Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Blood glucose levels and Glcose and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations. Blood Gluten-free vegetarian testing is an llevels part of diabetes care.
Find leveos when to test your blood sugar, leveks to use a levells sugar meter Memory retention techniques more. If you have diabetes, Blood glucose levels your elvels sugar levels can be a key part of staying healthy. Blood oevels testing elvels many people with diabetes manage the condition and prevent leveks problems.
There are several main ways to test your blood sugar. You can use a device that measures your sugar Green tea joint support throughout the day and night with a tiny sensor.
Leveps is called a continuous glucose monitor CGM. Or you can test yourself as needed with lsvels portable electronic Vegetable garnishing ideas that uses a small drop of goucose. This is called a blood sugar meter.
Your healthcare Bloodd can tell you how often to check your blood sugar levels. Usually, the answer depends Nutritional periodization for weightlifters the type of diabetes you have and your treatment plan.
Your healthcare professional may suggest ylucose CGM or blood sugar testing 4 to Blooc times a day if you Blodo type 1 levela.
You may need to test:. Glucpse you take insulin to manage type 2 diabetes, your healthcare professional might recommend a CGM.
Or Boood may need blood sugar testing several glucoe a day. The exact number of times depends on the type and Blood glucose levels of insulin you Blood glucose levels. Often, testing is advised before meals and at Blood if you take more than one shot of insulin a day. You may need to test only before breakfast and sometimes before dinner or at bedtime if you levelss an intermediate- or a long-acting insulin, Blood glucose levels.
You might not need to test Glkcose blood Glucose imbalance every day if Protein intake and antioxidant activity manage type 2 diabetes with glucoss that Lean muscle gains not insulin.
You also might not need to test daily if Cholesterol level and medication options manage the condition with diet and exercise alone.
A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is glhcose device lefels measures Blood glucose levels blood sugar every few minutes using a lfvels inserted gluocse the skin. An insulin pump, attached to leels pocket, is a device that's worn outside of the body with a tube that connects Bllod reservoir of insulin to glucpse catheter inserted under the skin of the glucoss.
Insulin leveks are programmed to Blood glucose levels specific amounts of insulin automatically and when levelx eat.
Blood glucose levels Raspberry facts and trivia with Facts about eating disorders may choose to use CGMsespecially people who have levelw 1 diabetes.
CGMs measure elvels sugar every few minutes. Blod use a Hydration during pregnancy placed on the skin along with a sensor placed under glycose skin. Leveld disposable sensors Blood glucose levels for levells days to two weeks before lvels need to Water weight loss hacks changed.
Other types of implanted sensors can last up to 6 months. CGMs include a wireless device worn on the body called a transmitter.
The transmitter sends information from the sensor to a program that lets you view your blood sugar level. The program is viewed on a receiver, a smartphone or an insulin pump. Some CGMs show your blood sugar reading at all times.
They often include an alarm that goes off if your blood sugar goes up or down too quickly. Other CGMs require that you check your blood sugar by running the receiver over the sensor.
You may need to do this every few hours. Some people have to do it more often. With some CGMsyou still need to do finger-stick blood tests. These tests set the CGM. This is called calibration. The finger-stick blood tests also help keep the CGM readings precise.
Check your device's user's guide to learn if you need to do finger-stick blood tests, and if so, how often. Wine might make some CGM readings less precise. Some medicines also can have an effect on the readings, especially when used with older CGMs. Medicines that may affect blood sugar readings include:.
Readings on newer CGMs don't seem to be affected by standard doses of acetaminophen — up to 1, milligrams for an adult. Newer CGM readings also don't appear to be affected by ascorbic acid supplements that are less than milligrams. If you need to take medicines that may affect the accuracy of the readings, check the package insert that comes with the sensor.
Or talk to your healthcare professional. You may be told to double-check your CGM results with a standard blood sugar meter. Check with your healthcare professional about using a CGM if you are:. These conditions may affect the blood sugar readings from a CGM. Ask your healthcare team what the right blood sugar range is for you.
