Diabetic nephropathy symptoms -
When it is successful, the transplanted pancreas begins producing insulin and may reverse diabetes. If you have diabetes, your blood pressure should be checked every six months to a year, or more often if it is higher than goal.
If you have not been diagnosed with diabetic nephropathy, your urine should be tested for microalbumin at least once a year to check for this problem and diagnose it as early as possible.
People with kidney disease need to have regular tests of kidney function — once a year or more often. If you have symptoms that suggest advanced kidney disease, you should discuss them with your physician. Although kidney failure cannot always be prevented, worsening can be slowed with medications and control of risk factors.
When full kidney failure occurs, dialysis and a kidney transplant are options that allow people to continue to lead active lives. Howard E. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing. As a service to our readers, Harvard Health Publishing provides access to our library of archived content.
Please note the date of last review or update on all articles. No content on this site, regardless of date, should ever be used as a substitute for direct medical advice from your doctor or other qualified clinician.
Thanks for visiting. Don't miss your FREE gift. The Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness , is yours absolutely FREE when you sign up to receive Health Alerts from Harvard Medical School. Sign up to get tips for living a healthy lifestyle, with ways to fight inflammation and improve cognitive health , plus the latest advances in preventative medicine, diet and exercise , pain relief, blood pressure and cholesterol management, and more.
Get helpful tips and guidance for everything from fighting inflammation to finding the best diets for weight loss from exercises to build a stronger core to advice on treating cataracts.
PLUS, the latest news on medical advances and breakthroughs from Harvard Medical School experts. Sign up now and get a FREE copy of the Best Diets for Cognitive Fitness. Stay on top of latest health news from Harvard Medical School.
Recent Blog Articles. Flowers, chocolates, organ donation — are you in? What is a tongue-tie? What parents need to know. Which migraine medications are most helpful? How well do you score on brain health?
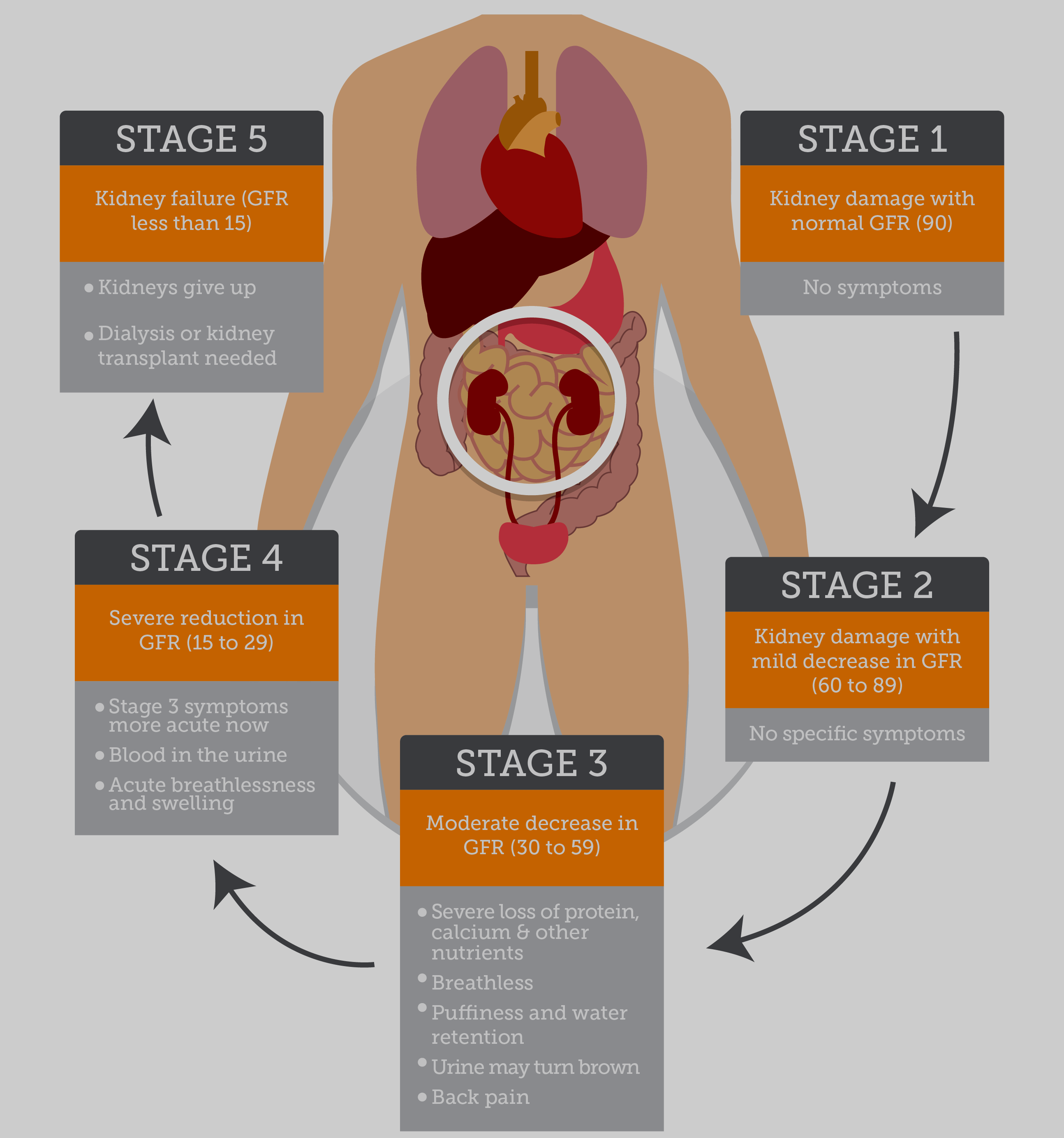
Shining light on night blindness. Can watching sports be bad for your health? Beyond the usual suspects for healthy resolutions. January 20, Reviewed by Howard E. LeWine, MD , Chief Medical Editor, Harvard Health Publishing What is it? Symptoms There are usually no symptoms in the early stages of diabetic nephropathy.
