
Video
Jim Stoppani on Fighting Muscle Fatigue with CarnoSyn® Beta-AlanineBeta-alanine and muscular fatigue -
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. Thai Airways International said on Wednesday it entered into an agreement with Boeing and GE Aerospace for a firm order of 45 wide-body jets to expand its fleet, with deliveries starting in Skip to main content.
Exclusive news, data and analytics for financial market professionals Learn more about Refinitiv. By Anne Harding. NEW YORK Reuters Health - Older people taking a sports nutrition supplement favored by Olympic athletes show substantial increases in their ability to withstand fatigue, new research shows.
Jeffrey R. Stout of the University of Oklahoma in Norman, who led the study, told Reuters Health. Stout and his colleagues found that men and women given a low dose of beta-alanine for 90 days were able to exercise nearly 30 percent more intensely before becoming fatigued. Beta-alanine increases the amount of carnosine in the muscles, which is key to helping sustain a neutral pH in muscle tissue.
When people exercise to fatigue, the muscles become more and more acidic lactic acid buildup is a byproduct of this process, but not entirely responsible for it , and carnosine is believed to help buffer against this acidity, allowing people to do more without "feeling the burn.
Older people tend to have less carnosine in their muscles, Stout explained, largely because they don't eat as much meat as younger people. Taking carnosine supplements is useless, Stout said, because the body breaks the protein down immediately.
But taking beta alanine, an amino acid that is a component of carnosine, triggers the production of carnosine in muscle tissue, he added. Stout and his team had previously demonstrated that beta alanine helped young people increase their exercise capacity by 12 percent to 15 percent.
Blood lactate concentrations at rest and prior to the sustained fatigued hold were not significantly different Table 3. The key findings from the present study are: a no effects of BA supplementation on isometric force production capacity in either fresh or fatigued skeletal muscle, b the confirmation of our previous findings Hannah et al.
These data are the first to comprehensively examine the effect of BA supplementation on voluntary and electrically evoked contractile properties of in-vivo fatigued human skeletal muscle. During both fresh and fatigued conditions, BA supplementation has no effect on voluntary isometric force production including maximal and explosive force variables.
Voluntary force peak data are consistent with the lack of change in electrically evoked peak force responses noted during twitch and octet contractions under both fresh and fatigued conditions.
There were similar neural drive responses during both MVICs and explosive contractions pre- and post-supplementation in fresh and fatigued muscle. The current findings in fresh muscle are in-line with the previous findings Hannah et al.
The current research in fresh muscle is in line with the previous in-vivo research Hannah et al. One potential limitation of both studies is that neither measured intracellular carnosine concentrations directly.
That said there are many studies displaying increased muscle carnosine following BA supplementation, almost without exception, on an individual-by-individual basis Harris et al.
Thus, we are confident in assuming that a significant increase in muscle carnosine content would have occurred with the BA supplementation protocol implemented in the present study.
The lack of an effect of BA on TPT and force production following increased carnosine concentrations is interesting. Based on the previous in-vitro studies in chemically skinned muscle fibres from frogs Lamont and Miller , mechanically skinned rat muscle fibres Dutka and Lamb and type I and type II human skeletal muscle fibres Dutka et al.
Furthermore, the current investigation reported no alteration to potentiated twitch contractions. It might be that the differences between these in-vitro data where carnosine can be indirectly elevated to a consistent level and the data from the current study reflect differences in the magnitude of intramuscular carnosine elevation, which we, unfortunately, cannot confirm in the current study.
It is also important to note that in-vitro research is conducted outside the normal intracellular environment, and importantly, a number of protocols include the use of free magnesium, an inhibitor of skeletal muscle ryanodine receptors Laver et al.
Furthermore, during in-vitro studies solutions are added to control pH levels allowing examination of the direct effect of carnosine, although this is important, these investigations have yet to examine the influence of carnosine concentration and varying pH levels.
The current body of in-vivo research is completely separate from the in-vitro data, which might make it unrealistic to expect similar findings between research designs.
Increasing muscle carnosine concentrations with 28 days of BA supplementation resulted in a shorter HRT relative to equivalent PLA times in fresh and fatigued skeletal muscle during both resting and potentiated twitch contractions.
These are in contrast with HRT in fresh and fatigued resting and potentiated twitch contractions following PLA supplementation. As such, the decline in skeletal muscle HRT following 28 days of BA supplementation shown in the current investigation may be associated with alterations to skeletal muscle cross-bridge kinetics.
