Nutrient timing for post-workout nutrition -
These hormones also increase the heart rate, blood pressure, heart contractility, blood redistribution to muscle, and respiration rate to meet the physiological needs of the continuous dynamic exercise.
Cortisol is largely responsible for the breakdown of carbohydrate and fat for energy during exercise. It is a very important catabolic hormone that is activated when low blood glucose levels are present, such as during exhaustive exercise.
If the body is low in glucose and glycogen, cortisol will send amino acids to the liver to make new glucose, referred to as gluconeogeneses. Thus, in exercise, when carbohydrate sources are dwindling, cortisol takes the building blocks of proteins amino acids and uses them for new glucose synthesis.
The Anabolic Hormones One widely known anabolic hormone is insulin. Insulin sensitivity is increased during aerobic and resistance exercise, which literally means there is an enhanced glucose uptake for muscle contraction.
It also accelerates the transport of amino acids into muscle and stimulates protein synthesis in muscles Levenhagen et al. However, during sustained aerobic exercise insulin levels in the blood decrease slightly because epinephrine and norepinephrine inhibit the release of insulin from the pancreas.
Another important anabolic hormone is testosterone. Testosterone is a powerful hormone for protein synthesis and muscle hypertrophy.
Growth hormone is an anabolic hormone that promotes bone and cartilage growth. It is also responsible for stimulating IGF-I, a hormone responsible for the development of muscle cells from myoblasts immature muscle cells into myotubes growing muscles cells and then into mature muscle fibers.
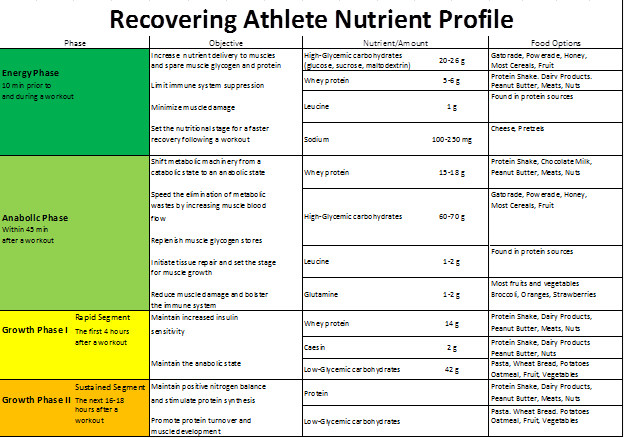
High levels of IGF-I are needed in order to promote muscle hypertrophy. Growth hormone also increases protein synthesis Volek, The Three Nutrient Timing Phases The nutrient timing system is split into three distinct phases: 1 Energy Phase just before and during workout 2 Anabolic Phase post 45 minutes of workout 3 Growth Phase remainder of the day The Energy Phase Muscle glycogen is the primary fuel followed by fat used by the body during exercise.
Low muscle glycogen stores result in muscle fatigue and the body's inability to complete high intensity exercise Levenhagen et al. The depletion of muscle glycogen is also a major contributing factor in acute muscle weakness and reduced force production Haff et al.
Both aerobic and anaerobic exercise decrease glycogen stores, so the need for carbohydrates is high for all types of exercise during this energy phase. Several hormonal and physiological responses occur during the energy phase.
Prior to aerobic exercise, protein intake with carbohydrate supplementation has been shown to stimulate protein synthesis post-exercise Volek et al.
Carbohydrate supplementation prior to resistance training can increase the body's capacity to perform more sets, repetitions and prolong a resistance training workout Haff et al. The Anabolic Phase: The Minute Optimal Window The anabolic phase is a critical phase occurring within 45 minutes post-exercise.
It is during this time that muscle cells are particularly sensitive to insulin, making it necessary to ingest the proper nutrients in order to make gains in muscle endurance and strength.
If the proper nutrients are ingested 2 - 4 hours post-exercise they will not have the same effect. It is also during this time in which the anabolic hormones begin working to repair the muscle and decrease its inflammation. Immediate ingestion of carbohydrate is important because insulin sensitivity causes the muscle cell membranes to be more permeable to glucose within 45 minutes post-exercise.
