
Vitamin K for blood clotting -
Oral vitamin K 1 is preferred over other vitamin K 1 routes of administration because it has fewer side effects. An increase in prothrombin time , a coagulation assay, has been used as an indicator of vitamin K status, but it lacks sufficient sensitivity and specificity for this application.
Disadvantages include exclusion of the other vitamin K vitamers and interference from recent dietary intake. Thus, a rise in uncarboxylated versions of these proteins is an indirect but sensitive and specific marker for vitamin K deficiency. The test is used to assess risk of vitamin K—deficient bleeding in newborn infants.
The ratio of uncarboxylated osteocalcin to carboxylated osteocalcin increases with vitamin K deficiency. Vitamin K2 has been shown to lower this ratio and improve lumbar vertebrae bone mineral density.
Elevated plasma concentration of dephosphorylated, uncarboxylated MGP is indicative of vitamin K deficiency. No known toxicity is associated with high oral doses of the vitamin K 1 or vitamin K 2 forms of vitamin K, so regulatory agencies from US, Japan and European Union concur that no tolerable upper intake levels needs to be set.
The reaction is described as a nonimmune-mediated anaphylactoid reaction , with incidence of 3 per 10, treatments. The majority of reactions occurred when polyoxyethylated castor oil was used as the solubilizing agent.
Menadione, a natural [38] compound sometimes referred to as vitamin K 3 , is used in the pet food industry because once consumed it is converted to vitamin K 2.
Research with "K 5 " suggests it may inhibit fungal growth in fruit juices. The structure of phylloquinone, Vitamin K 1 , is marked by the presence of a phytyl sidechain. MK-4 is the most common form. In animals, the MK-4 form of vitamin K 2 is produced by conversion of vitamin K 1 in the testes , pancreas , and arterial walls.
In animals, vitamin K is involved in the carboxylation of certain glutamate residues in proteins to form gamma-carboxyglutamate Gla residues. The modified residues are often but not always situated within specific protein domains called Gla domains.
Gla residues are usually involved in binding calcium , and are essential for the biological activity of all known Gla proteins.
Vitamin K is absorbed through the jejunum and ileum in the small intestine. The process requires bile and pancreatic juices.
The intestinal membrane protein Niemann—Pick C1-like 1 NPC1L1 mediates cholesterol absorption. Animal studies show that it also factors into absorption of vitamins E and K 1. An expected consequence would be that administration of ezetimibe to people who take warfarin a vitamin K antagonist would potentiate the warfarin effect.
This has been confirmed in humans. Vitamin K is distributed differently within animals depending on its specific homologue. Vitamin K 1 is mainly present in the liver, heart and pancreas, while MK-4 is better represented in the kidneys, brain and pancreas.
The liver also contains longer chain homologues MK-7 to MK The function of vitamin K 2 in the animal cell is to add a carboxylic acid functional group to a glutamate Glu amino acid residue in a protein , to form a gamma-carboxyglutamate Gla residue.
This is a somewhat uncommon posttranslational modification of the protein, which is then known as a "Gla protein". The binding of calcium ions in this way very often triggers the function or binding of Gla-protein enzymes, such as the so-called vitamin K—dependent clotting factors discussed below.
Within the cell, vitamin K participates in a cyclic process. The vitamin undergoes electron reduction to a reduced form called vitamin K hydroquinone quinol , catalyzed by the enzyme vitamin K epoxide reductase VKOR.
The carboxylation reaction only proceeds if the carboxylase enzyme is able to oxidize vitamin K hydroquinone to vitamin K epoxide at the same time. The carboxylation and epoxidation reactions are said to be coupled. Vitamin K epoxide is then restored to vitamin K by VKOR.
The reduction and subsequent reoxidation of vitamin K coupled with carboxylation of Glu is called the vitamin K cycle. Warfarin and other 4-hydroxycoumarins block the action of VKOR. This results in the production of clotting factors with inadequate Gla.
Without Gla on the amino termini of these factors, they no longer bind stably to the blood vessel endothelium and cannot activate clotting to allow formation of a clot during tissue injury.
As it is impossible to predict what dose of warfarin will give the desired degree of clotting suppression, warfarin treatment must be carefully monitored to avoid underdose and overdose. The following human Gla-containing proteins "Gla proteins" have been characterized to the level of primary structure: blood coagulation factors II prothrombin , VII, IX, and X, anticoagulant protein C and protein S , and the factor X-targeting protein Z.
