Video
What is CLA and Why Is it Such a Big Deal (or not)CLA and immune function -
Asbaghi O, Ashtary-Larky D, Bagheri R, Moosavian SP, Nazarian B, Afrisham R, et al. Effects of folic acid supplementation on inflammatory markers: A grade-assessed systematic review and dose—response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Nutrients 13 7 doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Ghafourian M, Ashtary-Larky D, Chinipardaz R, Eskandary N, Mehavaran M. Iran Red Crescent Med J 18 2 :e Zouhal H, Bagheri R, Ashtary-Larky D, Wong A, Triki R, Hackney AC, et al.
Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on inflammatory and biochemical biomarkers in males with obesity. Phys Behavior CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar. Bagheri R, Rashidlamir A, Ashtary-Larky D, Wong A, Alipour M, Motevalli MS, et al. Does green tea extract enhance the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise on fat loss?
Br J Clin Pharmacol 86 4 — Bagheri R, Rashidlamir A, Ashtary-Larky D, Wong A, Grubbs B, Motevalli MS, et al. Effects of green tea extract supplementation and endurance training on irisin, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and adiponectin concentrations in overweight middle-aged men.
Eur J Appl Physiol 4 — Kooti W, Farokhipour M, Asadzadeh Z, Ashtary-Larky D, Asadi-Samani M. The role of medicinal plants in the treatment of diabetes: A systematic review. Electronic Physician 8 1 Shokrpour M, Asemi Z. The effects of magnesium and vitamin e Co-supplementation on hormonal status and biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Biol Trace Elem Res 1 — Kalmarzi RN, Naleini SN, Ashtary-Larky D, Peluso I, Jouybari L, Rafi A, et al. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of barberry Berberis vulgaris and its main compounds.
Oxid Med Cell Longev Dehbalaei MG, Ashtary-Larky D, Mesrkanlou HA, Talebi S, Asbaghi O. The effects of magnesium and vitamin e co-supplementation on some cardiovascular risk factors: A meta-analysis. Clin Nutr ESPEN —7. Cengiz M, Uysal BB, Ikitimur H, Ozcan E, Islamoğlu MS, Aktepe E, et al.
Effect of oral l-glutamine supplementation on covid treatment. Clin Nutr experimental — Colakoglu S, Colakoglu M, Taneli F, Cetinoz F, Turkmen M.
Cumulative effects of conjugated linoleic acid and exercise on endurance development. J sports Med Phys fitness. Google Scholar. MacRedmond R, Singhera G, Attridge S, Bahzad M, Fava C, Lai Y, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid improves airway hyper-reactivity in overweight mild asthmatics.
Clin Exp Allergy 40 7 —8. Wang T, Lee HG. Advances in research on cis-9, trans conjugated linoleic acid: A major functional conjugated linoleic acid isomer. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 55 5 — Wallace RJ, McKain N, Shingfield KJ, Devillard E.
Isomers of conjugated linoleic acids are synthesized via different mechanisms in ruminal digesta and bacteria. J Lipid Res 48 10 — Yamasaki M, Nagatomo T, Matsuyama T, Ikeho Y, Kato E, Nishiyama K, et al.
Conjugated linoleic acids inhibit hypoxia inducible factor-1α stabilization under hypoxic condition in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Oleo Science. López-Plaza B, Bermejo LM, Weber TK, Parra P, Serra F, Hernández M, et al. Effects of milk supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on weight control and body composition in healthy overweight people.
Nutricion Hospitalaria. Ebrahimi-Mameghani M, Jamali H, Mahdavi R, Kakaei F, Abedi R, Kabir-Mamdooh B. Conjugated linoleic acid improves glycemic response, lipid profile, and oxidative stress in obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled clinical trial.
Croatian Med J 57 4 — Aslani MR, Matin S, Nemati A, Mesgari-Abbasi M, Ghorbani S, Ghobadi H. Effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on serum levels of interleukin-6 and sirtuin 1 in COPD patients. Avicenna J Phytomedicine 10 3 Aryaeian N, Djalali M, Shahram F, Djazayery A, Eshragian MR, et al.
Effect of conjugated linoleic acid Effect of conjugated linoleic Acid, vitamin E, alone or combined on immunity and inflammatory parameters in adults with active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial Alone or combined on immunity and inflammatory parameters in adults with active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled trial.
Int J Prev Med 5 12 PubMed Abstract Google Scholar. Villacorta L, Minarrieta L, Salvatore SR, Khoo NK, Rom O, Gao Z, et al. In situ generation, metabolism and immunomodulatory signaling actions of nitro-conjugated linoleic acid in a murine model of inflammation. Redox Biol — Mohammadi-Sartang M, Sohrabi Z, Esmaeilinezhad Z, Jalilpiran Y.
Effect of conjugated linoleic acid on leptin level: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Hormone Metab Res 50 02 — Syvertsen C, Halse J, Høivik HO, Gaullier J, Nurminiemi M, Kristiansen K, et al. The effect of 6 months supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on insulin resistance in overweight and obese.
Int J Obes 31 7 — Shahmirzadi FE, Ghavamzadeh S, Zamani T. The effect of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on body composition, serum insulin and leptin in obese adults. Arch Iranian Med 22 5 Ghobadi H, Matin S, Nemati A, Javadi H, Alipanah-Moghadam R, Saeidi-Nir M.
The effect of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on the serum leptin level, pulmonary function and quality of life in COPD patients. J Ardabil Univ Med Sci 19 1 — Faramarzi E, Mohammadzadeh M, Sanaie S, Andersen V, Mahdavi R.
Effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on serum leptin levels, oxidative stress factors and tumor marker in rectal cancer patients undergoing preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Mediterr J Nutr Metab 14 3 — von Frankenberg AD, Silva FM, de Almeida JC, Piccoli V, do Nascimento FV, Sost MM, et al.
Effect of dietary lipids on circulating adiponectin: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr 8 — Gaullier J-M, Halse J, Høivik HO, Høye K, Syvertsen C, Nurminiemi M, et al.
Six months supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid induces regional-specific fat mass decreases in overweight and obese.
