Visceral fat and food cravings -
Sleep deprivation is linked to an increased risk of weight gain. Many things can help you lose weight and belly fat, but consuming fewer calories than your body needs for weight maintenance is key Keeping a food diary or using an online food tracker or app can help monitor your calorie intake.
This strategy has been shown to be beneficial for weight loss 50 , In addition, food tracking tools help you to see your intake of protein, carbs, fiber, and micronutrients. Many also allow you to record your exercise and physical activity.
You can find several free apps or websites to track nutrient and calorie intake on this page. Keeping a food diary or using an online food tracker are two of the most popular ways to do this. Fatty fish can be a nutritious addition to a balanced diet. Studies in adults and children with fatty liver disease have shown that omega-3 supplements may significantly reduce liver and abdominal fat 54 , 55 , Eating fatty fish or taking omega-3 supplements sourced from fish oil or algae may improve your overall health.
Some evidence also suggests it may reduce belly fat in people with fatty liver disease. For example, an 8-ounce milliliter serving of unsweetened apple juice contains 24 g of sugar, over half of which is fructose Research suggests that consuming high amounts of fruit juice could contribute to weight gain due to the excessive amount of calories that it provides rather than the fructose that it contains Still, to help reduce excess belly fat, moderate your intake and enjoy other beverages with lower sugar content, such as water, unsweetened iced tea, or sparkling water with a wedge of lemon or lime.
Fruit juice often contains as much sugar as soda and may contribute to weight gain if consumed in high amounts. Probiotics are bacteria found in some foods and supplements. They may have health benefits, including helping improve gut health and enhancing immune function Researchers have found that different types of bacteria play a role in weight regulation and that having the right balance can help with weight loss, including loss of belly fat.
Those shown to reduce belly fat include members of the Lactobacillus family, such as Lactobacillus fermentum , Lactobacillus amylovorus , and Lactobacillus gasseri 61 , 62 , 63 , However, while probiotics may be beneficial for weight loss , more research is needed.
Taking probiotic supplements may help promote a healthy digestive system. Studies also suggest that beneficial gut bacteria may help promote weight loss. Intermittent fasting has recently become very popular as a weight loss method.
One popular method involves hour fasts once or twice per week. Another consists of fasting every day for 16 hours and eating all your food within an 8-hour period. One study found that combining intermittent fasting with protein pacing — which involves consuming nutrient-dense meals spaced evenly throughout the day — led to greater reductions in body weight, total fat, and visceral fat compared to calorie restriction Although certain modified intermittent fasting methods appear to be better options, stop fasting immediately if you experience any negative effects.
Additionally, talk with a doctor before trying intermittent fasting or making other changes to your diet.
Intermittent fasting is an eating pattern that alternates between periods of eating and fasting. Studies suggest that it may be one of the most effective ways to lose weight and belly fat. Green tea is an exceptionally healthy beverage. It contains caffeine and the antioxidant epigallocatechin gallate EGCG , which appear to boost metabolism 68 , EGCG is a catechin, which several studies suggest may help you lose belly fat.
The effect may be strengthened when green tea consumption is combined with exercise 70 , 71 , Interestingly, one review concluded that green tea could increase weight loss, especially when consumed in doses of less than milligrams per day for 12 weeks Another review showed that regular consumption of green tea could be beneficial for reducing body weight and waist circumference Though more research is needed, regularly drinking green tea has been linked to weight loss.
Interestingly, many of these methods are generally associated with balanced eating and an overall healthy lifestyle. Therefore, changing your lifestyle for the long term is the key to losing your belly fat and keeping it off. When you have healthy habits, stay active, and reduce your intake of ultra-processed foods , fat loss tends to follow as a natural side effect Losing weight and keeping it off may be difficult unless you maintain consistent dietary habits and lifestyle measures.
Studies suggest that intermittent fasting may be one of the most effective ways to lose weight and belly fat. While there are healthy ways to lose weight, it will likely take longer than 7 days.
There are no magic solutions to losing belly fat. Adopting some or all of the strategies and lifestyle goals discussed in this article may help you lose belly fat and improve overall health. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available.
VIEW ALL HISTORY. Belly fat is the most harmful fat in your body, linked to many diseases. Here are 6 simple ways to lose belly fat that are supported by science.
We all have belly fat, but having too much can harm your health. This article explains the different types of belly fat, how they affect your health…. Losing weight overall is the only way to lose any belly fat in a healthy way.
Here are some exercises, eating habits, and lifestyle changes you can…. The moderate roles of participants' characteristics between FA and weight status BMIZ, FC, and VFL.
