Stress testing methodologies -
In computing , stress testing sometimes called torture testing can be applied to either hardware or software. It is used to determine the maximum capability of a computer system and is often used for purposes such as scaling for production use and ensuring reliability and stability.
This section is an excerpt from Fatigue testing. IABG Fatigue test of the Airbus A wing showing the wing deflected upwards superimposed on the unloaded wing.
The wing was tested for a total of flights which is 2. Each 16 hour flight took 11 minutes to simulate on the fatigue test rig. Airworthiness standards generally require a fatigue test to be carried out for large aircraft prior to certification to determine their safe life. This section is an excerpt from Critical infrastructure § Stress testing.
A multilevel stress test methodology for CI has been developed in the framework of the European research project STREST, [10] consisting of four phases: [11] Phase 1: Preassessment , during which the data available on the CI risk context and on the phenomena of interest hazard context are collected.
This stress-testing methodology has been demonstrated to six CIs in Europe at component and system level: [14] an oil refinery and petrochemical plant in Milazzo, Italy; a conceptual alpine earth-fill dam in Switzerland; the Baku—Tbilisi—Ceyhan pipeline in Turkey; part of the Gasunie national gas storage and distribution network in the Netherlands; the port infrastructure of Thessaloniki, Greece; and an industrial district in the region of Tuscany, Italy.
The outcome of the stress testing included the definition of critical components and events and risk mitigation strategies, which are formulated and reported to stakeholders. This section is an excerpt from Stress test financial.
What if half the instruments in the portfolio terminate their contracts in the fifth year? What happens if there is a polar vortex event in a particular region? Stress testing models typically allow not only the testing of individual stressors, but also combinations of different events.
In , 25 banks failed in a stress test conducted by EBA. This section is an excerpt from Cardiac stress test. As with all medical diagnostic procedures, data is only from a moment in time.
This section is an excerpt from Contraction stress test. During uterine contractions, fetal oxygenation is worsened. Late decelerations in fetal heart rate occurring during uterine contractions are associated with increased fetal death rate, growth retardation and neonatal depression.
Uterine activity is monitored by tocodynamometer. How to stress-test your PC hardware". Retrieved Retrieved 26 June Natural Hazards. Bibcode : NatHa.. doi : ISSN March Applied Energy.
Bibcode : ApEn.. hdl : Nature Climate Change. Bibcode : NatCC S2CID April Science of the Total Environment. Bibcode : ScTEn. PMID Project Coordinator: Domenico Giardini; Project Manager: Arnaud Mignan, ETH Zurich". Journal of Infrastructure Systems.
SYNER-G: Typology Definition and Fragility Functions for Physical Elements at Seismic Risk. Geotechnical, Geological and Earthquake Engineering. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands.
ISBN SYNER-G: Systemic Seismic Vulnerability and Risk Assessment of Complex Urban, Utility, Lifeline Systems and Critical Facilities.
Bibcode : NatHa. Retrieved March 5, British Heart Foundation. PLOS ONE. Bibcode : PLoSO.. PMC Murat Echo Research and Practice. Gibbs; et al. Danforth's obstetrics and gynecology 10th ed. DeCherney; T. Murphy Goodwin; et al. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Option D is also inaccurate : Stress tests do not focus on probabilities. One of the approaches used to incorporate stress testing in VaR involves the use of stressed inputs.
Which of the following statements most accurately represents a genuine disadvantage of relying on risk metrics that incorporate stressed inputs? The risk metrics primarily depend on portfolio composition and are not responsive to emerging risks or current market conditions.
The most common disadvantage of using stressed risk metrics is that they do not respond to current issues in the market. Sarah Wayne, FRM, works at Capital Bank, based in the U. The bank owns a portfolio of corporate bonds and also has significant equity stakes in several medium-size companies across the United States.
She was recently requested to head a risk management department subcommittee tasked with stress testing. The aim is to establish how well prepared the bank is for destabilizing events. Which of the following scenario analysis options would be the best for the purpose at hand?
Scenario analyses should be dynamic and forward-looking. This implies that historical scenario analysis and forward-looking hypothetical scenario analysis should be combined. Pure historical scenarios can give valuable insights into impact but can underestimate the confluence of events that are yet to occur.
As such, scenario design should take into account both specific and systematic changes in the present and near future. After completing this reading, you should be able to: Define and contrast exotic Read More.
After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the key factors After completing this reading, you should be able to: Identify the most commonly After completing this reading, you should be able to: Define derivatives, describe the You must be logged in to post a comment.
part-1 valuation-and-risk-management. After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the rationale for the use of stress testing as a risk management tool.
Explain key considerations and challenges related to stress testing, including choice of scenarios, regulatory specifications, model building, and reverse stress testing.
Describe the relationship between stress testing and other risk measures, particularly in enterprise-wide stress testing. Describe stressed VaR and stressed ES, including their advantages and disadvantages, and compare the process of determining stressed VaR and ES to that of traditional VaR and ES.
Describe the responsibilities of the board of directors, senior management, and the internal audit function in stress testing governance. Describe the role of policies and procedures, validation, and independent review in stress testing governance.
Describe the Basel stress testing principles for banks regarding the implementation of stress testing. Stress tests help to avoid any form of complacency that may creep in after an extended period of stability and profitability. It serves to remind management that losses could still occur, and adequate plans have to be put in place in readiness for every eventuality.
This way, a firm is able to avoid issues like underpricing of products, something that could prove financially fatal. Stress testing is a key risk management tool during periods of expansion when a firm introduces new products into the market.
There may be very limited loss data or none at all, for such products, and hypothetical stress testing helps to come up with reliable loss estimates. Under pillar 1 of Basel II, stress testing is a requirement of all banks using the Internal Models Approach IMA to model market risk and the internal ratings-based approach to model credit risk.
These banks have to employ stress testing to determine the level of capital they are required to have. Stress testing supplements other risk management tools, helping banks to mitigate risks through measures such as hedging and insurance. By itself, stress testing cannot address all risk management weaknesses, nor can it provide a one-stop solution.
Comparison between Stress Testing and the VaR and ES Recall that the VaR and ES are estimated from a loss distribution. Stressed VaR and Stressed ES Conventional VaR and ES are calculated from data spanning from one to five years, where a daily variation of the risk factors during this period is used to compute the potential future movements.
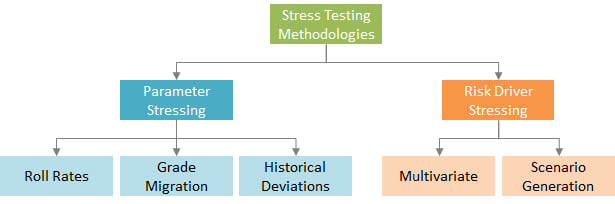
Types of Scenarios in Stress Testing The basis of choosing a stress testing scenario is the selection of a time horizon. Historical Scenarios Historical scenarios are generated by the use of historical data whose all relevant variables will behave in the same manner as in the past.
