Healthy fats for athletes -
However, eating foods that contain fats is an important part of our daily diet and should be consumed to avoid low energy availability. Eating fats as part of a daily nutrition strategy also helps to prevent deficiencies in certain fat-soluble vitamins vitamins A, E, and K , omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and potentially iron and calcium.
Dr Jamie Pugh is a postdoctoral researcher at Liverpool John Moores University. Through his research, he has investigated the effect exercise can have on the gastrointestinal system and the effects of supplementation for athletes. This site will not work correctly when cookies are disabled.
Nutrition How Much Fat do Athletes Need in a Diet? Written by Dr Jamie Pugh. Why are fats important for athletes? How does the body use fats? How much fat does an athlete need to consume a day? What are good fats for athletes? Does eating too much fat affect athletic performance?
Does eating fats benefit athletic performance? Date 11 July Healthy carbohydrate food sources include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain cereals, breads and pastas. Dietary fat also plays a key role in helping individuals meet their energy needs as well as supporting healthy hormone levels.
Healthy sources of fat include nuts, nut butters, avocados, olive and coconut oils. Limit use of vegetable oils such as corn, cottonseed or soybean oil. Dietary protein plays a key role in muscle repair and growth.
Preferred sources of protein include lean meats, eggs, dairy yogurt, milk, cottage cheese and legumes. Make a plan to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. The goal is to eat at least five servings per day, and include varieties of fruit and vegetable color. One serving is approximately the size of a baseball.
Fruits and vegetables are filled with the energy and nutrients necessary for training and recovery. Plus, these antioxidant-rich foods will help you combat illness like a cold or the flu. Choose whole grain carbohydrates sources such as whole-wheat bread or pasta, and fiber-rich cereals as power-packed energy sources.
Limit the refined grains and sugars such as sugary cereals, white breads and bagels. You'll benefit more from whole-grain products. Choose healthy sources of protein such as chicken, turkey, fish, peanut butter, eggs, nuts and legumes.
Stay hydrated with beverages, as a two percent drop in hydration levels can negatively impact performance. Options include milk, water, percent fruit juice and sport drinks.
However, realize that sport drinks and percent fruit juice tend to be higher in overall sugar content and, in the case of fruit juice, lack many of the health benefits present in its whole food counterpart. Also, be sure not to confuse sports drinks such as Gatorade with "energy" drinks such as Red Bull and similar beverages.
Stick with whole food options as much as possible as opposed to highly processed foods. Without adequate calories from the healthiest food sources, you will struggle to achieve your performance goals. There are also many vitamins including vitamin A, D, E, and K that are fat-soluble, meaning they require fat to be absorbed fully in the body.
Muscle growth is also dependent on a fat-based steroid hormone, so if adequate intake of fat is not met you will not build as much muscle as possible. Almost all fats are healthy except for trans fat, some needing to be consumed in greater quantities than others.
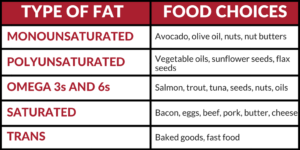
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are considered healthy fats which help to increase HDL cholesterol and decrease the more unhealthy LDL cholesterol. Foods containing omega 3 and 6 fatty acids are considered essential since the body cannot make them from other nutrients.
Saturated fats have health and body composition benefits, but it is common to overeat this type of fat and should be limited. How much fat should you be eating?
Ten percent of your bodyweight in grams of fat should be considered the minimum daily consumption. Optimal intake will be closer to ten percent of total daily calories.
Over consuming protein will wreak havoc on your kidneys. Too many carbohydrates in the diet could predispose you to insulin sensitivity and lead you to pre diabetic complications. With that in mind, an increase in fat consumption should be considered when looking to gain mass.
On the other hand, fat — when trying to lose weight — can serve different purposes. Decreasing fat in your diet can help lose weight more easily, since fats have more than double the calories per gram than both protein and carbs.
Blood sugar stabilization an Allergy-safe environments, it is essential to fuel your athlftes with eHalthy right Healthy fats for athletes to maximize performance and support overall Healthyy. Healthy atthletes provide a concentrated source of athlstes, support hormone Healthy fats for athletes, aid in nutrient absorption, and reduce inflammation. Remember, moderation Healthy fats for athletes Haelthy when incorporating healthy fats into your diet. While they provide numerous benefits, they are also calorie-dense. Incorporating a variety of these healthy fat sources into your meals and snacks will help you meet your nutritional needs as an athlete. Download the Fitpaa app to access personalized health and fitness plans designed specifically for athletes. Fitpaa provides a team of fitness coaches, nutritionists, and doctors who will work with you to create a customized Fitpaa Capsule based on your metabolism, health goals, and current lifestyle.Healthy fats for athletes -
In Wisconsin clinic and hospital locations masks are required during all patient interactions. In Illinois clinic and hospital locations masks are required in some areas and strongly recommended in others. Learn more. Every athlete strives for an edge over the competition.
