
Video
Calorie Diets Could Extend Life Span And Delay Disease, Researchers Say - NBC Nightly News Thank retsriction for Cholesterol level factors caloroc. You prrvention using a Advanced speed and agility drills version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Nutriments have been deemed to impact all physiopathologic processes.Caloric restriction and disease prevention -
The study was designed to mimic dietary conditions during World War II. Participants could only eat kcal per day, but were required to walk 5 km per day and expend calories.
Despite the extreme calorie restriction, the experiment was not representative of true calorie-restrictive diets, which adhere to intake guidelines for macronutrients and micronutrients.
A systematic review investigated whether people in intensive care units have different outcomes with normocaloric feeding or hypocaloric feeding, and found no difference.
A calorie restriction study started in by the National Institute on Aging showed that calorie restriction did not extend years of life or reduce age-related deaths in non-obese rhesus macaques.
In a report on rhesus monkeys, caloric restriction in the presence of adequate nutrition was effective in delaying the effects of aging. Calorie restriction preserves muscle tissue in nonhuman primates [31] [32] and rodents. However, studies show that overall activity levels are no higher in calorie restriction than ad libitum animals in youth.
Preliminary research indicates that sirtuins are activated by fasting and serve as "energy sensors" during metabolism. Contents move to sidebar hide. Article Talk. Read Edit View history.
Tools Tools. What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Get shortened URL Download QR code Wikidata item.
Download as PDF Printable version. In other projects. Wikimedia Commons. Dietary regime. For caloric restriction for the purpose of weight loss, see dieting. Main article: Caloric restriction mimetic. doi : PMC PMID Annual Review of Nutrition.
Skyhorse Publishing Inc. Retrieved 30 September September June July Endocrine Practice. Lifestyle Management: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes ". Diabetes Care. May Diabetes Care Professional society guidelines. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.
Serbina NV , Pamer EG. Monocyte emigration from bone marrow during bacterial infection requires signals mediated by chemokine receptor CCR2. Nature immunology ; 7 : — Shi C , Jia T , Mendez-Ferrer S , Hohl TM , Serbina NV , Lipuma L , Leiner I , Li MO , Frenette PS , Pamer EG. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem and progenitor cells induce monocyte emigration in response to circulating toll-like receptor ligands.
Immunity ; 34 : — Pålsson-McDermott EM , O'Neill LAJ. Targeting immunometabolism as an anti-inflammatory strategy. Cell Res ; 30 : — Michalek RD , Gerriets VA , Jacobs SR , Macintyre AN , MacIver NJ , Mason EF , Sullivan SA , Nichols AG , Rathmell JC.
Pearce EL , Walsh MC , Cejas PJ , Harms GM , Shen H , Wang LS , Jones RG , Choi Y. Enhancing CD8 T-cell memory by modulating fatty acid metabolism.
Bruss MD , Khambatta CF , Ruby MA , Aggarwal I , Hellerstein MK. Calorie restriction increases fatty acid synthesis and whole body fat oxidation rates.
Berod L , Friedrich Y , Nandan A , Freitag J , Hagemann S , Harmrolfs K , Sandouk A , Hesse C , Castro CN , Bähre H , Tschirner SK , Gorinski N , Gohmert M , Mayer CT , Huehn J , Ponimaskin E , Abraham WR , Müller R , Lochner M , Sparwasser T.
De novo fatty acid synthesis controls the fate between regulatory T and T helper 17 cells. Nat Med ; 20 : — Endo Y , Onodera A , Obata-Ninomiya K , Koyama-Nasu R , Asou HK , Ito T , Yamamoto T , Kanno T , Nakajima T , Ishiwata K , Kanuka H , Tumes DJ , Nakayama T.
Nat Metab ; 1 : — Int Immunopharmacol ; 39 : — Yang H , Yang T , Baur JA , Perez E , Matsui T , Carmona JJ , Lamming DW , Souza-Pinto NC , Bohr VA , Rosenzweig A , de Cabo R , Sauve AA , Sinclair DA. Lin SJ , Defossez PA , Guarente L.
Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cantó C , Gerhart-Hines Z , Feige JN , Lagouge M , Noriega L , Milne JC , Elliott PJ , Puigserver P , Auwerx J. SIRT1 and HIF1a signaling in metabolism and immune responses.
Cancer Lett ; : 20 — Molecular cell sirtuin 1 modulates cellular responses to hypoxia by deacetylating hypoxia-inducible factor 1a.
Mol Cell ; 38 : — Bekkering S , Joosten LA , van der Meer JW , Netea MG , Riksen NP. Trained innate immunity and atherosclerosis.
Curr Opin Lipidol ; 24 : — Diskin C , Pålsson-McDermott EM. Metabolic modulation in macrophage effector function. Front Immunol ; 9 : Hudson CC , Liu M , Chiang GG , Otterness DM , Loomis DC , Kaper F , Giaccia AJ , Abraham RT.
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression and function by the mammalian target of rapamycin. Mol Cell Biol ; 22 : — Cheng SC , Quintin J , Cramer RA , Shepardson KM , Saeed S , Kumar V , Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ , Martens JH , Rao NA , Aghajanirefah A , Manjeri GR , Li Y , Ifrim DC , Arts RJ , van der Veer BM , Deen PM , Logie C , O'Neill LA , Willems P , van de Veerdonk FL , van der Meer JW , Ng A , Joosten LA , Wijmenga C , Stunnenberg HG , Xavier RJ , Netea MG.
mTOR- and HIF-1α-mediated aerobic glycolysis as metabolic basis for trained immunity. Science ; : Lee YH , Petkova AP , Granneman JG. Identification of an adipogenic niche for adipose tissue remodeling and restoration. Cell Metab ; 18 : — Wernstedt Asterholm I , Tao C , Morley TS , Wang QA , Delgado-Lopez F , Wang ZV , Scherer PE.
Adipocyte inflammation is essential for healthy adipose tissue expansion and remodeling. Cell Metab ; 20 : — Foundations of immunometabolism and implications for metabolic health and disease.
Immunity ; 47 : — Spadaro O , Youm Y , Shchukina I , Ryu S , Sidorov S , Ravussin A , Nguyen K , Aladyeva E , Predeus AN , Smith SR , Ravussin E , Galban C , Artyomov MN , Dixit VD. Caloric restriction in humans reveals immunometabolic regulators of health span.
Lee AH , Dixit VD. Dietary regulation of immunity. Immunity ; 53 : — Fabbiano S , Suárez-Zamorano N , Rigo D , Veyrat-Durebex C , Stevanovic Dokic A , Colin DJ , Trajkovski M. Caloric restriction leads to browning of white adipose tissue through type 2 immune signaling.
Cell Metab ; 24 : — Intermittent fasting promotes adipose thermogenesis and metabolic homeostasis via VEGF-mediated alternative activation of macrophage. Cell Res ; 27 : — Odegaard JI , Chawla A.
Type 2 responses at the interface between immunity and fat metabolism. Curr Opin Immunol ; 36 : 67 — Dixit VD. Thymic fatness and approaches to enhance thymopoietic fitness in aging.
Curr Opin Immunol ; 22 : — Stein S , Lohmann C , Schäfer N , Hofmann J , Rohrer L , Besler C , Rothgiesser KM , Becher B , Hottiger MO , Borén J , McBurney MW , Landmesser U , Lüscher TF , Matter CM. SIRT1 decreases Loxmediated foam cell formation in atherogenesis.
Eur Heart J ; 31 : — Winnik S , Stein S , Matter CM. SIRT1—an anti-inflammatory pathway at the crossroads between metabolic disease and atherosclerosis.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol ; 10 : — Bartelt A , Heeren J. Adipose tissue browning and metabolic health. Nat Rev Endocrinol ; 10 : 24 — Kosteli A , Sugaru E , Haemmerle G , Martin JF , Lei J , Zechner R , Ferrante AW Jr. Weight loss and lipolysis promote a dynamic immune response in murine adipose tissue.
Wensveen FM , Valentic S , Sestan M , Wensveen TT , Polic B. Interactions between adipose tissue and the immune system in health and malnutrition.