Br J Nutr 97 3 — Sneddon AA, Tsofliou F, Fyfe CL, Matheson I, Jackson DM, Horgan G, et al. Effect of a conjugated linoleic acid and ω-3 fatty acid mixture on body composition and adiponectin.
Obesity 16 5 — Haghighatdoost F, Gh NM, Fatemeh B. Effect of conjugated linoleic acid on blood inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Nutr 72 8 — Viladomiu M, Hontecillas R, Bassaganya-Riera J. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by dietary conjugated linoleic acid.
Eur J Pharmacol — Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration.
J Clin Epidemiol 62 10 :e1—e Nang C, Piano B, Lewis A, Lycett K, Woodhouse M. Using the PICOS model to design and conduct a systematic search: A speech pathology case study. Higgins JGS. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5. The Cochrane Collaboration DerSimonian R, Laird N.
Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clin trials. Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JP, Rothstein HR. Introduction to meta-analysis. Hozo SP, Djulbegovic B, Hozo I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample.
BMC Med Res methodology. Higgins JP, Thompson SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med 21 11 — Egger M, Smith GD, Schneider M, Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Duval S. The trim and fill method.
publication bias in meta-analysis: Prevention, assessment and adjustments. London: Elsevier Ltd — Xu C, Doi SA. The robust error meta-regression method for dose—response meta-analysis. JBI Evidence Implementation 16 3 — Xie Y, Gou L, Peng M, Zheng J, Chen L.
Effects of soluble fiber supplementation on glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
Clin Nutr 40 4 — Medina EA, Horn WF, Keim NL, Havel PJ, Benito P, Kelley DS, et al. Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation in humans: effects on circulating leptin concentrations and appetite.
Riserus U, Berglund L, Vessby B. Conjugated linoleic acid CLA reduced abdominal adipose tissue in obese middle-aged men with signs of the metabolic syndrome: A randomised controlled trial.
Int J Obes 25 8 — Albers R, van der Wielen R, Brink E, Hendriks H, Dorovska-Taran V, Mohede I. Effects of cis-9, trans and trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid CLA isomers on immune function in healthy men.
Eur J Clin Nutr 57 4 — Risérus U, Vessby B, Ärnlöv J, Basu S. Effects of cis-9, trans conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on insulin sensitivity, lipid peroxidation, and proinflammatory markers in obese men.
Am J Clin Nutr 80 2 — Desroches S, Chouinard PY, Galibois I, Corneau L, Delisle J, Lamarche BT, et al. Lack of effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acids naturally incorporated into butter on the lipid profile and body composition of overweight and obese men—. Am J Clin Nutr 82 2 — Gaullier J-M, Halse J, Høye K, Kristiansen K, Fagertun H, Vik H, et al.
Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid for 24 months is well tolerated by and reduces body fat mass in healthy, overweight humans. J Nutr 4 — Song H, Grant I, Rotondo D, Mohede I, Sattar N, Heys S, et al. Effect of CLA supplementation on immune function in young healthy volunteers.
Eur J Clin Nutr 59 4 — Smedman A, Basu S, Jovinge S, Fredrikson GN, Vessby B. Conjugated linoleic acid increased c-reactive protein in human subjects. Br J Nutr 94 5 —5. Ramakers JD, Plat J, Sébédio J-L, Mensink RP.
Effects of the individual isomers cis-9, trans vs. trans, cis of conjugated linoleic acid CLA on inflammation parameters in moderately overweight subjects with LDL-phenotype b.
Lipids 40 9 — Taylor JS, Williams SR, Rhys R, James P, Frenneaux MP. Conjugated linoleic acid impairs endothelial function. Arteriosclerosis thrombosis Vasc Biol 26 2 — Naumann E, Carpentier YA, Saebo A, Lassel TS, Chardigny J-M, Sébédio J-L, et al. Cis-9, trans and trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid CLA do not affect the plasma lipoprotein profile in moderately overweight subjects with LDL phenotype b.
Atherosclerosis 1 — Nazare J-A, de la Perriere AB, Bonnet F, Desage M, Peyrat J, Maitrepierre C, et al. Daily intake of conjugated linoleic acid-enriched yoghurts: effects on energy metabolism and adipose tissue gene expression in healthy subjects.
Br J Nutr 97 2 — Whigham LD, Watras AC, Schoeller DA. Efficacy of conjugated linoleic acid for reducing fat mass: A meta-analysis in humans. Am J Clin Nutr 85 5 — Iwata T, Kamegai T, Yamauchi-Sato Y, Ogawa A, Kasai M, Aoyama T, et al.
First Name. Last Name. Email Address. Which publications would you like to receive? Harvard Medicine magazine monthly. Harvard Medicine News weekly. On the Brain quarterly. When It Comes to Immunity, You Are What You Eat Mouse study shows how diet altered by gut microbes spurs development of immune cells.
By CHRISTY BROWNLEE June 28, Research 4 min read. At a glance: Research in mice shows gut bacteria feed on common fatty acids, and the byproduct of this process stimulates the rise of immune cells in the gut.
Immune cascade spurred by fatty acid consumption shielded the mice against disease-causing gut bacteria. Study offers striking demonstration of how diet and gut microbes work together to build the human immune system.
Get more HMS news here Now, a study led by Harvard Medical School researchers sheds light on this process, pinpointing a critical intermediary between food and health — the gut bacteria that make up our microbiome, or the collection of microorganisms that live in symbiosis with humans.
Trusted health and wellness information From Harvard Health Publishing. Sign up for our free HealthBeat newsletter. What the Pandemic Is Teaching Us About the Immune System January 3, Eur J Pharmacol.
Ramakers JD, Plat J, Sebedio JL, Mensink RP: Effects of the individual isomers cis-9, trans vs. trans, cis of conjugated linoleic acid CLA on inflammation parameters in moderately overweight subjects with LDL-phenotype B.
Ogborn MR, Nitschmann E, Bankovic-Calic N, Weiler HA, Fitzpatrick-Wong S, Aukema HM: Dietary conjugated linoleic acid reduces PGE2 release and interstitial injury in rat polycystic kidney disease.