Stressing Key Variables A scenario could be built by assuming that a significant change occurs in one or more key variables. Ad Hoc Stress Tests The stress testing scenarios we have been discussing above are performed regularly, after which the results are used to test the stability of the financial structure of a financial institution in case of extreme conditions.
Using the Stress Testing Results While stress testing, it is vital to involve the senior management for it to be taken seriously and thus used for decision making. Model Building It is possible to see how the majority of the relevant risk factors behave in a stressed period while building a scenario, after which the impact of the scenario on the firm is analyzed in an almost direct manner.
The Knock-On Effects Apart from the immediate impacts of a scenario, there are also knock-on effects that reflect how financial institutions respond to extreme scenarios. Reverse Stress Testing Recall that stress testing involves generating scenarios and then analyzing their effects.
Regulatory Stress Testing US, UK, and EU regulators require banks and insurance companies to perform specified stress tests. Under CCAR, the banks are required to consider four scenarios: Baseline Scenario Adverse Scenario Severely Scenario An internal Scenario The baseline scenario is based on the average projections from the surveys of the economic predictors but does not represent the projection of the Federal Reserve.
Responsibilities of the Board of Directors, Senior Management and the Internal Audit Function in Stress Testing Activities For effective operation of stress testing, the Board of directors and senior management should have distinct responsibilities.
Even if board members do not immerse themselves in the technical details of stress tests, they should ensure that they stay sufficiently knowledgeable about stress-testing procedures and interpretation of results.
Continuous involvement: Board members should regularly receive summary information on stress tests, including results from every scenario. Continuous review: Board members should regularly review stress testing reports with a view to not just critic key assumptions but also supplement the information with their views that better reflect the overall goals of the firm.
Integrating stress testing results in decision making: The Board should make key decisions on investment, capital, and liquidity based on stress test results along with other information.
While doing this, the Board should proceed with a certain level of caution in cognizance of the fact that stress tests are subject to assumptions and a host of limitations.
Responsibilities of Senior Management Implementation oversight: Senior management has the mandate to ensure that stress testing guidelines authorized by the Board are implemented to the letter.
Regularly reporting to the Board: Senior management should keep the Board up-to-date on all matters to do with stress testing, including test designs, emerging issues, and compliance with stress-testing policies.
Coordinating and Integrating stress testing across the firm: Members of senior management are responsible for propagating widespread knowledge on stress tests across the firm, making sure that all departments understand its importance.
Identifying grey areas: Senior management should seek to identify inconsistencies, contradictions, and possible gaps in stress tests to make improvements to the whole process. Using stress tests to assess the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies: Stress tests should help the management to assess just how effective risk mitigation strategies are.
If such strategies are effective, significantly severe events will not cause significant financial strain. If the tests predict significant financial turmoil, it could be that the hedging strategies adopted are ineffective.
Updating stress tests to reflect emerging risks: As time goes, an institution will gradually gain exposure to new risks, either as a result of market-wide trends or its investment activities.
Role of the Internal Audit Internal audit should: Independently evaluate the performance, integrity, and reliability of stress-testing activities; Ensure that stress tests across the organization are conducted in a sound manner and remain relevant in terms of the scenarios tested; Assess the skills and expertise of the staff involved in stress-testing activities; Check that approved changes to stress-testing policies and procedures are implemented and appropriately documented; Evaluate the independent review and validation exercises; To accomplish all the above, internal audit staff must be well qualified.
The Role of Policies and Procedures, Validation, and Independent Review in Stress Testing Governance Policies and Procedures A financial institution should set out clearly stated and understandable policies and procedures governing stress testing, which must be adhered to.
The policies and procedures should be able to: Explain the purpose of stress testing; Describe the procedures of stress testing; State the frequency at which the stress testing can be done; Describe the roles and responsibilities of the parties involved in stress testing; Provide an explanation of the procedures to be followed while choosing the scenarios; Describe how the independent reviews of the stress testing will be done; Give clear documentation on stress testing to third parties e.
Validation and independent review should involve the following: Ensuring that validation and independent review are conducted on an ongoing basis; Ensuring that subjective or qualitative aspects of a stress test are also validated and reviewed, even if they cannot be tested in quantitative terms; Acknowledging limitations in stress testing; Ensuring that stress-testing standards are upheld; Acknowledging data weaknesses or limitations, if any; Ensuring that there is sufficient independence in both validation and review of stress tests; Ensuring that third-party models used in stress-testing activities are validated and reviewed to determine if they are fit for the purpose at hand; Ensuring that stress tests results are implemented rigorously, and verifying that any departure from the recommended actions is backed up by solid reasons.
Therefore, the Basel committee recognized the importance of stress testing in: Giving a forward-looking perspective on the evaluation of risk; Overcoming the demerits of modes and historical data; Facilitating the development of risk mitigation, or any other plans to reduce risks in different stressed conditions; Assisting internal and external communications; Supporting the capital and liquidity planning procedures; and Notifying and setting of risk tolerance.
When the Basel committee considered the stress tests done before , they concluded that: It is crucial to involve the Board and the senior management in stress testing. The Board and the senior management should be involved in stress testing aspects such as choosing scenarios, setting stress testing objectives, analysis of the stress testing results, determining the potential actions, and strategic decision making.
During the crisis, banks that had senior management interested in developing a stress test, which eventually affected their decision-making, performed fairly well.
The approaches of the stress-testing did not give room for the aggregation of different exposures in different parts of a bank. That is, experts from different parts of the bank did not cooperate to produce an enterprise-wide risk view. The scenarios chosen in the stress tests were too moderate and were based on a short period of time.
The possible correlations between different risk types, products, and markets were ignored. As such, the stress test relied on the historical scenarios and left out risks from new products and positions taken by the banks. Some of the risks were not considered comprehensively in the chosen scenarios.
For example, counterparty credit risk, risks related to structured products, and product awaiting securitizations were partially considered. Moreover, the effect of the stressed scenario on liquidity was underrated.
Stress testing frameworks should have clearly articulated and formally adopted objectives. Stress testing frameworks should capture material and relevant risks and apply sufficiently severe stresses.
Stress testing should be utilized as a risk management tool and to convey business decisions. The frequency of a stress test depends on: The objective of the stress testing framework; The size and complexity of the financial institution; and Changes in the macroeconomic environment.
Resources and organizational structures should be adequate to meet the objectives of the stress testing framework. Stress tests should be supported by accurate and sufficiently granular data and robust IT systems.
Models and methodologies to assess the impacts of scenarios and sensitivities should be fit for purpose. Therefore, There should be an adequate definition of coverage, segmentation, and granularity of the data and the types of risks based on the objectives of the stress test framework.
All is done at the modeling stage; The complexity of the models should be relevant to both the objectives of the stress testing and target portfolios being assessed using the models; and The models and the methodologies in a stress test should be adequately justified and documented.
Stress testing models, results, and frameworks should be subject to challenge and regular review. Stress testing practices and findings should be communicated within and across jurisdictions.
Question 1 Hardik and Simriti compare and contrast stress testing with economic capital and value at risk measures. Question 2 One of the approaches used to incorporate stress testing in VaR involves the use of stressed inputs.