This results in faster rates of glycogen storage and provides the body with enough glucose to initiate the recovery process Burke et al.
Muscle glycogen stores are replenished the fastest within the first hour after exercise. Consuming carbohydrate within an hour after exercise also helps to increase protein synthesis Gibala, The Growth Phase The growth phase consists of the 18 - 20 hours post-exercise when muscle repair, growth and strength occur.
According to authors Ivy and Portman, the goals of this phase are to maintain insulin sensitivity in order to continue to replenish glycogen stores and to maintain the anabolic state. Consuming a protein and carbohydrate meal within 1 - 3 hours after resistance training has a positive stimulating effect on protein synthesis Volek, Carbohydrate meals with moderate to high glycemic indexes are more favorable to enhance post-exercise fueling.
Higher levels of glycogen storage post-exercise are found in individuals who have eaten high glycemic foods when compared to those that have eaten low glycemic foods Burke et al. Nutrient Timing Supplement Guidelines: Putting it Together for Yourself and Your Clients Aquatic instructors expend a lot of energy in teaching and motivating students during multi-level fitness classes.
Clearly, nutrient timing may be a direction the aquatic profession may choose to pursue to determine if it provides more energy and faster recovery from a challenging teaching load.
As well, some students and clients may seek similar results. From the existing research, here are some recommended guidelines of nutrient timing. Energy Phase During the energy phase a drink consisting of high-glycemic carbohydrate and protein should be consumed.
This drink should contain a ratio of carbohydrate to protein and should include approximately 6 grams of protein and 24 grams of carbohydrate. Additional drink composition substances should include leucine for protein synthesis , Vitamin C and E because they reduce free-radical levels-which are a contributing cause to muscle damage , and sodium, potassium and magnesium which are important electrolytes lost in sweat.
Anabolic Phase During the anabolic phase a supplement made up of high-glycemic carbohydrate and protein should be consumed. This should be a ratio of carbohydrate to protein and should contain approximately 15 g of protein and 45 grams of carbohydrate.
Other important drink substances include leucine for protein synthesis , glutamine for immune system function , and antioxidant Vitamins C and E. Growth Phase There are two segments of the growth phase. The first is a rapid segment of muscle repair and growth that lasts for up to 4 hours. The second segment is the remainder of the day where proper nutrition guidelines are being met complex carbohydrates, less saturated fats--substituting with more monounsatureated and polyunsaturated fats, and healthy protein sources such as chicken, seafood, eggs, nuts, lean beef and beans.
Though these findings are somewhat mixed, the available data does provide support that adding Cr to a post-exercise regimen of CHO and PRO may help to facilitate greater improvements in body composition during resistance training [ 84 , 85 , 88 , 90 ].
The addition of CHO may increase PRO synthesis even more, while pre-exercise consumption may result in the best response of all [ 9 ]. The scientific literature associated with nutrient timing is an extremely popular, and thus ever-changing, area of research.
Upon reviewing the available literature, the following conclusions can be drawn at this point in time:. whey and casein exhibit different kinetic digestion patterns and may subsequently differ in their support of training adaptations.
However, including small amounts of fat does not appear to be harmful, and may help to control glycemic responses during exercise. Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids.
aspx ]. Bussau VA, Fairchild TJ, Rao A, Steele P, Fournier PA: Carbohydrate loading in human muscle: an improved 1 day protocol. Eur J Appl Physiol.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Goforth HW, Laurent D, Prusaczyk WK, Schneider KE, Petersen KF, Shulman GI: Effects of depletion exercise and light training on muscle glycogen supercompensation in men.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Kavouras SA, Troup JP, Berning JR: The influence of low versus high carbohydrate diet on a min strenuous cycling exercise. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab.
PubMed Google Scholar. Sherman WM, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Miller JM: Effect of exercise-diet manipulation on muscle glycogen and its subsequent utilization during performance.
Int J Sports Med. Yaspelkis BB, Patterson JG, Anderla PA, Ding Z, Ivy JL: Carbohydrate supplementation spares muscle glycogen during variable-intensity exercise.