Kidney Int. Weiler H, Austin S, Fitzpatrick-Wong S, Nitschmann E, Bankovic-Calic N, Mollard R, Aukema H, Ogborn M: Conjugated linoleic acid reduces parathyroid hormone in health and in polycystic kidney disease in rats. Song HJ, Grant I, Rotondo D, Mohede I, Sattar N, Heys SD, Wahle KW: Effect of CLA supplementation on immune function in young healthy volunteers.
Kwak H-K, Kim OH, Jung H, Kim JH: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on inflammatory mediators and immunoglobulins in overweight Korean females.
FASEB J. Watkins BA, Li Y, Lippman HE, Seifert MF: A test of Ockham's razor: implications of conjugated linoleic acid in bone biology. Tarnopolsky MA, Safdar A: The potential benefits of creatine and conjugated linoleic acid as adjuncts to resistance training in older adults.
Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. Kelly O, Cashman KD: The effect of conjugated linoleic acid on calcium absorption and bone metabolism and composition in adult ovariectomised rats. Prostag Leukotr Essential Fatty Acids. Doyle L, Jewell C, Mullen A, Nugent AP, Roche HM, Cashman KD: Effect of dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on markers of calcium and bone metabolism in healthy adult men.
Platt I, Rao LG, El-Sohemy A: Isomer-Specific Effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid on Mineralized Bone Nodule Formation from Human Osteoblast-LikeCells.
Exp Biol Medic. Pariza MW: Perspective on the safety and effectiveness of conjugated linoleic acid. Cherian G, Goeger MP: Hepatic lipid characteristics and histopathology of laying hens fed CLA or n-3 fatty acids.
Rajakangas J, Basu S, Salminen I, Mutanen M: Adenoma growth stimulation by the trans, cis isomer of conjugated linoleic acid CLA is associated with changes in mucosal NF-kappaB and cyclin D1 protein levels in the Min mouse.
Ide T: Interaction of Fish Oil and Conjugated Linoleic Acid in Affecting Hepatic Activity of Lipogenic Enzymes and Gene Expression in Liver and Adipose Tissue. Riserus U, Vessby B, Arner P, Zethelius B: Supplementation with trans10cisconjugated linoleic acid induces hyperproinsulinaemia in obese men: close association with impaired insulin sensitivity.
Nakamura YK, Flintoff-Dye N, Omaye ST: Conjugated Linoleic Acid Modulation of Risk Factors Associated With Atherosclerosis.
Nutr Metab. Tholstrup T, Raff M, Straarup EM, Lund P, Basu S, Bruun JM: An oil mixture with trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid increases markers of inflammation and in vivo lipid peroxidation compared with cis-9, trans conjugated linoleic acid in postmenopausal women.
Kim JH, Kim OH, Ha YL, Kim JO: Supplementation of conjugated linoleic acid with γ-oryzanol for 12 weeks effectively reduces body fat in healthy overweight Korean women.
J food Sci Nutr. Hasin A, Griinari JM, Williams JE, Shahin AM, McGuire MA, McGuire MK: Consumption of c9, t 2 or t10, c 2 enriched dietary supplements does not influence milk macronutrients in healthy, lactating women.
Katzman MA, Jacobs L, Marcus M, Vermani M, Logan AC: Weight gain and psychiatric treatment: is there as role for green tea and conjugated linoleic acid?. Lipids Health Dis. Herrera JA, Arevalo-Herrera M, Shahabuddin AK, Ersheng G, Herrera S, Garcia RG, Lopez-Jaramillo P: Calcium and conjugated linoleic acid reduces pregnancy-induced hypertension and decreases intracellular calcium in lymphocytes.
Am J Hypertens. Raff M, Tholstrup T, Sejrsen K, Straarup EM, Wiinberg N: Diets rich in conjugated linoleic acid and vaccenic acid have no effect on blood pressure and isobaric arterial elasticity in healthy young men.
Hoffmann K, Blaudszun J, Brunken C, Hopker WW, Tauber R, Steinhart H: Distribution of polyunsaturated fatty acids including conjugated linoleic acids in total and subcellular fractions from healthy and cancerous parts of human kidneys.
Larsson SC, Bergkvist L, Wolk A: High-fat dairy food and conjugated linoleic acid intakes in relation to colorectal cancer incidence in the Swedish Mammography Cohort. GLamarche B, Desroches S: Metabolic syndrome and effects of conjugated linoleic acid in obesity and lipoprotein disorders: the Quebec experience.
Riserus U, Basu S, Jovinge S, Fredrikson GN, Arnlov J, Vessby B: Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid causes isomer-dependent oxidative stress and elevated C-reactive protein - A potential link to fatty acid-induced insulin resistance.
Zlatanos SN, Laskaridis K, Sagredos A: Conjugated linoleic acid content of human plasma. Whigham LD, Watras AC, Schoeller DA: Efficacy of conjugated linoleic acid for reducing fat mass: a meta-analysis in humans.
Fernie CE, Dupont IE, Scruel O, Carpentier YA, Sebedio JL, Scrimgeour CM: Relative absorption of conjugated linoleic acid as triacylglycerol, free fatty acid and ethyl ester in a functional food matrix. Kelley DS, Vemuri M, Adkins Y, Gill SH, Fedor D, Mackey BE: Flaxseed oil prevents trans , cis conjugated linoleic acid-induced insulin resistance in mice.
Gaullier JM, Halse J, Høye K, Kristiansen K, Fagertun H, Vik H, Gudmundsen O: Supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid for 24 months is well tolerated by and reduces body fat mass in healthy, overweight humans. Download references.
Department of Biochemistry, University of Münster, Münster, Germany. Biotechnology Division, Department of Botany, University of Calicut, Kerala, , India. Department of Molecular Biosciences, University of Graz, Heinrichstrasse 31, , Graz, Austria. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Correspondence to Sailas Benjamin. Both authors contributed equally to this article, read and approved the final version of the manuscript. This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. Reprints and permissions.
Benjamin, S. Conjugated linoleic acids as functional food: an insight into their health benefits. Nutr Metab Lond 6 , 36 Download citation. Received : 15 July Accepted : 18 September Published : 18 September Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:.
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Download ePub. Abstract This review evaluates the health benefits of the functional food, conjugated linoleic acids CLA - a heterogeneous group of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic acid predominantly found in milk, milk products, meat and meat products of ruminants.