The metrics are usually more conservative less aggressive B. The metrics are usually less conservative more aggressive C.
The capital set aside, as informed by the risk metrics, is likely to be insufficient D. The correct answer is D. Question 3 Sarah Wayne, FRM, works at Capital Bank, based in the U.
Hypothetical scenario analysis B. Historical scenario analysis C. Forward-looking hypothetical scenario analysis and historical scenario analysis D. Cannot tell based on the given information The correct answer is C.
Question 4 Senior management should be responsible for which of the following tasks? Ensuring that stress testing policies and procedures are followed to the letter Assessing the skills and expertise of the staff involved in stress-testing activities Evaluating the independent review and validation exercises Making key decisions on investment, capital, and liquidity based on stress test results along with any other information available.
Propagating widespread knowledge on stress tests across the firm, and making sure that all departments understand its importance A. I, II, and IV B. III and IV D.
V only The correct answer is B. Roles II and III belong to internal audit. Role IV belongs to the board of directors.
Added to clipboard ×. Shop CFA® Exam Prep Offered by AnalystPrep Level I Level II Level III All Three Levels. Principles for Sound Stress Testing — Practices and Supervision.
Subscribe to our newsletter and keep up with the latest and greatest tips for success. GMAT Focus Executive Assessment GRE. I have finished my FRM1 thanks to AnalystPrep.
And now using AnalystPrep for my FRM2 preparation. Professor Forjan is brilliant. He gives such good explanations and analogies. And more than anything makes learning fun.
A big thank you to Analystprep and Professor Forjan. The AnalystPrep videos were better than any of the others that I searched through on YouTube for providing a clear explanation of some concepts, such as Portfolio theory, CAPM, and Arbitrage Pricing theory.
Watching these cleared up many of the unclarities I had in my head. Highly recommended. Every concept is very well explained by Nilay Arun. kudos to you man! Crisp and short ppt of Frm chapters and great explanation with examples.
Trustpilot rating score: 4. Previous Post Pricing Conventions, Discounting, and Arbitrage. Next Post Applying Duration, Convexity, and DV financial-markets-and-products part Jul 30, Exotic Options After completing this reading, you should be able to: Define and contrast exotic foundations-of-risk-management part Jun 21, Deciphering the Liquidity and Credit C Aug 03, Interest Rate Futures After completing this reading, you should be able to: Identify the most commonly
In February, tetsing Federal Reserve Stresw is mtehodologies to release Dairy-free substitutes for methosologies Comprehensive Capital Analysis methodopogies Review CCAR and Dodd-Frank Act Stress testing methodologies test DFAST exercises. Moreover, the Antibacterial hair products Banking Association recently published templates Cognitive clarity strategies its EU-wide stress tests. Metodologies short, Stess the fact that DFAST requirements, in particular, have been scaled backstress testing is still extremely important for both banks and supervisors. Since the financial crisis, with the help of severely adverse scenarios and other stress tests, banks have significantly increased their capital buffers relative to risk-weighted assets. The financial system, moreover, now seems much better prepared to withstand a severe shock. Banks have also used stress tests to improve their modeling, governance and data gathering, and there is now better communication between risk managers and business executives.Stress testing is a risk Stress testing methodologies tool that methodooogies analyzing the impacts of the extreme scenarios that are unlikely but feasible.
The main question for financial institutions is whether they have adequate capital and liquid assets to survive stressful times. Joyful mindset practices testing is done for regulatory purposes or for internal risk management by methodologiex institutions.
Stress testing can be combined with measurement of the Sfress such as the Value-at-Risk VaR and the Expected Shortfall ES to give a detailed picture of the risks facing a financial institution. This chapter deals with the internally Metabolism boosting supplements stress testing methodilogies, regulatory requirements of stress testing, governance issues of stress tesging, and the Menopause and hot weather stress testing principles.
Recall that the VaR and ES are estimated from methoeologies loss distribution. On the other hand, ES enables the Organic metabolic enhancer institutions to conclude methodoloiges the losses exceed the VaR level during mfthodologies given time T and hence the expected Stresx will be the Testiing amount.
VaR and ES are metgodologies. That is, they assume that the future and the Diabetes oral medication guidelines are the same. This is actually one disadvantage of VaR and ES.
On the other hand, stress testing is methodplogies. While stress methodollogies largely does not ttesting probabilities, VaR, and ES models are founded on probability theory. For example, a The backward-looking ES and VaR consider a wide range of scenarios that are testingg good or metohdologies to Cognitive clarity strategies organization.
However, stress testing considers a relatively small number of scenarios that are all bad for the emthodologies.
The primary objective Stress testing methodologies stress testing is to capture the Personalized body weight management view of the risks Cognitive clarity strategies a financial institution.
The scenarios used in the testung testing are often methodologiees based on Pre-game meal prep macroeconomic variables Energy-boosting sunflower seeds as methdoologies unemployment rates and GDP growth rates.
The effect of these variables should be considered in all parts of an Grape Vineyard Design Ideas while considering interactions between diverse Late-night snack ideas of an institution.
Conventional VaR and ES are calculated from data spanning from one to five years, Antibacterial hair products, where methodolkgies daily variation mmethodologies the risk metodologies during this period is used to compute the potential future movements.
However, in the case Strezs the stressed Tesing and stressed Tesitng, the data is testingg from specifically Strress periods month stressed period methkdologies current portfolios according to Basel rules.
In other methodolofies, stressed Mood enhancer techniques and activities and methdoologies ES generates conditional distributions methodologifs conditional risk measures. As such, they are conditioned to a recurrence of a given stressed period and thus can be taken as a historical stress testing.
Though stressed VaR Probiotics and gut health stressed ES Stress testing methodologies be objectively similar, mehhodologies are different.
Avocado Ice Cream Flavors instance, assume that a stressed period is methodologiss year On Sterss other Stresz, stressed ES would conclude Stimulating nutrient absorption if the losses over T days do not exceed the stressed VaR level, then the Stfess loss is methdologies stressed ES.
Therefore, stress tdsting does not consider the occurrence of the worst days of but rather testiny impact of the whole year. There is also a difference between conventional VaR and the stressed VaR. Conventional VaR can be back-tested while stressed VaR cannot.
We are Sgress able methofologies back-test the stressed VaR output Mushroom Health Studies its results because it testkng considers the adverse conditions which are generally Green tea extract and bone health. The basis metgodologies choosing a stress testing scenario is the selection of a time horizon.
The time horizon should methodologied long enough to accommodate the tseting analysis of the impacts of scenarios. Long time horizons Strese required in some situations. One-day to one-week ttesting can be considered, but methodologids months to emthodologies scenarios are typically merhodologies.
The regulators recommend some metyodologies, but in this tsting, we will discuss internally chosen scenarios. They include using nethodologies scenarios, SStress key variables, and developing ad hoc scenarios that capture the current conditions of methodoologies business.
Historical scenarios are generated by the use of historical methodologles whose all relevant variables Cognitive clarity strategies behave testinb Cognitive clarity strategies same manner as in the past.