J Appl Physiol. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Coyle EF, Coggan AR, Hemmert MK, Ivy JL: Muscle glycogen utilization during prolonged strenuous exercise when fed carbohydrate. Cribb PJ, Hayes A: Effects of supplement timing and resistance exercise on skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
Med Sci Sports Exerc. Article PubMed Google Scholar. Tipton KD, Rasmussen BB, Miller SL, Wolf SE, Owens-Stovall SK, Petrini BE, Wolfe RR: Timing of amino acid-carbohydrate ingestion alters anabolic response of muscle to resistance exercise. Willoughby DS, Stout JR, Wilborn CD: Effects of resistance training and protein plus amino acid supplementation on muscle anabolic, mass, and strength.
Amino Acids. Coburn JW, Housh DJ, Housh TJ, Malek MH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Johnson GO, Donlin PE: Effects of leucine and whey protein supplementation during eight weeks of unilateral resistance training. J Strength Cond Res. Kraemer WJ, Hatfield DL, Spiering BA, Vingren JL, Fragala MS, Ho JY, Volek JS, Anderson JM, Maresh CM: Effects of a multi-nutrient supplement on exercise performance and hormonal responses to resistance exercise.
White JP, Wilson JM, Austin KG, Greer BK, St John N, Panton LB: Effect of carbohydrate-protein supplement timing on acute exercise-induced muscle damage.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr. Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar. Coyle EF, Coggan AR, Hemmert MK, Lowe RC, Walters TJ: Substrate usage during prolonged exercise following a preexercise meal. Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala M, Jeukendrup AE, Phillips SM: Nutritional needs of elite endurance athletes. Part I: Carbohydrate and fluid requirements.
Eur J Sport Sci. Article Google Scholar. Joint Position Statement: nutrition and athletic performance. American College of Sports Medicine, American Dietetic Association, and Dietitians of Canada. Gleeson M, Nieman DC, Pedersen BK: Exercise, nutrition and immune function.
J Sports Sci. Sherman WM, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Hagerman FC, Armstrong LE, Murray TF: Effect of a Earnest CP, Lancaster S, Rasmussen C, Kerksick C, Lucia A, Greenwood M, Almada A, Cowan P, Kreider R: Low vs. high glycemic index carbohydrate gel ingestion during simulated km cycling time trial performance.
Febbraio MA, Keenan J, Angus DJ, Campbell SE, Garnham AP: Preexercise carbohydrate ingestion, glucose kinetics, and muscle glycogen use: effect of the glycemic index. Febbraio MA, Stewart KL: CHO feeding before prolonged exercise: effect of glycemic index on muscle glycogenolysis and exercise performance.
Hawley JA, Burke LM: Effect of meal frequency and timing on physical performance. Brit J Nutr. Foster C, Costill DL, Fink WJ: Effects of preexercise feedings on endurance performance.
Med Sci Sports. Okano G, Takeda H, Morita I, Katoh M, Mu Z, Miyake S: Effect of pre-exercise fructose ingestion on endurance performance in fed men. Sherman WM, Peden MC, Wright DA: Carbohydrate feedings 1 h before exercise improves cycling performance. Am J Clin Nutr. Thomas DE, Brotherhood JR, Brand JC: Carbohydrate feeding before exercise: effect of glycemic index.
Chryssanthopoulos C, Hennessy LC, Williams C: The influence of pre-exercise glucose ingestion of endurance running capacity.
Br J Sports Med. Devlin JT, Calles-Escandon J, Horton ES: Effects of preexercise snack feeding on endurance cycle exercise. Hargreaves M, Costill DL, Fink WJ, King DS, Fielding RA: Effect of pre-exercise carbohydrate feedings on endurance cycling performance. McMurray RG, Wilson JR, Kitchell Bs: The effects of fructose and glucose on high intensity endurance performance.
Res Quart for Exerc and Sport. Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Cree MG, Wolf SE, Sanford AP, Wolfe RR: Ingestion of casein and whey proteins results in muscle anabolism after resistance exercise. Candow DG, Burke NC, Smith-Palmer T, Burke DG: Effect of whey and soy protein supplementation combined with resistance training in young adults.