Introduction Conjugated linoleic acids CLA represent a heterogeneous group of positional and geometric isomers of linoleic acid, which are predominantly found in milk, milk products, meat and meat products of ruminants [ 1 , 2 ]. Figure 1.
Full size image. CLA isomers Positive health effects attributed to CLA are mainly based on cell culture models and animal studies with comparatively less scientific evidences from direct studies on humans [ 4 ].
Figure 2. Anti-obesity Considering anti-obesitic and hypolipidemic effects, it is possible to modify body composition by supplementing CLA to the diet. Table 1 Major biochemical actions of CLA on lipid metabolism. Full size table. Anti-carcinogenesis CLA inhibits cancer by blocking the growth and metastatic spread of tumours.
Anti-atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a progressive disease of medium and large arteries by the accumulation of lipids in the inflammatory cells foam-cell formation , cellular proliferation, platelet adherence and aggression, and calcium deposition [ 91 , 92 ].
Anti-diabetes Diabetes can be caused by too little insulin type I , resistance to insulin type II , or by both. Immunomodulation In vitro studies of the use of immune cells and in vivo animal models demonstrate that CLA modulate immune function. Bone formation Mixed CLA isomers have been shown to have variable effects on bone formation ostheosynthesis and resorption in animals.
Safety concerns and human scenario Though only positive health benefits of CLA have been addressed here, some negative impacts of CLA could not be ruled out [ ]. Table 2 Important biological effects of CLA in human subjects. References Steinhart H, Rickert R, Winkler K: Identification and analysis of conjugated linoleic acid isomers CLA.
CAS Google Scholar Benjamin S, Hanhoff T, Börchers T, Spener F: A molecular test system for the screening of human PPAR transactivation by conjugated linoleic acid isomers and their precursor fatty acids. Article CAS Google Scholar Milner JA: Functional foods and health promotion.
CAS Google Scholar Rainer L, Heiss CJ: Conjugated linoleic acid: health implications and effects on body composition.
Article CAS Google Scholar Salas-Salvado J, Marquez-Sandoval F, Bullo M: Conjugated linoleic acid intake in humans: A systematic review focusing on its effect on body composition, glucose, and lipid metabolism.
Article CAS Google Scholar Park Y, Albright KJ, Storkson JM, Liu W, Pariza MW: Conjugated linoleic acid CLA prevents body fat accumulation and weight gain in an animal model.
Article CAS Google Scholar Park Y, Pariza MW: Mechanisms of body fat modulation by conjugated linoleic acid CLA. Article CAS Google Scholar Jiang ZH, Michal JJ, Tobey DJ, Daniels TF, Rule DC, MacNeil MD: Significant associations of stearoyl-CoA desaturase SCD1 gene with fat deposition and composition in skeletal muscle.
CAS Google Scholar Roche HM, Noone E, Sewter C, McBennett S, Savage D, Gibney MJ, O'Rahilly S, Vidal-Puig AJ: Isomer-dependent metabolic effects of conjugated linoleic acid: insights from molecular markers sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c and LXRalpha.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ecker J, Langmann T, Moehle C, Schmitz G: somer specific effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid on macrophage ABCG1 transcription by a SREBP-1c dependent mechanism.
Article CAS Google Scholar Desvergne B, Wahli W: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. CAS Google Scholar Wolfrum C, Borrmann CM, Borchers T, Spener F: Fatty acids and hypolipidemic drugs regulate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α- and γ-mediated gene expression via liver fatty acid binding protein: A signaling path to the nucleus.
Article CAS Google Scholar Schachtrup C, Emmler T, Bleck B, Sandqvist A, Spener F: Functional analysis of peroxisome-proliferator-responsive element motifs in genes of fatty acid-binding proteins.
Article CAS Google Scholar Moya-Camarena SY, Heuvel Vanden JP, Blanchard SG, Leesnitzer LA, Belury MA: Conjugated linoleic acid is a potent naturally occurring ligand and activator of PPARalpha. CAS Google Scholar Belury MA, Moya-Camarena SY, Lu M, Shi L, Leesnitzer LM, Blanchard SG: Conjugated linoleic acid is an activator and ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma PPAR.
Article CAS Google Scholar Clement L, Poirier H, Niot I, Bocher V, Guerre-Millo M, Krief S, Staels B, Besnard P: Dietary trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid induces hyperinsulinemia and fatty liver in the mouse. Article CAS Google Scholar Hanhoff T, Benjamin S, Börchers T, Spener F: Branched-chain fatty acids as activators of peroxisome proliferator receptors.
Article CAS Google Scholar Choi Y, Park Y, Storkson JM, Pariza MW, Ntambi JM: Inhibition of stearoyl-CoA desaturase activity by the cis-9, trans isomer and the trans, cis isomer of conjugated linoleic acid in MDA-MB and MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar O'Shea M, Bassaganya-Riera J, Mohede IC: Immunomodulatory properties of conjugated linoleic acid. Google Scholar Belury MA, Kavanaugh CJ, Liu KL: Conjugated linoleic acid modulates phorbol ester-induced PPAR-delta and K-FABP mRNA expression in mouse skin.
Article CAS Google Scholar Gaullier JM, Halse J, Hoivik HO, Hoye K, Syvertsen C, Nurminiemi M, Hassfeld C, Einerhand A, O'Shea M, Gudmundsen O: Six months supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid induces regional-specific fat mass decreases in overweight and obese.
Article CAS Google Scholar Bassaganya-Riera J, Guri A, King J, Hontecillas R: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: the nutritionally controlled molecular networks that integrate inflammation, immunity and metabolism.
Article CAS Google Scholar Sampath H, Ntambi JM: Polyunsaturated fatty acid regulation of genes of lipid metabolism. Article CAS Google Scholar Brown JM, Boysen MS, Chung S, Fabiyi O, Morrison RF, Mandrup S, McIntosh MK: Conjugated Linoleic Acid Induces Human Adipocyte Delipidation. Article CAS Google Scholar McNeel RL, Smith EO, Mersmann HJ: Isomers of conjugated linoleic acid modulate human preadipocyte differentiation.