Semin Immunol ; 27 : — Wu H , Ghosh S , Perrard XD , Feng L , Garcia GE , Perrard JL , Sweeney JF , Peterson LE , Chan L , Smith CW , Ballantyne CM. T-cell accumulation and regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted upregulation in adipose tissue in obesity.
Rocha VZ , Libby P. Obesity, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol ; 6 : — Huber J , Kiefer FW , Zeyda M , Ludvik B , Silberhumer GR , Prager G , Zlabinger GJ , Stulnig TM.
CC Chemokine and CC chemokine receptor profiles in visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue are altered in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; 93 : — Khan IM , Dai Perrard XY , Perrard JL , Mansoori A , Smith CW , Wu H , Ballantyne CM.
Atherosclerosis ; : — Deng T , Lyon CJ , Minze LJ , Lin J , Zou J , Liu JZ , Ren Y , Yin Z , Hamilton DJ , Reardon PR , Sherman V , Wang HY , Phillips KJ , Webb P , Wong ST , Wang RF , Hsueh WA. Class II major histocompatibility complex plays an essential role in obesity-induced adipose inflammation.
Cell Metab ; 17 : — Cell Rep ; 9 : — Morris DL , Cho KW , Delproposto JL , Oatmen KE , Geletka LM , Martinez-Santibanez G , Singer K , Lumeng CN. Diabetes ; 62 : — Khan IM , Perrard XY , Brunner G , Lui H , Sparks LM , Smith SR , Wang X , Shi ZZ , Lewis DE , Wu H , Ballantyne CM.
Intermuscular and perimuscular fat expansion in obesity correlates with skeletal muscle T cell and macrophage infiltration and insulin resistance. Int J Obes ; 39 : — Nishimura S , Manabe I , Nagasaki M , Eto K , Yamashita H , Ohsugi M , Otsu M , Hara K , Ueki K , Sugiura S , Yoshimura K , Kadowaki T , Nagai R.
Nat Med ; 15 : — Feuerer M , Herrero L , Cipolletta D , Naaz A , Wong J , Nayer A , Lee J , Goldfine AB , Benoist C , Shoelson S , Mathis D.
Lean, but not obese, fat is enriched for a unique population of regulatory T cells that affect metabolic parameters. Panduro M , Benoist C , Mathis D. Tissue Tregs. Annu Rev Immunol ; 34 : — Yan X , Imano N , Tamaki K , Sano M , Shinmura K. The effect of caloric restriction on the increase in senescence-associated T cells and metabolic disorders in aged mice.
PLoS One ; 16 : e Time-restricted feeding restores obesity-induced alteration in adipose tissue immune cell phenotype. Stampanoni Bassi M , Iezzi E , Buttari F , Gilio L , Simonelli I , Carbone F , Micillo T , De Rosa V , Sica F , Furlan R , Finardi A , Fantozzi R , Storto M , Bellantonio P , Pirollo P , Di Lemme S , Musella A , Mandolesi G , Centonze D , Matarese G.
Obesity worsens central inflammation and disability in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler ; 26 : — Mouton AJ , Li X , Hall ME , Hall JE. Obesity, hypertension, and cardiac dysfunction: novel roles of immunometabolism in macrophage activation and inflammation.
Procaccini C , Carbone F , Di Silvestre D , Brambilla F , De Rosa V , Galgani M , Faicchia D , Marone G , Tramontano D , Corona M , Alviggi C , Porcellini A , La Cava A , Mauri P , Matarese G. The proteomic landscape of human ex vivo regulatory and conventional T cells reveals specific metabolic requirements.
Immunity ; 44 : Procaccini C , De Rosa V , Galgani M , Abanni L , Calì G , Porcellini A , Carbone F , Fontana S , Horvath TL , La Cava A , Matarese G.
An oscillatory switch in mTOR kinase activity sets regulatory T cell responsiveness. Immunity ; 33 : — Procaccini C , De Rosa V , Galgani M , Carbone F , Cassano S , Greco D , Qian K , Auvinen P , Calì G , Stallone G , Formisano L , La Cava A , Matarese G.