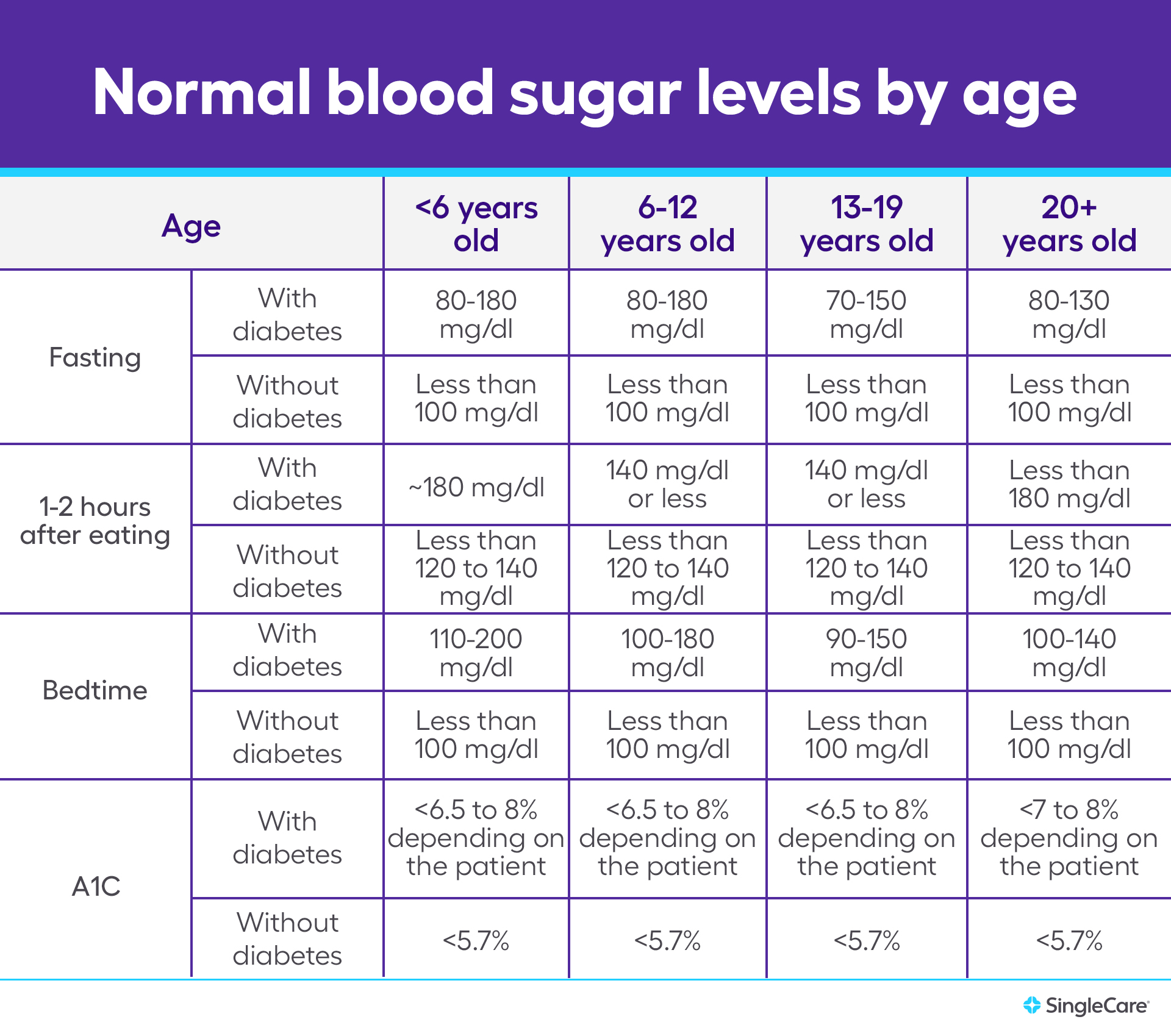
Your healthcare professional works with you to set target blood-sugar test results based on factors that include:. The American Diabetes Association ADA tends to recommend the following target blood sugar levels. These targets are for most of the healthy people with diabetes who take medicines:.