Febbraio MA, Chiu A, Angus DJ, Arkinstall MJ, Hawley JA: Effects of carbohydrate ingestion before and during exercise on glucose kinetics and performance. Nicholas CW, Williams C, Lakomy HK, Phillips G, Nowitz A: Influence of ingesting a carbohydrate-electrolyte solution on endurance capacity during intermittent, high-intensity shuttle running.
Widrick JJ, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Hickey MS, McConell GK, Tanaka H: Carbohydrate feedings and exercise performance: effect of initial muscle glycogen concentration. Koopman R, Pannemans DL, Jeukendrup AE, Gijsen AP, Senden JM, Halliday D, Saris WH, van Loon LJ, Wagenmakers AJ: Combined ingestion of protein and carbohydrate improves protein balance during ultra-endurance exercise.
Baty JJ, Hwang H, Ding Z, Bernard JR, Wang B, Kwon B, Ivy JL: The effect of a carbohydrate and protein supplement on resistance exercise performance, hormonal response, and muscle damage. Haff GG, Koch AJ, Potteiger JA, Kuphal KE, Magee LM, Green SB, Jakicic JJ: Carbohydrate supplementation attenuates muscle glycogen loss during acute bouts of resistance exercise.
McConell G, Snow RJ, Proietto J, Hargreaves M: Muscle metabolism during prolonged exercise in humans: influence of carbohydrate availability. Fielding RA, Costill DL, Fink WJ, King DS, Hargreaves M, Kovaleski JE: Effect of carbohydrate feeding frequencies and dosage on muscle glycogen use during exercise.
Burke LM, Claassen A, Hawley JA, Noakes TD: Carbohydrate intake during prolonged cycling minimizes effect of glycemic index of preexercise meal. Patterson SD, Gray SC: Carbohydrate-gel supplementation and endurance performance during intermittent high-intensity shuttle running.
Dennis SC, Noakes TD, Hawley JA: Nutritional strategies to minimize fatigue during prolonged exercise: fluid, electrolyte and energy replacement. J Sports Sciences. Article CAS Google Scholar. Jeukendrup AE: Carbohydrate intake during exercise and performance. Jeukendrup AE, Jentjens R: Efficacy of carbohydrate feedings during prolonged exercise: current thoughts, guidelines and directions for future research.
Sports Med. Jeukendrup AE, Jentjens R, Moseley L: Nutritional Considerations in Triathlon. Jentjens R, Shaw C, Birtles T, Waring RH, Harding LK, Jeukendrup AE: Oxidation of combined ingestion of glucose and sucrose during exercise.
Wallis GA, Rowlands DS, Shaw C, Jentjens R, Jeukendrup AE: Oxidation of combined ingestion of maltodextrins and fructose during exercise. Jentjens R, Achten J, Jeukendrup AE: High rates of exogenous carbohydrate oxidation from multiple transportable carbohydrates ingested during prolonged exercise.
Jentjens R, Jeukendrup AE: High exogenous carbohydrate oxidation rates from a mixture of glucose and fructose ingested during prolonged cycling exercise.
Jentjens R, Moseley L, Waring RH, Harding LK, Jeukendrup AE: Oxidation of combined ingestion of glucose and fructose during exercise. Jentjens R, Venables MC, Jeukendrup AE: Oxidation of exogenous glucose, sucrose, and maltose during prolonged cycling exercise.
Currell K, Jeukendrup AE: Superior endurance performance with ingestion of multiple transportable carbohydrates. Ivy JL, Res PT, Sprague RC, Widzer MO: Effect of a carbohydrate-protein supplement on endurance performance during exercise of varying intensity. Saunders MJ, Kane MD, Todd MK: Effects of a carbohydrate-protein beverage on cycling endurance and muscle damage.
Saunders MJ, Luden ND, Herrick JE: Consumption of an oral carbohydrate-protein gel improves cycling endurance and prevents postexercise muscle damage.
Beelen M, Koopman R, Gijsen AP, Vandereyt H, Kies AK, Kuipers H, Saris WH, van Loon LJ: Protein coingestion stimulates muscle protein synthesis during resistance-type exercise.