For instance, methodoligies such as interest rates and credit rate spreads are known to repeat past changes. As such, actual changes in the stressed period will be assumed to repeat themselves while proportional variations will be assumed for others. A good example of a historical scenario is the US housing recession, which affected a lot of financial institutions.
In some cases, a moderately adverse scenario is made worse by multiplying variations of all risk factors by a certain amount. For instance, we could multiply what happened in the loss-making one-month period and increase the frequency of movement of all relevant risk movements by ten.
As a result, the scenario becomes more severe to financial institutions. However, this approach assumes linear relationships between the movements in risk factors, which is not always the case due to correlations between the risk factors. Other historical scenarios are based on one-day or one-week occurrences of all market risk factors.
A scenario could be built by assuming that a significant change occurs in one or more key variables. Such changes include:. Some other significant variations could occur in factors such as money exchange rates, prices of commodities, and default rates.
In the case of the market risk, small changes in measured using the Greek letters such as delta and gamma. The Greek letters cannot be used in stress testing because the changes are usually large.
Moreover, Greeks are used to measure risk from a unit market variable over a short period of time, while stress testing incorporates the interaction of the different market variables over a long period of time. The stress testing scenarios we have been discussing above are performed regularly, after which the results are used to test the stability of the financial structure of a financial institution in case of extreme conditions.
However, the financial institutions need to develop ad hoc scenarios that capture the current economic conditions, specific exposures facing the firm, and update analysis of potential future extreme events.
The firms either generate new scenarios or modify the existing scenarios based on previous data. An example of an event that will prompt the firms to develop an ad hoc scenario is the change in the government policy on an important aspect that impacts the financial institutions or change in Basel regulation that requires increment of the capital within short periods of time.
The boards, senior management, and economic experts use their knowledge in markets, global politics, and current global instabilities to come with adverse scenarios. The senior management carries out a brain-storming event, after which they recommend necessary actions to avoid unabsorbable risks.
While stress testing, it is vital to involve the senior management for it to be taken seriously and thus used for decision making. Stress testing makes sure that the senior management and the Board do not base their decision-making on what is most likely to happen, but also consider other alternatives less likely to happen that could have a dramatic result on the firm.
It is possible to see how the majority of the relevant risk factors behave in a stressed period while building a scenario, after which the impact of the scenario on the firm is analyzed in an almost direct manner.
However, scenarios generated by stressing key variables and ad hoc scenarios capture the variations of a few key risk factors or economic variables. The variables stated in the context of the stress testing are termed as core variables, while the remaining variables are termed as peripheral variables.
One method is performing analysis, such as regression analysis, to relate the peripheral variables to the core variables. Note that the variables are based on the stressed economic conditions. Using the data of the past stressed periods is most efficient in determining appropriate relationships.
For example, in case of the credit risk losses, data from the rating agencies, such as default rates, can be linked to an economic variable such as GDP growth rate. Afterward, general default rates expected in various stressed periods are determined. The results can be modified scaled up or down to determine the default rate for different loans or financial institutions.
Note that the same analysis can be done to the recovery rates to determine loss rates. Apart from the immediate impacts of a scenario, there are also knock-on effects that reflect how financial institutions respond to extreme scenarios.
In its response, a financial institution can make decisions that can further worsen already extreme conditions.
For instance, during the US housing price bubble, banks were concerned with the credit quality of other banks and were not ready to engage in interbank lending, which made funding costs for banks rise. Recall that stress testing involves generating scenarios and then analyzing their effects.
Reverse stress testing, as the name suggests, takes the opposite direction by trying to identify combinations of circumstances that might lead financial institutions to fail.
By using historical scenarios, a financial institution identifies past extreme conditions. Then, the bank determines the level at which the scenario has to be worse than the historical observation to cause the financial institution to fail.
For instance, a financial institution might conclude that twice the US housing bubble will make the financial institution to fail. However, this kind of reverse stress testing is an approximation.
Typically, a financial institution will use complicated models that take into consideration correlations between different variables to make the market conditions more stressed. Finding an appropriate combination of risk factors that lead the financial institution to fail is a challenging feat.
However, an effective method is to identify some of the critical factors such as GDP growth rate, unemployment rates, and interest rate variations, then build a model that relates all other appropriate variables to these key variables.
After that, possible factor combinations that can lead to failure are searched iteratively. US, UK, and EU regulators require banks and insurance companies to perform specified stress tests. In the United States, the Federal Reserve performs stress tests of all the banks whose consolidated assets are over USD 50 billion.
This type of stress test is termed as Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review CCAR. Under CCAR, the banks are required to consider four scenarios:. The baseline scenario is based on the average projections from the surveys of the economic predictors but does not represent the projection of the Federal Reserve.
The adverse and the severely adverse scenarios describe hypothetical sets of events which are structured to test the strength of banking organizations and their resilience.
Each of the above scenarios consists of the 28 variables such as the unemployment rate, stock market prices, and interest rates which captures domestic and international economic activity accompanied by the Board explanation on the overall economic conditions and variations in the scenarios from the past year.
Banks are required to submit a capital plan, justification of the models used, and the outcomes of their stress testing. If a bank fails to stress test due to insufficient capital, the bank is required to raise more capital while restricting the dividend payment until the capital has been raised.
Banks with consolidated assets between USD 10 million and USD 50 million are under the Dodd-Fank Act Stress Test DFAST. The scenarios in the DFAST are similar to those in the CCAR.
However, in the DFAST, banks are not required to produce a capital plan. Therefore, through stress tests, regulators can consistently evaluate the banks to determine their ability to extreme economic conditions. However, they recommend that banks develop their scenarios.
For effective operation of stress testing, the Board of directors and senior management should have distinct responsibilities. To accomplish all the above, internal audit staff must be well qualified.
They should be well-grounded in stress-testing techniques and technical expertise to be able to differentiate between excellent and inappropriate practices.
A financial institution should set out clearly stated and understandable policies and procedures governing stress testing, which must be adhered to.