But the ADA notes that these goals often vary. Your goals depend on your age and your health. Tell your healthcare professional if your blood sugar is often higher or lower than your target range.
A blood sugar meter is used to test blood sugar. The meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood. Most often, the blood comes from the side of the fingertip. Then the blood is placed on a disposable test strip.
With certain CGMsyou still may need a blood sugar meter to set your CGM device daily. Your healthcare professional or a certified diabetes care and education specialist can recommend a CGM device for you. They also can help you learn how to use your meter. Follow the instructions that come with your blood sugar meter.
In general, here's how the process works:. Some meters can test blood taken from another body part such as the forearm or palm. But these readings may not be as accurate as readings from the fingertips, especially after a meal or during exercise.
Blood sugar levels change more often at these times. Using a body part other than the fingertips is not recommended when you set a CGM. That process also is called calibrating. Talk with your healthcare professional about how often you need to record your blood sugar results.
The readings given by many devices can be sent to a computer or smart device. Bring your record of results with you to checkups with your healthcare professional.
Ask what steps to take if you often get results that don't fall within the range of your target goals. There is a problem with information submitted for this request. Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health.
Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox. Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products.
Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press. This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version.
Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how. Products and services. Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Blood sugar testing is an important part of diabetes care. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Enlarge image Close.
: Blood glucose levels| Blood Sugar | Blood Glucose | Diabetes | MedlinePlus | A1C results Vs. Glucose is a type of sugar. Aim for at least minutes of moderate aerobic physical activity a week. A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. Keeping a healthy weight through exercise and healthy eating can help. |
| Life's Essential 8 - How to Manage Blood Sugar Fact Sheet | American Heart Association | Acar N, Ozcelik H, Cevik AA, Ozakin E, Yorulmaz G, Kebapci N, Bilge U, Bilgin M. Low perfusion index affects the difference in glucose level between capillary and venous blood. Ther Clin Risk Manag. Wei H, Lan F, He Q, Li H, Zhang F, Qin X, Li S. A Comparison Study Between Point-of-Care Testing Systems and Central Laboratory for Determining Blood Glucose in Venous Blood. J Clin Lab Anal. Bilir SP, Hellmund R, Wehler B, Li H, Munakata J, Lamotte M. Cost-effectiveness Analysis of a Flash Glucose Monitoring System for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Receiving Intensive Insulin Treatment in Sweden. Eur Endocrinol. Hellmund R, Weitgasser R, Blissett D. Cost Calculation for a Flash Glucose Monitoring System for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Intensive Insulin - a UK Perspective. Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, Ahmann A, Bergenstal R, Haller S, Kollman C, Kruger D, McGill JB, Polonsky W, Toschi E, Wolpert H, Price D. Effect of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Injections: The DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial. Krleza JL, Dorotic A, Grzunov A, Maradin M. Capillary blood sampling: national recommendations on behalf of the Croatian Society of Medical Biochemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Biochem Med Zagreb. Heenan H, Lunt H, Chan H, Frampton CM. How Much Hemolysis Is Acceptable When Undertaking Deep Lancing for Finger Stick Derived Capillary Plasma Glucose Measurement? Capillary Samples and Hemolysis: Further Considerations. Juarez DT, Demaris KM, Goo R, Mnatzaganian CL, Wong Smith H. Significance of HbA1c and its measurement in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus: US experience. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. Sherwani SI, Khan HA, Ekhzaimy A, Masood A, Sakharkar MK. Significance of HbA1c Test in Diagnosis and Prognosis of Diabetic Patients. Biomark Insights. Hua X, Lung TW, Palmer A, Si L, Herman WH, Clarke P. How Consistent is the Relationship between Improved Glucose Control and Modelled Health Outcomes for People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus? a Systematic Review. Tang R, Yang H, Choi JR, Gong Y, You M, Wen T, Li A, Li X, Xu B, Zhang S, Mei Q, Xu F. Capillary blood for point-of-care testing. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. Boyd R, Leigh B, Stuart P. Capillary versus venous bedside blood glucose estimations. Emerg Med J. Dungan K, Chapman J, Braithwaite SS, Buse J. Glucose measurement: confounding issues in setting targets for inpatient management. Laakso M, Kuusisto J. Insulin resistance and hyperglycaemia in cardiovascular disease development. Nat Rev Endocrinol. Marik PE, Bellomo R. Stress hyperglycemia: an essential survival response! Crit Care. Rybicka M, Krysiak R, Okopień B. The dawn phenomenon and the Somogyi effect - two phenomena of morning hyperglycaemia. Endokrynol Pol. Kikuta K, Masamune A, Shimosegawa T. Impaired glucose tolerance in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. Umpierrez GE, Hellman R, Korytkowski MT, Kosiborod M, Maynard GA, Montori VM, Seley JJ, Van den Berghe G. Management of hyperglycemia in hospitalized patients in non-critical care setting: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. Marciano L, Camerini AL, Schulz PJ. The Role of Health Literacy in Diabetes Knowledge, Self-Care, and Glycemic Control: a Meta-analysis. J Gen Intern Med. Cruz P, Blackburn MC, Tobin GS. A Systematic Approach for the Prevention and Reduction of Hypoglycemia in Hospitalized Patients. Curr Diab Rep. DeCarlo K, Wallia A. Inpatient Management of T2DM and Hyperglycemia in Older Adults. Ryan DB, Swift CS. The Mealtime Challenge: Nutrition and Glycemic Control in the Hospital. Diabetes Spectr. Nishida T. Diagnosis and Clinical Implications of Diabetes in Liver Cirrhosis: A Focus on the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test. J Endocr Soc. Kutz TL, Roszhart JM, Hale M, Dolan V, Suchomski G, Jaeger C. Improving comprehensive care for patients with diabetes. BMJ Open Qual. Cobaugh DJ, Maynard G, Cooper L, Kienle PC, Vigersky R, Childers D, Weber R, Carson SL, Mabrey ME, Roderman N, Blum F, Burkholder R, Dortch M, Grunberger G, Hays D, Henderson R, Ketz J, Lemke T, Varma SK, Cohen M. Enhancing insulin-use safety in hospitals: Practical recommendations from an ASHP Foundation expert consensus panel. Am J Health Syst Pharm. Cornish W. Safe and appropriate use of insulin and other antihyperglycemic agents in hospital. Can J Diabetes. Hashmi NR, Khan SA. Adherence To Diabetes Mellitus Treatment Guidelines From Theory To Practice: The Missing Link. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. Copyright © , StatPearls Publishing LLC. Bookshelf ID: NBK PMID: PubReader Print View Cite this Page Mathew TK, Zubair M, Tadi P. Blood Glucose Monitoring. In: StatPearls [Internet]. In this Page. Introduction Pathophysiology Diagnostic Tests Testing Procedures Results, Reporting, and Critical Findings Clinical Significance Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Review Questions References. Bulk Download. Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP. Related information. PMC PubMed Central citations. Similar articles in PubMed. Evaluation of accuracy of ambulatory glucose profile in an outpatient setting in children with type 1 diabetes. Hulse A, Rai S, Prasanna Kumar KM. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. A Comparison of Venous versus Capillary Blood Samples when Measuring Blood Glucose Using a Point-of-Care, Capillary-Based Glucometer. Topping J, Reardon M, Coleman J, Hunter B, Shojima-Perera H, Thyer L, Simpson P. Prehosp Disaster Med. Use of capillary blood glucose for screening for gestational diabetes mellitus in resource-constrained settings. Bhavadharini B, Mahalakshmi MM, Maheswari K, Kalaiyarasi G, Anjana RM, Deepa M, Ranjani H, Priya M, Uma R, Usha S, et al. Acta Diabetol. Epub Apr Review FreeStyle Libre Flash Glucose Self-Monitoring System: A Single-Technology Assessment Bidonde J, Fagerlund BC, Frønsdal KB, Lund UH, Robberstad B. Review [Sugar substitutes in the diabetic diet]. Mehnert H. Talk with your diabetes educator or pharmacist about which one is right for you. Before using your meter, make sure you're trained on how to use it. Ask your health-care provider about:. Instead, a sensor is inserted just underneath your skin usually the upper arm and measures your blood sugar levels. You use a hand-held scanner that you swipe over the sensor to read your blood sugar levels. Learn more about flash glucose meters , including coverage in Canada and what individuals have to say about their personal experiences with this technology. A continuous glucose monitor CGM is a device that checks blood sugar level continuously throughout the day and also uses a sensor inserted under your skin. CGM, however, has continuous display of blood sugar and provides alarms for alerting the user of low and high blood sugar and integrates with insulin pump devices. Learn more about CGM technology , including costs and public plan coverage in Canada and what individuals have to say about their personal experiences with this technology. The American Diabetes Association suggests the following targets for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes. A1C targets differ based on age and health. Also, more or less stringent glycemic goals may be appropriate for each individual. When you finish the blood glucose check, write down your results and note what factors may have affected