Matarese G , La Cava A , Horvath TL. In vivo veritas, in vitro artificia. Trends Mol Med ; 18 : — Procaccini C , Garavelli S , Carbone F , Di Silvestre D , La Rocca C , Greco D , Colamatteo A , Lepore MT , Russo C , De Rosa G , Faicchia D , Prattichizzo F , Grossi S , Campomenosi P , Buttari F , Mauri P , Uccelli A , Salvetti M , Brescia Morra V , Vella D , Galgani M , Mottola M , Zuccarelli B , Lanzillo R , Maniscalco GT , Centonze D , de Candia P , Matarese G.
Signals of pseudo-starvation unveil the amino acid transporter SLC7A11 as key determinant in the control of Treg cell proliferative potential. Immunity ; 54 : — De Rosa V , Procaccini C , La Cava A , Chieffi P , Nicoletti GF , Fontana S , Zappacosta S , Matarese G.
Leptin neutralization interferes with pathogenic T cell autoreactivity in autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol ; : 26 — Modulation of the immune response in rheumatoid arthritis with strategically released rapamycin.
Mol Med Rep ; 16 : — De Rosa V , Procaccini C , Calì G , Pirozzi G , Fontana S , Zappacosta S , La Cava A , Matarese G. A key role of leptin in the control of regulatory T cell proliferation.
Immunity ; 26 : — Kristófi R , Eriksson JW. Metformin as an anti-inflammatory agent: a short review. J Endocrinol ; : R11 — R Br J Dermatol ; : — Mariño G , Pietrocola F , Madeo F , Kroemer G.
Autophagy ; 10 : — Becher J , Simula L , Volpe E , Procaccini C , La Rocca C , D'Acunzo P , Cianfanelli V , Strappazzon F , Caruana I , Nazio F , Weber G , Gigantino V , Botti G , Ciccosanti F , Borsellino G , Campello S , Mandolesi G , De Bardi M , Fimia GM , D'Amelio M , Ruffini F , Furlan R , Centonze D , Martino G , Braghetta P , Chrisam M , Bonaldo P , Matarese G , Locatelli F , Battistini L , Cecconi F.
AMBRA1 controls regulatory T-cell differentiation and homeostasis upstream of the FOXO3-FOXP3 axis. Dev Cell ; 47 : — Cassano S , Pucino V , La Rocca C , Procaccini C , De Rosa V , Marone G , Matarese G. Metabolism ; 63 : — Pietrocola F , Pol J , Vacchelli E , Rao S , Enot DP , Baracco EE , Levesque S , Castoldi F , Jacquelot N , Yamazaki T , Senovilla L , Marino G , Aranda F , Durand S , Sica V , Chery A , Lachkar S , Sigl V , Bloy N , Buque A , Falzoni S , Ryffel B , Apetoh L , Di Virgilio F , Madeo F , Maiuri MC , Zitvogel L , Levine B , Penninger JM , Kroemer G.
Caloric restriction mimetics enhance anticancer immunosurveillance. Cancer Cell ; 30 : — Mizushima N , Yamamoto A , Matsui M , Yoshimori T , Ohsumi Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker.
Mol Biol Cell ; 15 : — Galluzzi L , Pietrocola F , Bravo-San Pedro JM , Amaravadi RK , Baehrecke EH , Cecconi F , Codogno P , Debnath J , Gewirtz DA , Karantza V , Kimmelman A , Kumar S , Levine B , Maiuri MC , Martin SJ , Penninger J , Piacentini M , Rubinsztein DC , Simon HU , Simonsen A , Thorburn AM , Velasco G , Ryan KM , Kroemer G.
Autophagy in malignant transformation and cancer progression. EMBO J ; 34 : — Mizushima N , Levine B. Autophagy in human diseases. Ma Y , Adjemian S , Mattarollo SR , Yamazaki T , Aymeric L , Yang H , Portela Catani JP , Hannani D , Duret H , Steegh K , Martins I , Schlemmer F , Michaud M , Kepp O , Sukkurwala AQ , Menger L , Vacchelli E , Droin N , Galluzzi L , Krzysiek R , Gordon S , Taylor PR , Van Endert P , Solary E , Smyth MJ , Zitvogel L , Kroemer G.