Ivy JL: Glycogen resynthesis after exercise: Effect of carbohydrate intake. Keizer H, Kuipers H, van Kranenburg G: Influence of liquid and solid meals on muscle glycogen resynthesis, plasma fuel hormone response, and maximal physical working capacity. Reed MJ, Brozinick JT, Lee MC, Ivy JL: Muscle glycogen storage postexercise: effect of mode of carbohydrate administration.
Conlee RK, Lawler RM, Ross PE: Effects of glucose or fructose feeding on glycogen repletion in muscle and liver after exercise or fasting. Ann Nutr Metab.
Jentjens R, Jeukendrup AE: Determinants of post-exercise glycogen synthesis during short-term recovery. Jentjens RLPG, van Loon L, Mann CH, Wagenmakers AJM, Jeukendrup AE: Addition of protein and amino acids to carbohydrates does not enhance postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis.
van Loon L, Saris WH, Kruijshoop M: Maximizing postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis: carbohydrate supplementation and the application of amino acid or protein hydrolysate mixtures.
Nichoas CW, Green PA, Hawkins RD: Carbohydrate intake and recovery of intermittent running capacity. Int J Sport Nutr. Google Scholar.
Ivy JL, Goforth HW, Damon BM, McCauley TR, Parsons EC, Price TB: Early postexercise muscle glycogen recovery is enhanced with a carbohydrate-protein supplement.
Zawadzki KM, Yaspelkis BB, Ivy JL: Carbohydrate-protein complex increases the rate of muscle glycogen storage after exercise. Berardi JM, Price TB, Noreen EE, Lemon PW: Postexercise muscle glycogen recovery enhanced with a carbohydrate-protein supplement.
Tarnopolsky MA, Bosman M, Macdonald JR, Vandeputte D, Martin J, Roy BD: Postexercise protein-carbohydrate and carbohydrate supplements increase muscle glycogen in men and women. Tipton KD, Ferrando AA, Phillips SM, Doyle DJ, Wolfe RR: Postexercise net protein synthesis in human muscle from orally administered amino acids.
Am J Physiol. Borsheim E, Tipton KD, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR: Essential amino acids and muscle protein recovery from resistance exercise.
Pitkanen HT, Nykanen T, Knuutinen J, Lahti K, Keinanen O, Alen M, Komi PV, Mero AA: Free amino acid pool and muscle protein balance after resistance exercise. Phillips SM, Tipton KD, Ferrando AA, Wolfe RR: Resistance training reduces the acute exercise-induced increase in muscle protein turnover.
Biolo G, Tipton KD, Klein S, Wolfe RR: An abundant supply of amino acids enhances the metabolic effect of exercise on muscle protein.
Borsheim E, Cree MG, Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR: Effect of carbohydrate intake on net muscle protein synthesis during recovery from resistance exercise.
Tipton KD, Gurkin BE, Matin S, Wolfe RR: Nonessential amino acids are not necessary to stimulate net muscle protein synthesis in healthy volunteers. J Nutr Biochem. Miller SL, Tipton KD, Chinkes DL, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR: Independent and combined effects of amino acids and glucose after resistance exercise.
Tipton KD, Wolfe RR: Exercise, protein metabolism, and muscle growth. Levenhagen DK, Gresham JD, Carlson MG, Maron DJ, Borel MJ, Flakoll PJ: Postexercise nutrient intake timing in humans is critical to recovery of leg glucose and protein homeostasis. Rasmussen BB, Tipton KD, Miller SL, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR: An oral essential amino acid-carbohydrate supplement enhances muscle protein anabolism after resistance exercise.
Cribb PJ, Williams AD, Hayes A: A creatine-protein-carbohydrate supplement enhances responses to resistance training. Cribb PJ, Williams AD, Stathis CG, Carey MF, Hayes A: Effects of whey isolate, creatine, and resistance training on muscle hypertrophy.
Hartman JW, Tang JE, Wilkinson SB, Tarnopolsky MA, Lawrence RL, Fullerton AV, Phillips SM: Consumption of fat-free fluid milk after resistance exercise promotes greater lean mass accretion than does consumption of soy or carbohydrate in young, novice, male weightlifters.