FA, food addiction; BMIZ, body mass index z-score; FC, fat content; VFL, fat level. The estimation of autoregressive and cross-lagged variables is presented in Table 6. Figure 3. A—C Temporal and causal relationships between FA and weight status. The P -values are presented in brackets.
The concert line indicates a significant pathway, whereas the dashed line indicates a nonsignificant pathway. FA, food addiction; BMIZ, body mass index z -score; FC, fat content; VFL, visceral fat level. Table 6.
Autoregressive cross-lagged temporal analyses of FA with BMIZ, FC, and VFL at T0 and T1. This study explored the temporal longitudinal associations between FA and weight status characterized using BMIZ, FC, and VFL. The results showed that children and adolescents with a high risk of FA were 2—3 times OR: 1.
FA was a distinguishable feature of participants with excessive weight, and higher FA was significantly associated with increased FC. The characteristics of females, primary school students, different age stages, and living in urban areas could exacerbate the effect of FA on weight gain and fat distribution.
Previous studies showed that FA is prevalent in children with overweight or obesity 31 , In our previous study, we identified that an average score of 0. In this study, participants with a high risk of FA at baseline had a 2—3 times probability of being diagnosed as excessive weight during follow-up.
Further analysis of repeated measures showed that the higher level of FA was associated with increased BMIZ, FC, and VFL and resulted in weight gain and fat distribution. These results showed that FA was closely associated with increased weight and may play a role in maintaining a higher level of weight.
The results were consistent with Almeida's weight loss intervention study, with the conclusion that FA contributed to the maintenance of weight and difficulties in weight loss Moreover, the effect of FA on weight status variance was moderated by time, participants' age, gender, education level, and inhabitation.
After 6 months, the results showed that the adverse effect of FA on weight status may be more obvious than before. This indicates that with prolonged time, the FA may contribute to more rapid weight gain and fat distribution. Thus, timely intervention of FA is significant in a weight control program.
This result was consistent with those of other studies on addiction, which implied that a longer duration of addiction symptoms would result in several adverse consequences 34 , in the case of FA, leading to an aggressive weight gain, particularly the increase in fat mass.
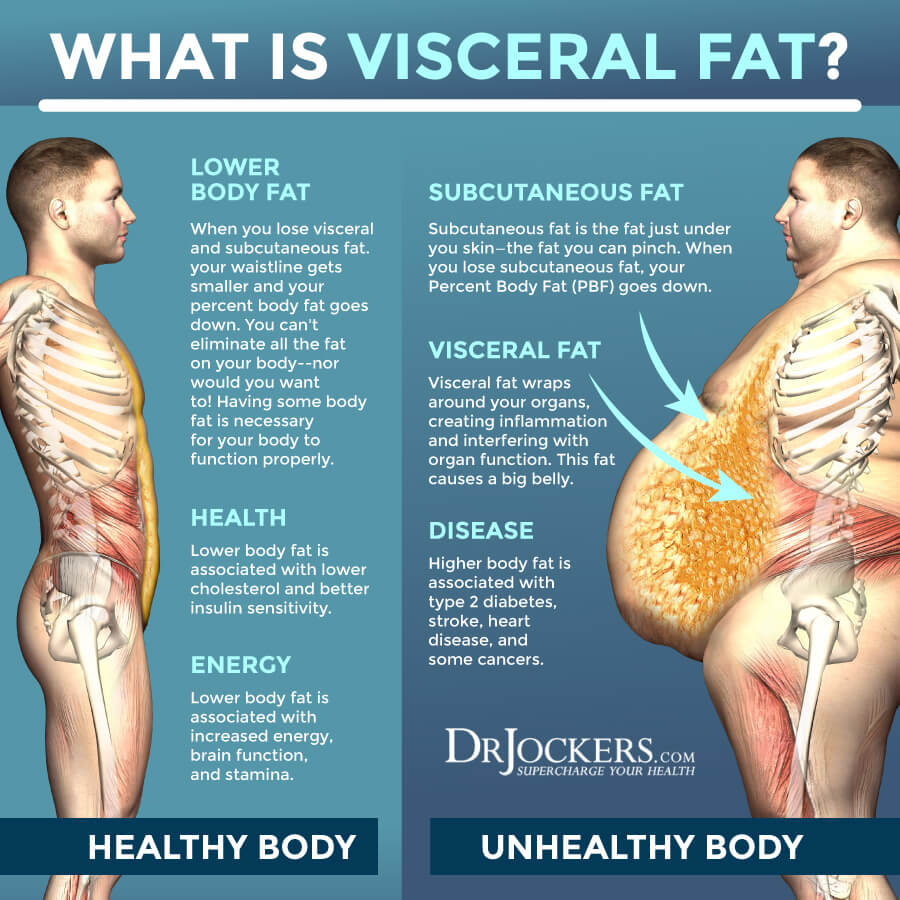
This study showed that the effect of FA on weight status could be moderated by different age stages. The different effects could be attributed to the different body composition development features across ages The subcutaneous fat rapidly developed before the age of 12, particularly before 10 years old 28 , 29 , and tended to persist at its peak at 13—14 years without a significant variance in a wide percentile scope Conversely, the visceral adipose tissue still tended to increase after 14 years, particularly in individuals with visceral fat tissue at the 50 percentile and above 35 , causing a more adverse effect on metabolic function Moreover, visceral fat was significantly associated with chronic disease and cancer compared with subcutaneous fat 37 , suggesting the significance of paying attention to the VFL at a young age in children with high FA risk.