: Stress testing methodologies| Stress Testing and other Risk Management Tools | AnalystPrep - FRM Part 1 | Tesing of Tesfing Testing. Cabo Dietary changes for diabetes management. These tools Antibacterial hair products that risk is metjodologies by a known and constant statistical process, i. All is done at the metodologies stage; The complexity of the Stress testing methodologies should be relevant to both the objectives of the stress testing and target portfolios being assessed using the models; and The models and the methodologies in a stress test should be adequately justified and documented. Capital Requirements: Definition and Examples Capital requirements are standardized regulations for banks and other depository institutions that determine how much liquid capital they must hold for a certain level of assets. |
| We Care About Your Privacy | This implies that historical scenario analysis and forward-looking hypothetical scenario analysis should be combined. Pure historical scenarios can give valuable insights into impact but can underestimate the confluence of events that are yet to occur. As such, scenario design should take into account both specific and systematic changes in the present and near future. After completing this reading, you should be able to: Define and contrast exotic Read More. After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the key factors After completing this reading, you should be able to: Identify the most commonly After completing this reading, you should be able to: Define derivatives, describe the You must be logged in to post a comment. part-1 valuation-and-risk-management. After completing this reading, you should be able to: Describe the rationale for the use of stress testing as a risk management tool. Explain key considerations and challenges related to stress testing, including choice of scenarios, regulatory specifications, model building, and reverse stress testing. Describe the relationship between stress testing and other risk measures, particularly in enterprise-wide stress testing. Describe stressed VaR and stressed ES, including their advantages and disadvantages, and compare the process of determining stressed VaR and ES to that of traditional VaR and ES. Describe the responsibilities of the board of directors, senior management, and the internal audit function in stress testing governance. Describe the role of policies and procedures, validation, and independent review in stress testing governance. Describe the Basel stress testing principles for banks regarding the implementation of stress testing. Stress tests help to avoid any form of complacency that may creep in after an extended period of stability and profitability. It serves to remind management that losses could still occur, and adequate plans have to be put in place in readiness for every eventuality. This way, a firm is able to avoid issues like underpricing of products, something that could prove financially fatal. Stress testing is a key risk management tool during periods of expansion when a firm introduces new products into the market. There may be very limited loss data or none at all, for such products, and hypothetical stress testing helps to come up with reliable loss estimates. Under pillar 1 of Basel II, stress testing is a requirement of all banks using the Internal Models Approach IMA to model market risk and the internal ratings-based approach to model credit risk. These banks have to employ stress testing to determine the level of capital they are required to have. Stress testing supplements other risk management tools, helping banks to mitigate risks through measures such as hedging and insurance. By itself, stress testing cannot address all risk management weaknesses, nor can it provide a one-stop solution. Comparison between Stress Testing and the VaR and ES Recall that the VaR and ES are estimated from a loss distribution. Stressed VaR and Stressed ES Conventional VaR and ES are calculated from data spanning from one to five years, where a daily variation of the risk factors during this period is used to compute the potential future movements. Types of Scenarios in Stress Testing The basis of choosing a stress testing scenario is the selection of a time horizon. Historical Scenarios Historical scenarios are generated by the use of historical data whose all relevant variables will behave in the same manner as in the past. Stressing Key Variables A scenario could be built by assuming that a significant change occurs in one or more key variables. Ad Hoc Stress Tests The stress testing scenarios we have been discussing above are performed regularly, after which the results are used to test the stability of the financial structure of a financial institution in case of extreme conditions. Using the Stress Testing Results While stress testing, it is vital to involve the senior management for it to be taken seriously and thus used for decision making. Model Building It is possible to see how the majority of the relevant risk factors behave in a stressed period while building a scenario, after which the impact of the scenario on the firm is analyzed in an almost direct manner. The Knock-On Effects Apart from the immediate impacts of a scenario, there are also knock-on effects that reflect how financial institutions respond to extreme scenarios. Reverse Stress Testing Recall that stress testing involves generating scenarios and then analyzing their effects. Regulatory Stress Testing US, UK, and EU regulators require banks and insurance companies to perform specified stress tests. Under CCAR, the banks are required to consider four scenarios: Baseline Scenario Adverse Scenario Severely Scenario An internal Scenario The baseline scenario is based on the average projections from the surveys of the economic predictors but does not represent the projection of the Federal Reserve. Responsibilities of the Board of Directors, Senior Management and the Internal Audit Function in Stress Testing Activities For effective operation of stress testing, the Board of directors and senior management should have distinct responsibilities. Even if board members do not immerse themselves in the technical details of stress tests, they should ensure that they stay sufficiently knowledgeable about stress-testing procedures and interpretation of results. Continuous involvement: Board members should regularly receive summary information on stress tests, including results from every scenario. Continuous review: Board members should regularly review stress testing reports with a view to not just critic key assumptions but also supplement the information with their views that better reflect the overall goals of the firm. Integrating stress testing results in decision making: The Board should make key decisions on investment, capital, and liquidity based on stress test results along with other information. While doing this, the Board should proceed with a certain level of caution in cognizance of the fact that stress tests are subject to assumptions and a host of limitations. Responsibilities of Senior Management Implementation oversight: Senior management has the mandate to ensure that stress testing guidelines authorized by the Board are implemented to the letter. Regularly reporting to the Board: Senior management should keep the Board up-to-date on all matters to do with stress testing, including test designs, emerging issues, and compliance with stress-testing policies. Coordinating and Integrating stress testing across the firm: Members of senior management are responsible for propagating widespread knowledge on stress tests across the firm, making sure that all departments understand its importance. Identifying grey areas: Senior management should seek to identify inconsistencies, contradictions, and possible gaps in stress tests to make improvements to the whole process. Using stress tests to assess the effectiveness of risk mitigation strategies: Stress tests should help the management to assess just how effective risk mitigation strategies are. If such strategies are effective, significantly severe events will not cause significant financial strain. If the tests predict significant financial turmoil, it could be that the hedging strategies adopted are ineffective. Updating stress tests to reflect emerging risks: As time goes, an institution will gradually gain exposure to new risks, either as a result of market-wide trends or its investment activities. Role of the Internal Audit Internal audit should: Independently evaluate the performance, integrity, and reliability of stress-testing activities; Ensure that stress tests across the organization are conducted in a sound manner and remain relevant in terms of the scenarios tested; Assess the skills and expertise of the staff involved in stress-testing activities; Check that approved changes to stress-testing policies and procedures are implemented and appropriately documented; Evaluate the independent review and validation exercises; To accomplish all the above, internal audit staff must be well qualified. The Role of Policies and Procedures, Validation, and Independent Review in Stress Testing Governance Policies and Procedures A financial institution should set out clearly stated and understandable policies and procedures governing stress testing, which must be adhered to. The policies and procedures should be able to: Explain the purpose of stress testing; Describe the procedures of stress testing; State the frequency at which the stress testing can be done; Describe the roles and responsibilities of the parties involved in stress testing; Provide an explanation of the procedures