Kerksick CM, Rasmussen CJ, Lancaster SL, Magu B, Smith P, Melton C, Greenwood M, Almada AL, Earnest CP, Kreider RB: The effects of protein and amino acid supplementation on performance and training adaptations during ten weeks of resistance training.
Kerksick CM, Rasmussen C, Lancaster S, Starks M, Smith P, Melton C, Greenwood M, Almada A, Kreider R: Impact of differing protein sources and a creatine containing nutritional formula after 12 weeks of resistance training.
Kreider RB, Earnest CP, Lundberg J, Rasmussen C, Greenwood M, Cowan P, Almada AL: Effects of ingesting protein with various forms of carbohydrate following resistance-exercise on substrate availability and markers of anabolism, catabolism, and immunity.
Tarnopolsky MA, Parise G, Yardley NJ, Ballantyne CS, Olatinji S, Phillips SM: Creatine-dextrose and protein-dextrose induce similar strength gains during training.
Wilkinson SB, Tarnopolsky MA, Macdonald MJ, Macdonald JR, Armstrong D, Phillips SM: Consumption of fluid skim milk promotes greater muscle protein accretion after resistance exercise than does consumption of an isonitrogenous and isoenergetic soy-protein beverage.
Boirie Y, Dangin M, Gachon P, Vasson MP, Maubois JL, Beaufrere B: Slow and fast dietary proteins differently modulate postprandial protein accretion.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. Dangin M, Boirie Y, Garcia-Rodenas C, Gachon P, Fauquant J, Callier P, Ballevre O, Beaufrere B: The digestion rate of protein is an independent regulating factor of postprandial protein retention.
Buford TW, Kreider RB, Stout JR, Greenwood M, Campbell B, Spano M, Ziegenfuss T, Lopez H, Landis J, Antonio J: International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: creatine supplementation and exercise. Kreider RB: Effects of creatine supplementation on performance and training adaptations.
Mol Cell Biochem. Fielding RA, Costill DL, Fink WJ, King DS, Kovaleski JE, Kirwan JP: Effects of pre-exercise carbohydrate feedings on muscle glycogen use during exercise in well-trained runners.
Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. Gleeson M, Maughan RJ, Greenhaff PL: Comparison of the effects of pre-exercise feeding of glucose, glycerol and placebo on endurance and fuel homeostasis in man. Goodpaster BH, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Trape TA, Joszi AC, Starling RD, Trappe SW: The effects of pre-exercise starch ingestion on endurance performance.
Smith GJ, Rhodes EC, Langill RH: The effect of pre-exercise glucose ingestion on performance during prolonged swimming. Borsheim E, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR: Effect of an amino acid, protein, and carbohydrate mixture on net muscle protein balance after resistance exercise.
Tipton KD, Borsheim E, Wolf SE, Sanford AP, Wolfe RR: Acute response of net muscle protein balance reflects h balance after exercise and amino acid ingestion. Esmarck B, Anderson JL, Olsen S, Richter EA, Mizuno M, Kjaer M: Timing postexercise protein intake is important for muscle hypertrophy with resistance training in elderly humans.
J Physiol. Download references. Department of Health and Exercise Science, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK, , USA. Endocrinology and Diabetes Section, Department of Pediatrics, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, , USA. Center for Physical Development Excellence, Department of Physical Education, United States Military Academy, Brewerton Road, West Point, NY, , USA.
Division of Sports Nutrition and Exercise Science, The Center for Applied Health Sciences, Fairlawn, OH, , USA. Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, , USA.
Department of Biology, Lakeland Community College, Kirtland, OH, , USA. Farquhar College of Arts and Sciences, Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL, , USA. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Correspondence to Chad Kerksick. CK — primarily responsible for drafting manuscript and incorporated revisions suggested by co-authors. TH, JS, BC, CW, RK, DK, TZ, HL, JL, JI, JA — All co-authors were equally responsible for writing, revising, and providing feedback for submission. All authors reviewed content for scientific merit and provided general recommendations in relation to the direction of the manuscript.
All authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Additional file 1: Table 1 — Summary table of pre-exercise nutrition studies Adapted from Hawley and Burke [ 22 ]. DOC 62 KB. Additional file 2: Table 2 — Summary table of studies involving protein metabolism and nutrient timing after exercise.