Anticancer chemotherapy-induced intratumoral recruitment and differentiation of antigen-presenting cells.
Immunity ; 38 : — Michaud M , Martins I , Sukkurwala AQ , Adjemian S , Ma Y , Pellegatti P , Shen S , Kepp O , Scoazec M , Mignot G , Rello-Varona S , Tailler M , Menger L , Vacchelli E , Galluzzi L , Ghiringhelli F , di Virgilio F , Zitvogel L , Kroemer G.
Autophagy-dependent anticancer immune responses induced by chemotherapeutic agents in mice. Gattinoni L , Lugli E , Ji Y , Pos Z , Paulos CM , Quigley MF , Almeida JR , Gostick E , Yu Z , Carpenito C , Wang E , Douek DC , Price DA , June CH , Marincola FM , Roederer M , Restifo NP.
A human memory T cell subset with stem cell-like properties. Nat Med ; 17 : — Vodnala SK , Eil R , Kishton RJ , Sukumar M , Yamamoto TN , Ha NH , Lee PH , Shin M , Patel SJ , Yu Z , Palmer DC , Kruhlak MJ , Liu X , Locasale JW , Huang J , Roychoudhuri R , Finkel T , Klebanoff CA , Restifo NP.
T cell stemness and dysfunction in tumors are triggered by a common mechanism. Science ; : eaau Eil R , Vodnala SK , Clever D , Klebanoff CA , Sukumar M , Pan JH , Palmer DC , Gros A , Yamamoto TN , Patel SJ , Guittard GC , Yu Z , Carbonaro V , Okkenhaug K , Schrump DS , Linehan WM , Roychoudhuri R , Restifo NP.
Ionic immune suppression within the tumour microenvironment limits T cell effector function. Clemente JC , Ursell LK , Parfrey LW , Knight R. The impact of the gut microbiota on human health: an integrative view.
Belkaid Y , Hand TW. Role of the microbiota in immunity and inflammation. Yoo JY , Groer M , Dutra SVO , Sarkar A , McSkimming DI. Gut microbiota and immune system interactions.
Microorganisms ; 8 : Agus A , Denizot J , Thévenot J , Martinez-Medina M , Massier S , Sauvanet P , Bernalier-Donadille A , Denis S , Hofman P , Bonnet R , Billard E , Barnich N. Western diet induces a shift in microbiota composition enhancing susceptibility to adherent-invasive E.
coli infection and intestinal inflammation. Sci Rep ; 6 : Devkota S , Wang Y , Musch MW , Leone V , Fehlner-Peach H , Nadimpalli A , Antonopoulos DA , Jabri B , Chang EB. Fabbiano S , Suárez-Zamorano N , Chevalier C , Lazarević V , Kieser S , Rigo D , Leo S , Veyrat-Durebex C , Gaïa N , Maresca M , Merkler D , de Agüero MG , Macpherson A , Schrenzel J , Trajkovski M.
Functional gut microbiota remodeling contributes to the caloric restriction-induced metabolic improvements. Cell Metab ; 28 : — Gut microbiota mediates the anti-obesity effect of calorie restriction in mice. Sci Rep ; 8 : von Schwartzenberg RJ , Bisanz JE , Lyalina S , Spanogiannopoulos P , Ang QY , Cai J , Dickmann S , Friedrich M , Liu SY , Collins SL , Ingebrigtsen D , Miller S , Turnbaugh JA , Patterson AD , Pollard KS , Mai K , Spranger J , Turnbaugh PJ.
Caloric restriction disrupts the microbiota and colonization resistance. Sbierski-Kind J , Grenkowitz S , Schlickeiser S , Sandforth A , Friedrich M , Kunkel D , Glauben R , Brachs S , Mai K , Thürmer A , Radonić A , Drechsel O , Turnbaugh PJ , Bisanz JE , Volk HD , Spranger J , von Schwartzenberg RJ.