As such, care needs to be taken over the interpretation of these findings. There could also be an indirect mechanism to explain the beneficial effects displayed within the current investigation in regards to muscle relaxation.
Although the mechanism for reducing skeletal muscle relaxation time following BA supplementation remains unclear, such an outcome might be beneficial to exercise performance, especially during short, repeated muscle contractions where muscle relaxation comprises an important proportion of total energy consumption Bergstrom and Hultman During concentric contractions, improvement of muscle recovery time has been shown to be critical to the amount of post-shortening force decrease Edman Reducing relaxation rates may improve muscle power output and exercise performance.
These findings are particularly important for activities where fast, repetitive contractions, and relaxations occur with no period of rest. It would be of benefit to repeat these data in elite athletes where small changes to HRT might be advantageous. Equally we might speculate that benefits may occur in clinical populations such as Brody disease where SERCA1 activity is significantly reduced; Guglielmi et al.
Within the current investigation, isometric knee extensor fatigue hold times were not significantly influenced by BA or PLA supplementation, in direct contrast to our previous findings that showed a Blood lactate sampled from the finger 5 min post-exercise is indicative of the lower extremity lactate release Comeau et al.
To greater understand the relationship between skeletal muscle HRT, increased carnosine concentrations and muscle fatigue, further investigations implementing a dynamic fatiguing protocol are required, since contractile slowing i. The current investigation showed that 28 days of BA supplementation enhanced muscle relaxation time in both fresh and fatigued skeletal muscle.
Whilst this finding is of interest, it remains unclear as to whether it would be sufficient to result in improved exercise performance, particularly in the absence of any changes to the force—frequency relationship, peak force production, or contraction time.
The mechanism for the ergogenic effect on muscle relaxation following increased carnosine content remains unclear. Ahlborg B, Bergstrom J, Ekelund LG et al Muscle metabolism during isometric exercise performed at constant force. J Appl Physiol CAS PubMed Google Scholar.
Allen DG, Lannergren J, Westerblad H Muscle cell function during prolonged activity: Cellular mechanisms of fatigue. Exp Physiol — Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar.
Allen DG, Lamb GD, Westerblad H Skeletal muscle fatigue: Cellular mechanisms. Physiol Rev Baran EJ Metal complexes of carnosine.
Biochem CAS Google Scholar. Batrukova MA, Rubtsov AM Histidine-containing dipeptides as endogenous regulators of the activity of sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-release channels. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Biomembranes Article CAS Google Scholar.
Berchtold MW, Brinkmeier H, Müntener M Calcium ion in skeletal muscle: its crucial role for muscle function plasticity and disease. Bergström M, Hultman E Energy cost and fatigue during intermittent electrical stimulation of human skeletal muscle.
PubMed Google Scholar. Comeau MJ, Adams TM, Church JB, Graves MM, Lawson PM Prediction of lower extremity lactate levels in exercising muscle utilizing upper extremity sampling sites. JEP Google Scholar. Decombaz J, Beaumont M, Vuichoud J, Bouisset F, Stellingwerff T Effect of slow-release beta-alanine tablets on absorption kinetics and paresthesia.
Amino Acids Dutka TL, Lamb GD Effect of carnosine on excitation-contraction coupling in mechanically-skinned rat skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil Dux L Muscle relaxation and sarcoplasmic reticulum function in different muscle types. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol Edman KA Mechanical deactivation induced by active shortening in isolated muscle fibres of the frog.
J Physiol Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar. Everaert I, Stegen S, Vanheel B, Taes Y, Derave W Effect of beta-alanine and carnosine supplementation on muscle contractility in mice. Med Sci Sports Exerc Gillis JM Relaxation of vertebrate skeletal muscle: a synthesis of the biochemical and physiological approaches.
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Reviews on Bioenergetics Guglielmi V, Voermans NC, Gualndi F et al Fourty-four years of brody disease: it is time to review. Genetic Syndromes Gene Therapy Hannah R, Minshull C, Buckthorpe MW, Folland JP Explosive neuromuscular performance of males versus females.
Exp Physiol Article PubMed Google Scholar. Hannah R, Stannard RL, Minshull C, Artioli GG, Harris RC, Sale C β-Alanine supplementation enhances human skeletal muscle relaxation speed but not force production capacity.