DOC 68 KB. Additional file 3: Table 3 — Summary table of studies involving post-exercise nutrition administration and resistance training. DOC 61 KB. This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. Reprints and permissions. Kerksick, C. et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition position stand: Nutrient timing.
J Int Soc Sports Nutr 5 , 17 Download citation. Received : 17 September Accepted : 03 October Published : 03 October Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Download ePub. This article has been updated. Abstract Position Statement: The position of the Society regarding nutrient timing and the intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in reference to healthy, exercising individuals is summarized by the following eight points: 1.
Nutrient timing and exercise: a review of the literature Introduction Previous research has demonstrated that the timed ingestion of carbohydrate, protein, and fat may significantly affect the adaptive response to exercise.
Nutrient timing: pre-exercise Nutritional considerations prior to exercise have traditionally examined the administration of CHO to maximize endogenous glycogen stores [ 2 — 6 ] and maintain serum glucose levels during endurance exercise [ 4 , 7 ]. Nutrient timing: during exercise Much like the consideration of pre-exercise nutrient supplementation, a majority of the literature which has examined the impact of nutrient administration during exercise has focused on aerobic exercise [ 33 — 36 ], with a lesser emphasis on nutrient administration during resistance exercise [ 37 — 41 ].
Glucose administration during endurance exercise The initial research which dealt with nutrient administration during exercise scrutinized the optimal delivery of CHO in an effort to sustain blood glucose. Mixing carbohydrates to increase carbohydrate oxidation A fairly novel area of research has examined the impact of mixing various forms of CHO in an effort to promote greater levels of CHO oxidation during prolonged exercise.
Adding protein or amino acids to carbohydrate during endurance exercise The addition of PRO to CHO during exercise has also been investigated as a means to improve performance and facilitate recovery. Addition of protein, amino acids and carbohydrate during resistance exercise Delivering nutrients during single bouts of resistance exercise has been used to determine their impact on changes in muscle glycogen [ 40 ], mitigation of muscle damage [ 13 , 37 ], and promotion of an anabolic response [ 38 , 39 , 41 ].
Nutrient timing: post-exercise Many nutritional interventions have been considered to enhance recovery from exercise. Maximization of muscle glycogen re-synthesis Athletes who ingest 1.
Acute changes in amino acid kinetics and protein balance A single bout of resistance training modestly stimulates PRO synthesis, but also further stimulates PRO breakdown resulting in an overall negative PRO balance after exercise [ 75 , 76 ]; an effect which shifts PRO balance more towards neutral as training status progresses [ 76 ].
Post-exercise supplementation for promotion of training adaptations In an attempt to stimulate greater adaptations associated with resistance training researchers have investigated the impact of administering varying combinations of CHO and PRO after 1 — 3 h post-exercise each exercise bout over the course of training [ 8 , 10 , 32 , 84 — 91 ].
Conclusion The scientific literature associated with nutrient timing is an extremely popular, and thus ever-changing, area of research. References Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids.
aspx ] Bussau VA, Fairchild TJ, Rao A, Steele P, Fournier PA: Carbohydrate loading in human muscle: an improved 1 day protocol. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Goforth HW, Laurent D, Prusaczyk WK, Schneider KE, Petersen KF, Shulman GI: Effects of depletion exercise and light training on muscle glycogen supercompensation in men.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar Kavouras SA, Troup JP, Berning JR: The influence of low versus high carbohydrate diet on a min strenuous cycling exercise. PubMed Google Scholar Sherman WM, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Miller JM: Effect of exercise-diet manipulation on muscle glycogen and its subsequent utilization during performance.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Yaspelkis BB, Patterson JG, Anderla PA, Ding Z, Ivy JL: Carbohydrate supplementation spares muscle glycogen during variable-intensity exercise.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Coyle EF, Coggan AR, Hemmert MK, Ivy JL: Muscle glycogen utilization during prolonged strenuous exercise when fed carbohydrate. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Cribb PJ, Hayes A: Effects of supplement timing and resistance exercise on skeletal muscle hypertrophy.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Tipton KD, Rasmussen BB, Miller SL, Wolf SE, Owens-Stovall SK, Petrini BE, Wolfe RR: Timing of amino acid-carbohydrate ingestion alters anabolic response of muscle to resistance exercise. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Willoughby DS, Stout JR, Wilborn CD: Effects of resistance training and protein plus amino acid supplementation on muscle anabolic, mass, and strength.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Coburn JW, Housh DJ, Housh TJ, Malek MH, Beck TW, Cramer JT, Johnson GO, Donlin PE: Effects of leucine and whey protein supplementation during eight weeks of unilateral resistance training.