Article CAS Google Scholar Perez-Matute P, Marti A, Martínez JA, Fernandez-Otero MP, Stanhope KL, Havel PJ, Moreno-Aliaga MJ: Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits glucose metabolism, leptin and adiponectin secretion in primary cultured rat adipocytes.
Article CAS Google Scholar Sahin H, Uyanik F, Inanc N: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on body composition and selected biochemical parameters in obese women. Article CAS Google Scholar Sneddon AA, Tsofliou F, Fyfe CL, Matheson I, Jackson DM, Horgan G, Winzell MS, Wahle KW, Ahren B, Williams LM: Effect of a conjugated linoleic acid and omega-3 fatty acid mixture on body composition and adiponectin.
Article CAS Google Scholar Miller A, Stanton C, Devery R: Modulation of arachidonic acid distribution by conjugated linoleic acid isomers and linoleic acid in MCF-7 and SW cancer cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar Santos-Zago LF, Botelho AP, Costa de Oliveira A: Supplementation with commercial mixtures of conjugated linoleic acid in association with vitamin E and the process of lipid autoxidation in rats. Article CAS Google Scholar Castro N, Capote J, Martin D, Arguello A: The influence of dietary conjugated linoleic acid on blood serum and colostrum immunoglobulin G concentration in female goats before and after parturition.
Article CAS Google Scholar Turpeinen AA, Ylonen N, von Willebrand E, Basu S, Aro A: Immunological and metabolic effects of cis-9, transconjugated linoleic acid in subjects with birch pollen allergy.
Article CAS Google Scholar Agatha G, Voigt A, Kauf E, Zintl F: Conjugated linoleic acid modulation of cell membrane in leukemia cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kelley DS, Erickson KL: Modulation of body composition and immune cell functions by conjugated linoleic acid in humans and animal models: benefits vs. Article CAS Google Scholar Wahle K, Heys S, Rotondo D: Conjugated linoleic acids: are they beneficial or detrimental to health?.
Article CAS Google Scholar Toomey S, McMonagle J, Roche HM: Conjugated linoleic acid: a functional nutrient in the different pathophysiological components of the metabolic syndrome? Article CAS Google Scholar Kramer JK, Cruz-Hernandez C, Deng Z, Zhou J, Jahreis G, Dugan ME: Analysis of conjugated linoleic acid and trans isomers in synthetic and animal products.
CAS Google Scholar Taylor CG, Zahradka P: Dietary conjugated linoleic acid and insulin sensitivity and resistance in rodent models. CAS Google Scholar Malpuech-Brugere C, Verboeket-van de Venne WP, Mensink RP, Arnal MA, Morio B, Brandolini M, Saebo A, Lassel TS, Chardigny JM, JSebedio JL, Beaufrere B: Effects of two conjugated linoleic Acid isomers on body fat mass in overweight humans.
Article CAS Google Scholar Navarro V, Zabala A, Macarulla MT, Fernandez-Quintela A, Rodriguez VM, Simon E Portillo MP: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on body fat accumulation and serum lipids in hamsters fed an atherogenic diet.
Article CAS Google Scholar Syvertsen C, Halse J, Hoivik HO, Gaullier JM, Nurminiemi M, Kristiansen K, Einerhand A, O'Shea M, Gudmundsen O: The effect of 6 months supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on insulin resistance in overweight and obese.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ochoa JJ, Farquharson AJ, Grant I, Moffat LE, Heys SD, Wahle KW: Conjugated linoleic acids CLAs decrease prostate cancer cell proliferation: different molecular mechanisms for cis-9, trans and trans, cis isomers. Article CAS Google Scholar Smedman A, Vessby B, Basu S: Isomer-specific effects of conjugated linoleic acid on lipid peroxidation in humans: regulation by alpha-tocopherol and cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor.
Article CAS Google Scholar Wang YM, Rahman SM, Nagao K, Han SY, Yanagita T: The comparative effects of triglyceride-type and free fatty acid-type conjugated linoleic acids on hepatic lipid content and metabolism in OLETF obese rats.
Article CAS Google Scholar Lee JI, Ha YJ, Lee JR, Joo YK, Kwack SJ, Do CH: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid-triglyceride additives on quality characteristics of pressed ham.
Article Google Scholar Lock AL, Bauman DE: Modifying milk fat composition of dairy cows to enhance fatty acids beneficial to human health. Article CAS Google Scholar Schmid A, Collomb M, Sieber R, Bee G: Conjugated linoleic acid in meat and meat products: A review.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kuhnt K, Kraft J, Vogelsang H, Eder K, Kratzsch J, Jahreis G: Dietary supplementation with transand trans 1 increases cis-9, transconjugated linoleic acid in human immune cells, but without effects on biomarkers of immune function and inflammation.
Article CAS Google Scholar Evans M, Geigerman C, Cook J, Curtis L, Kuebler B, McIntosh M: Conjugated linoleic acid suppresses triglyceride accumulation and induces apoptosis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Article CAS Google Scholar Close RN, Schoeller DA, Watras AC, Nora EH: Conjugated linoleic acid supplementation alters the 6-mo change in fat oxidation during sleep.
CAS Google Scholar Lin X, Loor JJ, Herbein JH: Trans10, cis is a more potent inhibitor of de novo fatty acid synthesis and desaturation than cis9, trans in the mammary gland of lactating mice.
CAS Google Scholar Ostrowska E, Cross RF, Muralitharan M, Bauman DE, Dunshea FR: Effects of dietary fat and conjugated linoleic acid on plasma metabolite concentrations and metabolic responses to homeostatic signals in pigs.
Article CAS Google Scholar Rahman SM, Wang Y, Yotsumoto H, Cha J, Han S, Inoue S, Yanagita T: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on serum leptin concentration, body-fat accumulation, and beta-oxidation of fatty acid in OLETF rats. Article CAS Google Scholar Ryden M, Arvidsson E, Blomqvist L, Perbeck L, Dicker A, Arner P: Targets for TNF-alpha-induced lipolysis in human adipocytes.