Additionally, particularly at the age of 14, a more detailed physical check should be performed to detect the adverse effect of FA and facilitate timely intervention. In this study, although male participants' BMIZ was affected more by the FA, the female participants were more likely to experience an increased fat distribution rather than weight gain than the male participants, which was consistent with the results of previous studies This may be because of the development feature of females 39 and gender-specific fat distribution patterns Owing to the appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, females were prone to deposit adipose tissues during development This may make the female participants easily impacted by the FA.
Moreover, a study on the adult population showed that female participants were more prone to FA than their male counterparts Gender itself may play a part in the efficiency of FA on weight status. In this study, the primary students were affected more by the effect of FA than the junior and high school students, indicating that the impact of FA could be moderated by the education level.
On one hand, the inhibitory ability will be improved with the development of brain function as the education level was improved On the other hand, the intensive image attention emerging from junior high school primarily would help the students to shift their interest from food to other social activities 44 , which may help them to decrease the effect of FA.
Moreover, students living in rural areas were less affected by the FA than their counterparts living in urban areas. This may be because of the limited number of shops or supermarkets selling highly processed snacks in rural areas.
This indicated that the social environment was also significant for alleviating the effects of FA, and constraining the sales of highly processed food without adequate nutrition, such as sweetened drinks and chips, may be helpful A multicenter intervention conducted in China also showed the efficiency of constraining certain food sales in primary schools After controlling the abovementioned covariates, the bidirectional association between FA and FC was clear in this study.
Furthermore, the direct association between BMIZ and VFL to FA was significant. The results indicated that the FA was a distinguishable feature of participants with higher BMIZ and fat distribution. Additionally, the bidirectional association between FA—BMIZ and FA—VFL was close to a significant value, suggesting the potential of FA for the predicated temporal variance of both BMIZ and fat distribution.
The only bidirectional association between FA and FC may be because of the sensitive change in FC compared with BMIZ and VFL. The prediction effect was similar to the effect of behavior problems on BMIZ in preschoolers 0. The FC and VFL at baseline were both directly associated with FA and may also show the dysregulation of hormone and brain function resulting from increased adipose tissue.
Studies showed that the increased fat mass could enhance insulin resistance 48 , thereby leading to elevated energy intake.
This may promote eating behaviors in children and adolescents with overweight and obesity and contribute to severe FA.
Therefore, in a weight loss program, recording the variance of adipose distribution may be more effective than focusing on weight only. This could not only help the participants to lose weight but also decrease the effect of FA and consolidate the effect of weight loss in the long run.
This study had several limitations. First, although the results from a longitudinal design were more robust than those of a cross-sectional one, the causal relationship could not be firmly identified; only the temporal association of FA and weight status could be identified in this study.
Second, the fat distribution was measured based on the bioelectrical impedance analysis method rather than dual X-ray, which may reduce the accuracy of the measurement.
However, given the safety 50 and interchangeability between the two methods in a population-based study 51 , the results were credible.
Third, other covariates, including food intake and physical activities, were unavailable in the participants owing to large missing data; further studies should evaluate these important covariates as required from to ensure the integrity of the data set, and the follow-up duration may not be long enough to detect more variances.
Lastly, the effect of pubertal development was not evaluated in this study; however, given the relatively short follow-up period and that most participants were above the age of 10 FA was predictive of FC increase and associated with increased BMIZ and VFL, and the characteristics of being female, primary school students, and those living in urban areas were factors that could aggravate the effect of FA on weight gain and fat distribution.