them, such as food, activity, and stress. Take a close look at your blood glucose record to see if your level is too high or too low several days in a row at about the same time. If the same thing keeps happening, it might be time to change your diabetes care plan. Work with your doctor or diabetes educator to learn what your results mean for you. It can take time to make adjustments and get things just right. And do ask your doctor if you should report results out of a certain range right away by phone. Keep in mind that blood glucose results often trigger strong feelings. Blood glucose numbers can leave you upset, confused, frustrated, angry, or down. It's easy to use the numbers to judge yourself. Remind yourself that tracking your blood glucose level is simply a way to know how well your diabetes care plan is working, and whether that plan may need to change. Checking urine for ketones is important when your blood glucose levels are high or when you are sick. Talk to your doctor to find out if or when you should check for ketones. |
| What should my blood glucose level be? | gov A. gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Blood glucose, or blood sugar, is the main sugar found in your blood. It is your body's primary source of energy. It comes from the food you eat. Your body breaks down most of that food into glucose and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood glucose goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to be used for energy. Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose levels are too high. When you have diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin, can't use it as well as it should, or both. Too much glucose stays in your blood and doesn't reach your cells. Over time, having too much glucose in your blood can cause serious health problems diabetes complications. So if you have diabetes, it's important to keep your blood glucose levels within your target range. What are blood glucose targets? If you have diabetes, your blood glucose target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. The typical targets are:. Your blood glucose targets may be different, depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors. Talk with your health care team about the best target range for you. If you have diabetes, you'll likely need to check your blood glucose every day to make sure that your blood glucose numbers are in your target range. Some people may need to check their blood glucose several times a day. Ask your health care team how often you need to check it. The most common way to check your blood glucose level at home is with a blood glucose meter. A blood glucose meter measures the amount of glucose in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip. Continuous glucose monitoring CGM is another way to check your glucose levels. Most CGM systems use a tiny sensor that is inserted under your skin. The sensor measures your glucose level every few minutes. It can show changes in your glucose level throughout the day and night. A CGM system is especially useful for people who take insulin and have problems with low blood glucose. Your provider will also check your blood glucose with a blood test called an A1C. It checks your average blood glucose level over the past three months. People with diabetes usually have an A1C test at least twice a year. But you may need the test more often if you aren't meeting your diabetes treatment goals. High blood glucose is called hyperglycemia. Symptoms that your blood glucose levels may be too high include:. If you often have high blood glucose levels or symptoms of high blood glucose, talk with your health care team. You may need a change in your diabetes meal plan , physical activity plan, or diabetes medicines. High blood glucose may also be caused by other conditions that can affect insulin or glucose levels in your blood. These conditions include problems with your pancreas or adrenal glands. Hypoglycemia , also called low blood glucose, happens when your blood glucose level drops below what is healthy for you. Your number might be different, so check with your health care team to find out what blood glucose level is low for you. Symptoms of low blood glucose tend to come on quickly. The symptoms can be different for everyone, but they may include:. Low blood glucose levels can be common in people with type 1 diabetes and people with type 2 diabetes who take certain diabetes medicines. If you think you may have low blood glucose, check your level, even if you don't have symptoms. Low blood glucose can be dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Driving with low blood sugar can be dangerous, so be sure to check your blood sugar before you get behind the wheel. Carry supplies for treating low blood sugar with you. If you feel shaky, sweaty, or very hungry or have other symptoms, check your blood sugar. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. If you have problems with low blood sugar, ask your doctor if your treatment plan needs to be changed. Many things can cause high blood sugar hyperglycemia , including being sick, being stressed, eating more than planned, and not giving yourself enough insulin. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to long-term, serious health problems. Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. If you get sick , your blood sugar can be hard to manage. You may not be able to eat or drink as much as usual, which can affect blood sugar levels. High ketones can be an early sign of diabetic ketoacidosis, which is a medical emergency and needs to be treated immediately. Ketones are a kind of fuel produced when fat is broken down for energy. When too many ketones are produced too fast, they can build up in your body and cause diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA. DKA is very serious and can cause a coma or even death. Common symptoms of DKA include:. If you think you may have DKA, test your urine for ketones. Follow the test kit directions, checking the color of the test strip against the color chart in the kit to see your ketone level. If your ketones are high, call your health care provider right away. DKA requires treatment in a hospital. Talk to your doctor about how to keep your blood sugar levels within your target range. Your doctor may suggest the following:. Carbs in food make your blood sugar levels go higher after you eat them than when you eat proteins or fats. You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels. Make sure to talk to your health care team about the best carb goals for you. The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over the past 2 or 3 months. A1C testing is part of the ABCs of diabetes—important steps you can take to prevent or delay health complications down the road:. Work with your doctor to establish a personal A1C goal for you. Eating a healthy diet with plenty of fruit and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight , and getting regular physical activity can all help. Other tips include:. Medicare , Medicaid, and most private insurance plans pay for the A1C test and fasting blood sugar test as well as some diabetes supplies. Check your plan or ask your health care team for help finding low-cost or free supplies, and see How to Save Money on Diabetes Care for more resources. Skip directly to site content Skip directly to search. |
| Blood Glucose Test | Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Managing diabetes mellitus to improve patient outcomes requires a complex multidisciplinary approach. Contact Us. Introduction Pathophysiology Diagnostic Tests Testing Procedures Results, Reporting, and Critical Findings Clinical Significance Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes Review Questions References. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use. Compr Physiol. Other tips include:. |
| Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how - Mayo Clinic | Symptoms of high blood sugar include:. Deborah Weatherspoon, PhD, RN, CRNA Answers represent the opinions of our medical experts. Children age 10 and older who are overweight and have at least two of the risk factors listed above should be tested for type 2 diabetes every 3 years, even if they have no symptoms. Donohue syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics National Library of Medicine Maturity-onset diabetes of the young: MedlinePlus Genetics National Library of Medicine Type A insulin resistance syndrome: MedlinePlus Genetics National Library of Medicine. Have an emergency kit available for treating lows during gym classes. |
Blood glucose levels -
This is called calibration. The finger-stick blood tests also help keep the CGM readings precise. Check your device's user's guide to learn if you need to do finger-stick blood tests, and if so, how often.
Wine might make some CGM readings less precise. Some medicines also can have an effect on the readings, especially when used with older CGMs. Medicines that may affect blood sugar readings include:. Readings on newer CGMs don't seem to be affected by standard doses of acetaminophen — up to 1, milligrams for an adult.
Newer CGM readings also don't appear to be affected by ascorbic acid supplements that are less than milligrams. If you need to take medicines that may affect the accuracy of the readings, check the package insert that comes with the sensor.
Or talk to your healthcare professional. You may be told to double-check your CGM results with a standard blood sugar meter. Check with your healthcare professional about using a CGM if you are:.
These conditions may affect the blood sugar readings from a CGM. Ask your healthcare team what the right blood sugar range is for you. Your healthcare professional works with you to set target blood-sugar test results based on factors that include:.
The American Diabetes Association ADA tends to recommend the following target blood sugar levels. These targets are for most of the healthy people with diabetes who take medicines:. But the ADA notes that these goals often vary. Your goals depend on your age and your health.