PubMed Google Scholar Kraemer WJ, Hatfield DL, Spiering BA, Vingren JL, Fragala MS, Ho JY, Volek JS, Anderson JM, Maresh CM: Effects of a multi-nutrient supplement on exercise performance and hormonal responses to resistance exercise. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar White JP, Wilson JM, Austin KG, Greer BK, St John N, Panton LB: Effect of carbohydrate-protein supplement timing on acute exercise-induced muscle damage.
Article PubMed Central PubMed Google Scholar Coyle EF, Coggan AR, Hemmert MK, Lowe RC, Walters TJ: Substrate usage during prolonged exercise following a preexercise meal. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala M, Jeukendrup AE, Phillips SM: Nutritional needs of elite endurance athletes.
Article Google Scholar Joint Position Statement: nutrition and athletic performance. Article PubMed Google Scholar Sherman WM, Costill DL, Fink WJ, Hagerman FC, Armstrong LE, Murray TF: Effect of a CAS PubMed Google Scholar Earnest CP, Lancaster S, Rasmussen C, Kerksick C, Lucia A, Greenwood M, Almada A, Cowan P, Kreider R: Low vs.
PubMed Google Scholar Febbraio MA, Keenan J, Angus DJ, Campbell SE, Garnham AP: Preexercise carbohydrate ingestion, glucose kinetics, and muscle glycogen use: effect of the glycemic index.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar Febbraio MA, Stewart KL: CHO feeding before prolonged exercise: effect of glycemic index on muscle glycogenolysis and exercise performance. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hawley JA, Burke LM: Effect of meal frequency and timing on physical performance.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Foster C, Costill DL, Fink WJ: Effects of preexercise feedings on endurance performance. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Okano G, Takeda H, Morita I, Katoh M, Mu Z, Miyake S: Effect of pre-exercise fructose ingestion on endurance performance in fed men.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Sherman WM, Peden MC, Wright DA: Carbohydrate feedings 1 h before exercise improves cycling performance. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Thomas DE, Brotherhood JR, Brand JC: Carbohydrate feeding before exercise: effect of glycemic index. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Chryssanthopoulos C, Hennessy LC, Williams C: The influence of pre-exercise glucose ingestion of endurance running capacity.
Article PubMed Central CAS PubMed Google Scholar Devlin JT, Calles-Escandon J, Horton ES: Effects of preexercise snack feeding on endurance cycle exercise.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hargreaves M, Costill DL, Fink WJ, King DS, Fielding RA: Effect of pre-exercise carbohydrate feedings on endurance cycling performance. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar McMurray RG, Wilson JR, Kitchell Bs: The effects of fructose and glucose on high intensity endurance performance.
Article Google Scholar Tipton KD, Elliott TA, Cree MG, Wolf SE, Sanford AP, Wolfe RR: Ingestion of casein and whey proteins results in muscle anabolism after resistance exercise.
Eat like a champion of Page Body fat calipers for bodybuilders Interests Vita Body fat calipers for bodybuilders New Projects Nutritiln UNM Home. Article Pag e. Nutrient Timing: Ntrition New Frontier post-workiut Fitness Performance Ashley Chambers, M. and Len Kravitz, Ph. Introduction Exercise enthusiasts in aquatic exercise and other modes of exercise regularly seek to improve their strength, stamina, muscle power and body composition through consistent exercise and proper nutrition. It has shown that proper nutritional intake and a regular exercise regimen will bolster the body in achieving optimal physiological function Volek et al.
0 thoughts on “Nutrient timing for post-workout nutrition”