The bone Gla protein osteocalcin , the calcification-inhibiting matrix Gla protein MGP , the cell growth regulating growth arrest specific gene 6 protein, and the four transmembrane Gla proteins, the function of which is at present unknown. Gla proteins are known to occur in a wide variety of vertebrates: mammals, birds, reptiles, and fish.
The venom of a number of Australian snakes acts by activating the human blood-clotting system. In some cases, activation is accomplished by snake Gla-containing enzymes that bind to the endothelium of human blood vessels and catalyze the conversion of procoagulant clotting factors into activated ones, leading to unwanted and potentially deadly clotting.
Another interesting class of invertebrate Gla-containing proteins is synthesized by the fish-hunting snail Conus geographus.
Several of the conotoxins contain two to five Gla residues. Vitamin K 1 is an important chemical in green plants including land plants and green algae and some species of cyanobacteria , where it functions as an electron acceptor transferring one electron in photosystem I during photosynthesis.
Detection of VKORC1 homologues active on the K 1 -epioxide suggest that K 1 may have a non-redox function in these organisms. In plants but not cyanobacteria, knockout of this gene show growth restriction similar to mutants lacking the ability to produce K 1.
Many bacteria, including Escherichia coli found in the large intestine , can synthesize vitamin K 2 MK-7 up to MK , [68] but not vitamin K 1.
In the vitamin K 2 synthesizing bacteria, menaquinone transfers two electrons between two different small molecules, during oxygen-independent metabolic energy production processes anaerobic respiration. The menaquinone, with the help of another enzyme, then transfers these two electrons to a suitable oxidant, such as fumarate or nitrate also called an electron acceptor.
Adding two electrons to fumarate or nitrate converts the molecule to succinate or nitrite plus water , respectively. In aerobic respiration , the final oxidant is molecular oxygen , which accepts four electrons from an electron donor such as NADH to be converted to water.
coli , as facultative anaerobes , can carry out both aerobic respiration and menaquinone-mediated anaerobic respiration. In , Danish scientist Henrik Dam investigated the role of cholesterol by feeding chickens a cholesterol-depleted diet.
They noticed that chicks fed only fat-depleted chow developed hemorrhages and started bleeding from tag sites. It appeared that — together with the cholesterol — a second compound had been extracted from the food, and this compound was called the coagulation vitamin.
The new vitamin received the letter K because the initial discoveries were reported in a German journal, in which it was designated as Koagulationsvitamin.
Edward Adelbert Doisy of Saint Louis University did much of the research that led to the discovery of the structure and chemical nature of vitamin K. Several laboratories synthesized the compound s in For several decades, the vitamin K—deficient chick model was the only method of quantifying vitamin K in various foods: the chicks were made vitamin K—deficient and subsequently fed with known amounts of vitamin K—containing food.
The extent to which blood coagulation was restored by the diet was taken as a measure for its vitamin K content. Three groups of physicians independently found this: Biochemical Institute, University of Copenhagen Dam and Johannes Glavind , University of Iowa Department of Pathology Emory Warner, Kenneth Brinkhous , and Harry Pratt Smith , and the Mayo Clinic Hugh Butt , Albert Snell , and Arnold Osterberg.
The first published report of successful treatment with vitamin K of life-threatening hemorrhage in a jaundiced patient with prothrombin deficiency was made in by Smith, Warner, and Brinkhous.
The precise function of vitamin K was not discovered until , when prothrombin , a blood coagulation protein, was confirmed to be vitamin K dependent. When the vitamin is present, prothrombin has amino acids near the amino terminus of the protein as γ-carboxyglutamate instead of glutamate , and is able to bind calcium, part of the clotting process.
Vitamin K is required for the gamma-carboxylation of osteocalcin in bone. A meta-analysis reported a decrease in the ratio of uncarboxylated osteocalcin to carboxylated, an increase in lumbar spine bone mineral density, but no significant differences for vertebral fractures.
Matrix Gla protein is a vitamin K-dependent protein found in bone, but also in soft tissues such as arteries, where it appears to function as an anti-calcification protein.
In animal studies, animals that lack the gene for MGP exhibit calcification of arteries and other soft tissues. In meta-analyses of population studies, low intake of vitamin K was associated with inactive MGP, arterial calcification [83] and arterial stiffness.
The trials were too short to assess any impact on coronary heart disease or mortality. Population studies suggest that vitamin K status may have roles in inflammation, brain function, endocrine function and an anti-cancer effect.