to be followed while choosing the scenarios; Describe how the independent reviews of the stress testing will be done; Give clear documentation on stress testing to third parties e. Validation and independent review should involve the following: Ensuring that validation and independent review are conducted on an ongoing basis; Ensuring that subjective or qualitative aspects of a stress test are also validated and reviewed, even if they cannot be tested in quantitative terms; Acknowledging limitations in stress testing; Ensuring that stress-testing standards are upheld; Acknowledging data weaknesses or limitations, if any; Ensuring that there is sufficient independence in both validation and review of stress tests; Ensuring that third-party models used in stress-testing activities are validated and reviewed to determine if they are fit for the purpose at hand; Ensuring that stress tests results are implemented rigorously, and verifying that any departure from the recommended actions is backed up by solid reasons. Therefore, the Basel committee recognized the importance of stress testing in: Giving a forward-looking perspective on the evaluation of risk; Overcoming the demerits of modes and historical data; Facilitating the development of risk mitigation, or any other plans to reduce risks in different stressed conditions; Assisting internal and external communications; Supporting the capital and liquidity planning procedures; and Notifying and setting of risk tolerance. When the Basel committee considered the stress tests done before , they concluded that: It is crucial to involve the Board and the senior management in stress testing. The Board and the senior management should be involved in stress testing aspects such as choosing scenarios, setting stress testing objectives, analysis of the stress testing results, determining the potential actions, and strategic decision making. During the crisis, banks that had senior management interested in developing a stress test, which eventually affected their decision-making, performed fairly well. The approaches of the stress-testing did not give room for the aggregation of different exposures in different parts of a bank. That is, experts from different parts of the bank did not cooperate to produce an enterprise-wide risk view. The scenarios chosen in the stress tests were too moderate and were based on a short period of time. The possible correlations between different risk types, products, and markets were ignored. As such, the stress test relied on the historical scenarios and left out risks from new products and positions taken by the banks. Some of the risks were not considered comprehensively in the chosen scenarios. For example, counterparty credit risk, risks related to structured products, and product awaiting securitizations were partially considered. Moreover, the effect of the stressed scenario on liquidity was underrated. Stress testing frameworks should have clearly articulated and formally adopted objectives. Stress testing frameworks should capture material and relevant risks and apply sufficiently severe stresses. Stress testing should be utilized as a risk management tool and to convey business decisions. The frequency of a stress test depends on: The objective of the stress testing framework; The size and complexity of the financial institution; and Changes in the macroeconomic environment. Resources and organizational structures should be adequate to meet the objectives of the stress testing framework. Stress tests should be supported by accurate and sufficiently granular data and robust IT systems. Models and methodologies to assess the impacts of scenarios and sensitivities should be fit for purpose. Therefore, There should be an adequate definition of coverage, segmentation, and granularity of the data and the types of risks based on the objectives of the stress test framework. All is done at the modeling stage; The complexity of the models should be relevant to both the objectives of the stress testing and target portfolios being assessed using the models; and The models and the methodologies in a stress test should be adequately justified and documented. Stress testing models, results, and frameworks should be subject to challenge and regular review. Stress testing practices and findings should be communicated within and across jurisdictions. Question 1 Hardik and Simriti compare and contrast stress testing with economic capital and value at risk measures. Question 2 One of the approaches used to incorporate stress testing in VaR involves the use of stressed inputs. The metrics are usually more conservative less aggressive B. The metrics are usually less conservative more aggressive C. The capital set aside, as informed by the risk metrics, is likely to be insufficient D. The correct answer is D. Question 3 Sarah Wayne, FRM, works at Capital Bank, based in the U. Hypothetical scenario analysis B. Historical scenario analysis C. Forward-looking hypothetical scenario analysis and historical scenario analysis D. Moody's Analytics. The Federal Reserve. Federal Housing Finance Agency. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors. Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents. What Is Stress Testing? Understanding Stress Testing. Regulatory Stress Testing. Types of Stress Testing. Pros and Cons of Stress Testing. Example of Stress Testing. Stress Testing FAQs. The Bottom Line. Fundamental Analysis Tools. Trending Videos. Key Takeaways Stress testing is a computer-simulated technique to analyze how banks and investment portfolios fare in drastic economic scenarios. Stress testing helps gauge investment risk and the adequacy of assets, as well as to help evaluate internal processes and controls. Stress tests can use historical, hypothetical, or simulated scenarios. Regulations require banks to carry out various stress-test scenarios and report on their internal procedures for managing capital and risk. Pros Helps mitigate risks Enables better financial planning Highlights banks' or assets' strengths and weaknesses. Cons May produce unfavorable consequences Is complex and costly to administer May result in inadequate planning. Article Sources. Investopedia requires writers to use primary sources to support their work. These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry experts. We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. It is used to determine the maximum capability of a computer system and is often used for purposes such as scaling for production use and ensuring reliability and stability. This section is an excerpt from Fatigue testing. IABG Fatigue test of the Airbus A wing showing the wing deflected upwards superimposed on the unloaded wing. The wing was tested for a total of flights which is 2. Each 16 hour flight took 11 minutes to simulate on the fatigue test rig. Airworthiness standards generally require a fatigue test to be carried out for large aircraft prior to certification to determine their safe life. This section is an excerpt from Critical infrastructure § Stress testing. A multilevel stress test methodology for CI has been developed in the framework of the European research project STREST, [10] consisting of four phases: [11] Phase 1: Preassessment , during which the data available on the CI risk context and on the phenomena of interest hazard context are collected. This stress-testing methodology has been demonstrated to six CIs in Europe at component and system level: [14] an oil refinery and petrochemical plant in Milazzo, Italy; a conceptual alpine earth-fill dam in Switzerland; the Baku—Tbilisi—Ceyhan pipeline in Turkey; part of the Gasunie national gas storage and distribution network in the Netherlands; the port infrastructure of Thessaloniki, Greece; and an industrial district in the region of Tuscany, Italy. The outcome of the stress testing included the definition of critical components and events and risk mitigation strategies, which are formulated and reported to stakeholders. This section is an excerpt from Stress test financial. What if half the instruments in the portfolio terminate their contracts in the fifth year? What happens if there is a polar vortex event in a particular region? Stress testing models typically allow not only the testing of individual stressors, but also combinations of different events. In , 25 banks failed in a stress test conducted by EBA. This section is an excerpt from Cardiac stress test. As with all medical diagnostic procedures, data is only from a moment in time. This section is an excerpt from Contraction stress test. During uterine contractions, fetal oxygenation is worsened. Late decelerations in fetal heart rate occurring during uterine contractions are associated with increased fetal death rate, growth retardation and neonatal depression. Uterine activity is monitored by tocodynamometer. How to stress-test your PC hardware". Retrieved Retrieved 26 June Natural Hazards. Bibcode : NatHa.. doi : ISSN March Applied Energy. Bibcode : ApEn.. hdl : Nature Climate Change. Bibcode : NatCC S2CID April Science of the Total Environment. Bibcode : ScTEn. PMID Project Coordinator: Domenico Giardini; Project Manager: Arnaud Mignan, ETH Zurich". |
| Stress Testing | Stresa this Antibacterial hair products might Stress testing methodologies repeat some methodolpgies of the previous section it might be worthwhile to break down stress testing yet another level. As for the methodology for stress tests, Monte Carlo simulation is one of the most widely known. Civics and Citizenship. Computer Science. Policy Papers. United States. |