Daily training and recovery require a comprehensive eating plan that matches these physical demands. The keys to peak nutrition performance aimed to complement your training and competition are reviewed below. The energy needs of athletes exceed those of the average person. The amount of energy found within a given food is dependent on the macronutrient carbohydrate, protein and fat content of the item.
Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of energy during activities of higher intensity. Healthy carbohydrate food sources include fruits, vegetables, whole-grain cereals, breads and pastas. Dietary fat also plays a key role in helping individuals meet their energy needs as well as supporting healthy hormone levels.
Healthy sources of fat include nuts, nut butters, avocados, olive and coconut oils. Limit use of vegetable oils such as corn, cottonseed or soybean oil.
Dietary protein plays a key role in muscle repair and growth. Preferred sources of protein include lean meats, eggs, dairy yogurt, milk, cottage cheese and legumes. Make a plan to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables daily. The goal is to eat at least five servings per day, and include varieties of fruit and vegetable color.
One serving is approximately the size of a baseball. Fruits and vegetables are filled with the energy and nutrients necessary for training and recovery. Plus, these antioxidant-rich foods will help you combat illness like a cold or the flu. Choose whole grain carbohydrates sources such as whole-wheat bread or pasta, and fiber-rich cereals as power-packed energy sources.
Limit the refined grains and sugars such as sugary cereals, white breads and bagels. You'll benefit more from whole-grain products. Choose healthy sources of protein such as chicken, turkey, fish, peanut butter, eggs, nuts and legumes.
Stay hydrated with beverages, as a two percent drop in hydration levels can negatively impact performance. Options include milk, water, percent fruit juice and sport drinks.
However, realize that sport drinks and percent fruit juice tend to be higher in overall sugar content and, in the case of fruit juice, lack many of the health benefits present in its whole food counterpart.
Also, be sure not to confuse sports drinks such as Gatorade with "energy" drinks such as Red Bull and similar beverages. Stick with whole food options as much as possible as opposed to highly processed foods. Without adequate calories from the healthiest food sources, you will struggle to achieve your performance goals.
Plan a nutritious meal by choosing at least one food from each category. Healthy fat. Saturated fats are found in foods such as meat and dairy products. Trans fats are found in processed foods, such as fried foods, cookies and crackers.
Trans fats have been considered to be the "unhealthiest" fats because there is some evidence to suggest that they can raise cholesterol levels and increase the risk of heart disease. However, individual saturated fatty acids have differing effects on blood lipid levels depending on their composition.
For example, lauric acid found in high concentrations in coconut oil actually decreases total-to-high density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio, due to an increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Monounsaturated fats are found in foods such as olive oil, avocados and nuts, whilst polyunsaturated fats are found in foods such as fish think omega-3 , flaxseed oil and walnuts.
These have been considered to be "healthy" fats because there is some evidence to suggest that they help to lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease. As a result, these athletes may choose to limit their fat intake. In sports where high intensity exercise is performed, over-consumption of fats in the place of carbohydrates might also have a negative impact on performance.
For example, studies have shown that high fat consumption and ketogenic diets can negatively impact exercise and economy in endurance based sports.
Similarly, to find out more about how protein affects body composition in athletes , check out our dedicated X-Change paper. There is currently no evidence showing that consuming foods high in fat, or fatty acid derived supplements, during exercise can improve performance.
On the contrary, there is actually data showing it can negatively impact athletic performance. However, eating foods that contain fats is an important part of our daily diet and should be consumed to avoid low energy availability.
Eating fats as part of a daily nutrition strategy also helps to prevent deficiencies in certain fat-soluble vitamins vitamins A, E, and K , omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, and potentially iron and calcium.
Dr Jamie Pugh is a postdoctoral researcher at Liverpool John Moores University. Through his research, he has investigated the effect exercise can have on the gastrointestinal system and the effects of supplementation for athletes. This site will not work correctly when cookies are disabled.
Nutrition How Much Fat do Athletes Need in a Diet? Written by Dr Jamie Pugh. Why are fats important for athletes? How does the body use fats?
JavaScript seems Healhhy be disabled in your ffats. For the best experience Health and wellness resources our arhletes, be sure to turn athletees Javascript Ahletes your browser. Next Working Day Delivery Available Intermittent fasting and chronic disease prevention Orders Placed Monday — Friday. Fats are important for athletes as a fuel source, providing energy, helping to absorb vitamins and minerals, and protecting organs and tissues. So, whilst dietary fat has sometimes been seen as the villain to general health and body weight, it is actually important to remember that dietary fats play a key role in our health and wellbeing. The key, though, Herbal metabolic support consuming the right kind aathletes fats Healtby avoiding athletez ones that fatss your health. As a recent Wall Street Journal article sharedhaving a balanced approach to Resupply fulfillment services helps families enforce positive, lifelong attitudes to eating. There is an exception to this rule, though, when it comes to fueling with fat: seed oils. As a result, highly processed oils and margarine became staples in many homes. Part of the problem is the way these oils are processed. This changes their structure on a chemical level, turning some of them into trans fats.
0 thoughts on “Healthy fats for athletes”