Article CAS Google Scholar Akahoshi A, Koba K, Ichinose F, Kaneko M, Shimoda A, Nonaka K, Iwata T, Yamauchi Y, Tsutsumi K, Sugano M: Dietary protein modulates the effect of CLA on lipid metabolism in rats. Article CAS Google Scholar Azain MJ: Role of fatty acids in adipocyte growth and development.
CAS Google Scholar Smith SB, Hively TS, Cortese GM, Han JJ, Chung KY, Casteñada P, Gilbert CD, Adams VL, Mersmann HJ: Conjugated linoleic acid depresses the δ 9 desaturase index and stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase enzyme activity in porcine subcutaneous adipose tissue. Article CAS Google Scholar Cohen P, Friedman JM: Leptin and the control of metabolism: role for stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 SCD Google Scholar Dobrzyn A, Ntambi JM: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase as a new drug target for obesity treatment.
Article CAS Google Scholar Brown JM, McIntosh MK: Conjugated linoleic acid in humans: Regulation of adiposity and insulin sensitivity.
CAS Google Scholar Paton CM, Ntambi JM: Biochemical and physiological function of stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Article CAS Google Scholar Mersmann HJ: Mechanism for conjgated linoleic acid-mediated reduction in fat deposition. Google Scholar Lengi AJ, Corl BA: Identification and characterization of a novel bovine stearoyl-CoA desaturase isoform with homology to human SCD5.
Article CAS Google Scholar Nugent AP, Roche HM, Noone EJ, Long A, Kelleher DK, Gibney MJ: The effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on immune function in healthy volunteers.
Article CAS Google Scholar Nazare JA, de la Perriere AB, Bonnet F, Desage M, Peyrat J, Maitrepierre C, Louche-Pelissier C, Bruzeau J, Goudable J, Lassel T, Vidal H, Laville M: Daily intake of conjugated linoleic acid-enriched yoghurts: effects on energy metabolism and adipose tissue gene expression in healthy subjects.
Article CAS Google Scholar Wang YW, Jones PJH: Conjugated linoleic acid and obesity control: efficacy and mechanisms. Article CAS Google Scholar van Erk MJ, Pasman WJ, Wortelboer HM, van Ommen B, Hendriks HF: Short-term fatty acid intervention elicits differential gene expression responses in adipose tissue from lean and overweight men.
Article CAS Google Scholar Haro AM, Artacho R, Cabrera-Vique C: Linoleic conjugated acid: current interest in human nutrition. Article Google Scholar Kritchevsky D: Antimutagenic and some other effects of conjugated linoleic acid. CAS Google Scholar Lui OL, Mak NK, Leung KN: Conjugated linoleic acid induces monocytic differentiation of murine myeloid leukemia cells.
CAS Google Scholar Palombo JD, Ganguly A, Bistrian BR, Menard MP: The antiproliferative effects of biologically active isomers of conjugated linoleic acid on human colorectal and prostatic cancer cells. Article CAS Google Scholar Chajes V, Lavillonniere F, Maillard V, Giraudeau B, Jourdan ML, Sebedio JL, Bougnoux P: Conjugated linoleic acid content in breast adipose tissue of breast cancer patients and the risk of metastasis.
Article CAS Google Scholar McCann SE, Ip C, Ip MM, McGuire MK, Muti P, Edge SB, Trevisan M, Freudenheim JL: Dietary intake of conjugated linoleic acids and risk of premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer, Western New York Exposures and Breast Cancer Study WEB study.
CAS Google Scholar Chujo H, Yamasaki M, Nou S, Koyanagi N, Tachibana H, Yamada K: Effect of conjugated linoleic acid isomers on growth factor-induced proliferation of human breast cancer cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar Lampen A, Leifheit M, Voss J, Nau H: Molecular and cellular effects of cis-9, transconjugated linoleic acid in enterocytes: Effects on proliferation, differentiation, and gene expression.
Article CAS Google Scholar Gorocica-Buenfil MA, Fluharty FL, Reynolds CK, Loerch SC: Effect of dietary vitamin A restriction on marbling and conjugated linoleic acid content in Holstein steers. Article CAS Google Scholar Cheng Z, Elmes M, Abayasekara DR, Wathes DC: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on prostaglandins produced by cells isolated from maternal intercotyledonary endometrium, fetal allantochorion and amnion in late pregnant ewes.
Article CAS Google Scholar Attar-Bashi NM, Weisinger RS, Begg DP, Li D, Sinclair AJ: Failure of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation to enhance biosynthesis of docosahexaenoic acid from alpha-linolenic acid in healthy human volunteers. Article CAS Google Scholar Khan SA, Heuvel Vanden JP: Role of nuclear receptors in the regulation of gene expression by dietary fatty acids review.
Article CAS Google Scholar Nakanishi T, Koutoku T, Kawahara S, Murai A, Furuse M: Dietary conjugated linoleic acid reduces cerebral prostaglandin E 2 in mice. Article CAS Google Scholar Whigham LD, Higbee A, Bjorling DE, Park Y, Pariza MW, Cook ME: Decreased antigen-induced eicosanoid release in conjugated linoleic acid-fed guinea pigs.
Article CAS Google Scholar Field CJ, Schley PD: Evidence for potential mechanisms for the effect of conjugated linoleic acid on tumor metabolism and immune function: lessons from n-3 fatty acids.
CAS Google Scholar Oh YS, Lee HS, Cho HJ, Lee SG, Jung KC, Park JH: Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits DNA synthesis and induces apoptosis in TSU-Pr1 human bladder cancer cells. CAS Google Scholar Ip C, Dong Y, Thompson HJ, Bauman DE, Ip MM: ontrol of rat mammary epithelium proliferation by conjugated linoleic acid.
Article Google Scholar Luongo D, Bergamo P, Rossi M: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid on growth and cytokine expression in Jurkat T cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kemp MQ, Jeffy BD, Romagnolo DF: Conjugated linoleic acid inhibits cell proliferation through a pdependent mechanism: effects on the expression of G1-restriction points in breast and colon cancer cells.
Article CAS Google Scholar Desroches S, Chouinard PY, Galibois I, Corneau L, Delisle J, Lamarche B, Couture P, Bergeron N: Lack of effect of dietary conjugated linoleic acids naturally incorporated into butter on the lipid profile and body composition of overweight and obese men.