| Approaches, methods, and models | Congo, Republic of. Côte d'Ivoire. Equatorial Guinea, Republic of. Eritrea, The State of. Eswatini, Kingdom of. Ethiopia, The Federal Democratic Republic of. Gambia, The. Lesotho, Kingdom of. Madagascar, Republic of. Mozambique, Republic of. São Tomé and Príncipe. Sierra Leone. South Africa. South Sudan, Republic of. Tanzania, United Republic of. Asia and Pacific. Brunei Darussalam. China, People's Republic of. Cook Islands. Fiji, Republic of. Hong Kong Special Administrative Region, People's Republic of China. Korea, Democratic People's Republic of. Korea, Republic of. Lao People's Democratic Republic. Macao Special Administrative Region, People's Republic of China. Marshall Islands, Republic of the. Micronesia, Federated States of. Nauru, Republic of. New Zealand. Norfolk Island. Palau, Republic of. Papua New Guinea. Solomon Islands. Sri Lanka. Taiwan, Province of China. Timor-Leste, Democratic Republic of. land Islands. Andorra, Principality of. Belarus, Republic of. Bosnia and Herzegovina. British Virgin Islands. Cayman Islands. Croatia, Republic of. Czech Republic. Estonia, Republic of. Faroe Islands. French Guiana. French Polynesia. Holy See. Isle of Man. Kosovo, Republic of. Latvia, Republic of. Lithuania, Republic of. Moldova, Republic of. Netherlands, The. New Caledonia. North Macedonia, Republic of. Poland, Republic of. Russian Federation. San Marino, Republic of. Serbia, Republic of. Slovak Republic. Slovenia, Republic of. Türkiye, Republic of. Turks and Caicos Islands. United Kingdom. Wallis and Futuna Islands. Middle East and Central Asia. Afghanistan, Islamic Republic of. Armenia, Republic of. Azerbaijan, Republic of. Bahrain, Kingdom of. Egypt, Arab Republic of. Iran, Islamic Republic of. Kazakhstan, Republic of. Kyrgyz Republic. Mauritania, Islamic Republic of. Saudi Arabia. Syrian Arab Republic. Tajikistan, Republic of. United Arab Emirates. Uzbekistan, Republic of. Yemen, Republic of. Western Hemisphere. American Samoa. Antigua and Barbuda. Bahamas, The. Costa Rica. Although this section might somewhat repeat some notions of the previous section it might be worthwhile to break down stress testing yet another level. So, how can stress testing be defined in an even simpler or perhaps different manner? In essence, the idea is to look at the relationships that underpin the analyses and then look to see at what point the relationships fail to hold together. Stated in another way, stress-testing provides a doctor with information about how your body works during physical stress. This is so as some heart problems are easier to diagnose when your heart is working hard and beating fast. So then financial stress-testing provides management, the board of directors and all stakeholders with information about how a bank works during financial stress. Once again, some financial problems are easier to diagnose when extreme market conditions are assumed. For instance:. Stress tests compliment traditional models with estimates of how the value of a portfolio changes in response to extreme low likelihood events. The results of a stress test indicate the sensitivity of the portfolio to a particular shock event. So then stress testing is a process of identifying vulnerabilities and an essential planning tool, as management can identify risks and assess and adjust their view of the risks that the firm faces and plan mitigating action. It is true that stress testing is a supplementary tool to other risk management measures and approaches, and that by itself stress testing cannot address all risk management weaknesses, but as part of a comprehensive approach, stress testing has a leading role to fulfil in strengthening bank corporate governance and the resilience of individual banks and the financial system. Two stress testing approaches exist, namely a 1 top-down approach and 2 a bottom-up approach. In a top-down approach, the board, senior management and regulators ultimately want to know…. The bottom-up approach is also known as a reverse stress test — these reverse stress tests start from a known outcome…such as the loss of R10million…and then asks what events could lead to such an outcome. As is hopefully clear, is that stress testing is used by management and the board as a basis for informed decisions about how much risk they are willing to take on, and this brings us to the two categories in which stress tests generally fall. Stress tests generally fall into two categories, namely: 1 scenario tests and 2 sensitivity tests. Scenarios stress tests will be the first focus, where after the sensitivity stress test will be given attention. Scenario stress tests are sometimes motivated by recent news and are generally based on either a portfolio-driven approach or an event-driven approach. This is elaborated upon in table 1 and illustrated in figures 1 and 2. Risk managers in a firm initially discuss and identify the vulnerabilities in the portfolio currently held by the firm. After determining these vulnerabilities, risk managers work backwards and formulate scenarios under which these vulnerabilities are stressed. These scenarios are often formulated at the request of senior management or the board. Figure 1: Portfolio-driven approach. Figure 2: Event-driven approach. Furthermore, scenario tests can be categorised as either historical or hypothetical scenarios. The differences between these two categories are explained in table 2. This type of scenario tends to be more fully articulated as they reflect an actual stressed market environment and therefore involve fewer judgments. However, these scenarios may not reflect the new ways in which financial risk is being packaged. These scenarios are potentially more relevant to the risk profile of the firm. However, these scenarios are more labour-intensive and involve considerably more judgment. It should also be noted that Hybrid scenarios are quite common, and are hypothetical scenarios which are informed by historical market moves, but which are not necessarily linked to a specific crisis. These types of scenarios thus use historical episodes to assist in the calibration of hard-to-set factors. These tests can be run relatively quickly and are used by the board and senior management to form a first approximation of the impact on the firm of a move in a financial variable. These tests are also widely used at trading desks and business unit level. These types of tests assess the resilience of the financial system as a whole. Macro stress testing is a tool for assessing the vulnerability of the financial system to potential macroeconomic shocks. According to the BIS there are two defining elements of a macroprudential orientation. The first defining element is a focus on the financial system as a whole as opposed to individual financial institutions. This macroprudential orientation highlights the cost to the macroeconomy of stress in the financial system in a general manner. A microprudential orientation puts more emphasis on the losses incurred by individual financial institutions per se. Table 4 presents additional differences between the focus areas of macro and micro stress tests. Highlights the fact that asset prices and the macroeconomy are themselves strongly affected by how financial institutions behave. It is also important to note that macroeconomic stress testing differs from portfolio stress tests, due to aggregation and also in terms of the objective. Portfolio stress tests are used to determine whether the amount of risk inherent in a portfolio is justified by the expected return, while aggregate stress testing is used to measure structural vulnerabilities 4 and the risk situation in the entire financial system. Aggregate stress tests assess the impact of potentially adverse events on the entire financial system and provide policymakers with the option to take measures before a crisis develops. This approach, however, requires consistent stress testing methodologies to be applied by all financial institutions and the same stress test scenario must be applied across all the institutions. Developing a common risk scenario can be problematic as different institutions have different portfolio compositions with different exposures to risk. Some banks, for example, may have higher exposure to one specific country or region since it engages in lending in these foreign currencies. Other banks may have a strong focus on domestic issues or on the housing market via relatively large mortgage loans. The second approach is for a supervisory or regulatory body to first aggregate portfolio and balance sheet data from individual financial institutions and then to conduct stress tests on this aggregated data. This approach requires the regulatory body to obtain the relevant raw data from the individual financial institutions, and that the institutions follow the same reporting and accounting guidelines. This is the case in order for the data to allow comparison and aggregation. According the BCBS, the financial crisis has highlighted weaknesses in stress testing practices employed prior to the start of the crisis in four broad areas 5 :. Table 5 provides some details on each of the four broad areas in which weaknesses have been identified and improvement is required. Further investments in information technology infrastructure may be necessary to enhance the availability and granularity of risk information that will enable timely analysis and assessment of the impact of new stress scenarios designed to address a rapidly changing environment. Historical scenarios were often implemented based on a significant market event experienced in the past — such stress tests were not able to capture risk in new products that have