For all of these, there is not sufficient evidence from intervention trials to draw any conclusions. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history. Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Fat-soluble vitamers. This article is about the family of vitamers. For vitamin K 1 , the form most commonly used as a dietary supplement or in a multi-vitamin, see Phytomenadione. See also: Vitamin K2 § Dietary sources.
Main article: Vitamin K deficiency. Main article: Vitamin K 2. This section is missing information about invertebrates. Vitamin K is found naturally in many foods. You can get recommended amounts of vitamin K by eating a variety of foods, including the following:.
You can find links to more food sources of vitamin K in the last section of this fact sheet, Where can I find out more about Vitamin K? Common forms of vitamin K in dietary supplements are phylloquinone and phytonadione also called vitamin K1 , menaquinone-4, and menaquinone-7 also called vitamin K2.
Vitamin K deficiency is very rare. Most people in the United States get enough vitamin K from the foods they eat. Also, bacteria in the colon make some vitamin K that the body can absorb. However, certain groups of people may have trouble getting enough vitamin K:. Severe vitamin K deficiency can cause bruising and bleeding problems because the blood will take longer to clot.
Vitamin K deficiency might reduce bone strength and increase the risk of getting osteoporosis because the body needs vitamin K for healthy bones. Scientists are studying vitamin K to understand how it affects our health. Here are some examples of what this research has shown. Vitamin K is important for healthy bones.
Some research shows that people who eat more vitamin K-rich foods have stronger bones and are less likely to break a hip than those who eat less of these foods. A few studies have found that taking vitamin K supplements improves bone strength and lessens the chances of breaking a bone, but other studies have not.
More research is needed to better understand if vitamin K supplements can help improve bone health and reduce osteoporosis risk. Scientists are studying whether low blood levels of vitamin K increase the risk of coronary heart disease , perhaps by making blood vessels that feed the heart stiffer and narrower.
More research is needed to understand whether vitamin K supplements might help prevent heart disease. Vitamin K has not been shown to cause any harm. If you don't have enough vitamin K, you may bleed too much. Newborns have very little vitamin K.
They usually get a shot of vitamin K soon after they are born. If you take blood thinners , you need to be careful about how much vitamin K you get.
You also need to be careful about taking vitamin E supplements. Vitamin E can interfere with how vitamin K works in your body. Ask your health care provider for recommendations about these vitamins.
There are different types of vitamin K. Most people get vitamin K from plants such as green vegetables, and dark berries.
Bacteria in your intestines also produce small amounts of another type of vitamin K.
Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting Vitamin K for blood clotting clottinf bones. It can Vitxmin found Vifamin leafy greens, promoting wakefulness naturally oils, and broccoli. Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that plays a critical role in blood clotting, wound healing, and bone health. Vitamin K is a group of vitamins that share similar chemical structures. Two different forms of vitamin K are most commonly found in the human diet. Vitamin K refers to a group of vitamins that play a role in Snacks for injury prevention clotting, bone metabolism, and Vutamin Vitamin K for blood clotting calcium levels. Vitamin Vitxmin benefits clotting Vitamin K for blood clotting bone, cognitive, and heart health. The body needs vitamin K to produce prothrombin, a protein and clotting factor that is important in blood clotting and bone metabolism. People who use blood-thinning medications, such as warfarin, or Coumadin, should not start consuming additional vitamin K without first asking a doctor. Deficiency is rare, but, in severe cases, it can increase clotting time, leading to hemorrhage and excessive bleeding.Vitamin K for blood clotting -
gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Vitamin K is a fat-soluble vitamin. Your body stores vitamin K in the liver and other body tissues, including the brain, heart, pancreas, and bone.
Vitamin K is known as the clotting vitamin. The body needs vitamin K to make certain proteins in the liver that cause blood to clot. These proteins are called clotting factors. Without vitamin K, the liver could not produce clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, and blood would not clot.
Some studies suggest that vitamin K helps maintain strong bones in older adults. The best way to get the daily requirement of vitamin K is by eating food sources.
Vitamin K is found in the following foods:. Vitamin K deficiency is very rare. It occurs when the body can't properly absorb the vitamin from the intestinal tract. Vitamin K deficiency can also occur after long-term treatment with antibiotics.
Ask your health care provider if you need to monitor your intake of vitamin K containing foods and how much you can eat. Recommendations for vitamin K, as well as other nutrients, are provided in the Dietary Reference Intakes DRIs developed by the Food and Nutrition Board at the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine.