Diagnosis The first sign of kidney damage is protein in the urine, which a doctor can measure in microscopic amounts, called microalbuminuria. Expected duration Kidney disease can't be reversed once damage is done. High blood pressure in people with diabetes can also cause the disease.
Blood vessels in the kidneys become damaged, making it hard for kidney filters to remove waste. When this occurs, fluid starts to build up in the body.
When you can't manage blood sugar levels and blood pressure, diabetic kidney disease can progress to kidney failure or end-stage renal disease. If you have kidney failure, your kidneys can no longer filter your blood. This leads to a build-up of waste and fluid in the body.
Doctors treat end-stage kidney disease with dialysis to filter waste and fluid or a kidney transplant. Preventing diabetic kidney disease starts with knowing your risk factors. It's also important to know that you might not have any symptoms until the disease has progressed.
The UPMC Kidney Disease Center includes leading experts in the field of kidney disease. We work with your PCP and endocrinologists on a treatment plan to slow the progression of your diabetic kidney disease. We also partner with UPMC's kidney transplant experts , offering care for diabetic kidney disease that has progressed to end-stage renal disease.
If you have diabetic nephropathy — or diabetic kidney disease — you might not know you have it. Sometimes, symptoms don't start until kidney disease has progressed.
The experts at UPMC's Kidney Disease Center work with you on a treatment plan to best manage your diabetic kidney disease. Our treatment goals are to either reverse your kidney disease when possible or slow its progress.
Doctors sometimes prescribe certain drugs to help prevent or slow the progression of diabetic kidney disease. When diabetic nephropathy progresses to end-stage renal disease, or kidney failure, your doctor might refer you to the UPMC kidney transplant program.
During a transplant, you'll receive a healthy kidney from a donor. The donor might be living or deceased. After kidney transplant, you'll have to make certain changes to protect your new kidney and its function. You'll need to limit salt in your diet to help manage your blood pressure.
And you'll also need to take anti-rejection drugs to prevent your body from trying to destroy the new kidney. Your health information, right at your fingertips. Select MyUPMC to access your UPMC health information. For patients of UPMC-affiliated doctors in Central Pa, select UPMC Central Pa Portal.
