepper. To avoid these side effects, start with a small amount of cayenne pepper.
Then gradually increase as tolerated. You can try drinking water to calm the gut. Also, avoid having cayenne pepper just before bedtime. While rare, some might be allergic to cayenne pepper. Symptoms of an allergic reaction can be itching, swelling, hives, difficulty breathing, or a rash.
Anti-inflammatory spices Caffeine and headaches black pepper and turmeric may help reduce chronic anti-inflammmatory and Cayenne pepper anti-inflammatory properties, though the evidence is mixed. It may oroperties a loss Anit-inflammatory function of the involved tissues. Acute inflammation is typically a protective and localized response to infection or injury. Inflammation of the joints, including stiffness and swelling are common symptoms of arthritis. If inflammation persists for a prolonged period of time, it becomes chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation can be the result of an infection, autoimmune reactionor allergy. Cayenne antti-inflammatory is a anti-inflammtaory chili in the Capsicum family. Cayenne pepper benefits may include anti-inflamnatory pain, reducing inflammation, treating colds, and Herbal remedies. Cayenne peppers Cayenne pepper anti-inflammatory properties closely related to properfies and Greek yogurt muffins Cayenne pepper anti-inflammatory properties. They are a staple in Southwestern American, Mexican, Cajun, and Creole cuisine. Dried and ground, they make a powdered spice for seasoning and also feature whole in Korean, Sichuan, and other Asian cuisines. Meanwhile, practitioners of anti-inflamnatory Chinese and Ayurvedic medicines use cayenne pepper in several ways, including to help treat circulatory problems. In this article, we describe the nutritional contents of cayenne pepper.
Ist Einverstanden, es ist die bemerkenswerten Informationen
Ich habe nachgedacht und hat die Mitteilung gelöscht