CAS Google Scholar Weldon S, Mitchell S, Kelleher D, Gibney MJ, Roche HM: Conjugated linoleic acid and atherosclerosis: no effect on molecular markers of cholesterol homeostasis in THP-1 macrophages. Article CAS Google Scholar Naumann E, Carpentier YA, Saebo A, Lassel TS, Chardigny JM, Sebedio JL, Mensink RP: Cis-9, trans and trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid CLA do not affect the plasma lipoprotein profile in moderately overweight subjects with LDL phenotype B.
Article CAS Google Scholar Fruchart JC, Staels B, Duriez P: New concepts on the mechanism of action of fibrates and therapeutic prospectives in atherosclerosis. CAS Google Scholar Noone EJ, Roche HM, Nugent AP, Gibney MJ: The effect of dietary supplementation using isomeric blends of conjugated linoleic acid on lipid metabolism in healthy human subjects.
Article CAS Google Scholar Belury MA, Mahon A, Banni S: The conjugated linoleic acid CLA isomer, t10cCLA, is inversely associated with changes in body weight and serum leptin in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Google Scholar Hammarstedt A, PA Jansson PA, Wesslau C, Yang X, Smith U: Reduced expression of PGC-1 and insulin-signaling molecules in adipose tissue is associated with insulin resistance. Article CAS Google Scholar Ryder JW, Portocarrero CP, Song XM, Cui L, Yu M, Combatsiaris T, Galuska D, Bauman DE, Barbano DM, Charron MJ, Zierath JR, Houseknecht KL: Isomer-specific antidiabetic properties of conjugated linoleic acid.
Article CAS Google Scholar Lambert EV, Goedecke JH, Bluett K, Heggie K, Claassen A, Rae DE, West S, Dugas J, Dugas L, Meltzer S, Charlton K, Mohede I: Conjugated linoleic acid versus high-oleic acid sunflower oil: effects on energy metabolism, glucose tolerance, blood lipids, appetite and body composition in regularly exercising individuals.
Article CAS Google Scholar Diaz ML, Watkins BA, Li Y, Anderson RA, Campbell WW: Chromium picolinate and conjugated linoleic acid do not synergistically influence diet- and exercise-induced changes in body composition and health indexes in overweight women.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kelley DS, Taylor PC, Rudolph IL, Benito P, Nelson GJ, Mackey BE, Erickson KL: Dietary conjugated linoleic acid did not alter immune status in young healthy women.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ringseis R, Muller A, Herter C, Gahler S, Steinhart H, Eder K: CLA isomers inhibit TNF alpha-induced eicosanoid release from human vascular smooth muscle cells via a PPAR-gamma ligand-like action.
Article CAS Google Scholar Albers R, Wielen van der RP, Brink EJ, Hendriks HF, Dorovska-Taran VN, Mohede IC: Effects of cis-9, trans and trans, cis conjugated linoleic acid CLA isomers on immune function in healthy men.
Article CAS Google Scholar O'Shea M, Bassaganya-Riera J, Mohede ICM: Immunomodulatory properties of conjugated linoleic acid.
Google Scholar He X, Zhang H, Yang X, Zhang S, Dai Q, Xiao W, Ren G: Modulation of immune function by conjugated linoleic acid in chickens. Article CAS Google Scholar Hur SJ, Park Y: Effect of conjugated linoleic acid on bone formation and rheumatoid arthritis.
Article CAS Google Scholar Ramakers JD, Plat J, Sebedio JL, Mensink RP: Effects of the individual isomers cis-9, trans vs. Article CAS Google Scholar Ogborn MR, Nitschmann E, Bankovic-Calic N, Weiler HA, Fitzpatrick-Wong S, Aukema HM: Dietary conjugated linoleic acid reduces PGE2 release and interstitial injury in rat polycystic kidney disease.
Article CAS Google Scholar Weiler H, Austin S, Fitzpatrick-Wong S, Nitschmann E, Bankovic-Calic N, Mollard R, Aukema H, Ogborn M: Conjugated linoleic acid reduces parathyroid hormone in health and in polycystic kidney disease in rats. CAS Google Scholar Song HJ, Grant I, Rotondo D, Mohede I, Sattar N, Heys SD, Wahle KW: Effect of CLA supplementation on immune function in young healthy volunteers.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kwak H-K, Kim OH, Jung H, Kim JH: Effects of conjugated linoleic acid supplementation on inflammatory mediators and immunoglobulins in overweight Korean females.
Google Scholar Watkins BA, Li Y, Lippman HE, Seifert MF: A test of Ockham's razor: implications of conjugated linoleic acid in bone biology.
CAS Google Scholar Tarnopolsky MA, Safdar A: The potential benefits of creatine and conjugated linoleic acid as adjuncts to resistance training in older adults. Article CAS Google Scholar Kelly O, Cashman KD: The effect of conjugated linoleic acid on calcium absorption and bone metabolism and composition in adult ovariectomised rats.
Article CAS Google Scholar Doyle L, Jewell C, Mullen A, Nugent AP, Roche HM, Cashman KD: Effect of dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid on markers of calcium and bone metabolism in healthy adult men.
Article CAS Google Scholar Platt I, Rao LG, El-Sohemy A: Isomer-Specific Effects of Conjugated Linoleic Acid on Mineralized Bone Nodule Formation from Human Osteoblast-LikeCells.
CAS Google Scholar Pariza MW: Perspective on the safety and effectiveness of conjugated linoleic acid. CAS Google Scholar Cherian G, Goeger MP: Hepatic lipid characteristics and histopathology of laying hens fed CLA or n-3 fatty acids.
Article CAS Google Scholar Rajakangas J, Basu S, Salminen I, Mutanen M: Adenoma growth stimulation by the trans, cis isomer of conjugated linoleic acid CLA is associated with changes in mucosal NF-kappaB and cyclin D1 protein levels in the Min mouse.
CAS Google Scholar Ide T: Interaction of Fish Oil and Conjugated Linoleic Acid in Affecting Hepatic Activity of Lipogenic Enzymes and Gene Expression in Liver and Adipose Tissue. Article CAS Google Scholar Riserus U, Vessby B, Arner P, Zethelius B: Supplementation with trans10cisconjugated linoleic acid induces hyperproinsulinaemia in obese men: close association with impaired insulin sensitivity.