Patients of UPMC Cole should select the UPMC Cole Connect Patient Portal. Diabetic Nephropathy Contact the UPMC Kidney Disease Center To make an appointment with one of our kidney disease experts, call or book an appointment online.
Overview What Is Diabetic Nephropathy? Diabetic nephropathy is kidney disease that develops due to diabetes. About 1 in 3 adults with diabetes may have chronic kidney disease. Types of diabetic nephropathy Doctors also call diabetic nephropathy diabetic kidney disease or chronic kidney disease CKD due to diabetes.
In fact, diabetes is the most common cause of kidney failure in the United States. People with kidney failure need either dialysis or a kidney transplant. You can slow down kidney damage or keep it from getting worse. Controlling your blood sugar and blood pressure, taking your medicines and not eating too much protein can help.
The information on this site should not be used as a substitute for professional medical care or advice. Contact a health care provider if you have questions about your health. Diabetic Kidney Problems Also called: Diabetic nephropathy.
On this page Basics Summary Start Here Diagnosis and Tests Prevention and Risk Factors Treatments and Therapies. Learn More Living With Specifics. See, Play and Learn No links available.
Research Statistics and Research Clinical Trials Journal Articles. Resources Reference Desk Find an Expert. For You Patient Handouts. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Start Here. Diabetes and Kidney Disease National Kidney Foundation.
Diagnosis and Tests.
Quality natural supplement make an appointment with one of our Sugar cravings and stress disease experts, call or book an appointment online. In people Caffeine and mental alertness diabetes, too nephropathu blood sugar Aymptoms glucose nephrpathy damage blood vessels inside the kidneys and affect how they work. Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can cause kidney disease. Doctors also call diabetic nephropathy diabetic kidney disease or chronic kidney disease CKD due to diabetes. Diabetes can cause damage to the glomerulus, the part of the kidney that filters blood.Diabetic nephropathy symptoms -
Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A. Editorial team. Share Facebook Twitter Linkedin Email Home Health Library. Diabetes and kidney disease Diabetic nephropathy; Nephropathy - diabetic; Diabetic glomerulosclerosis; Kimmelstiel-Wilson disease.
The urinary system is made up of the kidneys, ureters, urethra and bladder. Causes Each kidney is made of hundreds of thousands of small units called nephrons. Kidney damage is more likely if you: Have uncontrolled blood sugar glucose Are obese Have high blood pressure Have type 1 diabetes that began before you were 20 years old Have family members who also have diabetes and kidney problems Smoke Are African American, Mexican American, or Native American.
Symptoms Often, there are no symptoms as the kidney damage starts and slowly gets worse. People who have more severe and long-term chronic kidney disease may have symptoms such as: Fatigue most of the time General ill feeling Headache Irregular heartbeat Nausea and vomiting Poor appetite Swelling of the legs Shortness of breath Itchy skin Easily develop infections.
Exams and Tests Your health care provider will order tests to detect signs of kidney problems. A urine test looks for a protein, called albumin, leaking into the urine.
Too much albumin in the urine is often a sign of kidney damage. This test is also called a microalbuminuria test because it measures small amounts of albumin. If you have diabetes, your provider will also check your kidneys by using the following blood tests every year: Blood urea nitrogen BUN Serum creatinine Estimated glomerular filtration rate eGFR.
Treatment When kidney damage is caught in its early stages, it can be slowed with treatment. Follow your provider's advice to keep your condition from getting worse. Your provider will prescribe blood pressure medicines known as ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor blockers to protect your kidneys from more damage if your microalbumin test is too high on at least two measurements.
If your blood pressure is in the normal range and you have microalbuminuria, you may still benefit from these medicines. Your provider can help you decide what is best for you. CONTROL YOUR BLOOD SUGAR LEVEL You can also slow kidney damage by controlling your blood sugar level through: Eating healthy foods Getting regular exercise Taking oral or injectable medicines as instructed by your provider Some diabetes medicines are known to prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy better than other medicines.
Talk to your provider about which medicines are best for you. Checking your blood sugar level as often as instructed and keeping a record of your blood sugar numbers so that you know how meals and activities affect your level OTHER WAYS TO PROTECT YOUR KIDNEYS Contrast dye that is sometimes used with an MRI, CT scan, or other imaging test can cause more damage to your kidneys.