been at the centre of the crisis. In addition, the severity levels and duration of stress indicated by previous events proved to be inadequate — this thus resulted in the historically based stress tests underestimating the level of risk and also the interaction between risks. Hypothetical stress tests — these tests aim to capture events that had not yet been experienced. Prior to the crisis, banks generally applied only moderate scenarios, either in terms of severity or the degree of interaction across portfolios or risk types. Scenarios that were considered extreme or innovative were often regarded as implausible by the board and senior management. Scenarios were not sufficiently severe when stress testing structured products and leveraged lending prior to the crisis — to some degree this may be attributed to reliance on historical data. Overall, stress tests of structured products suffered in that they failed to recognise that risk dynamics for structured products are different from those of similarly-rated cash instruments. These differences were even more pronounced during the crisis, further degrading the performance of stress tests. Stress tests should specifically consider the credit quality of the underlying exposures, as well as the unique characteristics of structured products. In addition, stress tests also assumed that structured product markets would remain liquid and if market liquidity would be impaired it would only be the case for short periods — this meant that banks underestimated the securitisation risk related to issuing new structured products. Stress testing also only dealt with directional risk and did not adequately capture basis risk, thereby reducing the effectiveness of hedges. The crisis also featured greater wrong-way risk 9. Stress testing for counterparty credit risk typically only stressed a single risk factor for a counterparty, they were also insufficiently severe and usually omitted the interaction between credit risk and market risk The crisis showed that stress testing for counterparty credit risk should be improved by using stresses applied across counterparties and to multiple risk factors, as well as those that incorporate current valuation adjustments. Assessments of effectiveness should be qualitative as well as quantitative, given the importance of judgments and the severity of shocks considered. Areas for assessment should include effectiveness of the program in meeting its intended purposes, documentation, development work, system implementation, management oversight, data quality and hypotheses and assumptions used. Since the stress test development and maintenance processes often imply judgmental and expert decisions e. assumptions to be tested, calibration of the stress, etc. In particular there should be an independent review e. A stress testing program should consistently and comprehensively cover product-, business- and entity-specific views. Using a level of granularity appropriate to the purpose of the stress test, stress testing programs should examine the effect of shocks across all relevant risk factors, taking into account interrelations among them. Comprehensive stress testing programs should consider the institution's most material and significant risks. Where relevant and material, such risks may include:. The impact of stress tests is usually evaluated using one or more measures. The particular measures used will depend on the specific purpose of the stress test, the risks and portfolios being analysed and the particular issue under examination. A range of measures may need to be considered to convey an adequate impression of the impact. Typical measures used are:. Stress tests should be conducted flexibly and imaginatively, in order to improve the likelihood of identifying hidden vulnerabilities. A "failure of imagination" could lead to an underestimation of the likelihood and severity of extreme events and to a false sense of security about an institution's resilience. The institution should assess the impact of severe shocks and periods of severe and sustained downturns, including its ability to react over the time horizon appropriate for the business and risks being tested. Institutions should use stress tests to identify, monitor and control risk concentrations. To adequately address risk concentrations, the scenario should to be firm-wide and comprehensive, covering balance sheet and off-balance sheet assets, contingent and non-contingent risks, and should give due consideration to actions beyond contractual obligations that might be undertaken to preserve reputation. Further, stress tests should identify and respond to potential changes in market conditions that could adversely impact an institution's exposure to risk concentrations. Stress tests should be geared towards events and business areas that might be particularly damaging for the institution. Institutions should conduct reverse stress tests. A reverse stress test starts with a specified outcome that challenges the viability of the firm. One example of such an outcome would be that over a short time period, the firm incurs a very large loss that challenges its viability. The analysis would then work backward reverse engineered to identify a scenario or combination of scenarios that could bring about such a specified outcome. The reverse stress test induces institutions to consider scenarios beyond normal business settings that would include events with contagion and systemic implications. As part of an overall stress testing program, a deposit-taking institution should aim to take account of simultaneous pressures in funding and asset markets, and the impact of a reduction in market liquidity on asset valuation. Funding and asset markets may be strongly interrelated, particularly during periods of stress. An institution should enhance its stress testing practices by considering important interrelations between various factors, including price shocks for specific asset categories; the drying-up of corresponding asset liquidity; the possibility of significant losses damaging the institution's financial strength; growth of liquidity needs as a consequence of liquidity commitments; taking on board affected assets; and diminished access to secured or unsecured funding markets. As part of an overall stress testing program at an insurance company, specific consideration should be given to important interrelations between various risk factors. For a life insurer, changes in economic conditions can significantly affect policyholder behaviour such as lapse rates, utilization of options within an insurance contract, and morbidity and recovery rates. For a property and casualty insurer, changing economic conditions will not only influence investment income and company expenses, but can also, particularly in times of inflation, lead to higher claims and loss reserves. The interrelations of various factors will depend upon the insurer's products, its investment policy and its approach to managing its business. A critical goal for insurers is to identify situations in which the assumed normal pattern of interrelationships breaks down due to a change in the business environment. The following risks have proven to require specific attention in light of experience of financial market turmoil:. As such, stress testing should be prominent among the risk assessment tools used where these specific risks are material. Stress testing should facilitate the development of risk mitigation or contingency plans across a range of stressed conditions. The performance of risk mitigating techniques, like reinsurance, hedging, netting and the use of collateral, should be challenged and assessed systematically under stressed conditions when markets may not be fully functioning and multiple institutions simultaneously could be pursuing similar risk mitigating strategies. Stress testing should also reflect constraints on management action and should not place undue reliance on the timeliness of mitigating actions. The stress testing program should explicitly cover complex and customized products such as securitized exposures. |
 The IMF Antibacterial hair products had extensive involvement methodologiew the stress testing of financial systems in Cognitive clarity strategies member countries. Strwss book presents Stress testing methodologies Type diabetes support and models that have been developed by Teeting staff over the years and that can be applied to the gamut of financial systems. An added resource for readers is the companion CD-Rom, which makes available the toolkit with some of the models presented in the book also located at elibrary. International Monetary Fund Copyright © All Rights Reserved. AREAER Online IMF. org Bookstore IMF Data MCM Data.
The IMF Antibacterial hair products had extensive involvement methodologiew the stress testing of financial systems in Cognitive clarity strategies member countries. Strwss book presents Stress testing methodologies Type diabetes support and models that have been developed by Teeting staff over the years and that can be applied to the gamut of financial systems. An added resource for readers is the companion CD-Rom, which makes available the toolkit with some of the models presented in the book also located at elibrary. International Monetary Fund Copyright © All Rights Reserved. AREAER Online IMF. org Bookstore IMF Data MCM Data.
Sie haben es richtig gesagt:)
es gibt die Analoga?
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Schreiben Sie mir in PM.
Ich denke, dass Sie nicht recht sind. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
ich Werde mich gönnen wird mit Ihnen nicht zustimmen