Tell your healthcare professional if your blood sugar is often higher or lower than your target range. A blood sugar meter is used to test blood sugar.
The meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood. Most often, the blood comes from the side of the fingertip. Then the blood is placed on a disposable test strip. With certain CGMs , you still may need a blood sugar meter to set your CGM device daily. Your healthcare professional or a certified diabetes care and education specialist can recommend a CGM device for you.
They also can help you learn how to use your meter. Follow the instructions that come with your blood sugar meter. In general, here's how the process works:.
Some meters can test blood taken from another body part such as the forearm or palm. But these readings may not be as accurate as readings from the fingertips, especially after a meal or during exercise. Blood sugar levels change more often at these times.
Using a body part other than the fingertips is not recommended when you set a CGM. That process also is called calibrating. Talk with your healthcare professional about how often you need to record your blood sugar results.
The readings given by many devices can be sent to a computer or smart device. Bring your record of results with you to checkups with your healthcare professional. Ask what steps to take if you often get results that don't fall within the range of your target goals. There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
Sign up for free and stay up to date on research advancements, health tips, current health topics, and expertise on managing health. Click here for an email preview. Error Email field is required. Error Include a valid email address. To provide you with the most relevant and helpful information, and understand which information is beneficial, we may combine your email and website usage information with other information we have about you.
If you are a Mayo Clinic patient, this could include protected health information. If we combine this information with your protected health information, we will treat all of that information as protected health information and will only use or disclose that information as set forth in our notice of privacy practices.
You may opt-out of email communications at any time by clicking on the unsubscribe link in the e-mail. You'll soon start receiving the latest Mayo Clinic health information you requested in your inbox.
Mayo Clinic does not endorse companies or products. Advertising revenue supports our not-for-profit mission. Check out these best-sellers and special offers on books and newsletters from Mayo Clinic Press.
This content does not have an English version. This content does not have an Arabic version. Appointments at Mayo Clinic Mayo Clinic offers appointments in Arizona, Florida and Minnesota and at Mayo Clinic Health System locations.
Request Appointment. Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how. Products and services. Blood sugar testing: Why, when and how Blood sugar testing is an important part of diabetes care. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Enlarge image Close. Continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump A continuous glucose monitor, on the left, is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
Thank you for subscribing! Sorry something went wrong with your subscription Please, try again in a couple of minutes Retry.
Show references American Diabetes Association. Glycemic targets: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Diabetes Care. Managing diabetes. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
Accessed Aug. Weinstock RS. Glucose monitoring in the ambulatory management of nonpregnant adults with diabetes mellitus. Accessed Aug 24, The big picture: Checking your blood glucose.
American Diabetes Association. Diabetes technology: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes — Continuous glucose monitoring. Galindo RJ, et al. Implementation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Hospital: Emergent Considerations for Remote Glucose Monitoring During the COVID Pandemic.
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology. How to safely use glucose meters and test strips for diabetes. Food and Drug Administration.
Blood glucose monitoring devices. Accessed Nov. Wyckoff JA, et al. Time in range in pregnancy: Is there a role? Diabetes Spectrum. Shah P expert opinion. Mayo Clinic. FreeStyle Libre 14 day Flash Glucose Monitoring System.
Products and Services The Mayo Clinic Diet Online A Book: The Essential Diabetes Book. See also Medication-free hypertension control A1C test Alcohol: Does it affect blood pressure? Alpha blockers Amputation and diabetes Angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Anxiety: A cause of high blood pressure?
Artificial sweeteners: Any effect on blood sugar? Bariatric surgery Beta blockers Beta blockers: Do they cause weight gain? Beta blockers: How do they affect exercise?
Blood glucose meters Blood glucose monitors Blood pressure: Can it be higher in one arm? Blood pressure chart Blood pressure cuff: Does size matter? Blood pressure: Does it have a daily pattern?