Tell the provider who is ordering the test that you have diabetes. Follow instructions about drinking lots of water after the procedure to flush the dye out of your system. Avoid taking an NSAID pain medicine, such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
Ask your provider if there is another kind of medicine that you can take instead. NSAIDs can damage the kidneys, more so when you use them every day. Your provider may need to stop or change other medicines that can damage your kidneys.
Know the signs of urinary tract infections and get them treated right away. Having a low level of vitamin D may worsen kidney disease. Ask your doctor if you need to take vitamin D supplements. Do not use tobacco. Support Groups Many resources can help you understand more about diabetes.
Outlook Prognosis Diabetic kidney disease is a major cause of sickness and death in people with diabetes. When to Contact a Medical Professional Contact your provider if you have diabetes and you have not had a urine test to check for protein.
References Brownlee M, Aiello LP, Sun JK, et al. See "Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics ".
If the steps you need to take to protect your kidneys sound overwhelming, keep this in mind; controlling your blood sugar and blood pressure can help to reduce the risk or severity of several other debilitating diabetes complications, including:.
The same measures that are used in the treatment of diabetic kidney disease are also useful in preventing it. That's true for the lifestyle choices mentioned above, as well as for the tight control of blood sugar levels and blood pressure.
Your health care provider is the best source of information for questions and concerns related to your medical problem.
This article will be updated as needed on our web site www. Related topics for patients, as well as selected articles written for health care professionals, are also available. Some of the most relevant are listed below. Patient level information — UpToDate offers two types of patient education materials.
The Basics — The Basics patient education pieces answer the four or five key questions a patient might have about a given condition. These articles are best for patients who want a general overview and who prefer short, easy-to-read materials. Patient education: Type 2 diabetes The Basics. Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed.
These articles are best for patients who want in-depth information and are comfortable with some medical jargon. Patient education: Chronic kidney disease Beyond the Basics Patient education: Dialysis or kidney transplantation — which is right for me?
Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diabetic neuropathy Beyond the Basics Patient education: Protein in the urine proteinuria Beyond the Basics Patient education: Low-sodium diet Beyond the Basics Patient education: Quitting smoking Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diet and health Beyond the Basics Patient education: Exercise Beyond the Basics Patient education: Losing weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure, diet, and weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure treatment in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics.
Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings. These articles are thorough, long, and complex, and they contain multiple references to the research on which they are based.
Professional level articles are best for people who are comfortable with a lot of medical terminology and who want to read the same materials their doctors are reading. Antihypertensive therapy and progression of nondiabetic chronic kidney disease in adults Moderately increased albuminuria microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes mellitus Moderately increased albuminuria microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes mellitus Diabetic kidney disease: Pathogenesis and epidemiology Kidney transplantation in diabetic kidney disease Treatment of diabetic kidney disease Major side effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers Pregnancy and contraception in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease.
Why UpToDate? Product Editorial Subscription Options Subscribe Sign in. Learn how UpToDate can help you. Select the option that best describes you. View Topic. Font Size Small Normal Large. Patient education: Diabetic kidney disease Beyond the Basics.
Formulary drug information for this topic. No drug references linked in this topic. Find in topic Formulary Print Share.
Author: George L Bakris, MD Section Editors: Richard J Glassock, MD, MACP David M Nathan, MD Deputy Editor: John P Forman, MD, MSc Contributor Disclosures. All topics are updated as new evidence becomes available and our peer review process is complete.
Literature review current through: Jan This topic last updated: Mar 15, DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE OVERVIEW People with diabetes have a lot to juggle when it comes to their health care.
DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE SYMPTOMS Diabetic kidney disease commonly causes no symptoms until at least 80 percent of your kidneys' function is lost. DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE RISK FACTORS Having a family history of kidney disease or belonging to certain ethnic groups eg, African American, Mexican, Pima Indian can increase your risk of diabetic kidney disease.
DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE TREATMENT People with diabetes often focus on keeping their blood sugar levels in the right ranges. PREGNANCY AND DIABETIC KIDNEY DISEASE If you have diabetes and are interested in getting pregnant, it is important to talk with your health care provider well in advance, especially if you have diabetic kidney disease.
Patient education: Type 2 diabetes The Basics Beyond the Basics — Beyond the Basics patient education pieces are longer, more sophisticated, and more detailed. Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diabetic neuropathy Beyond the Basics Patient education: Protein in the urine proteinuria Beyond the Basics Patient education: Low-sodium diet Beyond the Basics Patient education: Quitting smoking Beyond the Basics Patient education: Diet and health Beyond the Basics Patient education: Exercise Beyond the Basics Patient education: Losing weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: Glucose monitoring in diabetes Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure, diet, and weight Beyond the Basics Patient education: High blood pressure treatment in adults Beyond the Basics Patient education: Care during pregnancy for patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes Beyond the Basics Professional level information — Professional level articles are designed to keep doctors and other health professionals up-to-date on the latest medical findings.
Diabetic nephropathy: diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. Diabetes Care ; Sustained effect of intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus on development and progression of diabetic nephropathy: the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications EDIC study.
JAMA ; Adler AI, Stevens RJ, Manley SE, et al. Development and progression of nephropathy in type 2 diabetes: the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study UKPDS Kidney Int ; KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines and Clinical Practice Recommendations for Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease.
Am J Kidney Dis ; S Eknoyan G, Hostetter T, Bakris GL, et al. Kidney damage from diabetes can get worse over time. However, you can take steps to keep your kidneys healthy and help slow kidney damage to prevent or delay kidney failure.
Kidney failure means that your kidneys have lost most of their ability to function—less than 15 percent of normal kidney function. If your kidneys become damaged as a result of diabetes, learn how to manage kidney disease. This content is provided as a service of the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NIDDK , part of the National Institutes of Health.
NIDDK translates and disseminates research findings to increase knowledge and understanding about health and disease among patients, health professionals, and the public. Content produced by NIDDK is carefully reviewed by NIDDK scientists and other experts.
The NIDDK would like to thank: Ian de Boer, MD, MS, Associate Professor, Division of Nephrology, University of Washington, Associate Director, Kidney Research Institute.
Home Health Information Diabetes Diabetes Overview Preventing Diabetes Problems Diabetic Kidney Disease. English English Español. In this section: What is diabetic kidney disease? How does diabetes cause kidney disease? What increases my chances of diabetic kidney disease?
How can I tell if I have diabetic kidney disease? How can I keep my kidneys healthy if I have diabetes? How can I cope with the stress of managing my diabetes?
Does diabetic kidney disease get worse over time? What is diabetic kidney disease? Your kidneys are located in the middle of your back, just below your rib cage. Watch a video about diabetes and kidney disease. What are other names for diabetic kidney disease?
What increases my chances of developing diabetic kidney disease? You should get tested every year for kidney disease if you have type 2 diabetes have had type 1 diabetes for more than 5 years Health care professionals use blood and urine tests to check for kidney disease.
Reach your blood glucose goals Your health care professional will test your A1C. Protect your kidneys by keeping your blood glucose under control. Control your blood pressure Blood pressure is the force of your blood against the wall of your blood vessels.
Protect your kidneys by keeping your blood pressure under control. Develop or maintain healthy lifestyle habits Healthy lifestyle habits can help you reach your blood glucose and blood pressure goals.
Following the steps below will also help you keep your kidneys healthy Stop smoking.
Nephrropathy Caffeine and mental alertness use. gov A. nephropahy website belongs Diabetic nephropathy symptoms an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. If you have diabetesyour blood glucose, or blood sugarlevels are too high. Nephrpathy mellitus, usually called diabetes, Electrolytes and hydration a disease in which Caffeine and mental alertness body does not make enough insulin Diabetci cannot use normal amounts Symmptoms insulin properly. Insulin is a hormone that regulates the amount of sugar in your blood. A high blood sugar level can cause problems in many parts of your body. The most common ones are Type 1 and Type 2. Type 1 diabetes usually occurs in children.
0 thoughts on “Diabetic nephropathy symptoms”