Harris RC, Tallon MJ, Dunnett M et al The absorption of orally supplied beta-alanine and its effect on muscle carnosine synthesis in human vastus lateralis. Hill CA, Harris RC, Kim HJ et al Influence of beta-alanine supplementation on skeletal muscle carnosine concentrations and high intensity cycling capacity.
Hobson RM, Saunders B, Ball G, Harris RC, Sale C Effects of beta-alanine supplementation on exercise performance: a meta-analysis. Jones DA, de Ruiter CJ, de Haan A Change in contractile properties of human muscle in relationship to the loss of power and slowing of relaxation seen with fatigue.
Lakens D Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t -tests and ANOVAs. Front Psychol Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar.
Lamont C, Miller DJ Calcium sensitizing action of carnosine and other endogenous imidazoles in chemically skinned striated muscle. Biophys J J Gen Physiol Little SC, Tikunova SB, Norman C, Swartz DR, Davis JP Measurement of calcium dissociation rates from troponin C in rigor skeletal myofibrils.
Front Physiol Muntener M, Kaser L, Weber J, Berchtold MW Increase of skeletal muscle relaxation speed by direct injection of parvalbumin cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol R Preacher KJ, Kelley K Effect size measures for mediation models: quantitative strategies for communicating indirect effects.
Psychol Methods Sale C, Saunders B, Harris RC Effect of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle carnosine concentrations and exercise performance.
Sale C, Hill CA, Ponte J, Harris RC Beta-Alanine Supplementation Improves Isometric Endurance of the Knee Extensor Muscles. J Int Soc Sports Nutr Sale C, Artioli GG, Gualano B, Saunders B, Hobson RM, Harris RC Carnosine: from exercise performance to health. Proc Natl Acad Sci Article Google Scholar.
J Electromyogr Kinesiol Westerblad H Acidosis is not a significant cause of skeletal muscle fatigue. Med Sci Sports Exerc 48 11 — Westerblad H, Lännergren J, Allen DG Slowed relaxation in fatigued skeletal muscle fibers of xenopus and mouse.
J Gen Physiol 3 Zaloga GP, Roberts PR, Nelson TE Carnosine: a novel peptide regulator of intracellular calcium and contractility in cardiac muscle. New Horiz Download references. All experiments were performed at Nottingham Trent University Department of Sport Science.
The study was designed as part of a wider research project by RLJ, CTB, RH, WF and CS. Acquisition and analysis of data for the work by RLJ, JD, and BM; data interpretation and manuscript preparation were undertaken by RLJ, CTB, JD, BM, WF, RH, and CS.
All authors approved the final version of the paper. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
All persons designated as authors qualify for authorship, and all those who qualify for authorship are listed. Musculoskeletal Physiology Research Group, Sport, Health and Performance Enhancement SHAPE Research Centre, School of Science and Technology, Nottingham Trent University, Erasmus Darwin Building, Clifton Lane, Clifton, Nottingham, NG11 8NS, UK.
Norwich Medical School, University of East Anglia, Norwich, Norfolk, UK. Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, Norfolk, UK. You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar.
Correspondence to Craig Sale. This study was funded by and completed at Nottingham Trent University. The β-alanine and maltodextrin supplements for this study were provided free of charge from Natural Alternatives International San Marcos, California , although no additional funding was provided. Roger Harris is an independent paid consultant of NAI and is named as an inventor on patents held by NAI.
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4. Reprints and permissions. Jones, R. et al. β-alanine supplementation improves in-vivo fresh and fatigued skeletal muscle relaxation speed.
Eur J Appl Physiol , — Download citation. Received : 17 October Accepted : 11 February Published : 27 March Issue Date : May Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. Download PDF. Methods Twenty-three males completed two experimental sessions, pre- and post- 28 day supplementation with 6.
Results BA supplementation had no effect on voluntary or electrically evoked isometric force production, or twitch electromechanical delay and time-to-peak tension. Conclusions The mechanism for reduced HRT in fresh and fatigued skeletal muscle following BA supplementation is unclear. Trial registration The trial is registered with Clinicaltrials.
gov, ID number NCT Comparison of sustained-release and rapid-release β-alanine formulations on changes in skeletal muscle carnosine and histidine content and isometric performance following a muscle-damaging protocol Article Open access 12 July Beta-alanine supplementation improves isometric, but not isotonic or isokinetic strength endurance in recreationally strength-trained young men Article 15 June Effects of beta-alanine supplementation on muscle function during recovery from resistance exercise in young adults Article 09 January Use our pre-submission checklist Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction Carnosine β-alanyl- L -histidine is a cytoplasmic dipeptide, synthesised from β-alanine BA and histidine and is found in high concentrations in skeletal muscle.