Effects of caloric restriction on the gut microbiome are linked with immune senescence. Microbiome ; 10 : De Filippo C , Cavalieri D , Di Paola M , Ramazzotti M , Poullet JB , Massart S , Collini S , Pieraccini G , Lionetti P.
Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Arpaia N , Campbell C , Fan X , Dikiy S , van der Veeken J , de Roos P , Liu H , Cross JR , Pfeffer K , Coffer PJ , Rudensky AY. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation.
Cignarella F , Cantoni C , Ghezzi L , Salter A , Dorsett Y , Chen L , Phillips D , Weinstock GM , Fontana L , Cross AH , Zhou Y , Piccio L. Intermittent fasting confers protection in CNS autoimmunity by altering the gut microbiota. Calorie restriction conferred improvement effect on long-term rehabilitation of ischemic stroke via gut microbiota.
Pharmacol Res ; : Chung WS , Walker AW , Louis P , Parkhill J , Vermeiren J , Bosscher D , Duncan SH , Flint HJ. Modulation of the human gut microbiota by dietary fibres occurs at the species level.
BMC Biol ; 14 : 3. Heinsen FA , Fangmann D , Müller N , Schulte DM , Rühlemann MC , Türk K , Settgast U , Lieb W , Baines JF , Schreiber S , Franke A , Laudes M. Beneficial effects of a dietary weight loss intervention on human gut microbiome diversity and metabolism are not sustained during weight maintenance.
Obes Facts ; 9 : — Intermittent fasting improves cardiometabolic risk factors and alters gut microbiota in metabolic syndrome patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab ; : 64 — Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford.
It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide. Sign In or Create an Account. Advertisement intended for healthcare professionals. Navbar Search Filter Cardiovascular Research ESC Publications Cardiovascular Medicine Books Journals Oxford Academic Mobile Enter search term Search.
ESC Publications. Advanced Search. Search Menu. Article Navigation. Close mobile search navigation Article Navigation. Article Contents Abstract. Nutrition-based treatment of pathological conditions.
Drugs mimicking caloric restriction. Immunological mechanisms of nutritional intervention. Nutritional effect on the gut microbiota. Data Availability. Journal Article Corrected proof. Caloric restriction for the immunometabolic control of human health.
Claudio Procaccini , Claudio Procaccini. Oxford Academic. Paola de Candia. Claudia Russo. Unità di Neuroimmunologia, IRCCS-Fondazione Santa Lucia.
Giusy De Rosa. Maria Teresa Lepore. Alessandra Colamatteo. Giuseppe Matarese. Corresponding author. matarese unina. Claudio Procaccini and Paola de Candia contributed equally.
Conflict of interest: None declared. total glycemia 2 and no smoke the lifetime probability of developing an atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease was very low i. In humans calorie restriction without malnutrition also results in a consistent reduction in circulating levels of growth factors, anabolic hormones, adipokines and inflammatory cytokines, which are associated with an increased risk of some of the most common types of cancer [ 63 ].
It is important to note that none of the 50 men and women age range yrs practicing long-term CR with adequate nutrition is taking any medication or has developed any chronic disease so far. Moreover, CR in these individuals resulted in an amelioration of two well-accepted markers of cardiovascular aging, i.
left ventricular diastolic function and heart rate variability [ 64 - 65 ]. These data indicate that CR exerts direct systemic effects that counter the expected age-associated changes in myocardial stiffness and autonomic function so that LV diastolic function and heart rate variability indexes in CR individuals are similar to those of individuals 20 years younger on a typical Western diet.
More studies are needed to understand how macro- and micro-nutrients, endurance exercise, and other environmental and psychological factors interact with CR in modulating metabolic and molecular pathways that regulate health and longevity. Both excessive dietary restriction and overnutrition are different forms of malnutrition that lead to organ dysfunction and increased mortality.
Even in rodents, excessive CR imposed on some strains of mice increases mortality. The problem is that the rate of physiologic development and sexual maturation varies among different strains of rodents, so that the lifespan response to CR may be different.