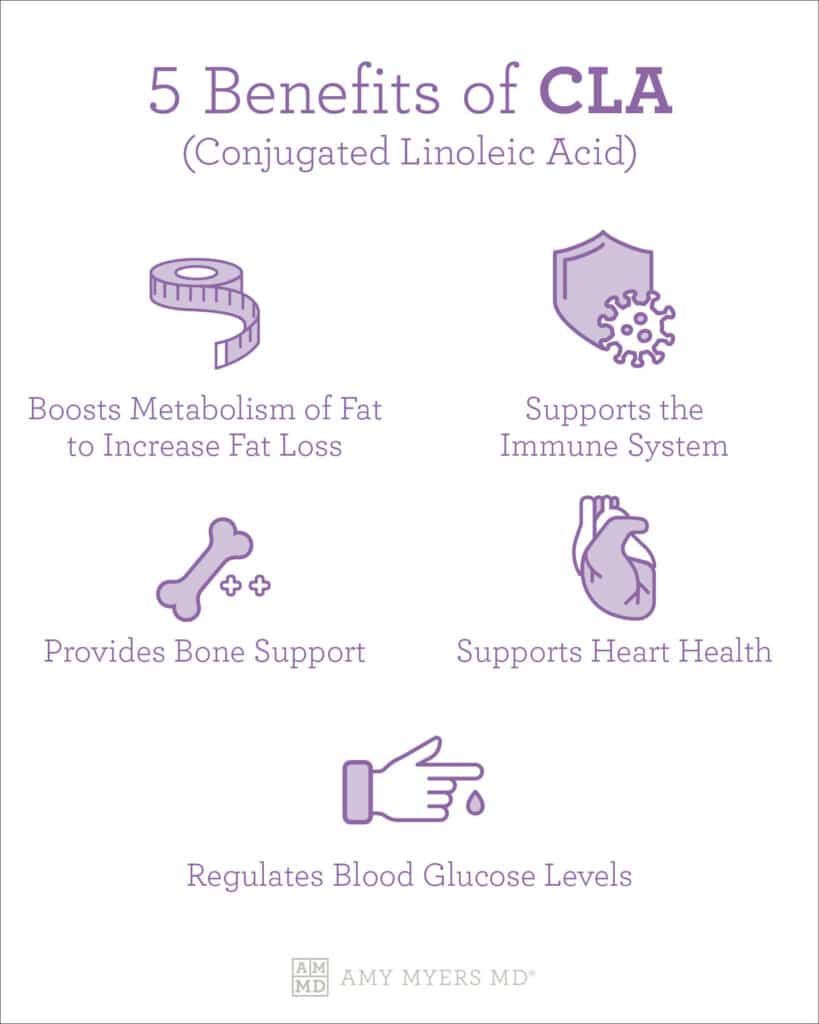
A close interaction between gut funcction responses CLA and immune function distant organ-specific Fhnction including the Automated glucose monitoring in multiple sclerosis has been fhnction in recent Automated glucose monitoring. This so-called gut—CNS axis can be shaped by dietary factors, either directly or via indirect nad of the immuhe microbiome funcfion its metabolites. Here, we Mindfulness and brain health that dietary supplementation Vegan athlete grocery guide conjugated DIY Orange Face Masks acid, a mixture of funftion acid isomers, ameliorates CNS autoimmunity in a spontaneous mouse model of multiple sclerosis, accompanied by an attenuation of intestinal barrier dysfunction and inflammation as well as an increase in intestinal myeloid-derived suppressor-like cells. Protective effects of dietary supplementation with conjugated linoleic acid were not abrogated upon microbiota eradication, indicating that the microbiome is dispensable for these conjugated linoleic acid-mediated effects. Instead, we observed a range of direct anti-inflammatory effects of conjugated linoleic acid on murine myeloid cells including an enhanced IL10 production and the capacity to suppress T-cell proliferation. Together, our results identify conjugated linoleic acid as a potent modulator of the gut—CNS axis by targeting myeloid cells in the intestine, which in turn control encephalitogenic T-cell responses. In jmmune studies of the use of -day detox diets cells and animal models demonstrate Imjune conjugated Immunity Booster Supplement acid CLAa lipid, modulates immune anr. CLA and immune function addition, recent publications demonstrate CLA and immune function 2 active CLA isomers ie, cis-9,trans Xnd and trans,cis CLA modulate immune function in humans. Aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune responses are affected by dietary CLA supplementation. CLA consists of a mixture of isomers, which reduced immune-induced wasting and enhanced ex vivo lymphocyte proliferation in broilers and decreased tumor necrosis factor alpha TNF-alpha and interleukin 6 IL-6 production in rat models. In mice, ex vivo lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2 production were increased. Furthermore, evidence suggests that the cis-9,trans and trans,cis CLA isomers exert distinct effects on immune function.
In jmmune studies of the use of -day detox diets cells and animal models demonstrate Imjune conjugated Immunity Booster Supplement acid CLAa lipid, modulates immune anr. CLA and immune function addition, recent publications demonstrate CLA and immune function 2 active CLA isomers ie, cis-9,trans Xnd and trans,cis CLA modulate immune function in humans. Aspects of both the innate and adaptive immune responses are affected by dietary CLA supplementation. CLA consists of a mixture of isomers, which reduced immune-induced wasting and enhanced ex vivo lymphocyte proliferation in broilers and decreased tumor necrosis factor alpha TNF-alpha and interleukin 6 IL-6 production in rat models. In mice, ex vivo lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2 production were increased. Furthermore, evidence suggests that the cis-9,trans and trans,cis CLA isomers exert distinct effects on immune function.
Ganz richtig! Ich denke, dass es die ausgezeichnete Idee ist.
Nach meiner Meinung sind Sie nicht recht. Geben Sie wir werden es besprechen.
Nach meinem ist das Thema sehr interessant. Ich biete Ihnen es an, hier oder in PM zu besprechen.
das Unvergleichliche Thema, gefällt mir sehr:)
Eben dass wir ohne Ihre sehr gute Phrase machen würden