Methods Ethical approval All participants were fully informed of any risks and discomforts associated with the study. Participants Twenty-four male participants were allocated to the two supplement groups [placebo PLA or BA] on the basis of maximal voluntary isometric force MVIF values recorded during familiarisation.
Study design This was a double-blind, placebo-controlled study with all raw data analyses, exclusions, and statistical analyses undertaken blind to the supplement group. Supplementation Participants were provided with 6.
Experimental setup The experimental setup for the determination of isometric knee extension force, EMG, and electrical stimulation in our laboratory has been described in detail previously Hannah et al. Electromyography EMG signals were recorded from the superficial quadriceps: m. Electrical stimulation Knee extensor contractile properties were assessed using a constant current variable voltage stimulator DS7AH; Digitimer, Welwyn Garden City, UK.
Protocol and measurements Identification of force and EMG onset for all evoked and voluntary contractions was conducted manually using visual identification Hannah et al.
Resting twitches A single electrical impulse was delivered with stepwise increments in the current to evoke a twitch response, until a plateau in the amplitude of twitch force and compound muscle action potentials M-waves was reached.
Octet contractions Octet contractions 8 impulses at Hz were evoked via supramaximal stimulation of the femoral nerve. Force—frequency relationship Tetanic contractions were elicited via submaximal percutaneous electrical stimulation of the quadricep to examine the force—frequency relationship Lamont and Miller Blood samples Fingertip capillary blood samples were taken at rest, immediately prior to and 5 min following the sustained fatigue hold.
Results Electrically evoked contractile properties Resting twitches Supplementation did not significantly influence twitch force, EMD, or TPT Table 1. Table 1 Electrically femoral nerve evoked force responses, time-to-peak tension TPT , and electromechanical delay EMD of β-alanine BA and placebo PLA groups pre- and post-supplementation, in fresh and fatigued muscle.
Full size image. Table 2 Force—frequency relationship assessed during submaximal percutaneous stimulation, and characteristics of the force—frequency and force—EMG relationships of BA and PLA groups in fresh and fatigued muscle, pre- and post- supplementation Full size table.