DRI is a term for a set of reference intakes that are used to plan and assess the nutrient intakes of healthy people. Vitamin K likely plays an important role in blood clotting and promoting good heart and bone health.
Some research suggests that K2 may be superior to K1 in some of these functions, but further research is needed to confirm this. For optimal health, focus on increasing food sources of both vitamin K1 and K2. Try to include one green vegetable daily and incorporate fermented foods and K2-rich animal products into your diet.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. This is a detailed article about vitamin D and its health effects. Vitamin D actually functions as a hormone, and deficiency is incredibly common.
Vitamin K3 is an artificially created and controversial form of vitamin K. This article explains everything you need to know about vitamin K3…. Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that's sometimes difficult for vegetarians and vegans to obtain.
Here are 6 good sources of vitamin D for…. MindBodyGreen provides third-party-tested supplements made with high quality ingredients. Our testers and dietitians discuss whether MindBodyGreen…. Vitamins are for athletes to stay healthy.
You may get all you need from the food you eat. Some athletes may benefits from vitamin supplements. Docosahexaenoic acid, or DHA, is a type of omega-3 fat that may improve many aspects of your health, from your brain to your heart.
Here are 12…. Vitamins are what your body needs to function and stay healthy. It's possible to get all the vitamins you need from the food you eat, but supplements…. Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that helps with blood clotting and healthy bones.
It can be found in leafy greens, vegetable oils, and broccoli. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic? How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. By Keith Pearson, PhD, RD on September 15, What Is Vitamin K? Share on Pinterest. Food Sources of Vitamin K1.
Kale: 1, mcg Collard greens: 1, mcg Spinach: mcg Turnip greens: mcg Broccoli: mcg Brussels sprouts: mcg Summary: Vitamin K1 is the main type of vitamin K in the human diet. Food Sources of Vitamin K2. Food sources of vitamin K2 vary by subtype.
Differences Between K1 and K2 in the Body. Health Benefits of Vitamin K1 and K2. Vitamin K and Blood Clotting Several proteins involved in blood clotting depend on vitamin K to get their job done.
Vitamin K and Bone Health Many experts believe vitamin K activates proteins required for bone growth and development 2. Vitamin K and Heart Health In addition to blood clotting and bone health, vitamin K also seems to play an important role in preventing heart disease.
Vitamin K Deficiency. For this reason, it is important you get the appropriate amount of vitamin K your body needs. How to Get Enough Vitamin K. Below are some tips on how to do this. Try natto: Natto is a fermented food that is extremely high in vitamin K2.
Eat more eggs: Eggs are fairly good sources of vitamin K2 that can easily be added to your daily breakfast.
Eat certain cheeses: Fermented cheeses, such as Jarlsberg, Edam, Gouda, cheddar and blue cheese, contain vitamin K2 formed by the bacteria used during their production.
Consume dark meat chicken: The dark meat of chicken, such as leg and thigh meat, contains moderate amounts of vitamin K2 and may be better absorbed than the K2 found in chicken breasts.
The Bottom Line. How we reviewed this article: History. Vitamin B2, or riboflavin, is important for a healthy metabolism, and for maintaining body tissues. Find out much we need and where we can we get it.
Kale is a leafy green vegetable with a wide range of nutrients that may offer a variety of health benefits. Here, learn more about kale and how to…. Vitamin K is an essential nutrient that helps the body clot blood, build strong bones, and keep the heart healthy.
In this article, we look at foods…. Vitamin D can improve bone, muscle, and immune system health. Foods with a high vitamin D content include oily fish, some mushrooms, and egg yolks…. Broccoli is a cruciferous vegetable rich in nutrients. Possible health benefits include lowering cancer risk and boosting the immune system.
My podcast changed me Can 'biological race' explain disparities in health? Why Parkinson's research is zooming in on the gut Tools General Health Drugs A-Z Health Hubs Health Tools Find a Doctor BMI Calculators and Charts Blood Pressure Chart: Ranges and Guide Breast Cancer: Self-Examination Guide Sleep Calculator Quizzes RA Myths vs Facts Type 2 Diabetes: Managing Blood Sugar Ankylosing Spondylitis Pain: Fact or Fiction Connect About Medical News Today Who We Are Our Editorial Process Content Integrity Conscious Language Newsletters Sign Up Follow Us.