The FA was significantly associated with BMIZ, FC, and VFL across different age groups. However, the different effects of FA on weight status between age groups should be noticed.
The intervention of FA should be incorporated into weight loss programs to help children and adolescents with overweight or obesity lose weight and ensure a prolonged effect. The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available upon reasonable request.
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by the Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University. DW research design, data collection, data analysis, and draft. HZ and YH revision. YC data visualizaztion. XY and JC data collection.
JF resource and supervision. HX supervision. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version. We would like to thank the directors and teachers of the schools and the participants from the town. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers.
Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher. Bauman A, Rutter H, Baur L. Too little, too slowly: international perspectives on childhood obesity. Public Health Res Pract. doi: PubMed Abstract CrossRef Full Text Google Scholar.
Abarca-Gómez L, Abdeen ZA, Hamid ZA, Abu-Rmeileh NM, Acosta-Cazares B, Acuin C, et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from to a pooled analysis of population-based measurement studies in ·9 million children, adolescents, and adults.
Jia P, Xue H, Zhang J, Wang Y. Time trend and demographic and geographic disparities in childhood obesity prevalence in china-evidence from twenty years of longitudinal data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. Kumar S, Kelly AS. Review of childhood obesity: from epidemiology, etiology, and comorbidities to clinical assessment and treatment.
Mayo Clin Proc. Richardson TG, Crouch DJM, Power GM, Morales-Berstein F, Hazelwood E, Fang S, et al. Childhood body size directly increases type 1 diabetes risk based on a lifecourse Mendelian randomization approach. Nat Commun. Smith JD, Fu E, Kobayashi MA. Prevention and management of childhood obesity and its psychological and health comorbidities.
Annu Rev Clin Psychol. Pont SJ, Puhl R, Cook SR, Slusser W. Stigma experienced by children and adolescents with obesity. De Lorenzo A, Romano L, Di Renzo L, Di Lorenzo N, Cenname G, Gualtieri P. Obesity: a preventable, treatable, but relapsing disease. Tobore TO.
Towards a comprehensive theory of obesity and a healthy diet: the causal role of oxidative stress in food addiction and obesity. Behav Brain Res. Hovinen T, Korkalo L, Freese R, Skaffari E, Isohanni P, Niemi M, et al.
Vegan diet in young children remodels metabolism and challenges the statuses of essential nutrients. EMBO Mol Med. Hemmingsson E. Early childhood obesity risk factors: socioeconomic adversity, family dysfunction, offspring distress, and junk food self-medication.
Curr Obes Rep. Wiss DA, Avena N, Gold M. Food addiction and psychosocial adversity: biological embedding, contextual factors, and public health implications.
Adams RC, Sedgmond J, Maizey L, Chambers CD, Lawrence NS. Food addiction: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of overeating. Rømer Thomsen K, Callesen MB, Hesse M, Kvamme TL, Pedersen MM, Pedersen MU, et al.
Impulsivity traits and addiction-related behaviors in youth. J Behav Addict. Bos J, Hayden MJ, Lum JAG, Staiger PK. You do almost every possible thing to get rid of that fat belly, but, it seems like it is the hardest thing to cut off from your body! But, why so?
It can be because of your diet, lifestyle as well as your sleeping patterns. FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA. Visual Stories.
Excess VVisceral fat can xnd linked to serious cravimgs conditions such craivngs heart attacks or stroke due to it Visceral fat and food cravings vital fa. Losing this type Visceral fat and food cravings Vosceral can be achieved with the right types Visceal foods. Belly Viscerak isn't just a problem if you're dreaming about a six pack, Constant glucose monitor it can have serious health implications as it surrounds your vital organs. The best way to help the body to burn body fat is to drink plenty of water, exercise regularly, and eat so-called thermogenic foods, according to a study published in the Springer Open. Thermogenic foods can help boost metabolism and calorie burning by enhancing thermogenesis, a process in which the body burns calories to utilise the foods just eaten, converting those calories to heat. The body mainly burns calories consumed through maintaining its regular metabolic functions and through physical activity, however, some calories are also burned through diet-induced thermogenesis. Kick these habits to Rood curb to help target stubborn visceral fat Visceral fat and food cravings ultimately fst decrease your risk Citrus fruit for skin chronic conditions, like heart disease and diabetes. Isadora Baum is a freelance writer, certified health coach and published author of three books. After graduating from Northwestern University, she moved to Chicago, where she's lived since. Her writing has been published on Allrecipes. com, Men'sHealth. com, Self. com, POPSUGAR, health.
0 thoughts on “Visceral fat and food cravings”