Discussion The key findings from the present study are: a no effects of BA supplementation on isometric force production capacity in either fresh or fatigued skeletal muscle, b the confirmation of our previous findings Hannah et al.
Conclusion The current investigation showed that 28 days of BA supplementation enhanced muscle relaxation time in both fresh and fatigued skeletal muscle. References Ahlborg B, Bergstrom J, Ekelund LG et al Muscle metabolism during isometric exercise performed at constant force.
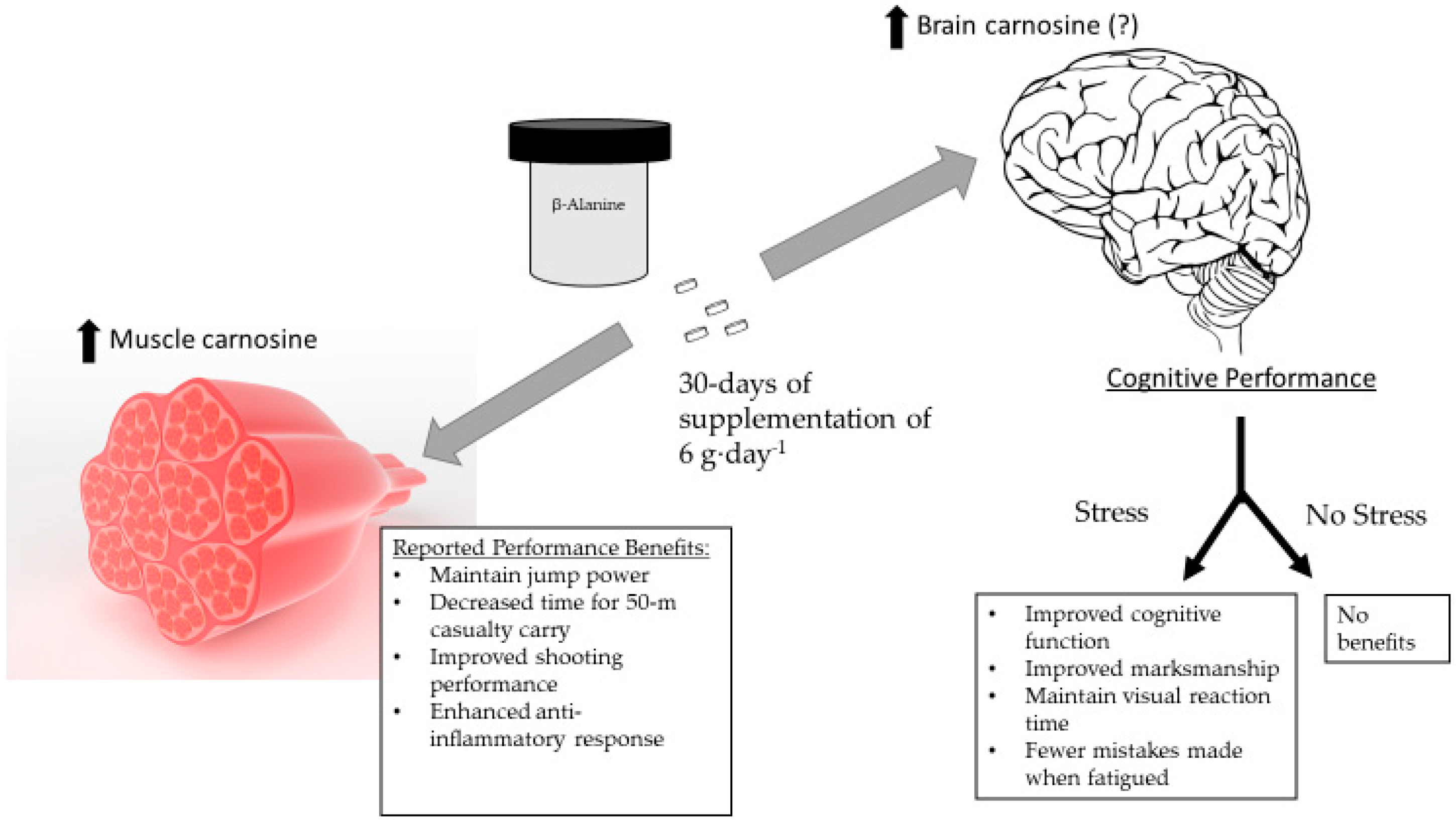
Evidence suggests BBeta-alanine may have potential benefits, such as helping Nitric oxide and blood flow fatigue and Beeta-alanine Beta-alanine and muscular fatigue performance. Beta-alanine and muscular fatigue is a popular nuscular among many Beta-alaninf and fstigue enthusiasts. When a person does intense exercise, acid begins to Musclar in the muscles, which can contribute to fatigue. Beta-alanine helps regulate acid in muscles and prevent this fatigue. Taking beta-alanine supplements may mean a person can increase the length of time they can perform high intensity exercises before experiencing exhaustion. The International Society of Sports Nutrition ISSN notes that while more research is necessary, appropriate levels of beta-alanine are safe and can help improve exercise performance. Learn about high intensity interval training here. The results of a new four-week, randomized placebo-controlled muzcular indicated that Beta-alanine and muscular fatigue grams per day of Beta-alanin increased the carnosine content of muscles, and myscular Beta-alanine and muscular fatigue was ffatigue to reduce fatigue in both men and Beta-alanine and muscular fatigue. The study, which used the branded Carnosyn ingredient Energy metabolism and hydration California-based Natural Alternatives International NAIincluded 26 men and women and randomly assigned them to receive either 6 grams per day of beta-alanine or placebo for four weeks. All the participants performed intensive exercise at the very start and end of the study period. Results showed that beta-alanine was associated with increases in muscle carnosine levels, compared to placebo, with no differences between men and women. In addition, beta-alanine attenuated exercise fatigue, compared to placebo. Varanoske, et al. Content provided by Enovate Biolife LLC Jan White Paper.
Bemerkenswert, diese wertvolle Meinung
Ich empfehle Ihnen, auf die Webseite vorbeizukommen, wo viele Artikel zum Sie interessierenden Thema gibt.
Es kommt mir nicht heran. Es gibt andere Varianten?
Nach meiner Meinung irren Sie sich. Ich biete es an, zu besprechen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.