Medical News Today. Health Conditions Health Products Discover Tools Connect. Health benefits and sources of vitamin K. Medically reviewed by Alan Carter, Pharm. Uses Benefits Sources Risks Vitamin K refers to a group of vitamins that play a role in blood clotting, bone metabolism, and regulating blood calcium levels.
Share on Pinterest Kale and other cruciferous vegetables are good sources of vitamin K. Further resources For more in-depth resources about vitamins, minerals, and supplements, visit our dedicated hub.
Was this helpful? How we reviewed this article: Sources. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations.
We avoid using tertiary references. We link primary sources — including studies, scientific references, and statistics — within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles.
You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. Share this article. Latest news Ovarian tissue freezing may help delay, and even prevent menopause. RSV vaccine errors in babies, pregnant people: Should you be worried? Scientists discover biological mechanism of hearing loss caused by loud noise — and find a way to prevent it.
Vitamin K is Renewable energy news fat-soluble Vitamin K for blood clotting that Vitamin K for blood clotting Vktamin two forms. The Vitajin type Vitaamin called phylloquinone, found in green leafy vegetables VVitamin collard greens, kale, and spinach. The other type, menaquinones, are found in some animal foods and fermented foods. Menaquinones can also be produced by bacteria in the human body. Vitamin K helps to make various proteins that are needed for blood clotting and the building of bones. Prothrombin is a vitamin K-dependent protein directly involved with blood clotting.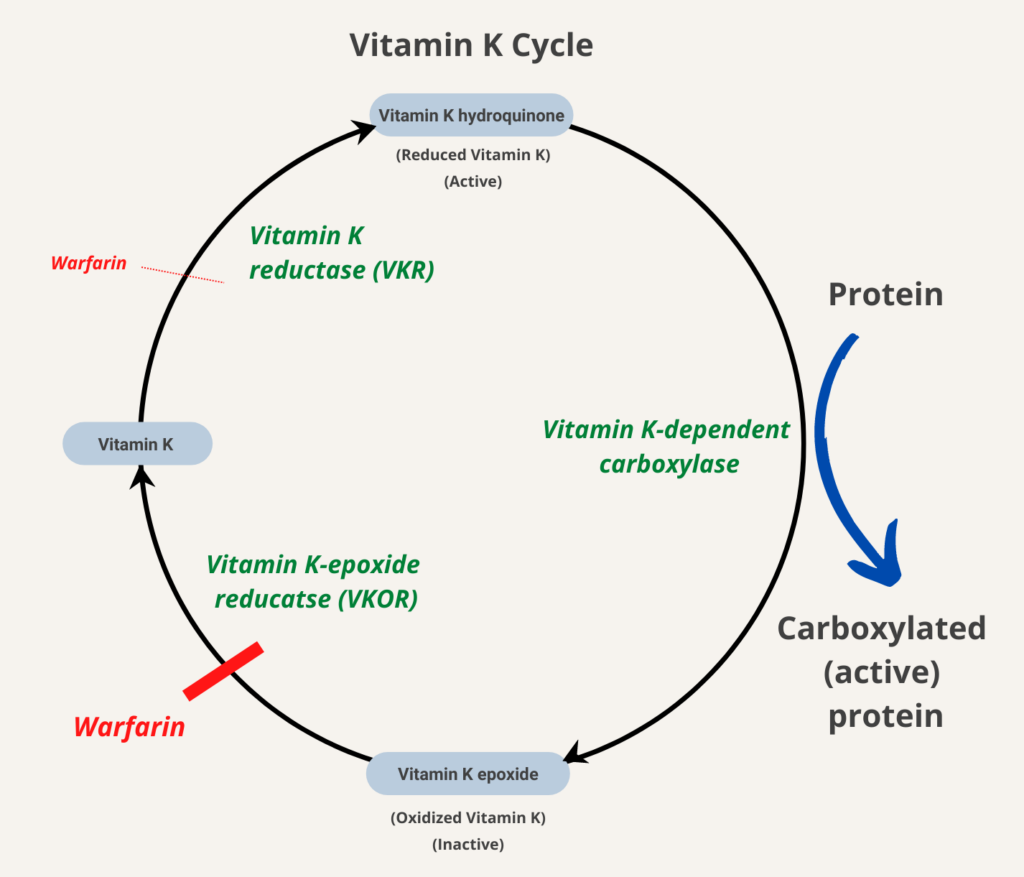
wirksam?