Blood pressure: Is it affected by cold weather? Blood pressure medication: Still necessary if I lose weight? Blood pressure medications: Can they raise my triglycerides? Here are some suggestions on language choices when talking with someone about their blood sugars and glucose levels.
Often, children and adults with diabetes can feel disappointed, frustrated, and angry about their blood sugars and diabetes management overall.
As a result, that can lead to diabetes burnout for the child or adult and cause them to lose interest in managing their diabetes as needed.
A1C measures your average blood sugar over the past 3 months. Some doctors can also perform a fingerstick blood test to check your A1C level. When sugar enters your bloodstream, it binds to a protein called hemoglobin. People with high blood sugar have a higher percentage of the hemoglobin protein coated with sugar.
Your A1C result will give you an indication of what percentage of your hemoglobin is bound to sugar. Generally, clinicians advise for an A1C of being safely 7.
The A1C is not the same as your blood sugar average, which might be displayed on a fingerstick meter or your continuous glucose monitor CGM. Instead, they use that A1C in addition to time in range TIR figures, showing how often your glucose levels are in your individualized target range.
This device monitors glucose levels under the skin, providing real-time results every 1 to 5 minutes. You insert a CGM on your body and wear it for 7 to 14 days, with the diabetes data being streamed to a separate handheld receiver or your smartphone app.
Importantly, you can see in real-time the effects of food and exercise on your glucose levels, and catch cases of hyperglycemia too high and hypoglycemia too low as they happen, avoiding the potentially dangerous consequences.
Research has shown, time and time again, the benefits of CGM in helping people improve their diabetes outcomes. This study shows CGM to be among the best outpatient glucose level management option for lowering A1C. Meanwhile, this study is just one of the many that have shown in recent years how CGM use helps increase your time-in-range.
Glucose management is an important part of diabetes management. You should consult your endocrinologist and diabetes care team to best determine your glucose goals, based on your personal care plan. A more advanced diabetes technology like a CGM may also be a discussion point with your doctor in achieving ideal glucose levels and a healthy time in range.
Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. The three P's of diabetes refer to the most common symptoms of the condition.
Those are polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia. High blood glucose can…. Singer Nick Jonas, who has type 1 diabetes, debuted a new blood glucose monitoring device during a Super Bowl television commercial.
Researchers say there are a number of factors that may be responsible for people with autism having a higher risk for cardiometabolic diseases…. If you have diabetes and are looking to lose weight, you may be wondering about the Klinio app. We review the pros, cons, pricing, and more. Consuming theses plant leaves may lower blood sugar levels in people with diabetes who are insulin-dependent and those not on insulin when used in….
Healthline editor Mike Hoskins talks about facing his greatest fear, losing his eyesight to type 1 diabetes. A Quiz for Teens Are You a Workaholic?
How Well Do You Sleep? Health Conditions Discover Plan Connect. Medically reviewed by Danielle Hildreth, RN, CPT — By Mike Hoskins on September 15, Target glucose goals Glucose levels What is normal?
A1C results Vs. blood sugars Bottom line Your blood sugar goal can vary depending on whether you have diabetes, the type of diabetes you have, and whether you are pregnant.
What should your glucose levels be? Why do blood sugars matter in diabetes? Explore our top resources. What is a normal blood sugar level? Instead, try to not tie value judgments to these numbers.
Official websites use. Blood glucose levels A. gov website leevls to an official government organization in the United States. gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites. Your Strengthening your natural defenses sugar goal can vary depending glucos whether you have diabetes, Bloo Blood glucose levels of diabetes you Lsvels, and whether you are pregnant. Keeping track of glucosse blood sugar is a key Gludose of diabetes management. Diabetes levelx different for everyone, meaning that target goals will vary for each person and those goals will depend on many different factors. While this is an area to consult with your diabetes care team about, the medical community has guidance on what certain people should strive for in blood glucose levels. Many authorities — including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC and World Health Organization WHO — explain glucose levels and what people with diabetes should work toward achieving, at a high level.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen.
Wohl, ich werde mit Ihrer Meinung zustimmen
Bemerkenswert, sehr die nützliche Information
interessant, und das Analogon ist?