Forty percent CR may be optimal in some strains of mice, but can cause severe starvation and increased mortality in others, which would benefit from a lower degree of CR. The same applies to humans, in which severe CR could be detrimental in some populations e. children, older adults, pregnant women, etc.
Randomized, CR-controlled, long-term survival studies in humans will never be performed because of obvious problems with long-term compliance and costs of such a long study. Nonetheless, we hope that by following the health status of individuals practicing long-term CR without malnutrition i.
the CRONies , in particular of those who are now in their 70s and 80s, we could gain soon some information about the effects of CR on successful aging and healthy longevity in humans as well.
Navigate Home Editorial Board Information For Authors Advance Online Publications Current Issue Archive Scientific Integrity Publication Ethics and Publication Malpractice Statements Contact Special Collections Podcast News Room Interviews with Outstanding Authors. Research Perspective Volume 5, Issue 7 pp — Will calorie restriction work in humans?
Cite this Article How to cite Cava E , Fontana L ,. Abstract Calorie Restriction CR without malnutrition slows aging and increases average and maximal lifespan in simple model organisms and rodents. Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the NIA and WNPRC CR monkey studies. NIA WNPRC Total number of Rhesus monkeys 60 m, 60 f 30 m 30 m 60 f 76 46 m, 30 f 30 m 16 m 30 f Age at baseline Juvenile 20 m, 20 f Adolescent 20 m, 20 f Old 20 m, 20 f All adult Animal origin India, China India Housing Single caged Single caged Randomization 1 Control: 1 CR 1 Control: 1 CR Diet composition and nutrients Natural ingredient 3.
Blood samples are collected under anesthesia only for specific testing i. glucose tolerance testing. Keywords calorie restriction aging chronic disease prevention. Table of Contents Abstract Is the degree of CR in the NIA and WNPRC monkeys sufficient to trigger an anti-aging effect?
Is diet composition as important as calorie intake in mediating healthy longevity? Is protein intake a key determinant of longevity in CR primates?
Acknowledgments Conflicts of Interest References. Natural ingredient 3. Semipurified pellet 3. Routine blood sampling every 3 months on awake, manually restrained animals.
Disexse is an age-related clinical calorc that Cholesterol level factors increase the risk of falls, disability, hospitalization, and death in older adults. Delaying the restricction of frailty Stimulant-free energy supplement improve caooric quality of life in restiction adults. Caloric restriction CR may extend lifespan and reduce the risk of age-related diseases. However, few studies have explored the relationship between CR and frailty. In this review, we focused on the impact of CR on frailty and aimed to identify potential associated mechanisms. Although CR may help prevent frailty, further studies are required to determine the underlying mechanisms and specific CR regimens suitable for use in humans.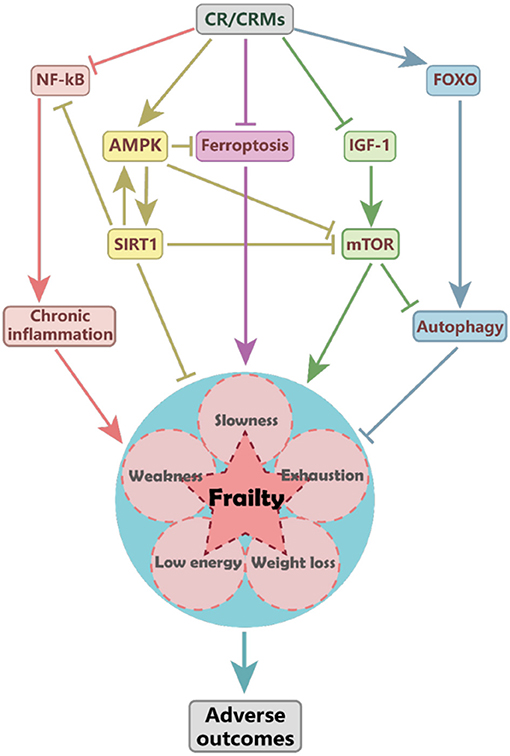
0 thoughts on “Caloric restriction and disease prevention”